Author: DeMan
Polygon's recent asset price movements have excited its investors.
Since January 23, the price of Polygon token MATIC has increased from $0.71 to $0.997 on February 20. At the same time, its 24-hour trading volume increased significantly, reaching $616,451,842, an increase of 25.30%. In the past 7 days, the price of MATIC has increased by 12.30%, showing strong momentum.
On February 9, Polygon released the Type 1 Prover of the next-generation zkEVM prover, which is Polygon’s next-generation proof technology that can be used for any EVM chain (side chain, Optimistic Rollup, or even Ethereum itself) ) to generate a proof. Polygon said the Type 1 upgrade will be able to generate ZK proofs for Ethereum mainnet blocks at an average cost per transaction as low as $0.002-$0.003 (more than 36 times faster than any other Type 1 Prover), with the addition of Plonky3 and zkEVM Improvements are expected to reduce costs by 30 to 50 times next year.

So, what exactly is a Type 1 Prover? Is there any room for optimization of Polygon’s zkEVM technology? What does this mean for the L2 track? This is introduced below.
How does Type 1 Prover affect ZK technology? How does Etrog upgrade enhance zkEVM functionality?
Polygon can occupy a key position in the Ethereum L2 track by relying on zero-knowledge proof (ZK) technology. Type 1 Prover is a major innovation of Polygon in zero-knowledge proof (ZK) technology. Its principles and impacts are as follows:
1. Optimization of proof generation: Type 1 Prover can provide solutions for Ethereum virtual machines ( EVM) generates ZK proofs for any chain, including sidechains, Optimistic Rollup, and even Ethereum itself. This capability is based on complex mathematical and cryptographic principles and ensures the privacy and security of transactions by generating zero-knowledge proofs to verify transactions without exposing all transaction data.
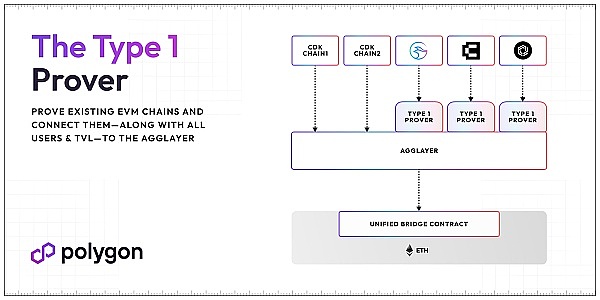
2. Significant improvements in cost and speed: The introduction of Type 1 Prover has significantly reduced the cost of generating ZK proofs. The average cost per transaction is expected to drop to US$0.002 to US$0.003, while increasing the speed of proof generation. More than 36 times faster than any other Type 1 Prover.
3. Future cost reduction expectations: With further improvements in technology, Polygon expects costs to be further reduced by 30 to 50 times in the future, which will bring wider application possibilities to the Ethereum ecosystem. and lower operating costs.

It is also worth noting that at almost the same time, Polygon used the Etrog upgrade to carry out key technical transformations on the beta version of the zkEVM mainnet, mainly including the following aspects:
1. Expansion of pre-compilation support: The Etrog upgrade greatly enhances the capabilities of the Polygon zkEVM by introducing four additional precompilations, making it almost a complete Type 2 ZK-EVM. The addition of these precompilations provides developers with more tools and resources, allowing them to build and deploy decentralized applications (dApps) more efficiently.
2. New transaction processing method: The upgrade also includes a new transaction processing mechanism, which optimizes the verification and execution process of transactions, thus improving the overall performance and efficiency of the network.
3. Compatibility and seamless migration: Most notably, the Etrog upgrade allows dApp developers to rebuild their code and smart contracts intact without any audit or modification. Deployed on Ethereum, it greatly reduces migration costs and simplifies the development process.
In short, the Etrog upgrade and the introduction of Type 1 Prover not only improve the performance and compatibility of Polygon zkEVM, but also provide new solutions for the expansion and optimization of the Ethereum ecosystem.
Polygon ecological project Keom is carrying out a series of DeFi innovations to imbue ZK technology with financial imagination
While Polygon is carrying out technological upgrades, DeFi projects within its ecosystem are also Using ZK technology to complete Web3 financial innovation will be of great help to the development of the Polygon ecosystem.
In the field of DeFi, the Polygon ecological project Keom is leading a theoretical and practical change through its pioneering work on the Polygon Miden platform. Utilizing zero-knowledge proof (ZK) technology, Keom not only redefines the infrastructure of decentralized finance at a technical level, but also sets new standards in ensuring transaction privacy and security.
Keom’s core innovation lies in its reimagining of the on-chain order book, which is based on ZK technology. By implementing this concept on Polygon Miden, Keom demonstrates how to achieve efficient execution of decentralized transactions without sacrificing user privacy and security. The theoretical basis of this approach is that ZK proofs allow the verifier to confirm the correctness of a calculation without knowing the specifics of its execution.
Polygon Miden provides a unique execution environment that combines the advantages of Ethereum’s account model with UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) models such as Bitcoin and Zcash, and introduces ZK proof to enhance Privacy and security. Under this framework, accounts communicate through notes, which are messages that carry assets and define how to spend those assets. This structure enables developers to execute transactions locally and verify them through ZK proof, thus ensuring the privacy and security of transactions without exposing all transaction data.
Keom leverages Miden’s unique execution environment to solve the specific problems of placing decentralized order book exchanges on-chain. The theoretical significance of this solution is that it allows all functions – such as order matching, order creation, bid-ask spreads and market depth visualization – to be executed without actually holding liquidity. In other words, the decentralized order book will be a service that organizes the execution of all these functions, while liquidity is shared by any account wishing to exchange assets on the same blockchain.
Under Miden's note-taking framework, each note is like its own independent contract. The theoretical advantage of this design is that while there may be exploitable vulnerabilities in the consumption conditions of notes, the differences between different notes and the selective disclosure transparency of the consumption conditions of notes mean that an attacker would need to exploit notes individually rather than in batches. User's funds. This brings fundamental changes to user security in DeFi.
Blockbuster moves have never stopped since the beginning of the year. Can Polygon exceed investor expectations in 2024?
Recently, Polygon has made significant progress in promoting blockchain technology innovation. On January 28, Polygon announced that it will be upgraded to Type 2 ZK-EVM. This change will greatly simplify the process for developers to deploy code on Polygon zkEVM, achieving the same seamless experience as the Ethereum mainnet. In addition, Polygon also launched the Cardona test network, providing developers with a brand new testing environment.
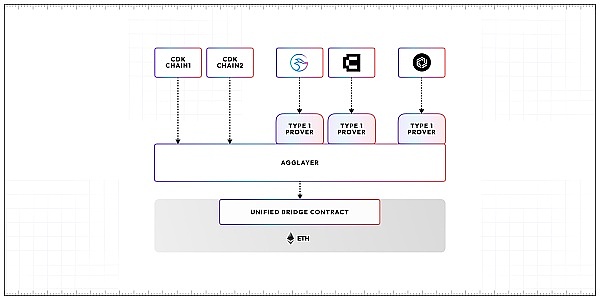
On February 13, Polygon further announced that the AggLayer v1 mainnet will be launched soon. AggLayer aims to connect different blockchain networks using zero-knowledge proof technology, marking an important step forward for Polygon in blockchain interoperability and scalability.
In addition, Polygon's strategic cooperation with the Bitcoin second-layer network B² Network, through the "B² Hub + Polygon CDK" technology stack, aims to help developers build secure and powerful Bitcoin Rollups, further enhancing Improved interoperability between Rollups.
These developments demonstrate Polyon’s ambitions within the L2 technology ecosystem, but its future results still need to be tested through specific practice.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance









