Hyperliquid airdrops are gaining popularity, promoting the rapid expansion of Hyperliquid’s ecosystem
Hyperliquid的生态系统正在迅速扩张,这得益于成功的现货代币发行和奖励积分计划。
 Bernice
Bernice
Translated by: Bai Ding, Geek Web3

The exchange is the core of the crypto market, supporting the market through transactions between users. The primary goal of any exchange is to achieve efficient (low transaction costs and low slippage), fast and secure transaction matching. Based on this goal, DEX has made many innovations on the basis of CEX, such as eliminating trust assumptions, avoiding intermediaries and centralized control, allowing users to retain control of funds, and allowing the community to actively participate in discussions and governance of product updates and iterations.
However, looking back at the development history of DeFi, we can see that although DEX has several advantages, it often comes at the cost of higher latency and lower liquidity, which is mainly due to the throughput and latency limitations of blockchain.
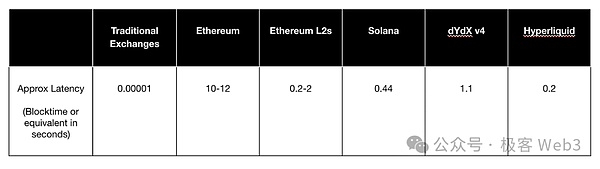 (Transaction delay data of major public chains)
(Transaction delay data of major public chains)
According to data from Chainspect and some blockchain browsers, DEX spot trading volume now accounts for 15%-20% of the total trading volume of the crypto market, while perpetual contract trading only accounts for 5%.
In fact, it is not easy to develop perpetual contract business on DEX, because CEX's perpetual contract trading has several advantages:
1. Better product experience
2. Efficient control of market makers provides more sophisticated spreads
3. Better liquidity (especially for mainstream assets, and the ultimate goal of new projects is to go online on large CEX)
4. One-stop combination of multiple functions (spot trading, derivatives, OTC and other scenarios can be directly nested)
CEX's centralization and monopoly have become a problem that users cannot ignore, especially the collapse of FTX has further aggravated the trend of centralization. Today's CEX field is almost completely dominated by several giants. This centralization has brought systemic risks to the crypto ecosystem. By increasing the use rate of DEX and increasing market share, such risks can be effectively reduced, thereby promoting the sustainable development of the entire crypto ecosystem.
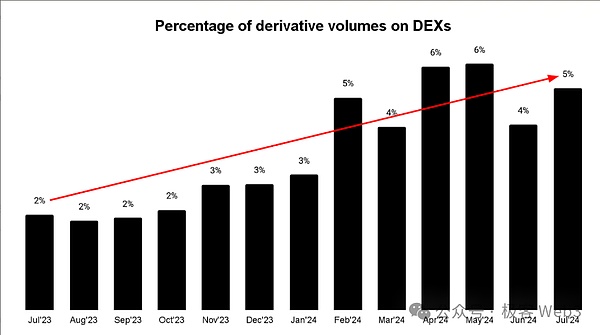
(DEX derivatives trading volume share)
The rise of Ethereum Layer 2 and multi-chain ecology has provided innovations in liquidity sources and UX, which has created excellent conditions for the development of DEX, and now is a good time for the development of perpetual contract DEX. This article will conduct an in-depth discussion on the current status of perpetual contract DEX and introduce some DEX design concepts.
Perpetual contracts allow traders to hold positions indefinitely, which is very similar to the over-the-counter futures trading in the traditional financial (TradFi) market for many years. The difference is that perpetual contracts, by introducing the concept of funding rates, popularize futures, a trading method that is only available to certified investors in traditional finance, so that more retail investors can participate in it. At the same time, it also constructs an "underdamping effect" to prevent excessive imbalance in the long-short structure to a certain extent.
(The funding rate system can prevent the contract price from deviating too much from the spot price. The rate is often determined by the comparison of long and short forces in the market. When the bulls are dominant, the price of the long contract will rise, slightly higher than the spot price. At this time, the funding rate is positive, and the bulls need to pay a certain fee to the bears. In this way, people's willingness to go long will be moderately weakened, preventing the price of the bullish contract from rising excessively)
The current monthly trading volume of the perpetual contract market has exceeded US$120 billion. Such a market size is due to the good user experience provided by the exchange, the order book mechanism promotes trading efficiency, and the vertically integrated clearing system enables clearing to be completed quickly and safely.
(A vertically integrated clearing system refers to a system where a single entity or platform fully controls and manages the entire clearing process, without relying on external clearing institutions or third-party services. In contrast, a separated clearing system is one where the exchange and clearing house are independent of each other and each performs different functions. A vertically integrated clearing system is more efficient, while a separated clearing system is more transparent and regulated)
In addition, projects like Ethena that use perpetual contracts as an underlying mechanism have brought perpetual contracts a variety of uses other than speculation. Generally speaking, perpetual contracts have four advantages over traditional futures contracts:
1. Traders save on rollover fees and other related costs each time a contract expires
In traditional futures trading, if a trader wants to continue holding a position when a contract expires, he or she needs to close the current contract first and then buy a new contract to renew it. This is called "rollover", which means replacing an old contract with a new one. During the rollover process, traders need to pay related fees, bear the bid-ask spread, and other costs. Perpetual contracts do not have an expiration date and do not need to be rolled over, thus avoiding additional fees.
2. Avoid making forward contracts more expensive
In traditional futures markets, the price of forward contracts (futures contracts with longer expiration dates) is usually higher than that of near-term contracts (futures contracts with closer expiration dates). This phenomenon is called "positive market structure". When investors roll over, they usually need to buy new contracts at a higher price, thereby increasing the cost of holding positions. Perpetual contracts avoid this through a funding rate mechanism.
For example, suppose the March futures price of a commodity is $100, while the June futures price is $105. If you hold a March contract and switch to a June contract at expiration, you need to buy it at $105, increasing the holding cost by $5. Since perpetual contracts have no expiration date, you can always hold the original position without paying a higher price.
3. The funding rate system provides continuous real-time profit and loss, simplifying the back-end processing of contract holders and clearing systems
Perpetual contracts use the funding rate system to balance the positions of both long and short parties, and the settlement cycle is short (the industry standard is 8 hours, Binance, Bybit, etc. all follow this standard). After each cycle is settled, funds will be automatically deducted or added from the contract holder's account to provide the holder with real-time profit and loss. At the same time, this real-time settlement can reflect the profit and loss of each trader's contract. Compared with the daily settlement and daily marking to the market of traditional futures, the real-time settlement of perpetual contracts is more efficient, simplifying the fund management of contract holders and the back-end processing of the clearing system.
4. Perpetual contracts provide a smoother price discovery process, avoiding violent fluctuations caused by too coarse price granularity
Price discovery refers to the process of pricing assets between market participants through various mechanisms. As mentioned above, while reflecting the market supply and demand, the funding rate can continuously adjust the contract price to closely follow the spot price, ensuring the continuity and stability of price changes. At the same time, because the settlement cycle is short, the price discovery process is smoother, and compared with the daily or monthly settlement of traditional futures, price fluctuations caused by rollover or delivery are avoided.
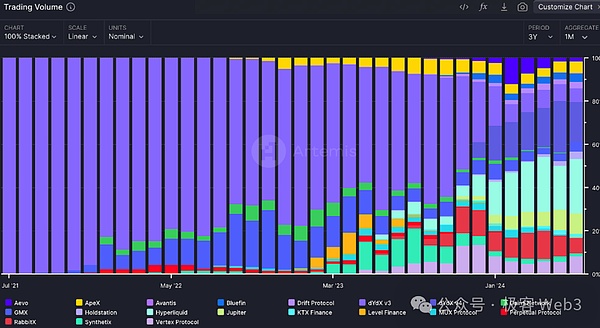
(Perpetual Contract DEX Market Share)
Since BitMEX first introduced perpetual contracts in 2016, perpetual contract DEXs have begun to develop rapidly, and now there are more than 100 DEXs supporting perpetual contracts in the market. In the early days, the scale of perpetual contract DEX was very small. In 2017, dYdX was launched on the Ethereum ecosystem and dominated the perpetual contract market for a long time. Therefore, decentralized perpetual contract transactions were also mainly concentrated on Ethereum, and the contract trading volume was very low at that time. Today, we can see active perpetual contract DEXs on various chains, and contract trading has become an indispensable part of the crypto ecosystem.
Multiple studies have shown that as the scale of perpetual contract transactions grows, the perpetual contract market has begun to have the function of price discovery when the spot market is not active. The perpetual contract trading volume on DEX has also increased from US$1 billion in July 2021 to US$120 billion in July 2024, with an annual compound growth rate of approximately 393%.
However, perpetual contract DEX faces bottlenecks due to the performance limitations of the blockchain. If the perpetual contract market is to be further developed, the two core problems of low liquidity and high latency on the chain must be solved. High liquidity can reduce slippage, make the transaction process smoother, and reduce user losses; low latency can enable market makers to quote more compact prices, enable transactions to be executed quickly, and improve market fluency.
In perpetual contract DEX, the pricing mechanism is the key to ensuring that market prices accurately reflect the dynamics of supply and demand. Different perpetual contract DEXs use a variety of different pricing mechanisms to balance liquidity and reduce volatility. Below we will popularize several major models:
Oracle model refers to the perpetual contract DEX obtaining price data from the head exchanges with large trading volumes and providing services based on this data. Although this method has the risk of price manipulation, it can reduce the pricing cost of DEX. For example, the decentralized perpetual contract exchange GMX.
By using Chainlink oracles to obtain price data, GMX ensures the accuracy and integrity of prices, creates a friendly trading environment for price takers (small institutions and individuals), and provides generous rewards for price makers (large institutions and market makers). However, such exchanges that use the oracle model to complete pricing generally face a problem, that is, they are extremely dependent on the price data source of the head exchange, and can only act as price takers and cannot actively conduct price discovery.
The virtual automated market maker (vAMM) model is inspired by Uniswap's AMM model, but the difference between the two is that the AMM model provides liquidity and pricing through an actual pool of funds and the corresponding exchange rate, while the vAMM's pool of funds is virtual and does not actually hold assets. It only simulates the buying and selling behavior of trading pairs through a mathematical model to achieve pricing.
The vAMM model can support perpetual contract transactions without investing a lot of money or being associated with spot. At present, the vAMM model has been adopted by perpetual contract DEXs such as Perpetual Protocol and Drift Protocol. Although vAMMs have problems with high slippage and impermanent loss, it is still an excellent on-chain pricing mechanism because of its transparency and decentralization.

(Classification of product models of different perpetual contract DEXs)
In order to overcome the performance limitations of on-chain order matching, some DEXs adopt a hybrid model of off-chain order book and on-chain settlement. In this model, the transaction matching process is completed off-chain, while transaction settlement and asset custody are still on-chain. In this way, the user's assets are always under their own control, which is the so-called "self-custodial". At the same time, since the transaction matching is carried out off-chain, risks such as MEV are greatly reduced. This design not only retains the security and transparency of decentralized finance, but also solves problems such as MEV, providing users with a safer and more reliable trading environment.
Some well-known projects, such as dYdX v3, Aevo and Paradex, have adopted this hybrid model. This method improves efficiency while also ensuring security, which is similar to the concept of Rollup.
The full-chain order book, that is, all data and operations related to transaction orders are completely published and processed on the chain, is the best among the traditional solutions for maintaining transaction integrity. The full-chain order book is almost the safest solution, but its shortcomings are also very obvious, and it is obviously limited by the latency and throughput of the blockchain.
In addition, the full-chain order book model also faces risks such as "front-end trading" and "market manipulation". Front-end trading means that when someone submits an order, other users (usually MEV Searchers) monitor pending transactions and rush to execute the target transaction before it is executed, thereby making a profit. This situation is more common in the full-chain order book model because all order data is publicly recorded on the chain and anyone can view and formulate MEV strategies. At the same time, in the full-chain order book model, since all orders are transparent, some participants may take advantage of this and influence market prices through large orders and other means to obtain improper benefits.
Despite the above problems of the full-chain order book, it still has considerable narrative appeal in terms of decentralization and security. Public chains such as Solana and Monad are working hard to improve infrastructure and prepare for the realization of the full-chain order book. Some projects such as Hyperliquid, dYdX v4, Zeta Markets, LogX and Kuru Labs are also constantly expanding the scope of the full-chain order book model. They are either innovating on existing public chains or building their own application chains to develop high-performance full-chain order book systems.
Liquidity is the foundation for the survival of every exchange, but how to obtain initial liquidity is a thorny issue for exchanges. In the development of DeFi, emerging DEXs generally obtain liquidity through incentives and market forces. Incentives often refer to liquidity mining, and the so-called market force is to provide traders with opportunities for arbitrage between different markets. However, as more and more DEXs emerge, the market share of a single DEX is decreasing, and it is difficult to attract enough traders to reach the "critical mass" of liquidity.
The critical mass here refers to the "effective scale", which means that after something reaches a sufficient scale, it will break through the minimum cost that can maintain the development of things in order to obtain the maximum profit in the long run. If the product exceeds or fails to reach the effective scale, it will not be able to maximize profits. Good products must operate for a long time at the effective scale. As shown in the figure below, the horizontal axis is the product scale and the vertical axis is the total cost.
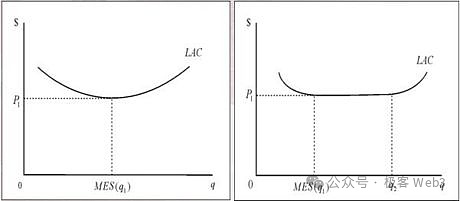
(Critical mass effective scale diagram)
In DEX, critical mass refers to the transaction volume and liquidity thresholds. Only by reaching such thresholds can a stable trading environment be provided to attract more users. In perpetual contract DEX, liquidity is provided spontaneously by LPs, so a common way to achieve critical mass is to set up an LP pool with economic incentives. In this model, LPs deposit their assets into a pool and receive certain incentives to support transactions on DEX.
Many traditional DEXs offer high annualized yields (APY) or airdrops to attract LPs, but this approach has a drawback. In order to meet high APY and airdrop returns, DEXs must use a large portion of tokens as LP mining rewards. Such an economic model cannot last long and will fall into the vicious flywheel of LP mining "mining, withdrawing and selling". DEXs may also collapse soon and cannot continue to operate.
In response to the problem of initial liquidity acquisition for DEXs, two new ideas have recently emerged: community-supported active liquidity vaults and cross-chain liquidity acquisition.
Hyperliquid, a perpetual contract DEX on Arbitrum, is a typical example of using community-supported active liquidity vaults.HLP Vault is one of Hyperliquid's core products, using community users' funds to provide liquidity for Hyperliquid. HLP Vault calculates fair prices by integrating data from Hyperliquiquid and other exchanges, and executes profitable liquidity strategies across multiple assets. The gains and losses (P&L) generated through these operations will be distributed according to the community participants' shares in the treasury.
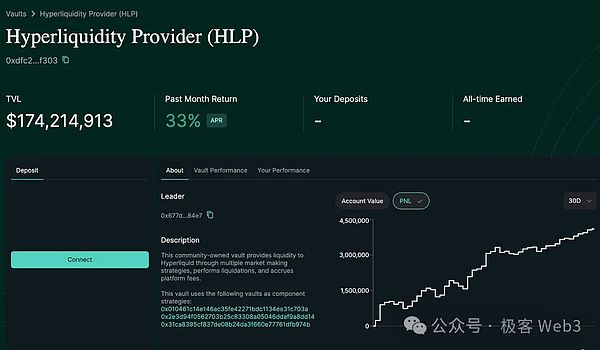
(Hyperliquid product interface)
Cross-chain liquidity allocation was proposed by Orderly Network and LogX Network. These projects allow the creation of a front end for perpetual contract trading on any chain and leverage liquidity across all markets. The so-called "inter-market liquidity leverage" refers to the integration and utilization of liquidity resources across multiple markets or public chains. This method enables trading platforms to obtain liquidity on different markets or public chains.
By combining native on-chain liquidity, cross-chain aggregated liquidity, and creating discrete asset market neutral (DAMN) AMM pools, LogX is able to maintain liquidity during periods of market volatility. These pools use stable assets such as USDT, USDC, and wUSDM to trade perpetual contracts with the help of oracles. Currently, this infrastructure also makes it possible to develop a variety of applications.
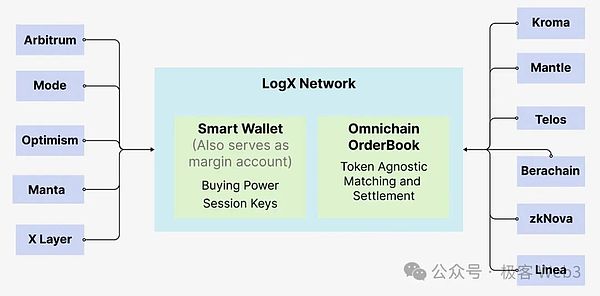
(LogX Network cross-chain liquidity allocation)
In today's DEX field, competition in user experience UX is intensifying. When DEXs first emerged, simple improvements to the user interface could significantly improve UX, and as user interfaces gradually converged, DEXs began to compete on UX by introducing features such as gas-free transactions, session keys, and social logins.
In fact, CEXs are usually more deeply integrated in the ecosystem, not only providing core trading services, but also acting as user portals and cross-chain bridges, while DEXs are usually limited to a single ecosystem. Nowadays, cross-chain DEXs are breaking this limitation. For example, DEX aggregators can integrate the liquidity and price information of multiple DEXs into one interface to help users find the best trading pairs and slippages. It can be understood as a trading router.
Many DEX aggregators, such as Vooi.io, are developing intelligent routing systems that integrate the functions of multiple DEXs and cross-chain bridges to provide a simple and friendly trading experience. Such DEX aggregators can find the most effective trading paths on multiple chains, making the trading process simpler and less costly. Most importantly, users can manage complex trading paths through a simple interface.
In addition, Telegram trading robots are also constantly optimizing UX. Such robots can provide real-time trading reminders, execute transactions, and manage portfolios, and can be conveniently completed directly in the Telegram chat interface. This deep integration enhances the convenience and participation of transactions, making it easier for traders to obtain information and seize market opportunities. Of course, Telegram robots also have significant risks: users need to provide their private keys to the robots, which may face security risks.
Many perpetual contract DEXs on the market have been continuously launching new financial products, or optimizing the trading mechanism of existing products to simplify the trading process, in order to better meet the changing needs of traders. Let us briefly introduce such products below.
Variance is a common statistical indicator that aims to reflect the degree of dispersion of a set of data. As the name implies, the trading content of the variance perpetual contract is no longer the price of the underlying asset, but the volatility of the asset.
For example, if you think that the price of BTC will fluctuate violently, but you are not sure about the direction of change, you can buy the variance perpetual contract of BTC and bet on the event that "the price of BTC will fluctuate violently within a period of time". Whether BTC rises or falls, or fluctuates, you will make a profit.
In addition, the variance perpetual contract also has the function of hedging risks. For example, in the above example, once BTC falls sharply, since you hold the variance perpetual contract, the contract income will offset part of the loss.
The decentralized perpetual contract exchange Opyn is using existing market resources to develop novel variance perpetual contract products. These contracts can not only simulate complex strategies and hedge risks, but also improve capital efficiency.
Opyn's perpetual contract products include Stable Perps (0-perps), Uniswap LP Perps (0.5-perps), Normal Perps (1-perps) and Squared Perps (2-perps, also known as Squeeth). Each contract product has its own specific purpose:
Stable Perps provides a solid foundation for trading strategies; Uniswap LP Perps can reflect LP's performance without directly providing liquidity; Normal Perps is the most common contract type; and Squared Perps can amplify the profit potential through secondary exposure.
These perpetual contracts can be combined into more complex strategies. For example, the "Crab Strategy": by shorting 2-perps and going long 1-perps, you can earn funding rates in the stable market while maintaining a balanced directional exposure. Another example is the "Zen Niu Strategy": combining shorting 2-perps, longing 1-perps and shorting 0-perps, you can earn funding rate income while maintaining long exposure in a stable market.
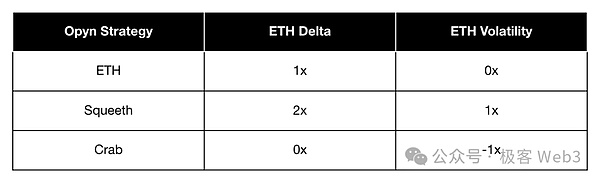
(Decentralized Perpetual Contract Exchange Opyn)
Pre-Launch perpetual contracts allow traders to speculate on the future price of a token before it is officially launched, which can be understood as an on-chain version of IPO OTC, allowing investors to build positions in advance based on expected market value. Multiple perpetual contract DEXs such as Aevo, Helix and Hyperliquid have pioneered a new model for Pre-Launch. The main advantage of the Pre-Launch contract is that it can provide exclusive assets that are not available in other channels, attracting and retaining users.
RWA asset perpetual contract may become the main way to put real assets on the chain. Compared with directly tokenizing RWA assets in the spot market, it is simpler to put them on the chain in the form of perpetual contracts, which only requires liquidity and price oracles. Moreover, even if there is no spot market on the chain, a perpetual contract market with good liquidity can be built, because perpetual contract transactions can operate independently from spot.
Perpetual contract trading is the first step for RWA assets to move towards spot tokenization. Once enough attention and liquidity are accumulated through the perpetual contract market, spot tokenization can be further promoted. Combining spot and perpetual contracts for RWA can provide new ways to predict market sentiment, event-driven trading, and execute cross-asset arbitrage strategies. At present, companies such as Ostium Labs and Sphinx Protocol are gradually emerging in the field of RWA contracts.
ETPs track the performance of some underlying asset or index, and their value is usually based on the performance of the underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, or other asset combinations. Common ETPs include:
ETFs:Track the performance of a specific index or industry.
ETNs:Similar to bonds, but their returns are tied to the performance of the underlying index or asset.
ETCs:Focus on commodity markets and track commodity prices.
ETP perpetuals can also be used to create ETPs that hold expiring futures contracts, such as the ETF USO (futures on West Texas Intermediate crude oil WTI) and the ETN VXX (futures on the S&P 500 Volatility Index VIX). Because there is no need to roll over, ETP perpetuals can reduce transaction costs and reduce the risk of depreciation of net asset value (NAV). Perpetual swaps can significantly reduce operating costs for companies that need protection against long-term economic exposure but do not require physical delivery.
In addition, for those situations where speculation or hedging of foreign currency risk is limited, 30-day or 90-day forward contracts are often involved. Such contracts are not standardized and are traded over the counter, which is very risky. However, this situation can be replaced by perpetual swaps settled in US dollars, simplifying operations and reducing the associated risks.
Prediction markets is a term and a branch of financial markets in which participants can trade and bet on the outcomes of future events, such as election results, sports game wins and losses, changes in economic indicators, etc.
Perpetual contract DEXs can revolutionize prediction markets by providing a flexible and continuous trading mechanism, especially for irregular events such as elections or non-regular weather forecasts. Unlike traditional prediction markets that rely on real events or oracles, perpetual contracts allow prediction markets to be created based on data that is constantly updated by the market itself.
This brings significant advantages: the continuous updating of data can generate multiple sub-markets in the long-term prediction market. For example, during the election, the sub-market can trade around the change in support for a candidate after a specific debate. And because of the existence of sub-markets, users do not have to wait for the final outcome of long-term events to participate in transactions, but can buy and sell based on short-term market fluctuations, such as the impact of a news event, the release of data at a certain moment, etc. This provides users with short-term trading opportunities and brings instant trading satisfaction.
The continuous real-time settlement of perpetual contracts ensures the stability of market activities, enhances liquidity and improves user participation. In addition, the community-controlled perpetual contract market incentivizes participation through reputation and token reward mechanisms, laying the foundation for decentralized prediction markets. This design makes market creation more democratic and provides scalable solutions for various prediction scenarios.
With the development of the crypto-financial system, the design of perpetual contract DEX is also constantly being optimized. The focus in the future may not only be to replicate the functions of CEX, but to better play the unique advantages of decentralization - transparency, composability and user empowerment, so as to design some new functions. The ideal perpetual contract DEX design needs to find a delicate balance between efficiency and security.
In addition, perpetual contract DEX also pays more and more attention to the participation of the community and developers, and increases the sense of belonging and loyalty of users through various mechanisms. Community-led measures such as using Hyperliquid robots for market making can enable more users to participate in trading activities fairly and truly implement the inclusiveness of decentralized trading.
In order to promote the large-scale popularization of cryptocurrency, it is crucial to create a platform that is integrated and has excellent user experience like iOS. To this end, it is necessary to develop a more intuitive user interface and ensure the smoothness of the entire usage process. In addition, perpetual contract DEXs such as Hyperliquid, LogX and dYdX cover markets beyond finance, including elections, sports and other fields, providing new ways for the public to participate in crypto trading.

(Roadmap of LogX Network)
In the past decade, the development of DeFi has been mainly concentrated in the fields of DEX, lending and stablecoins. In the next decade, DeFi may cross-integrate with multiple fields such as news, politics, and sports, and is expected to become a widely used tool, further promoting the mass adoption of cryptocurrencies.
Hyperliquid的生态系统正在迅速扩张,这得益于成功的现货代币发行和奖励积分计划。
 Bernice
BerniceThis article looks at the mechanics of CEX/DEX arbitrage trading, focusing on the AMM aspects of execution, aiming to show the relationship between block time, block base fee, and the participants involved in these trades.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceSince FTX’s collapse in 2022, crypto market makers and asset managers have rapidly cut exposure to CEXs.
 Junde Yu (Head of Global Sales, Cobo)
Junde Yu (Head of Global Sales, Cobo)He explains previous methods, such as Merkle trees, and improvements, like ZK-SNARKs.
 Beincrypto
BeincryptoIn the wake of the downfall of SBF’s FTX exchange, crypto traders are increasingly turning toward DeFi protocols – as ETH tokens flow off big CEXs like Binance and OKX.
 Coindesk
CoindeskUSDC, USDP, and TUSD will be all converted to BUSD at a 1:1 ratio. Together, all the spot trading pairs will be removed as well. You may notice that USDT is not on the list. Good news? In fact, not really.
 Nell
NellYep, it’s true. The FBI recently issued a warning over cybercriminal exploits targeting DeFi. In fact, DeFi platforms have been ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistGlobiance is the world's first combined banking and digital-exchange platform. Hong Kong -- Globiance is an exchange platform that combines ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistData points to capital flight among most major DeFi protocols.
 Cointelegraph
CointelegraphThe Terra collapse demonstrates why crypto exchanges need advanced risk management systems — especially when providing access to DeFi protocols offering favorable yields.
 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph