What is Solana?
Solana is a powerful open source project implementing a new, permissionless, high-speed layer-1 blockchain.
Founded in 2017 by former Qualcomm executive Anatoly Yakovenko, Solana aims to scale throughput while keeping costs low, beyond what popular blockchains typically achieve. Solana implements an innovative hybrid consensus model that combines a unique Proof-of-History (PoH) algorithm with a lightning-fast sync engine (aka another version of Proof-of-Stake, PoS). Therefore, the Solana network can theoretically handle more than 710,000 transactions per second (TPS) without requiring any scaling solutions.
Solana's third-generation blockchain architecture is designed to facilitate the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). The project supports a range of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms as well as non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces.
The Solana blockchain was launched during the blockchain boom of 2017. The project's internal testnet was launched in 2018, followed by multiple testnet phases before finally officially launching the mainnet in 2020.
What is unique about Solana?
Solana's ambition is to solve the blockchain trilemma in its own unique way, a concept coined by Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin. This trilemma describes three major challenges developers face when building blockchains: decentralization, security, and scalability.
It is widely believed that the way blockchains are built forces developers to sacrifice one of these aspects in favor of the other two, since at any given time, they can only choose two out of three.
The Solana blockchain platform proposes a hybrid consensus mechanism that compromises decentralization to maximize speed. The innovative combination of PoS and PoH makes Solana a unique project in the blockchain industry.
In general, blockchains are more scalable based on the number of transactions per second (TPS) they support - the higher the TPS, the more scalable they are. However, in decentralized blockchains, time variance and higher throughput slow them down, meaning that the more nodes and timestamps there are to verify a transaction, the more time it takes.
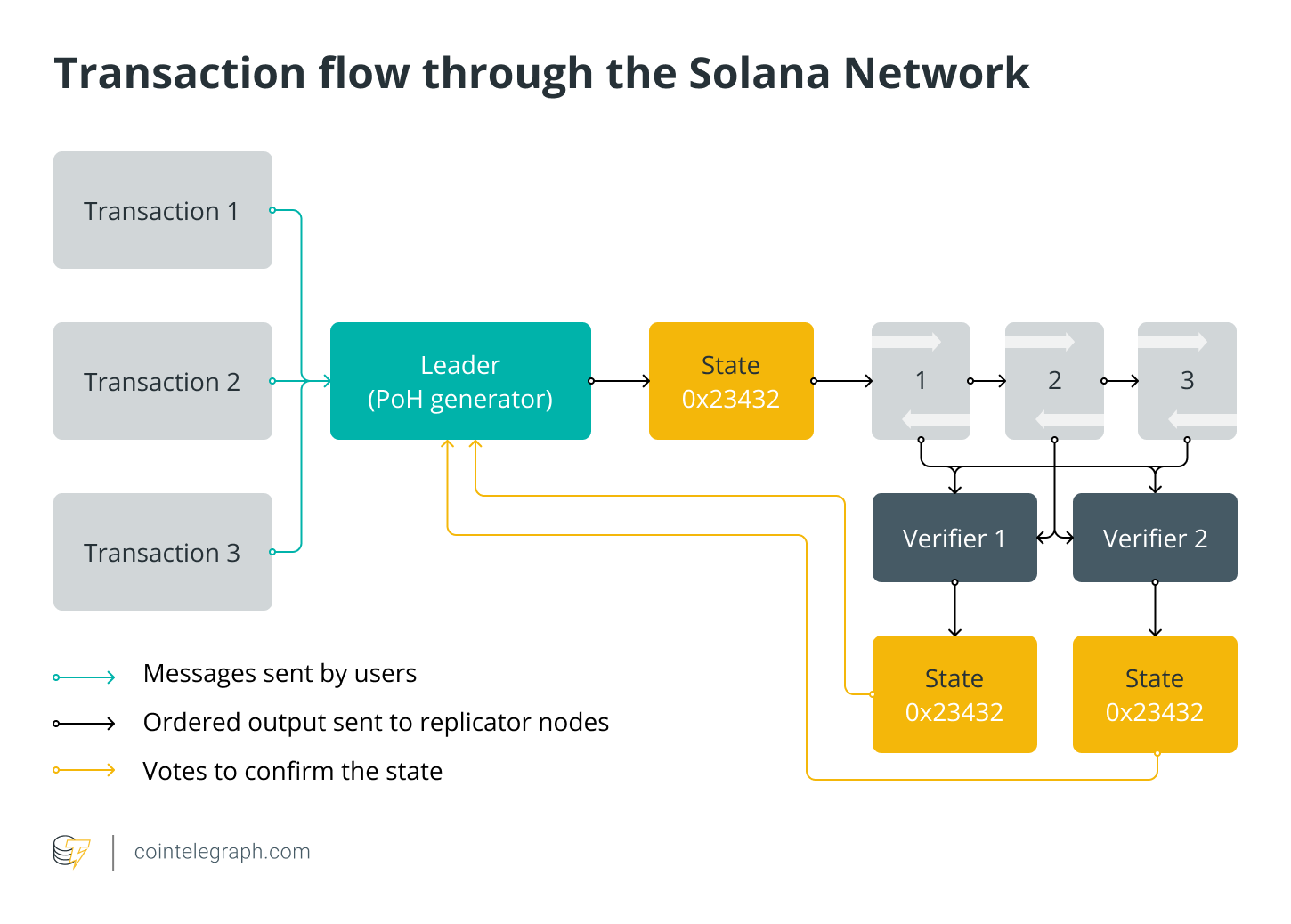
Simply put, Solana's design solves this problem by selecting a leader node based on a PoS mechanism that orders messages among nodes. Thus, the benefit of the Solana network is that it reduces workloads and thus increases throughput even without a centralized and precise source of time.
Additionally, Solana creates a chain of transactions by hashing the output of one transaction and using it as the input for the next transaction. The name of Solana's main consensus mechanism comes from the history of this transaction: PoH (Proof of History), a concept that endows the protocol with greater scalability, thereby improving usability.
How does Solana work?
At the heart of the Solana protocol is a proof-of-history, a sequence of computations that provide a digital record for confirming transactions that occurred at any point in time on the network. It can be represented as a cryptographic clock that provides a timestamp for every transaction on the network, and a data structure that can be simply added.
PoH relies on PoS using the Base Station Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) algorithm, an optimized version of the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerant (pBFT) protocol. Solana uses it to achieve consensus. Base Station Byzantine Fault Tolerance (Tower BFT) keeps the network running securely and additionally serves as a tool for validating transactions.
Furthermore, PoH can be thought of as a high-frequency verifiable delay function (VDF), a triple function (setup, evaluation, verification) that can produce a unique and reliable output. VDF maintains order in the network by proving that block producers have waited enough time for the network to advance.
Solana uses the 256-bit Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-256), a set of proprietary cryptographic functions that output 256-bit values. The network periodically samples numbers and SHA-256 hashes, providing real-time data based on the set of hashes contained by the central processing unit.
Solana validators can use this hash sequence to record specific data that was created before a specific hash index was generated. The timestamp of the transaction was created after this particular block of data was inserted. In order to achieve the claimed high TPS and block creation times, all nodes on the network must have cryptographic clocks to keep track of events rather than waiting for other validators to validate transactions.
Solana (SOL) Token
Solana's cryptocurrency is SOL. It is Solana's native and utility token, providing a way to transfer value and also secure the blockchain through staking. Launched in March 2020, SOL has now become one of the top ten cryptocurrencies by market capitalization in the crypto space.
The scheme of operation of the SOL token is similar to that used in the Ethereum blockchain. Although they function similarly, SOL holders stake tokens in order to validate transactions through the PoS consensus mechanism. Additionally, Solana tokens are used to receive rewards and pay transaction fees, while SOL also allows users to participate in governance.
Regarding the total amount of Solana tokens, there will be more than 500 million circulating tokens, and the total Solana supply is currently over 511 million tokens - Solana's circulating supply is just over half of that number. About 60% of all SOL tokens are controlled by Solana founders and the Solana Foundation, with only 38% reserved for the community.
SOL can be purchased on most exchanges. Solana’s top cryptocurrency exchanges include Binance, Coinbase, KuCoin, Huobi, FTX, and more.
Solana vs. Ethereum
Solana has received many accolades for its speed and performance, and has even been considered a close competitor to crypto industry leaders such as Ethereum.
So, how is Solana different from Ethereum? Could it be considered a potential Ethereum killer?
In terms of processing speed, Solana can challenge the dominance of smart contract platforms, and it is said that its speed can reach more than 50,000 TPS. Solana uses a different consensus algorithm to avoid slow transaction confirmations. This feature makes Solana one of the fastest blockchains in the industry and extremely competitive in other industries outside of the crypto space.
Compared to this huge number, the current less scalable Ethereum proof-of-work model can only handle 15 TPS. Therefore, Solana is thousands of times faster than Ethereum. Another advantage of Solana is that the network is extremely cost-effective as it implements new token economics that lower fees.
Also, it’s worth mentioning that Solana’s blockchain implements a variant of PoS that is more environmentally friendly and sustainable. In contrast, Ethereum's current PoW model consumes a huge amount of computing power.
However, everyone in the crypto community is looking forward to Ethereum’s upgrade to PoS. A new type of ethereum that is being worked on will consist of an execution layer (formerly known as ethereum 1.0) and a consensus layer (formerly known as ethereum 2.0). It can greatly increase throughput, increase scalability, reduce transaction fees, and stop unsustainable power consumption.
Disadvantages of Solana
If you're still wondering if Solana is a good investment and should be purchased, the answer is still up to you. Despite its obvious advantages, Solana, like any existing crypto project, has its disadvantages.
First, while the Solana blockchain can compete with high-end blockchain projects, it is still vulnerable to centralization because there are not many validators on its blockchain. Anyone on the network can become a Solana validator, but doing so is still difficult as it requires a lot of computing resources.
At the same time, the Solana protocol still marks itself as a beta version of the mainnet, in other words, it does not deny that there may be bugs and errors.
Despite these issues, Solana remains one of the largest ecosystems in the crypto industry and appears to be on the right path for growth.
Cointelegraph Chinese is a blockchain news information platform, and the information provided only represents the author's personal opinion, has nothing to do with the position of the Cointelegraph Chinese platform, and does not constitute any investment and financial advice. Readers are requested to establish correct currency concepts and investment concepts, and earnestly raise risk awareness.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance Catherine
Catherine JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance CharlieXYZ
CharlieXYZ Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph