Source: OneBlock Community
Without macroeconomics, the crypto world may not exist. Perhaps Satoshi Nakamoto would never have written that groundbreaking white paper. As one of the cores of the exponential era, blockchain technology occupies an important position in macroeconomic theory. The traditional economic growth formula is population growth plus productivity growth plus debt growth. However, debt growth has stagnated and global population growth is also decreasing. When we incorporate artificial intelligence and robotics into the mix, they are able to expand infinitely over time. So, what does this mean for GDP and businesses?
Blockchain and cryptocurrency are therefore seen as the biggest macroeconomic bets ever. As early as 2012, Bitcoin aroused people's thinking about building a new financial system, and with the emergence of Ethereum smart contracts, people realized that the potential of blockchain technology is far more than that, it actually builds the entire value layer of the Internet, a large and distributed database with powerful application capabilities.
In the latest episode of The Journey Man, financial veteran Raoul Pal invites Polkadot founder Dr. Gavin Wood to discuss in depth how Polkadot, an innovative blockchain protocol, achieves interoperability between blockchains. This episode will fully explain how the Polkadot protocol addresses the challenges of scalability, security, and governance of traditional blockchain networks. By analyzing Polkadot’s unique architecture, we will understand how these technologies enable seamless communication and data transfer between independent blockchains. At the same time, this episode will also touch on the role and impact of blockchain in the field of artificial intelligence.
Watch the full interview video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9SAxnF2sys8
From Academic to Blockchain PioneerGavin Wood’s Technical Journey
First Encounter with Blockchain
Gavin Wood’s technical journey began with a passion for computer science and a deep exploration of game theory. Before he came into contact with blockchain, Gavin Wood already had a strong background in computer science. But it was an article about Emin Gün Sirer in 2013 that changed his career trajectory and introduced him to the world of cryptocurrency. Gavin Wood recalled: "When I first read about Bitcoin and cypherpunks, I was deeply attracted by the idea of decentralization." During their first meeting in London, Emin Gün Sirer introduced him to some important figures in the Bitcoin circle, including Vitalik Buterin, the later founder of Ethereum. He described the meeting: "It was a small party in an abandoned building in London, where I met many people who later had a profound influence on me." This meeting not only deepened his interest in blockchain, but also laid the foundation for his subsequent entrepreneurial journey.

Inseparable bond with Ethereum
In 2013, when Vitalik Buterin showed Gavin Wood the initial white paper of Ethereum,Gavin Wood immediately saw the huge potential of the project. Ethereum proposed a brand new concept, not just a digital currency, but also a platform capable of executing smart contracts.Gavin Wood realized that Ethereum was not just a simple copy of Bitcoin, but an attempt to push blockchain technology to new boundaries.
At that time, no one was committed to building such a project, which aroused Gavin Wood's interest and prompted him to start writing code for Ethereum. In addition, as the co-founder and CTO of Ethereum, Gavin Wood developed the first functional client software of Ethereum. Through this series of experiences, Gavin Wood not only laid the foundation for his own career in the blockchain field,but also laid a solid technical and personal foundation for the establishment of Polkadot in the future.

Polkadot's conception and implementation
Original intention
Although Ethereum has taken a leading position in global blockchain technology,Gavin Wood still feels that there is an unmet demand in the market. Regarding the motivation for deciding to establish Polkadot, Gavin Wood further explained that although Ethereum is extremely innovative, it has limitations in scalability and interoperability. He saw an opportunityto create a platform that can connect different blockchains. It is this deep insight into the market and pursuit of the forefront of technology that prompted Gavin Wood to launch the Polkadot project in 2016, aiming to achieve interoperability and shared security between different blockchains.
Multi-chain system and interoperability
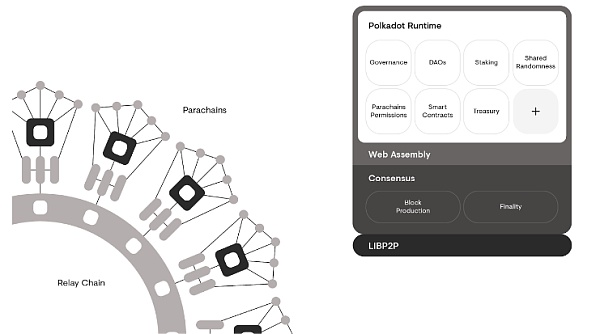
One of the core concepts of Polkadot is multi-chain system and interoperability.Gavin Wood envisioned creating a beacon chain similar to Ethereum in the early days, which is called the relay chain in Polkadot. Polkadot consists of two major parts: the relay chain and the parachain.The relay chain is the heart of the Polkadot network, responsible for providing security, consensus, and verification of cross-chain transactions.Parallels are independent blockchains that can have their own specific functions and uses, but are interconnected through the relay chain. This architecture allows each parachain to share the security provided by the relay chain while maintaining its independence.
Gavin Wood further explained that these chains do not need to perform the same tasks and can each focus on specific areas, but the shared security enables them to interact in a unified security environment. He described this vividly: "Instead of a permanent split, we have a more flexible temporary split, splitting the state into small pieces and redistributing it every few seconds." This approach not only provides greater flexibility, but also ensures better interoperability.
Security and Flexibility
When talking about the security of Polkadot, Gavin Wood believes that it is not reasonable to split the security model. Therefore, Polkadot adopts a shared security model, which allows different chains to operate under the same security guarantee and interact easily. Gavin Wood explained that the Polkadot relay chain is not only used to protect and deliver messages, but also to realize the concept of global computing. It is like a ubiquitous multi-core single virtual machine that can host and process large amounts of data and computing tasks. With this design, Polkadot not only improves security, but also provides flexibility for different blockchains, enabling them to optimize and scale according to their respective needs, thereby promoting the development of the entire blockchain ecosystem.

SPREE and Accords
When talking about specific applications in the Polkadot ecosystem, Gavin Wood mentioned some innovative solutions, such as SPREE (Shared Protected Runtime Execution Enclaves) and Accords. SPREE is an independent logic module that can run on the Polkadot relay chain, allowing parachains to selectively use these modules, thereby ensuring that cross-chain messages are trusted and consistent in the process of transmission and interpretation.
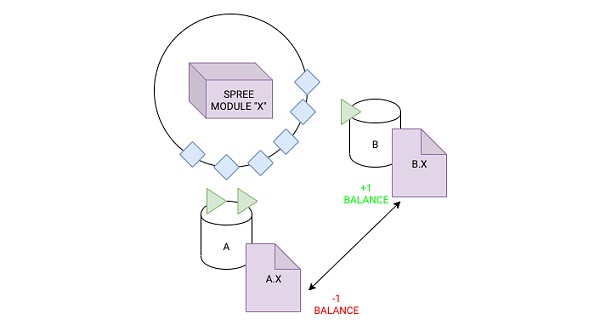
However, Polkadot does not stop there. Gavin Wood added that Accords further expands this concept. The Accords protocol is a cross-chain smart contract that manages the interaction between different blockchains. Through Accords, parts of different blockchains can know each other's existence like international law and commit to abide by common rules. Accords greatly simplifies cross-chain operations and improves the interoperability and security of the entire ecosystem.
For example, Token Accord is a token agreement that ensures that when a user destroys a token on one chain, a new token will be minted on another chain accordingly. This two-way direct information transmission mechanism ensures the security and reliability of cross-chain operations. Gavin Wood said that Polkadot is creating a blueprint that can handle global-level transaction data. This not only helps solve the scalability problem of the current blockchain, but also provides a solid foundation for future Web3 applications.
The next-generation blockchain technology with challenges and opportunities - JAM
The current status and challenges of the JAM project
JAM (Join-Accumulate Machine) is the next-generation chain of Polkadot, which will greatly enhance the scalability and flexibility of the blockchain. Gavin Wood pointed out that the JAM chain is currently in an active development stage and has made some important progress. JAM was originally designed to be able to run more ordinary computer codes, not just smart contract codes. Gavin Wood emphasized that the goal of JAM is to allow users to use the blockchain at almost no cost, thereby lowering the entry barrier and attracting more projects and users. In addition, Gavin Wood has recently released the gray paper of the JAM chain, which contains detailed information about the project design, implementation and expected results.
See the gray paper for more details: https://graypaper.com

Although the JAM project has made significant progress, Gavin Wood also admitted that the project still faces some important challenges, especially in decentralization and team building. He emphasized that the key to the JAM project is that multiple teams need to be involved from the beginning to achieve true decentralization, rather than focusing on one development team. This is also the part that Gavin Wood is most uncertain about the JAM project.
Funding and Incentives
In order to encourage more teams to participate in JAM development, Gavin Wood announced that the Web3 Foundation will set up a JAM Award with a prize of 10 million DOT (about 74.5 million US dollars) to promote the diversified development of the JAM project. Gavin Wood said that by holding technical seminars and conferences, he hopes to attract more teams to participate and achieve the common progress of multiple teams and expertise.

Gavin Wood is confident in the future of the JAM project and hopes that with the support of the community, through continuous efforts, the technical level will be improved and the decentralization and diversification of the blockchain field will be promoted. Gavin concluded that it is hoped that these measures will achieve Polkadot's goals in the next few years and contribute to the development of blockchain technology.
Future-oriented blockchain and AI integration
Blockchain as a tool to alleviate AI centralization
The nature of artificial intelligence (AI) is highly centralized, which is contrary to the decentralized concept of Web3. Gavin Wood explained that AI is basically a system based on a single economy having enough GPUs and data to surpass all strategic competitors. AI is not a shared, consensus-driven system by nature. This centralization makes AI more easily controlled by a few entities.
Despite being pessimistic about the centralization of AI, Gavin Wood still believes that blockchain technology can alleviate this problem to some extent. Web3 makes data and computing resources more dispersed through decentralization, reducing dependence on a single entity. This decentralized strategy will make AI technology more transparent and fair, and can also ensure the reliability and security of data through consensus mechanisms.

Decentralized Global AI Vision
Gavin Wood envisions a future that combines blockchain and AI, using blockchain technology to achieve decentralized training and data sharing of AI on a global scale. He noted that although there are certain transaction costs in actual operation of this combination, it is possible to achieve it in the near future. Gavin Wood also mentioned that Web3's infrastructure is strong enough to make AI systems subject to these mechanisms, thereby mitigating the risks of AI centralization. He believes that this decentralized approach will make AI technology more widely used, while maintaining protection for user privacy and data security. Through blockchain technology, the development of global AI can be more decentralized, using the existing Web3 infrastructure to build a more open and transparent system.
The Combination of Digital Identity and AI
When it comes to the practical application of AI and blockchain, personal identity verification will be particularly important. Gavin Wood emphasized that current identity verification relies on centralized institutions, but blockchain provides a decentralized and more reliable solution. The use of AI introduces new challenges and opportunities in identity management. For example, AI can be used to generate realistic fake identities and conduct phishing attacks, increasing the risk of identity theft.

To meet these challenges, advanced technologies, such as AI-driven intelligent identity authentication and behavior detection systems are being developed to enhance security. For example, Cisco's Identity Intelligence system uses AI to detect abnormal behavior and improve the accuracy of authentication. Gavin Wood said that as these technologies mature and become more popular, decentralized identity solutions will allow users to better control their identity credentials and permissions, thereby improving transparency and security.
Conclusion
At the end of the interview, Gavin Wood said that as a senior practitioner in this field, he is pleased to see that people's understanding and application of blockchain are deepening. Although progress is slow, blockchain technology is steadily advancing and gradually finding application scenarios in the real world. He mentioned that some applications have begun to take shape, whether in the field of games or more stringent fields such as supply chain management and trade finance,blockchain technology is beginning to show its potential. In the future, blockchain technology will not only be limited to the financial field, but will also expand to supply chain management, virtual economy, identity authentication and other aspects.
As the navigator of multi-chain systems, Polkadot is leading blockchain technology to new heights with its innovative technical architecture and a wide range of application scenarios. Gavin Wood firmly believes that through continuous technological improvement and innovative applications, Polkadot will bring profound changes and development to various industries.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance WenJun
WenJun JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Sanya
Sanya Olive
Olive