Source: Chain Tea House
LayerZero is an interoperability protocol that uses new technology to instantly verify cross-chain transactions to connect different blockchains, overcome the challenges of liquidity fragmentation, and aims to create paths and platforms for communication between independent blockchain networks, enabling them to share assets, status, liquidity, etc.

LayerZero was founded in 2021 by a team of engineers led by Bryan Pellegrino (co-founder and CEO) and co-founded by Caleb Banister (co-founder) and Ryan Zarick (co-founder and CTO).
At the time, because many blockchains operated in isolation, users were forced to split their resources and liquidity, limiting their options for transferring liquidity and status between closed ecosystems.
Therefore, LayerZero Labs' mission is to solve the interoperability problem between blockchains and provide decentralized application (dApp) developers with the ability to message on multiple blockchains without intermediaries. LayerZero uses an innovative architecture that includes ultra-light nodes, independent oracles, and relayers to transfer messages between chains securely and efficiently.
1. How it works
LayerZero uses a set of smart contracts called LayerZero endpoints on each supported chain. In addition to connecting all chains supported by LayerZero, they can also be deployed on new chains to incorporate them into the network. Cross-chain lending is an example, where transaction details are sent from one blockchain (such as Ethereum) to a LayerZero endpoint on another chain (such as Avalanche), facilitated by independent off-chain entities, Oracles and Relayers.
Specifically, the main components of the LayerZero protocol operation include:
Relayer: Responsible for sending transaction proofs and transaction data from chain A to chain B, while matching the block header hashes of chain A and chain B.
Oracle: Works with decentralized oracles such as Chainlink to provide reliable data transmission for the LayerZero network.
Endpoints: A set of smart contracts divided into communicators, validators, networks, and library modules. The library module contains the code for each blockchain network. When a new network needs to be added, only the library module needs to be updated. It is a facility that interacts directly with users or applications, or it can also be regarded as a series of smart contracts that handle logic. These endpoints are responsible for handling message transmission, verification, and reception. Their purpose is to ensure effective delivery when users send messages using the protocol.
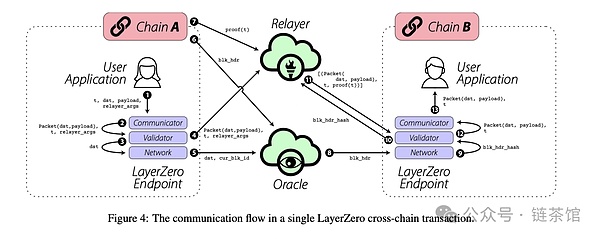
The message delivery process of LayerZero relies on two main entities: oracles and relays. When a user agent (UA) sends a message from chain A to chain B, the message is first delivered through the endpoint on chain A. The endpoint then notifies the designated oracle and relayer about the details of the message and its target chain. The oracle passes the block header to the endpoint on chain B, while the relayer submits a proof of the transaction. After the proof is verified on the receiving chain, the message is forwarded to the final destination address.
LayerZero's security is based on the idea that if two independent entities can confirm a transaction on one chain, then the other chain can be trusted to execute the transaction. After receiving the transaction details, the Oracle creates a block header, and the Relayer independently generates a proof. If both parties agree, the transaction is considered valid and completed on the second chain.
2. Functionality and its ecological use cases
1) Bridging
Bridging is currently the most popular interoperability solution. Cross-chain bridging allows asset holders to transfer assets between different Layer 1 and Layer 2 platforms. There are many reasons why investors bridge their assets to another network, such as taking advantage of the fee structure on the target chain, or benefiting from the application on the target chain. Thanks to cheaper Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chains like Polygon, Fantom, and BNB Smart Chain (BSC), bridging is more important than ever. But in addition to the poor security already discussed, current bridging platforms have shortcomings.
The capital intensity of running a bridge lies in the need to develop new infrastructure for each bridge direction. For example, a bridge platform supporting 5 networks would require writing 5 different codes and running 5 intermediate chains or light nodes.
LayerZero claims to solve this problem; firstly, the requirements for ultra-light nodes are lower, and universal data exchange means that bridges can be created for multiple networks using the same infrastructure and code. Such bridges are more efficient and cost-effective, without the need to use different code sets to bridge different chains.
2) Aptos Bridge
Aptos was launched in October 2022, with the Aptos Token (APT) as the network's native currency. Aptos’ claim to fame is primarily due to the unique technology it uses and its connection to Facebook’s failed Diem project, as Aptos’ modified Move language was originally developed for the Diem blockchain.
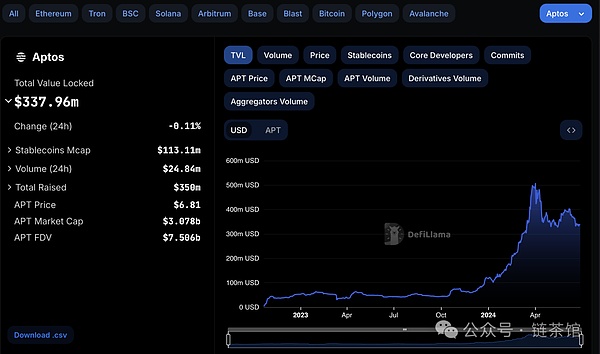
As of now, Aptos has a market cap of over $3 billion, and DefiLlama reports a TVL of $330 million in assets on the network, making its ecosystem a significant one. However, Aptos is not EVM-compatible, and this is where LayerZero comes in. The LayerZero Aptos bridge was launched shortly after the mainnet mined its genesis block, connecting Aptos with other EVM-compatible networks and even the Ethereum network.
Through the Aptos bridge, users can bridge Aptos-supported assets with other networks such as BNB Smart Chain (BSC), Avalanche, Polygon, Ethereum, and Ethereum Layer 2 networks such as Optimism and Arbitrum. According to the platform information, the bridging process is expected to take 2-5 days.
3) Stargate Finance (STG)
Stargate is a building bridge platform developed using LayerZero interoperability technology. Stargate enables blockchain enthusiasts to transfer assets across chains in their original form with guaranteed finality.
This is achieved through Stargate's use of a unified pool system to handle transfer requests across supported chains. Liquidity providers stake their assets in Stargate's single asset pool and receive staking rewards in the form of stablecoins, which are derived from the fees paid by users to bridge assets on the platform.
The bridge currently supports about 8 networks, including Layer 2 vertical scaling solutions such as Arbitrum and Optimism. Full-chain technology provides a layer for supported tokens, allowing them to run seamlessly and move across other chains. Stargate Finance also provides cross-chain swaps, where users can send an asset from a source network and receive and receive another asset on the target chain.
Data from the project page shows that more than $200 million worth of assets have been locked on the platform. This reflects the liquidity of the pool that services the bridge request. Stargate Token (STG) is the native token of the Stargate ecosystem and is used for rewards and governance purposes. Liquidity providers can stake their LP tokens and receive additional rewards in STG tokens.
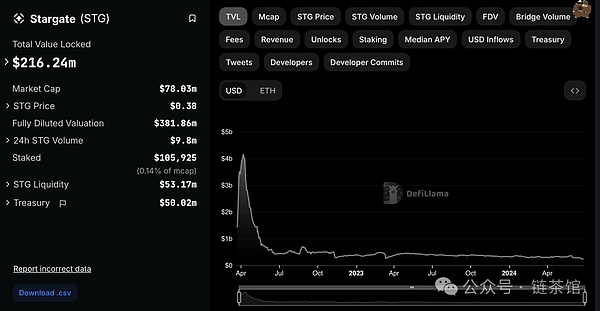
To contribute to the project governance, STG holders must stake their tokens on the governance portal to obtain VeSTG. This is used to vote on improvement proposals. STG is actively traded on centralized and decentralized exchanges. You can click here to view the active trading pairs of STG tokens.
3. Cross-chain exchange and unified liquidity
Investors who want to buy crypto assets on different networks first need to bridge the unified asset to the target chain and then use the decentralized exchange on the target chain to make the purchase. LayerZero's test bridge can directly exchange Ethereum in the mainnet and Layer 2 solutions such as Arbitrum and Optimism for Goerli ETH. Similar systems can be developed on a larger scale to support cross-chain exchanges, eliminating the process of bridging and connecting to exchanges on the target platform.
Current bridges use separate liquidity pools, for example, different liquidity pools serve bridge requests from Ethereum to the Polygon PoS chain and bridge requests from Fantom's Opera chain to Polygon. This may lead to efficiency differences. The liquidity on the Ethereum to Polygon bridge may be sufficient to handle all requests, while the assets of both chains on the Fantom to Polygon bridge are not enough to complete the bridge request immediately.
LayerZero co-founder Ryan Zarick mentioned that LayerZero can use a unified liquidity pool to meet bridge requests from multiple target chains.
"LayerZero achieves the ultimate goal of bridging: unified liquidity across all chains and guaranteed finality on the source chain. This means that when a user transfers an asset from chain A to chain B, the user is guaranteed the asset on chain B, and the LP provider earns fees from all incoming transactions to chain B, regardless of the source chain."
1) Base
Base is an Ethereum Layer 2 solution launched by Coinbase, using Optimism's OP Stack software. Base provides a simple integration path for decentralized applications, ensuring the security, stability and scalability of decentralized applications, while providing a convenient channel for users and assets from Ethereum L1, Coinbase and other interoperable chains.
The LayerZero protocol was launched on Coinbase's Base mainnet, facilitating cross-chain communication through a full-chain interoperability solution, including token swaps, transfers and other functions, improving the overall efficiency and accessibility of the decentralized ecosystem.
There are many practical applications released by the cooperation between LayerZero and Base. For example, the Parallel project has used the LayerZero protocol to smoothly move tokens between Base and Ethereum, demonstrating the practicality and efficiency of the protocol.
2) SushiSwap
SushiSwap is a multi-chain decentralized exchange powered by AMM. It claims to have more than 400 crypto assets available for instant decentralized exchange. More than $200 million worth of crypto assets are locked in its liquidity pool. These statistics are from the official website of the project and are valid at the time of writing. Its governance and reward system is provided by the SUSHI token.
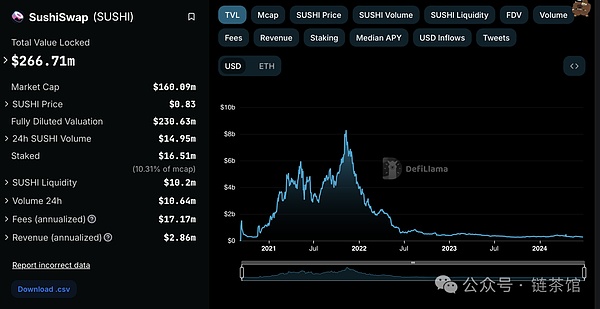
In July 2022, SushiSwap announced the launch of SushiXSwap. The new platform was developed using LayerZero's interoperability technology to solve the pain points of using multi-chain DeFi applications. In the announcement, SushiSwap reflected on the main issues affecting cross-chain interaction facilities and how LayerZero's technology was deployed to solve this problem. At the time of release, SushiXSwap supports asset bridging across Ethereum, Fantom, and approximately 5 other networks.
LayerZero's technology enabled SushiSwap to develop a unified liquidity system that pools resources across supported networks to cater to asset transfers and ensure that these transactions are completed in the shortest possible time. As an already existing liquidity pool project, SushiSwap uses its liquidity pool to power bridges between the chains where the project is located, solving the problem of fragmented liquidity.
SushiSwap also solves the fee structure problem of asset bridges by providing users with the cheapest cross-chain transfer route. This cost-effective solution utilizes Stargate Finance's bridging infrastructure to find the cheapest route to transfer assets from a source chain to a target chain. SushixSwap will also use Stargate's facilities to expand its bridges and expand to other networks over time. Cross-chain swaps are also available on SushiXSwap.
4. Full-chain tokens and NFTs
By design, LayerZero's technology creates a true zero layer: an ecosystem that can interact with any other network, share resources, and operate freely without platform restrictions - full chain. LayerZero can be the first to launch "non-native" crypto assets. Non-native means that they can be used on every chain without the need to transplant them to the target chain and back through a bridge that changes their original form. Full-chain tokens and NFTs will be unique and enjoy faster adoption because investors can easily buy and store them on their favorite blockchain.
1) TofuNFT
TofuNFT is a multi-chain NFT market deployed on more than 20 blockchain networks. NFT enthusiasts can list their NFTs on supported networks and sell them on TofuNFT's market, and can also collect works from other NFT creators. TofuNFT Selected by LayerZero Ecosystem for Development of Full-Chain NFTs Marketplace
Full-Chain NFTs, like Full-Chain Fungible Tokens (OFTs), are non-native NFTs that can be easily transferred across different networks in their original form. TofuNFT's Full-Chain Marketplace has already received a small number of Full-Chain NFT listings, such as LayerZero Punk, which has a reserve price of 0.015ETH at the time of writing.
2) Oasys

Oasys is a blockchain optimized for gaming that provides a highly scalable Layer 1 hub and a dedicated Layer 2 using Ethereum's Layer 2 scaling solution. The ecosystem provides game developers with a secure and scalable blockchain infrastructure to create more efficient, secure, and interoperable games.
Oasys’ validators include leaders in gaming and Web3, such as SEGA, Ubisoft, and Yield Guild Games, who are initial validators for our Proof of Stake (PoS)-based blockchain. Oasys’ professional blockchain team, combined with the biggest names in gaming, is revolutionizing the gaming industry.
Oasys is committed to creating an ecosystem for gamers and developers to distribute and develop games, addressing the challenges game developers face when building blockchain-based games. The company’s trifecta approach includes a fast network powered by the gaming community, a scalable network powered by AAA game developers, and a blockchain that provides the best user experience with fast transactions and zero gas fees. This approach prepares participants to enter Oasys and play games.
After integrating with LayerZero, Oasys will leverage LayerZero’s interoperability technology to enhance cross-chain operations of games and NFTs, providing a richer and inclusive gaming experience. LayerZero also enables the flow of fungible tokens through the Omnichain Fungible Token (OFT) standard. Bryan Pellegrino, co-founder and CEO of LayerZero Labs, added: "LayerZero's addition of endpoints to Oasys is a major leap forward in in-game asset interoperability. LayerZero is committed to connecting communities and empowering players by making their favorite games more accessible and enjoyable across different networks."
Overall, LayerZero is primarily used by decentralized application developers who need to communicate across multiple blockchain networks. The LayerZero ecosystem also includes projects in multiple different categories, covering NFTs, payments, wallets, bridges, infrastructure, DeFi, DEX, GameFi and other aspects, and the ecosystem is relatively prosperous
5. ZRO Token
$ZRO tokens are the main tokens in the LayerZero ecosystem, used to promote various activities and incentive mechanisms within the ecosystem.
$ZRO tokens play multiple roles in the LayerZero ecosystem, including:
Incentives and Rewards: Used to reward participants and contributors in the ecosystem.
Governance: Users holding $ZRO tokens can participate in the governance decisions of the protocol.
Payments and Transactions: Used to pay for cross-chain operations and other transaction fees within the ecosystem.
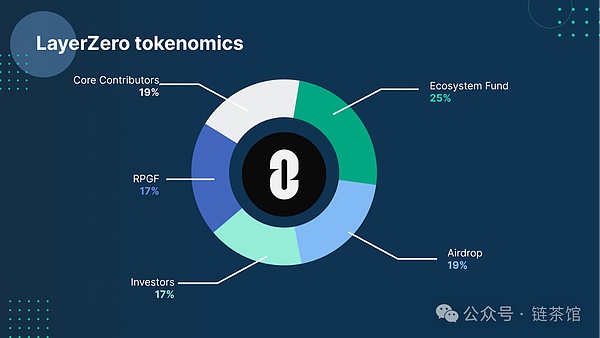
The initial distribution of $ZRO tokens is as follows:
Ecosystem Fund: 25% (2500)
Airdrop: 19% (1900): 5% for IDO
Core Contributors: 19% (1900)
Investors: 17% (1700)
RPGF(Retroactive Public Goods Funding): 20% (2000)
The circulating supply of $ZRO tokens is 110,000,000 ZRO, with a total supply of 1,000,000,000 ZRO and a maximum supply of 1,000,000,000 ZRO.
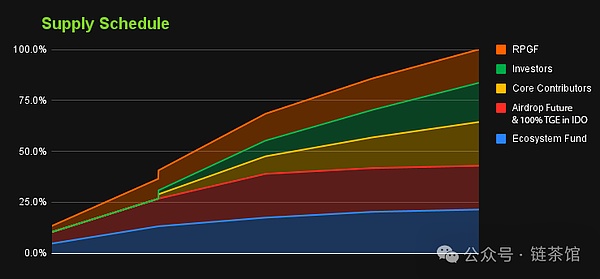
The release cycle of $ZRO tokens is shown in the figure below:
6. Team/Financing
Bryan Pellegrino, co-founder and CEO of LayerZero Labs, graduated from the University of New Hampshire with a degree in Computer Science. He has served as an entrepreneur in residence, lead engineer for machine learning architecture, and co-founder of OpenToken.
Co-founder Caleb Banister is good at writing and auditing smart contracts for blockchain-related projects. Caleb is a professional Solidity developer with a bachelor's degree in computer science from the University of New Hampshire. He is a skilled Java and Linux programmer who is building the future and the multi-chain metaverse.
Another co-founder, Ryan Zarick, is the CTO of LayerZero Labs. He is an experienced software developer and entrepreneur with more than 10 years of experience in the technology industry. He co-founded Minimal AI, Coder Den, and 80Trill, and served as CTO at Buzzdraft. He holds a master's degree in computer science from the University of New Hampshire.
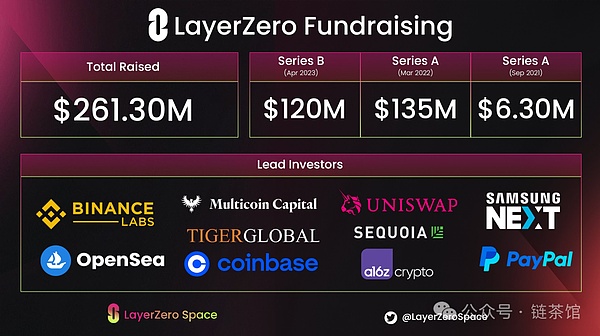
Since its inception, LayerZero has successfully completed multiple rounds of financing, with a total financing amount of US$263 million and its market valuation reaching US$3 billion.
In the most recent round of Series B financing, LayerZero successfully raised US$120 million on April 4, 2023, which brought its valuation to US$3 billion. This financing attracted the participation of several well-known investors, including Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), Sequoia Capital, and Circle.
Previously, LayerZero also completed a round of A1 financing on March 30, 2022, with a financing amount of US$135 million and a valuation of US$1 billion. The main investors in this round of financing include Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) and Sequoia Capital, which shows the market's confidence in LayerZero's technology and development.
Earlier on September 16, 2021, LayerZero completed a round of A financing and successfully raised US$6 million with a valuation of US$50 million. With these early financial support, LayerZero laid its foundation in the field of blockchain interoperability and promoted the initial development of the project.
7. Project Evaluation
LayerZero belongs to the cross-chain interoperability track in blockchain technology. The goal of this field is to solve the communication and asset transfer problems between different blockchain networks and enhance the interconnectivity of the blockchain ecosystem.
Another cross-chain interoperability project similar to LayerZero is Wormhole.
Created by Jump Crypto, Wormhole is a decentralized cross-chain protocol that aims to achieve data and token transmission between different blockchains through a universal messaging protocol. Supported blockchains include Ethereum, Solana, Sui, Injective, etc.
Wormhole consists of 17 highly verified Guardian nodes, which must confirm each transaction to ensure the security of the system. It also supports cross-chain token and NFT transfers, has processed more than 1 billion cross-chain messages, and interoperates with the message systems of Cosmos and Polkadot. In addition, wormhole also supports the transfer of NFT assets between multiple blockchain networks.
Wormhole can be said to be the most mature protocol on the track and the only one that has been unconditionally approved to be used by Uniswap. It also claims to be able to process over 1 billion cross-chain messages and can interoperate with Cosmos and Polkadot messaging systems. Although Wormhole may not be valued as highly as LayerZero, it has the most adopted protocol and momentum doesn’t seem to be changing anytime soon.
However, there are differences between LayerZero and Wormhole. Wormhole mainly relies on a fixed network of Guardian nodes, which is less flexible. LayerZero can freely choose oracles and relayers, which improves the flexibility and modularity of the system. Wormhole uses a trust-based technical solution (packaged assets are stored on the bridge chain and controlled by a multi-signature account), while LayerZero uses light nodes to run on the target chain. These nodes are able to package and send all transactions at once, directly transferring native assets between chains, avoiding the complexity and risks of transferring assets between different chains.
So Wormhole was exploited by hackers in 2022, resulting in a loss of 120,000 ETH (about $325 million), but security has been significantly enhanced since then, and LayerZero's cross-chain system has not yet been successfully attacked by hackers.
In addition to security, LayerZero has the following advantages,
Scalability: LayerZero is designed with scalability in mind and can handle high transaction volumes without affecting performance, making it suitable for large-scale applications and enterprise integration.
Developer-friendly: It provides a powerful set of tools and APIs to facilitate developers to build and deploy cross-chain applications.
Cost-effectiveness: Through LayerZero's architecture, users can achieve cross-chain functions without incurring high costs.
Ecosystem Support: LayerZero has received broad support from the blockchain community and industry stakeholders, forming a vibrant ecosystem of developers, users, and partners.
While LayerZero is designed to be scalable, performance may be sacrificed when handling extremely high transaction volumes or complex cross-chain operations. Ensuring optimal performance under all conditions remains a challenge that the protocol must continue to address. In addition, LayerZero's security model relies on external validators, such as oracles and relayers. While this enhances decentralization and security, it also introduces potential points of failure if these validators are compromised. Ensuring the reliability and trustworthiness of these external entities is critical to the long-term viability of the protocol.
However, since LayerZero is still in the early stages of the project and has only recently issued coins, there is still potential for future development. As long as its solution continues to work as it claims, the LayerZero ecosystem will surely become larger as more and more projects adopt a sound interoperability solution.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Xu Lin
Xu Lin JinseFinance
JinseFinance decrypt
decrypt Numen Cyber Labs
Numen Cyber Labs Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph