Introduction
RWA (real world assets on the chain) is rapidly becoming the mainstream narrative in the Web3 world, and one of the particularly "down-to-earth" directions - Tokenized Stocks is one of the most feasible directions at present.
The reason is simple:
The underlying assets are mature enough, and there is no need to spend energy on "proving value";
The technical threshold is relatively controllable, and there are already mature tools for on-chain issuance and mapping;
The regulatory path is gradually becoming clear, especially in Europe and some offshore regions, where real projects have been implemented.
However, when many people hear the word "stock", they will subconsciously think: Is this a security? Can it be sold to retail investors? Do I need a license?
But in reality, some projects have found a way to "take both ends into account". They can not only reduce compliance pressure, but also reach the retail market. Representative cases are:
Robinhood: The most popular retail securities platform in the United States;
xStocks: Stock token transactions are implemented in non-EU and non-US regions, and can be bought and sold on the chain.
As a lawyer focusing on Web3 compliance, I also began to frequently receive similar inquiries:
How does the stock tokenization platform work?
Do small and medium-sized teams like us have a chance to do it?
If we want to do it, where should we start and how to build a legal structure?
This article does not talk about big words or concepts, but focuses on answering one question:
If you want to make a stock tokenization platform that retail investors can participate in and where compliance pressure is controllable, what should you do?
Robinhood model: the ultimate productization of retail securities trading
Robinhood is not a traditional on-chain platform, but its operating model is extremely inspiring for Web3 product design.
1.Core features:
Extremely simple interface, abandoning the complex terminology of traditional securities firms;
Zero commission, no threshold for deposit, direct service to retail investors;
All securities clearing and custody are completed by cooperative institutions;
2. Place of registration and compliance structure:
Robinhood Markets Inc. was established in Menlo Park, California, USA;
Subsidiaries Robinhood Financial LLC and Robinhood Securities LLC hold U.S. securities trading licenses and are subject to dual supervision by the SEC and FINRA;
In addition to securities business, Robinhood also has subsidiaries in the UK and other places engaged in crypto asset services,but its stock trading services are explicitly not open to non-U.S. users.
3. Reasons for regional restrictions:
Robinhood only serves the U.S. market, mainly for two considerations:
If securities trading is opened to overseas users, it will face complex securities sales licenses and registration obligations in the European Union, Canada, Japan and other regions;
There is a trend of localized and strong supervision in securities supervision in various places, and the compliance cost of overseas expansion is high and the risk is uncertain.
xStocks Model: TokenReal stock + non-securities statement + for retail investors
xStocks is one of the few platforms that makes "stock price mapping" into Token and provides trading, allowing retail investors to participate, but deliberately avoids the red line of securities identification.
1. Core structure:
Each xStock Token is mapped 1:1 to a stock and is actually held by a brokerage or custodian institution;
Tokens do not confer voting rights, dividend rights or governance rights, and the platform does not promote them as "securities";
The platform adopts an "automatic reinvestment" token-based structure for the "dividends" of Token holders.
That is, if the stock dividends are paid, the user's wallet will not receive cash, but will receive an equivalent token increment;
Users need to complete basic KYC, and tokens can be traded on the chain, but users from highly regulated jurisdictions are not allowed to access.
2. Entity structure and registration place:
The issuer of Token isBacked Assets (JE) Limited, which is registered in Jersey,not belonging to the EU, nor directly subject to MiCA or Prospectus Regulation;
The service provider isPayward Digital Solutions Ltd., which is registered in Bermuda,a loose financial regulatory zone;
xStocks products are issued by non-U.S. entities and are intentionally issued to avoid the application of U.S. law.
3. Prohibited regions and restriction logic:
xStocks explicitly lists that it does not provide services to the following countries or regions:
the United States (including all U.S. Persons),European Union member states,the United Kingdom,Canada,Japan,Australia.
The reasons are:
1. These regions have extremely strict supervision on the issuance of securities. If xStocks is sold locally, it is very likely to be classified as illegal securities issuance;
2. The platform has not obtained the license or
regional text="">Compliance exemption, so actively circumvent regulation through IP restriction + KYC restriction;
3. The issuing entity chooses to register in Jersey and Bermuda, which is also a common strategy to reduce compliance risks.
The essential differences and common revelations of the two models
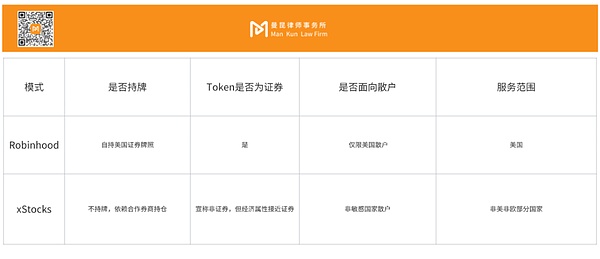
The two paths essentially represent two logics:
Robinhood:“Doing securities within the regulatory framework”
xStocks:
Entrepreneurs do not have to choose sides, but should learnhow they use legal structure, technical paths and compliance isolation to make the platform “capable of going online, able to grow, and not step on landmines”.
Ifyoureally want to doone,how should it be implemented from a structural perspective?
Stock tokenization is not as simple as copying a contract. You need to at least design the following roles:
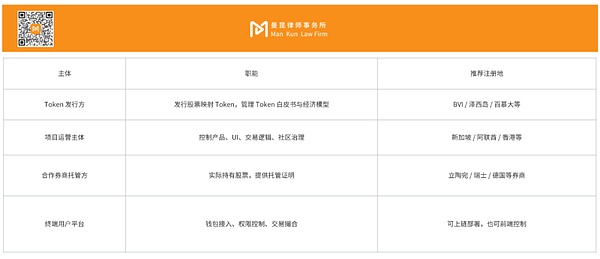
The key is:
The platform is responsible for “price mapping + Token issuance + user interaction”;
The partner is responsible for “position + report + Risk isolation”;
The two parties are linked through an agreement and information synchronization mechanism, but the regulatory responsibilities are clearly separated.
Which institutions need to cooperate with and which agreements need to be signed?
Stock tokenization is not an isolated system, but must rely on the following resource linkage:
1. Partners:
Licensed securities firms (responsible for real stock custody or transaction execution);
Blockchain issuance platform and technology party (deployment contract + permission control module + oracle);
Legal advisor (Token qualitative analysis, structural design, user agreement);
KYC/AML service provider;
Smart contract auditor.
2. The agreements to be signed include:
Token Issuance White Paper + Legal Disclosure Statement (Offering Terms);
Asset Custody Service Agreement / Custody Certificate (Custodial Agreement);
Platform User Agreement + Risk Disclosure Statement (T&C);
text="">Compliance service integration agreement (KYC, IP blocking, etc.);
Token and platform linkage contract description document.
Several points you may not be aware of but must consider
Once these points are hit, you will not face community FUD, but real regulatory action:
Tokens cannot be granted any "income commitment", "governance rights", or "claim rights";
Not open to users in highly sensitive jurisdictions such as the European Union, the United States, and Japan;
Do not use expressions such as "stock", "shareholder rights" and "dividends";
The region and identity must be controlled through both technology and protocol;
A legal qualitative opinion, risk disclosure statement and KYC audit records should be prepared for reference.
Whether you can do it does not depend on the license, but on the structure
Stock tokenization is a project direction that can be implemented but requires careful design. It is neither "unregulated" like NFT nor "closed rules" like traditional securities. What you need to do is not to make a radical breakthrough, but to:
Find a suitable landing point
Design a clear structure
Make it clear what your token represents
Avoid touching the three red lines of users, market and law
This market is not saturated
text="">, but it is in a vacancy period where institutions value it but act cautiously, and entrepreneurs are interested but dare not enter the market. Stop looking at what others have done. The stock tokenization track is not full yet. When the market is occupied by giants, you can only be a user.
As a Web3 compliance lawyer, I would rather help you design a platform that "regulators can understand, users are willing to participate, and technology can run". Don't ask for everything in one step, but make sure to get it right from the beginning.
 Catherine
Catherine








