Introduction
Under the strategic shift of the Trump administration to fully embrace crypto assets, the scale of crypto reserves of listed companies is about to exceed the 100 billion US dollar mark. This article systematically sorts out the global corporate crypto reserve map, deeply analyzes the capital operation model with MicroStrategy as the core, and explores the differentiated paths and potential risks of altcoin reserve companies - this "digital assetization" experiment led by traditional companies is reshaping the future paradigm of corporate financial management.
Global Panorama of Cryptocurrency Reserve Companies
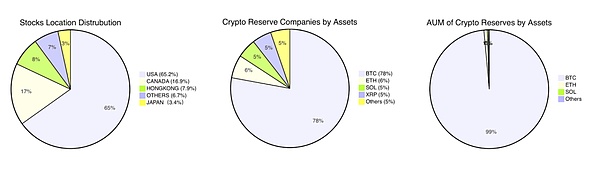
From the distribution of listed companies, US listed companies account for 65.2%, Canada accounts for 16.9%, Hong Kong accounts for 7.9%, Japan also has a small number of companies with reserves (3.4%), and the rest of the world accounts for 6.7%.
From the types of crypto assets reserved by listed companies, BTC accounts for 78%, ETH, SOL, XRP and other proportions are similar, all at the level of 5%-6%, while companies with reserves of other crypto assets account for the remaining 5%.
From the perspective of the value of crypto assets reserved by listed companies, BTC is in an absolute leading position, accounting for 99% of the value, and the remaining assets account for the remaining 1%.
Based on the statistical analysis of the time when companies first announced their crypto strategic reserves, the results are shown in the figure below.
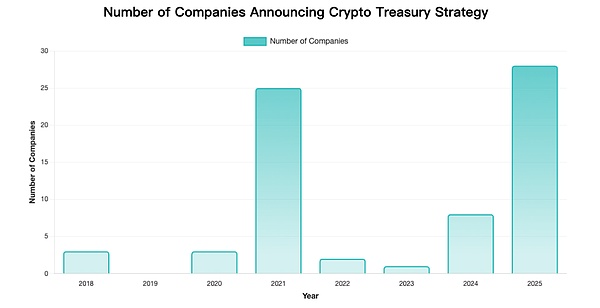
Note: Only some accurate data are included
From the chart we can observe obvious peaks and troughs, which also coincides with the bull and bear cycles of the cryptocurrency market itself.
Two significant peaks:
2021: 25 companies announced strategic reserves, mainly driven by the rise in Bitcoin prices and the demonstration effect of MicroStrategy.
2025: 28 companies, the highest peak in history, showing that the acceptance of cryptocurrency as a corporate reserve asset has further increased.
Trough characteristics:
Recently, more and more companies have announced their crypto reserves. It is expected that the number of listed companies with crypto reserves this year is expected to exceed 200, and the adoption of cryptocurrencies in traditional industries continues to increase.
Strategic reserves, capital operations and stock price performance
From the current capital operation models of various digital asset reserve companies, they can be summarized into the following models:
1. Leveraged coin hoarding model: The main business is relatively weak, and the funds raised through debt and financing are used to purchase encrypted assets. After the encrypted assets rise, the net assets are promoted, the stock price is promoted and further financing is carried out, forming a positive feedback flywheel effect. In essence, the company's stock is made into a spot leverage of encrypted assets. If operated properly, the stock price and net assets can be leveraged to rise simultaneously at a low cost. Typical cases: MicroStrategy ($MSTR BTC reserve), SharpLink Gaming ($SBET ETH reserve), DeFi Development Corp ($DFDV SOL reserve), Nano Labs ($NA BNB reserve), Eyenovia ($EYEN HYPE reserve).
2. Cash financial management model: Companies with excellent main business (main business has nothing to do with encryption) obtain investment returns by purchasing high-quality crypto assets when there is sufficient cash flow on the account. Usually there is no significant impact on the stock price, and it may even cause a decline due to investors' concerns that the company has neglected its main business. Typical cases: Tesla ($TSLA BTC reserve), Boyaa Interactive (HK0403 BTC reserve), Meitu (HK1357 BTC+ETH reserve).
3. Business reserve model: the direct or indirect reserve behavior of the company due to its main business related to encryption. For example, the business needs of exchanges, and mining companies retaining the mined Bitcoin as reserves to deal with possible business risks. Typical cases: Coinbase ($COIN various crypto asset reserves), Marathon Digital ($MARA BTC reserves).
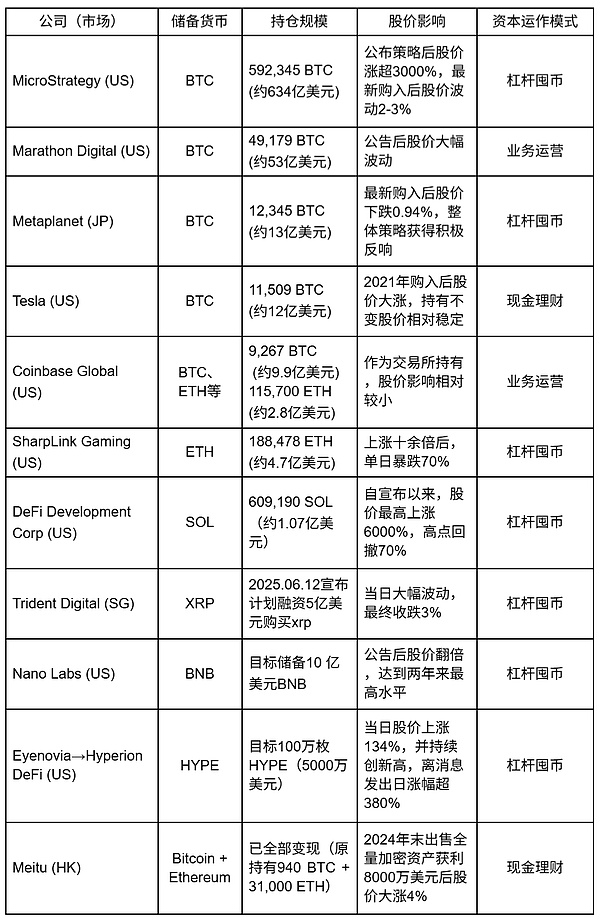
Among many companies, MicroStrategy flexibly uses leverage to transform from a software service provider that has been losing money for many years to a Bitcoin whale with a market value of hundreds of billions. Its operating model is worthy of in-depth study.
MicroStrategy: Crypto Reserve Leverage Operation Textbook
5 years and 30 times increase: Bitcoin leverage agent
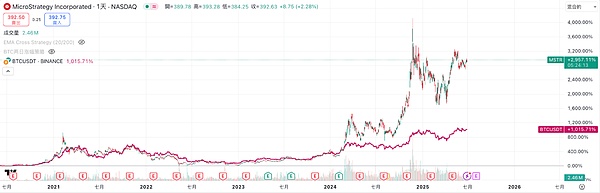
Since MicroStrategy announced the implementation of Bitcoin strategic reserves in 2020, the stock price has been highly correlated with the price of Bitcoin, and the volatility is much higher than Bitcoin itself. The following figure can give an intuitive feeling. From August 2020 to date, MSTR's cumulative increase has been close to 30 times, while the price of Bitcoin has only increased by 10 times during the same period.
Statistics of the volatility and correlation between Bitcoin and MSTR by month show that,most of the time the price correlation between MSTR and Bitcoin is in the range of 0.6-0.8, showing a strong correlation;at the same time, most of the time the volatility of MSTR is several times higher than that of Bitcoin.From the results, MSTR can be regarded as a spot leveraged security of Bitcoin. From another perspective, the Bitcoin leverage attribute of MSTR can also be verified: The implied volatility of MSTR 1-month call option in June 2025 is 110%, 40 percentage points higher than the spot price of Bitcoin, indicating that the market gives it a leverage premium. The core of the micro-strategy model is to use a lower financing cost to obtain funds for the purchase of Bitcoin. As long as the expected rate of return of Bitcoin is higher than the actual financing cost, the model can continue to be established.
MicroStrategy has created a set of capital tool matrices to transform the volatility of Bitcoin into structured financing advantages. Its capital operations use a variety of financing strategies to form a self-reinforcing capital cycle. VanEck analysts have described it as "a pioneering experiment in combining digital currency economics with traditional corporate finance."
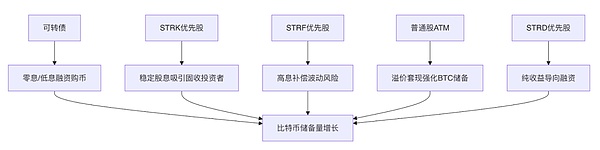
MicroStrategy's capital operations have two core goals: control the debt ratio and increase the number of BTC per share (BTC per Share). Assuming that BTC rises in the long term and the two core goals are achieved, the value of MicroStrategy's stock will also increase.
For MicroStrategy, mortgage lending has hidden costs and limitations such as insufficient capital efficiency (requiring a 150% excess mortgage rate), uncontrollable liquidation risk, and limited financing scale.
Compared with mortgage lending, financing methods with implicit options such as convertible bonds and preferred stocks can further reduce costs and have less impact on the asset-liability structure. The sale of ATM common stock can quickly and flexibly obtain cash. In accounting treatment, preferred stocks are included in equity rather than debt, which can further reduce the debt ratio compared to convertible bonds.
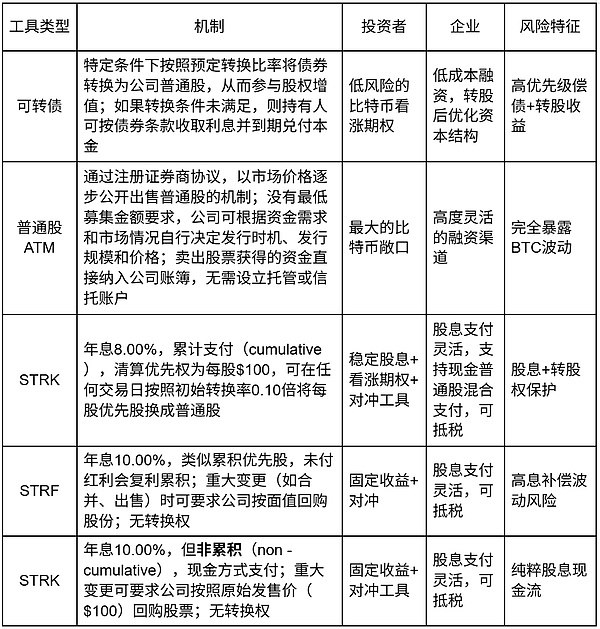
This complex matrix of capital tools is favored by professional investors, enabling them to arbitrage the differences in actual volatility, implied volatility and other components of the option pricing model, which also lays a foundation for loyal buying of Micro Strategy's financing tools.
Combining the quarterly Bitcoin holdings and liabilities, and important capital operation events, we can observe that:
Through the combination of various financing tools, MicroStrategy issued convertible bonds and preferred stocks in the bull market when Bitcoin volatility was high and stocks had a positive premium to expand its Bitcoin holdings, and sold common stocks through ATMs in the bear market when Bitcoin volatility was low and stocks had a negative premium to prevent the risk of chain liquidation caused by excessive debt ratio.
Convertible bonds and preferred stocks are preferred during high premium periods. The possible reasons are as follows:
1. Dilution delay effect
Direct issuance of common stock (ATM) will immediately dilute the equity of existing shareholders. Convertible bonds and preferred stocks, by embedding conversion options, postpone the equity dilution to the future.
2. Tax-efficient structure
Preferred stock dividends can be deducted from 30% of taxable income, reducing the actual cost of STRK with an 8% dividend rate to 5.6%, which is lower than the 7.2% interest rate of comparable corporate bonds. Common stock financing does not generate tax deduction benefits.
3.Avoid reflexive risk
Large-scale ATMs are seen as a signal that management believes the stock price is overvalued, which may trigger programmatic selling.
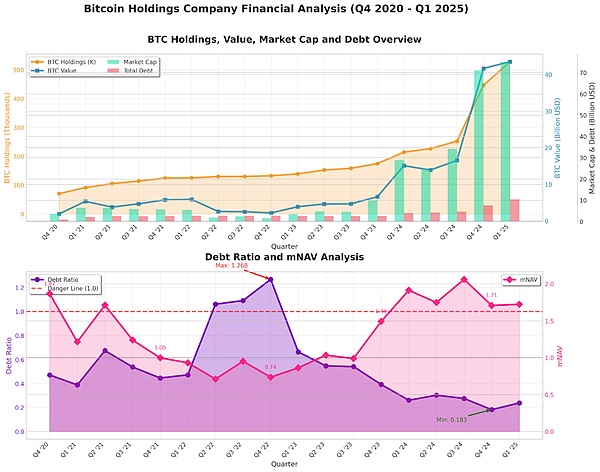
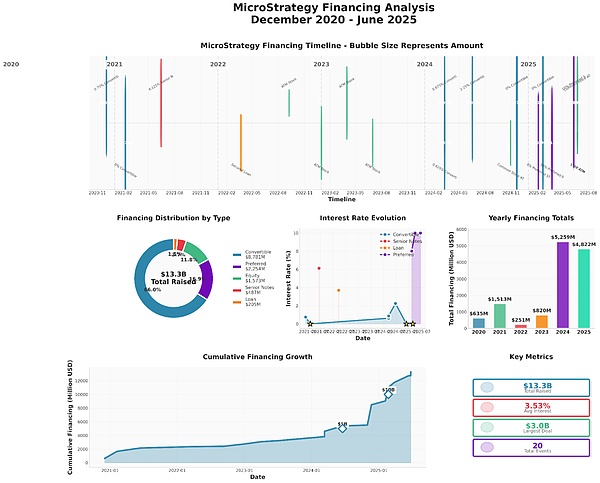
Because of its unique financing structure, when Bitcoin rises, MSTR rises at a higher rate, and a large amount of debt will be converted into stock. In fact, since MicroStrategy announced the purchase of Bitcoin, MicroStrategy's total share capital has risen from 100M to 256M, an increase of 156%.
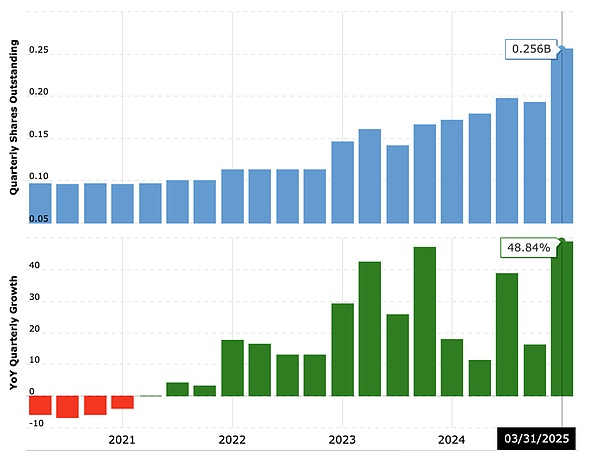
Will a large amount of share issuance dilute shareholders' interests? From the data, from Q4 2020 to now, MicroStrategy's equity has increased by 156%, but the stock price has only increased by 30 times, and the shareholders' equity has not been diluted but increased significantly. In order to better characterize the shareholders' equity, MicroStrategy proposed the BTC equity per share (BTC per Share) indicator, and the goal of capital operation is to continuously increase BTC per Share. As can be seen from the figure, in the long run, BTC per Share has always been on an upward trend, and has risen tenfold from the initial 0.0002 BTC per Share.
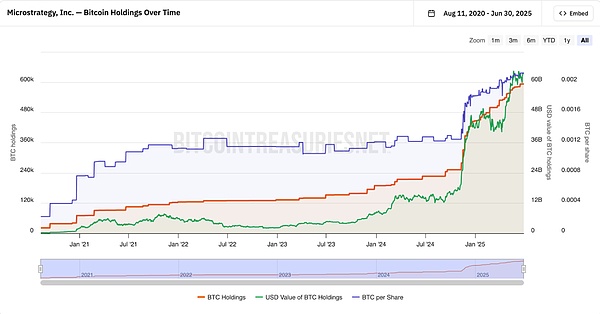
Mathematically, when MSTR's stock price has a high positive premium to Bitcoin (mNAV>1), potential equity dilution to finance the purchase of Bitcoin can continue to push up BTC pre Share. mNAV > 1 means that the BTC that can be purchased by each share of raised funds is greater than the current BTC per Share. Although the original shares are diluted, the BTC value contained in each share after dilution is still rising.
MicroStrategy's Future Deduction
I think there are three key factors for the success of the MicroStrategy model: regulatory arbitrage, correct bets on the rise of Bitcoin, and excellent capital operation capabilities. At the same time, risks are also hidden in it.
Legal and regulatory changes
1. The abundance of Bitcoin investment tools squeezes MicroStrategy buying:When MicroStrategy first announced its strategic reserve of Bitcoin, the Bitcoin spot ETF had not yet been approved, and a large number of investment institutions could not directly obtain Bitcoin risk exposure under the compliance framework, so they purchased it through MicroStrategy as a proxy asset. After Trump came to power, cryptocurrencies were vigorously promoted at the government level, and a large number of compliant crypto-related investment tools are emerging, and the space for regulatory arbitrage is gradually narrowing.
2. SEC restricts excessive debt of "non-productive assets":Although MicroStrategy has maintained its debt ratio at a controllable level through sophisticated debt management, its current debt ratio is significantly lower than that of a large number of listed companies with the same market value. However, the debt of listed companies is usually used for business expansion. MicroStrategy's debt is entirely used for investment, and it may be reclassified as an investment company by the SEC, which will increase its capital adequacy ratio requirements by more than 30% and compress leverage space.
3. Capital gains tax:If the company's unrealized capital gains are taxed, MicroStrategy will face a lot of cash tax pressure. (The current OBBB Act stipulates that taxes are only levied when selling).
Risk of Bitcoin Market Dependence
1. Volatility Amplifier:MicroStrategy currently holds 2.84% of the total Bitcoin. When the volatility of Bitcoin rises, the volatility of MicroStrategy's stock price will also increase several times that of Bitcoin. In the downward cycle, the stock price will be under great pressure.
2.Irrational Premium:MicroStrategy's market value has been at a premium of more than 70% to the net value of Bitcoin it owns for a long time. Most of this premium comes from the market's irrational expectations of Bitcoin's rise.
Risks of Ponzi-like structure of debt leverage
1. Revolving financing dependence of convertible bonds:The cycle of "borrowing new bonds → buying BTC → pushing up stock prices → issuing bonds again" has double Ponzi characteristics. When large bonds mature, if the price of Bitcoin fails to continue to rise to support the stock price, the issuance of new bonds will be blocked, which will trigger a liquidity crisis (debt continuation risk); if the price of BTC falls and the stock price falls below the convertible bond conversion threshold, the company will be forced to repay the debt in cash (conversion price inversion).
2. Lack of stable cash flow:Since the company has no stable source of cash flow and cannot sell Bitcoin, MicroStrategy's way of repaying debts is basically through issuing additional shares (debt-to-equity swaps, ATMs). When the stock price or Bitcoin price falls, the financing cost increases significantly, and there may be a risk of financing channels being closed or significantly diluted, making it difficult to continue to increase holdings or maintain operating cash flow. In the long run, when entering the downward cycle of risky assets, the superposition of multiple risks may trigger a chain reaction, forming a technical risk transmission mechanism and triggering a death spiral:
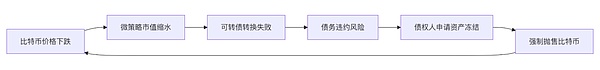
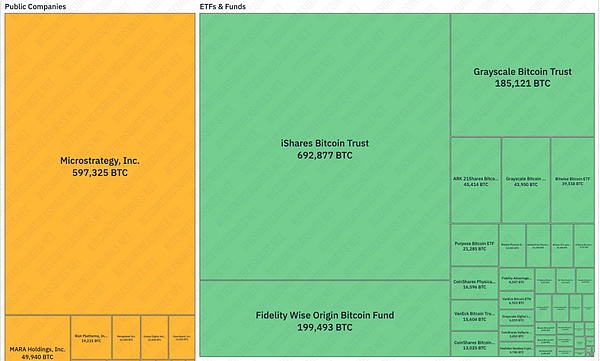
Another possibility is active regulatory intervention to convert micro-strategies into Bitcoin ETFs or similar financial products. MicroStrategy currently holds 2.88% of the total BTC. If it really falls into a sell-off and liquidation trend, it may directly lead to the collapse of the crypto market. It is much safer to convert it into an ETF or other type. Although MicroStrategy holds a large amount of Bitcoin, it is not outstanding when compared with other ETFs. In addition, on July 2, 2025, the SEC approved the conversion of Grayscale Digital Large Cap Fund into an ETF holding a portfolio of assets such as BTC, ETH, XRP, SOL, ADA, etc., which indirectly illustrates the possibility.
Altcoin reserve experiment: Taking $SBET and $DFDV as examples
Valuation regression analysis: From sentiment-driven to fundamental pricing
$SBET's volatility path and stabilization signals
Causes of sharp rise and fall:
In May 2025, $SBET announced that it had acquired 176,271 ETH (worth $463 million at the time) with $425 million PIPE financing, becoming the world's largest ETH holder among listed companies, and its stock price soared 400% in a single day. Subsequently, SEC documents showed that PIPE investors could resell their shares, triggering a panic sell-off in the market due to dilution, and the stock price plummeted 70%. Ethereum co-founder Joseph Lubin (Chairman of the $SBET Board of Directors) clarified that "no shareholders sold", but market sentiment has been frustrated.
Signs of valuation repair:
As of July 2025, $SBET's share price has stabilized around $10, with mNAV of approximately 1.2 (approximately 2.67 after including PIPE issuance).
The driving force for stabilization comes from:
1. ETH holdings increased in value:Added $30.6 million to purchase 12,207 ETH, with a total holding of 188,478 ETH (about $470 million), accounting for 80% of the market value;
2. Staking income realized:120 ETH has been earned through liquidity staking derivatives (LSD);
3. Improved liquidity:The average daily trading volume is 12.6 million shares, and the short position ratio has dropped to 8.53%.
$DFDV's ecological integration premium
Compared with $SBET, although $DFDV's volatility is also very high, its stock price has a stronger support for decline. Despite a 36% drop in a single day, $DFDV has a stock price return of 30 times that of before the transformation. This is partly due to the low market value of the company before the transformation, and partly due to the diversity of its business, especially its investment in infrastructure, which gives it more valuation support.
Valuation support of SOL reserves:
$DFDV holds 621,313 SOL (about $107 million) and has three sources of income:
1. SOL price appreciation(accounting for 90% of the holding value);
2.Staking rewards(annualized 5%-7%); 3. Validator commission (charged to $BONK and other ecological projects). PoW vs. PoS: The impact of staking returns The annualized returns brought by native staking of POS-based cryptocurrencies such as ETH and SOL may not directly affect the valuation model, but circulating staking is expected to enhance the flexibility of capital operations.
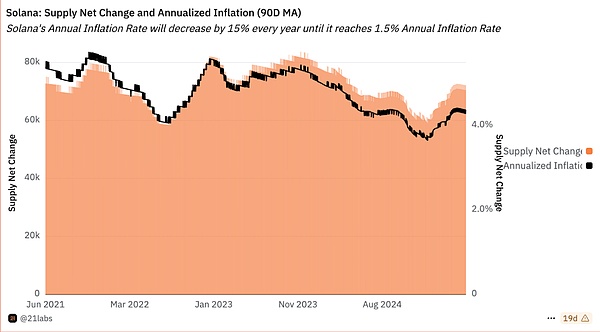
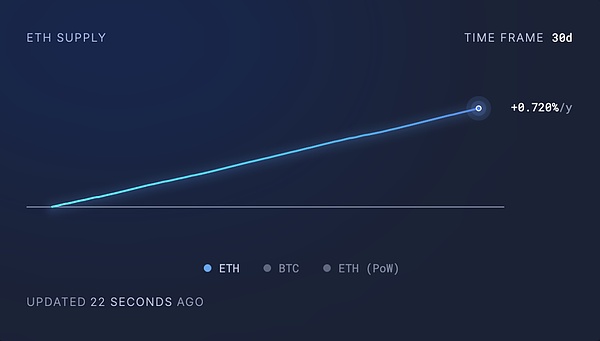
1. Bitcoin is a POW token, with no interest-bearing mechanism, but a fixed total amount, a continuously decreasing inflation rate (currently 1.8%), and assets with scarcity. PoS tokens can earn returns through staking. When the staking return rate is higher than the token inflation rate, the pledged assets gain nominal value. The current SOL staking annualized return is 7%-13%, with an inflation rate of 5%; the ETH staking annualized return is 3%-5%, with an inflation rate of less than 1%. The current ETH/SOL staking can generate additional income, but it is necessary to pay attention to changes in inflation rates and staking returns.
2. The income generated by staking is based on the currency standard and cannot be converted into purchasing power in the secondary market to drive the further increase in the currency price.
3. Liquidity staking allows you to obtain staking income and use liquid assets for DeFi activities. It can be used for activities such as mortgage lending to improve the flexibility of capital operations. (For example, DFDV has issued its own liquidity asset DFDVSOL).
Verification of the applicability of $MSTR success factors in the Altcoin Reserve Company
Regulatory arbitrage: space is narrowing
The approval speed of ETF applications has been significantly accelerated recently. Many institutions are applying for ETFs of different cryptocurrencies. It is only a matter of time before they are approved. Before more and more complex financial instruments related to specific cryptocurrencies appear, the stock and bond instruments of the Altcoin Reserve Company can still meet the needs of some investors, but the regulatory arbitrage space is gradually shrinking.
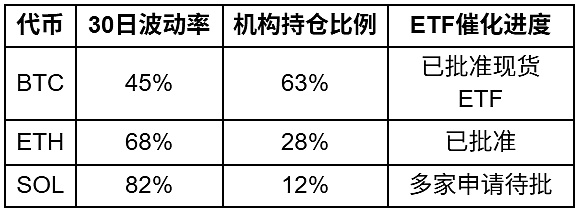
Token Rise Bet: The Future Performance of Altcoins is in Doubt
Bitcoin has a global liquidity consensus as "digital gold", while ETH/SOL lacks the same status. BTC has the attributes of a reserve asset, but ETH/SOL is mostly regarded as a utility asset.
During 2024-2025, altcoins underperformed relative to Bitcoin:
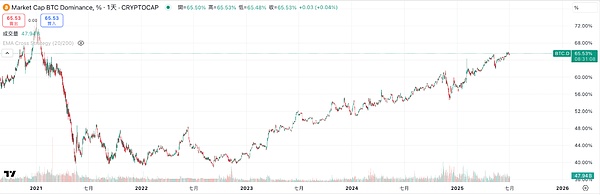
Bitcoin dominance continued to rise in 2024, reaching a high of around 65%.
Historically, the alternative coin season usually starts after Bitcoin reaches its peak, but in this round of cycle, alternative coins lag behind.
When Bitcoin hit a new high in this round, ETH and SOL were still less than 50% of their historical highs.
Capital operation capabilities: flexibility upgrade
Compared with the strategic reserve of Bitcoin, the strategic reserve companies of altcoins can participate more deeply in the public chain ecological business to generate cash income, and at the same time can use DeFi to improve capital utilization.
For example:
1. $SBET is chaired by the founder of Consensys and is expected to expand cash flow businesses such as wallets, public chains, and staking services in the future;
2. $DFDV and Solana's largest Meme coin $BONK jointly acquired the validator network, with commission income accounting for 34% of Q2 revenue;
3. $DFDV packages the staking income into DeFi tradable assets through dfdvSOL to attract on-chain capital;
4. $HYPD (formerly Eyenovia $EYEN) uses the reserved $HYPE for staking and lending, and expands node operation and referral rebate business;
5. $BTCS (Ethereum node and staking service provider) uses $ETH for staking, and uses LST and BTC as collateral to obtain low-cost funds through AAVE.
In summary, the narrowing of regulatory arbitrage space and the uncertainty of token appreciation space will force altcoin reserve companies to innovate their operating models, deeply participate in the on-chain ecosystem, and build cash flow through ecological business to improve risk resistance.
When MicroStrategy uses sophisticated capital tools to convert Bitcoin into "volatility leverage", the altcoin reserve company is trying to solve the valuation dilemma through DeFi operations. However, the shrinking regulatory arbitrage window, the difference in the strength of token consensus, and the inflation concerns of the POS mechanism make this experiment still full of variables. It is foreseeable that as more traditional companies enter the market, the strategic reserve of crypto assets will move from aggressive bets to rational allocation - its ultimate significance may not lie in short-term arbitrage, but inpromoting corporate balance sheets into the programmable era.
As Michael Saylor said: "We are not buying Bitcoin, we are building a fiscal system for the digital age." The ultimate test of this experiment will be whether the balance sheet can withstand the double squeeze when Bitcoin enters a bear market - this is also a proposition that traditional companies must answer before entering the market.
 Jixu
Jixu





















