Evolution of MEME Coin
Meme, the evolution of MEME coin Golden Finance, only this kind of simplicity and purity can create a classic.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Author: YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core
Layer2 should be an expansion path rich in "Ethereum correctness" in our minds, but it has been affected by market rumors that Metis The founding team was influenced by "Vitalik Buterin's mother/best friend", and Metis was given the title MEME Layer 2, which undoubtedly hit the key point of market investors' belief in the orthodoxy of Ethereum. However, the current essential attribute of blockchain is still "code + finance". From an investment perspective, technology and market have always been a pair of happy enemies who are both separated and reunited. Can Metis use other Rollup centralized sequencers and Can you stand out from many Layer 2s by controlling the disadvantages of the economic model?

(left Natalia Ameline, right Elena ; Sinelnikova)
The origin of the MEME attribute. According to Metis official website, Metis co-founder and CEO Elena Sinelnikova has been promoting education and education in the blockchain industry. Popularization work, and is also one of the co-founders of CryptoChicks, the world's largest female blockchain community, an educational non-profit organization. Another co-founder of CryptoChicks is Natalia Ameline, who is the mother of Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin. In addition, Vitalik Buterin’s father Dmitry Buterin also took the lead in founding the blockchain education company Blockgeeks, which is dedicated to developing blockchain technology-related course. Metis Network was established in 2018 and released in May 2021.
Metis is a Layer 2 based on the Ethereum chain. It is the earliest fork project of Optimism. Its working principle is the same as other Layer 2. The biggest highlight is that it is the first successful Optimistic Rollup to implement sorter decentralization. The network employs a Proof-of-Stake Sequencer Pool mechanism to ensure the network’s continued availability and censorship resistance, while enabling fee sharing and sequencer staking. These sequencers are responsible for determining the packaging order of transactions. During the process, they must obtain the signatures of at least 2/3 of the sequencers in the sequencer pool before the data can be packaged and uploaded to the Layer 1 network. In order to prevent malicious behavior, Metis also introduced the role of a validator to conduct sample surveys on blocks to ensure that the ordering of transactions by the orderer is correct.
MPC (multi-party computation) has advantages in privacy protection and decentralization. However, it also has some obvious problems in blockchain networks that require consensus. disadvantages. Due to the lack of relay nodes to distribute information, the number of communications increases, which in turn leads to a significant increase in communication costs within the network. Metis’s solution is to transform a single point orderer into a orderer pool, achieving decentralization through the node staking mechanism and rotation mechanism, so that the decentralized orderer can reach consensus and complete signatures. Although this may ultimately make the network cost not much lower than Layer 1, it can achieve MEV resistance and solve the single point of failure problem, while distributing benefits to node stakers.
The recent rapid growth of Metis TVL has attracted people's attention to the importance of decentralized sorters. According to L2BEAT data, the current OP scheme in all Layer2 networks TVL ranks fifth. Metis’ decentralized sorter is designed to proactively distribute the pie while also allowing the market to see the value capture of Layer 2 native tokens.
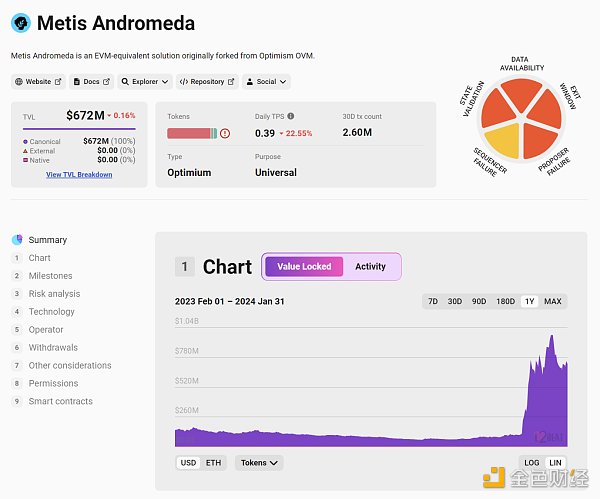
Picture source: L2BEAT Data time 24/02/01
Rollup is one of the Layer2 solutions, also known as rollup. Its working principle is to migrate the transaction calculation and storage performed on the Ethereum main network (i.e. Layer 1) to Layer 2 for processing and compression, and then upload the compressed data to the Ethereum main network, thereby expanding the performance of Ethereum.
Rollup can be divided into ZK Rollup and Optimistic Rollup according to different schemes to ensure the validity of compressed data (that is, data correctness). It involves off-chain computation, packaging transactions onto the chain every few minutes, rolling verification and accounting, hence the name. However, although we usually call it a Rollup chain, the off-chain part of Rollup is not a complete blockchain. Rollup literally rolls up a bunch of transactions to form a Rollup transaction. After receiving this Rollup transaction, all nodes Do not execute the wrapped logic but only accept the execution results of these logics.
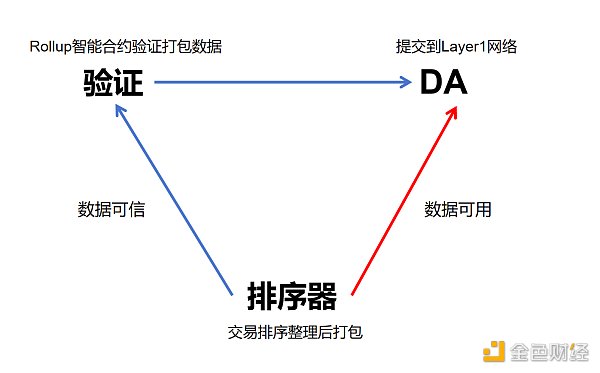
Source: Ac-Core Homemade
Sort The sequencer is the role in L2 responsible for sorting, sorting, packaging and submitting transactions to the L1 network. Currently, most L2 projects rely on a single sequencer (usually the project party itself) to complete the above work. There are two security issues here. : 1. Single point of failure. If the sequencer has problems due to attacks or technical failures, the entire network will be shut down;
2. Scalability issues, a single Sequencers may struggle to cope with increasing transaction volumes.
Verification
During the transaction process, the packaged data sent by the sequencer needs to be verified. Currently, most of the verification of Ethereum Rollup is executed by the Ethereum Rollup smart contract to ensure the data. credibility. There are mainly two different verification methods: ZK Rollup (zero-knowledge proof Rollup) and Optimistic Rollup (optimistic rollup). For example:
ZK Rollup:
Verification method: ZK Rollup uses Zero-Knowledge Proofs to verify the correctness of all transactions that occur in Layer 2. Zero-knowledge proof allows the verifier to confirm the validity without knowing the specific transaction details;
Privacy protection: ZK Rollup emphasizes user privacy because on Layer1 What is submitted is a “proof” of the calculation rather than the details of the transaction. The specific transaction content is carried out on Layer 2, while Layer 1 only verifies the validity of the zero-knowledge proof.
Optimistic Rollup:
Verification method: Optimistic Rollup adopts The "optimistic" strategy assumes that all transactions are legitimate and then verifies them only when necessary. Verification is completed through fraud proofs (Fraud Proofs), that is, proofs are submitted on Layer1 to prove that transactions on Layer2 violate the rules;
Real-time: due to Assuming that all transactions are legal, Optimistic Rollup's transactions on Layer 2 can be carried out quickly, and verification occurs when disputes or objections arise.
DA(Data Availability)
DA refers to data availability, which publicly releases the status data of each transaction processed off-chain so that other participants can also access and use these transaction statuses. data. Some Layer2 writes the status data of the transaction to Ethereum Layer1, thereby realizing DA. There are also some Rollup Layer2s that write key transaction data on third-party blockchains. The premise of data availability is that the data is trustworthy.
For example:
DA in Optimistic Rollup: Ensure that Layer1 can obtain all data on Layer2 Transaction data. If the data is not available, anyone can raise a objection on Layer1, which helps prevent potential data tampering or omission;
Commitment in ZK Rollup: In Layer2, all calculations and storage of transactions occur, but only the result of the calculation (called a Commitment) is submitted to Layer1. Zero-knowledge proofs are used to prove the correctness of these Commitments.
Note: In ZK Rollup, "Commitment" focuses more on verifying the correctness of the transaction calculation results on Layer2, while "data availability" focuses more on ensuring that Layer1 can obtain The data of all transactions on Layer 2, the two usually complement each other to ensure the security and reliability of the entire system.
Among the three key elements of Rollup, the sorter is considered the most critical. The sorter is responsible for performing the process of sorting and compressing Layer 2 transaction information off-chain. Since this process involves verification of the authenticity of the data, achieving data availability is crucial. However, when the sorter is decentralized, the implementation of data trustworthiness verification and availability may no longer be so critical.

Image source: Metis L2
Selection of sorter< /p>
Lock $Metis on Metis and have a chance to become a node. The weight will be calculated based on the number of $Metis locked. The algorithm will be Each of these nodes is assigned a range. Metis Rollup has improved the "Transaction Data Verification Section". In the calculation process of Layer 2, a role called "verifier" is introduced, and the verification node is encouraged to quickly verify transactions through a competitive mining mechanism, and this process is realized through a competition mechanism. Similar to other Layer 1 networks that adopt the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism, Metis transactions also require nodes to verify. Therefore, there is no dispute about the data packaged and transmitted from Metis to L1, which avoids the problems of intervals and delays in withdrawing assets from Metis to the Ethereum mainnet.
A significant difference of Metis Rollup compared to Optimistic Rollup is that it only takes a few hours or minutes to withdraw assets from Metis to the Ethereum L1 layer. This highlights the advantages of Metis Rollup in terms of efficiency and speed in processing transactions. Generally speaking, nodes with higher lock-up amounts have a higher probability of joining the sorter. Of course there is some randomness involved.
MPC (multi-party computation) of the sorter
Metis’ implementation of the decentralization of the sorter involves three key roles: administrator (Admin), sorter and PoS-based consensus layer .
Administrator: Responsible for setting key parameters of the overall network and managing the qualifications of sequencers to join the sequencer pool. The parties to the agreement no longer directly have absolute control over such matters, but will be executed by the administrator after the proposal is approved. One of the difficulties in achieving decentralization is that the management of the sorter must be carried out in a decentralized manner while maintaining efficiency and convenience;
Sort Server:Metis uses MPC (Multi-Party Computation) signature based on TSS (Threshold Signature Scheme) to manage the signature permissions of multiple sequencers. Each sequencer has the right to decide a batch, and all sequencers participate through MPC signature. If the number of signatures exceeds 2/3, the batch is considered valid and can be submitted to the Rollup contract on L1. MPC signing by the sequencer pool is managed by another contract in the PoS-based network. When the PoS network cannot detect the MPC address, the MPC module will be triggered to generate the key;
PoS-based consensus layer:PoS The network is responsible for managing the contract for the sequencer’s signature authority, monitoring MPC addresses, and triggering key generation. The generated key will be sharded and distributed to each sequencer in the pool for MPC signing. The settings of this module cover the life cycle management of keys, including multi-signature generation, key re-sharing, application signatures, deletion signatures, etc.;
Adopting TSS The reason is its high fault tolerance and high flexibility properties. Compared with multi-signature, TSS does not need to verify each signature on the chain. Instead, the signatures of all signers are aggregated and verified uniformly, thereby increasing the transaction confirmation rate. In addition, communication between PoS nodes uses independent Tendermint channels, while communication during the MPC runtime uses the libp2p protocol. This entire system is designed to achieve efficient and secure decentralized management of sequencers.
Metis sequencer transaction process
< /li>1. Start the user to start the transaction; 2. The transaction is forwarded to the network sequencer node; 3. Block generation: the sequencer accepts the transaction when it is valid Create the block; 4. Finalize: the multi-party computation (MPC) node merges the block and forwards it to the Ethereum main chain.
MetisEDF
Metis Ecological Development Fund (MetisEDF) provides financial support for this, covering multiple aspects, such as the development and deployment of incentive protocols, providing liquidity support, and conducting security audits and implement liquidity mining plans, etc. Allocation includes:
Sequencer Mining: 65.4% ($3 million METIS / >$260 million);
Ecosystem funding: 34.6% ($1.6 million METIS / > $140 million).

Source: Ac -Core Homemade
The principle of Ethereum is that each node stores and executes every transaction submitted to it by users. This high-level security method also As a result, the entire network is very expensive, so a Rollup solution is needed to expand the capacity of the entire network. To put it simply, Rollup = a set of contracts of Layer1 + Layer2’s own network nodes, that is, on-chain smart contracts + off-chain aggregators, which rely on Ethereum in terms of settlement, consensus, and data availability, and are only responsible for executing Rollup.
The smart contract on the chain indicates that its trust model is an intelligence on Ethereum The contract borrows the security of Ethereum;
The off-chain aggregator means that it will execute and aggregate transactions off-chain. Compress large batches of transactions and eventually put them on the Ethereum mainnet to achieve faster and cheaper results.
Layer2 network node is composed of many parts, among which the sorter component is the most important. It is responsible for receiving transaction requests on Layer 2 to determine their execution order and batch the transaction sequence, and finally transmits it to the contract of the Rollup project on Layer 1. Currently, the sequencers of all Layer 2 Rollups in Ethereum are centralized, Metis But it happens to take advantage of the decentralized sorter.
The full node of Layer2 can obtain the transaction sequence in two ways: one is to obtain it directly from the sorter, and the other is to read the Batch sent by the sorter to Layer1. But the latter has stronger unmodifiable properties. Since transaction execution will change the status of the blockchain ledger, in order to ensure consistency, in addition to obtaining the transaction order, the Layer 2 full node must also synchronize the ledger status with the sequencer. Therefore, the task of the sequencer is not only to send the transaction batch to the Rollup contract of Layer1, but also to transmit the state update result StateRoot/StateDiff after transaction execution to Layer1. Generally speaking, the job of the sequencer is to process and sort the transactions as Blocks added to the blockchain are responsible for batching transactions and publishing them to Layer1 smart contracts.
For the full node of Layer2, as long as the transaction sequence and initial StateRoot of Rollup on Layer1 are obtained, the blockchain ledger of Layer2 can be restored. And calculate the latest StateRoot. On the contrary, if the StateRoot calculated by the Layer2 full node is inconsistent with the StateRoot published by the sorter to Layer1, it means that the sorter has committed fraud. In summary, compared to Layer 2’s own network, Layer 1 will be more decentralized, trustless and more secure.
Optimistic Rollup gives an example. It allows all Layer2 nodes to provide fraud proof, proving that the data published by the sorter on Layer1 is wrong. But for Optimism, which has no fraud proof, if it really wants to steal Layer 2 user assets through the sequencer, it only needs to ask the sequencer operator to forge transaction instructions and transfer other people’s Layer 2 assets to their own address. Finally, the stolen coins are transferred to Layer1 through the Bridge contract that comes with Rollup.

Source: ChaindebriefLayer2's biggest recent hot spot of hype is undoubtedly the Cancun upgrade, but this will not have unique benefits for Metis but is universal. Putting aside the impact of the market sentiment of "Vitalik Buterin's mother/best friend", the biggest competitive point between Metis and other Layer 2 is its decentralized sorter and decentralized economic model. The overall market value shown by TVL is more in line with market users' expectations for Metis Confident feedback.
Metis is different from other Layer 2 companies in the way they hold on to financial power. Instead, they distribute more revenue to users. The overall economic model of OP Rollup is a state of strong control. Through a centralized approach, OP Token rewards are continuously distributed to the ecosystem to stimulate development and interaction, thereby profiting from the Gas price difference. Different from this method, Metis uses The income rights and interests are delegated to the pledgers to participate in the competition, greatly releasing the financial attributes of Layer 2 infrastructure, thereby attracting a lot of market attention.
MEME represents more of a culture and some socioeconomic factors. For example, when we buy MEME, we not only treat it ten times, a hundred times or even a thousand times, In addition to investment expectations, part of it comes from our recognition and love for its narrative style and various factors. But in the end, pulling the market is justice, and Metis's growing TVL is also a feedback from the market on its investment expectations. The issue of MEME attributes should be considered from a market perspective aside from the technical aspect. My point of view is that if Inscription is a tester of public chain performance, then MEME is a touchstone of market recognition to a certain extent.
Meme, the evolution of MEME coin Golden Finance, only this kind of simplicity and purity can create a classic.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceA16z Crypto released Jolt, a zero-knowledge solution to accelerate and simplify blockchain scaling operations.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceMEME plays a vital role in Web3 culture
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceTo build a successful MEME, you need to consider factors such as token economics design, mascot, airdrop method, and the chain you choose to issue on.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAs the first Ethereum Rollup to feature a decentralized orderer, Metis is significantly positioned in the highly competitive layer-2 (L2) network space.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceThe Ethereum ecosystem has always faced scalability challenges, and the rise of Metis is bringing new solutions to this problem.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAfter a period of market movement, the market will have a concentrated MEME season. This is because there is a lot of money in the market at this time and FOMO is high. Still want to find new opportunities to get rich.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceDecentralization, Metis: Leading the way to decentralization Golden Finance, how to achieve decentralization?
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance Coinlive
Coinlive  Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph