In recent years, generative AI has been gaining popularity, and products such as ChatGPT and MidJourney have become the focus of public discussion. Recently, from Google's release of a 40-page white paper on "AI Agent" to the comprehensive layout of giants such as Microsoft and OpenAI on the B-end and C-end, AI Agent has become the hottest topic in the field of science and technology. It is not only an extension of the large language model, but also a key path to general artificial intelligence (AGI).
This article will take you to an in-depth understanding of the core concepts, working principles, application scenarios and future trends of AI Agent, revealing the logic and opportunities behind this intelligent revolution.
1. What is AI Agent?
Definition and Core Features
AI Agent is an intelligent system that can autonomously plan, make decisions, and execute tasks. It combines the powerful understanding ability of the large language model (LLM) with tool use, memory management, task planning and other functions, so that it can not only "understand" human instructions, but also "hands-on" complete tasks. For example, AI Agent can automatically book restaurants, generate reports, and even complete complex programming tasks according to user needs.
Difference from Large Language Model
Large language models (such as ChatGPT) are more like a "super brain" that is good at generating content and answering questions, but lacks the ability to act. AI Agent is a "complete body" that not only has a "brain", but also has "hands and feet" and "tools". For example, when a user asks to "compare the differences between Company A and our company's products and send a report to the mailbox", AI Agent will actively call the search engine, database and email tool to complete the entire task process.
II. Technical architecture of AI Agent
According to Google's white paper, the technical architecture of AI Agent consists of three key modules:
Reasoning Layer
As the decision-making core, it supports instruction-based reasoning and logical framework. This is the "brain" of AI Agent, which can understand the complex needs of user input and perform logical reasoning based on large language models (such as LLM). For example, when you tell it: "Help me arrange a three-day trip to Dubai suitable for the whole family", it can generate a practical plan based on your needs.
Tool Layer
Extensions:Connect APIs and agents to support dynamic selection of appropriate tools.
Functions:Execute API calls on the client side to provide more detailed control.
Data Storage:Provides access to structured and unstructured data through a vector database to support Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)16.
AI Agents do not work alone, they can call external tools and data sources, such as calendars, emails, search engines, and even interact with smart home devices. In this way, it can perform specific tasks such as "booking a doctor" and "managing schedules".
Orchestration Layer
This is the "command center" of the AI Agent, responsible for scheduling the reasoning layer and the tool layer to ensure that the tasks are carried out in an orderly manner. For example, when completing a three-step task, it can ensure that all steps are smoothly connected without omission or confusion.
3. The difference between AI Agent and Model

AI Agent significantly improves the capabilities of the model through the tool and orchestration layers, enabling it to handle more complex tasks.
Fourth, the working principle of AI Agent
Jarvis, the AI assistant in "Iron Man", shows the ultimate imagination of human beings for intelligent assistants: it can not only connect to any computer terminal and control the complex Iron Man suit, but also assist in formulating action plans and become Tony Stark's "digital partner". For a long time, this vision has only existed in science fiction works, while the functions of real voice assistants (such as Siri and Alexa) are limited and far from the intelligence level of Jarvis. However, with the breakthrough progress of large language models (LLM), AI Agent came into being. It can autonomously plan tasks, perform operations and seamlessly integrate with other services, truly realizing the efficient collaboration between humans and artificial intelligence.
AI Agent is an intelligent system that can autonomously plan, make decisions and perform tasks. The core of AI Agent is to combine the powerful understanding ability of the large language model (LLM) with functions such as tool calling, memory management, and task planning, so that it can not only understand human instructions, but also actively complete complex tasks. The following is a detailed analysis of the workflow and logic of AI Agent. (1) Workflow of AI Agent The workflow of AI Agent can be summarized into three core steps: perception and reception → understanding and reasoning → planning and execution. a. Perception and reception AI Agent receives information through multimodal input (such as text, images, voice, and sensor data). For example, when a user enters "Will it rain tomorrow?", AI Agent can recognize that this is a query request about the weather.
b. Understanding and Reasoning
AI Agent uses knowledge base and reasoning frameworks (such as ReAct, thinking chain, and thinking tree) to analyze the received information. For example, it will call the weather API to obtain the latest meteorological data and determine the probability of precipitation through logical reasoning.
c. Planning and Execution
AI Agent can not only generate text answers, but also call external tools to complete tasks. For example, it will output: "According to current weather data and forecasts, the probability of precipitation tomorrow is 80%. It is recommended that you bring an umbrella." In addition, AI Agent can also control physical devices (such as automatic umbrella delivery) to further meet user needs.
(2) AI Agent Technical Logic Example
Scenario: User asks “Will it rain tomorrow?”
Perception and Reception:AI Agent receives the user’s question through text, voice or image.
Understanding and Reasoning:
Call the weather API to query the latest weather forecast data.
Analyze the data and determine the probability of precipitation.
Develop an action plan, such as reminding the user to bring rain gear.
Planning and Execution:
Generate text answer: "The probability of precipitation tomorrow is 80%. It is recommended that you bring an umbrella."
If equipped with physical devices, the AI Agent can also automatically hand over an umbrella or adjust smart home devices (such as closing windows).
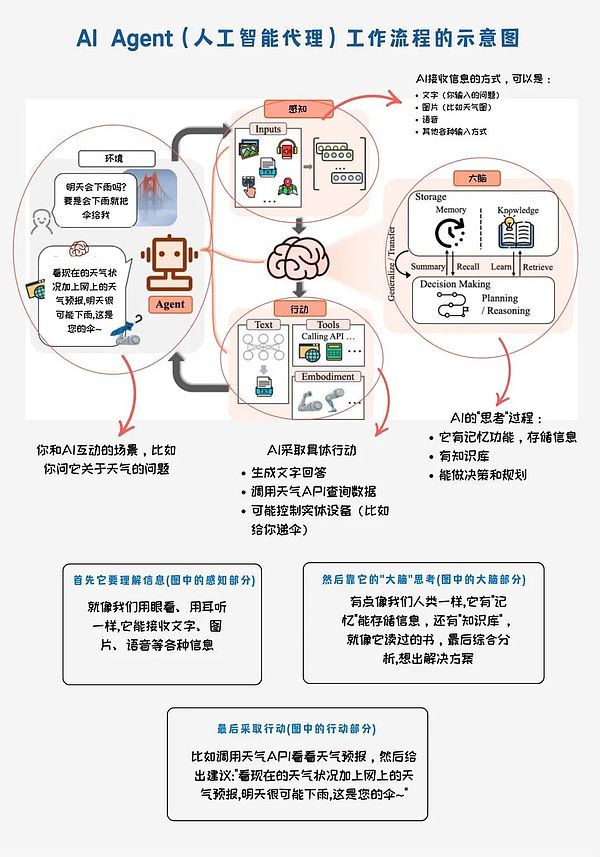
(3)Logical advantages of AI Agent
a. Autonomy and task planning
AI Agent can autonomously plan tasks and execute them without step-by-step guidance from the user. For example, when a user says "I want to travel to Sanya", AI Agent will automatically plan the itinerary, book air tickets and hotels, and generate a personalized travel plan.
b. Tool invocation and environmental adaptation
AI Agent can call external tools and data sources to complete complex tasks. For example, it can query real-time weather data through APIs, or control smart home devices (such as adjusting the temperature of the air conditioner). In addition, AI Agents can learn to use new software tools by observing human operations, further expanding the boundaries of their capabilities.
c. Multi-step task processing and dynamic adjustment
AI Agents can efficiently handle multi-step tasks and ensure that each step is seamlessly connected. For example, when completing a workflow with multiple subtasks, AI Agents can execute each step in sequence and dynamically adjust the plan according to environmental changes.
V. Application scenarios of AI Agents
AI Agents have shown strong application potential in many fields:
Finance:Automatically execute transactions, generate financial reports, and optimize investment portfolios11.
Medical:Assisted diagnosis, medical record management, surgical support, improve diagnosis and treatment efficiency and accuracy11.
E-commerce:Optimize product recommendations, automated customer service, and intelligent marketing strategies14.
Games:Introduce autonomous AI NPCs to enhance player immersion8.
Law:Automated legal document drafting, case research, and contract review11.
VI. Industry dynamics and giants’ layout
Google
The 40-page AI Agent white paper released by Google details the architecture and applications of Agent, emphasizing its potential in the field of generative AI. Google’s Vertex AI platform provides developers with tools to build and deploy Agents, supporting the rapid implementation of complex tasks.
Microsoft
Microsoft has built the world’s largest enterprise-level AI Agent ecosystem through Copilot Studio. Microsoft’s AI Agent has been used in multiple industries to help companies improve efficiency and innovation.
OpenAI
OpenAI plans to launch Operator AI Agent to support complex tasks such as automated code writing and travel booking. OpenAI's AI Agent has significant advantages in natural language processing and task planning.
Zhipu AI
Zhipu AI has launched AutoGLM, GLM-PC and other intelligent agents, covering mobile phone, PC and web page operations. Zhipu AI's Agent performs well in personalized services and multimodal interactions.
VII. Future Trends of AI Agent
2025 is considered the first year of commercialization of AI Agent. As the technology matures, AI Agent will find a wide range of application scenarios in the fields of finance, medicine, law, etc., significantly improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Stronger Autonomy and Intelligence
Future AI Agents will have stronger autonomous decision-making capabilities and be able to complete tasks autonomously in more scenarios. For example, through continuous learning and environmental adaptation, AI Agents will be able to handle more complex multi-step tasks.
Ethical and Security Challenges
As AI Agents become more powerful, their security and ethical issues have received unprecedented attention. The research community is developing new security frameworks to ensure that AI Agents always behave in accordance with predetermined ethical standards.
The emergence of AI Agents marks the transition of artificial intelligence from a "tool" to an "intelligent partner". From the workplace to life, its application prospects are broad and exciting. Just as smartphones have reshaped the way we communicate, AI Agents may become a "new necessity" in our lives and work, deeply integrated into our daily lives, and bring unprecedented convenience and efficiency to everyone.
However, the development of technology never stops at being amazing, it also requires prudent reflection and planning. While we enjoy the dividends brought by AI Agents, we must face up to important issues such as privacy protection and security, lay a more solid foundation for its popularization and application, and promote artificial intelligence towards a more reliable and more humane future.
The era of AI Agent has quietly begun, and it is changing the way we understand and use technology. Are you ready to join hands with it to move towards a new intelligent future?
 Joy
Joy









