Background
Recently, SlowMist was invited to participate in the Ethereum Web3 Security BootCamp held by DeFiHackLabs. As a guest speaker, Thinking, the head of SlowMist's security audit, led the students to have a deep understanding of the evil methods and concealment methods of phishing hackers from eight chapters of "fake, bait, lure, attack, concealment, skills, identification, and defense", combined with actual cases, and proposed relevant preventive measures. Phishing is one of the hardest hit areas in the industry. Only by knowing yourself and the enemy can you do a good job of defense. This article will extract the key content of the sharing session to help users understand the current situation of phishing attacks and effectively avoid the threat of phishing attacks.
Why are you phished?

In the Web3 world, phishing attacks have become one of the main security threats. Let's first look at why users are phished. In fact, even users with a high level of security awareness sometimes feel that "you can't avoid getting your feet wet if you walk by the river often", after all, it is difficult to always maintain the highest level of vigilance. Attackers select high-profile targets and carefully disguise themselves by analyzing recent hot projects, community activity, user scale and other factors, and then use baits such as airdrops and high returns to attract users. These attack methods are usually accompanied by social engineering, and attackers are very good at using user psychology to achieve fraud goals:
Benefits:Airdrop qualification whitelist, mining head mines, wealth passwords, etc.
Curiosity/Greed:Fearless selling strategy, don't miss the potential 100x coin, see you at 10 o'clock tonight, meeting link https://us04-zoom[.]us/ (malicious); $PENGU airdrop whitelist can't be missed, https://vote-pengu[.]com/ (malicious).
Fear:Emergency warning: XX project has been hacked, please use revake[.]cash (malicious) to cancel authorization to avoid financial losses.
Efficient tools:Airdrop tools, AI quantitative tools, one-click mining, etc.
The attackers take the trouble to create and place baits simply because it is profitable. Through the above means, the attackers can easily obtain the user's sensitive information/authority, and then steal the user's assets:
Steal mnemonics/private keys:Trick users into entering mnemonics or private keys.
Trick users into using wallet signatures:Authorization signatures, transfer signatures, etc.
Steal account passwords: Telegram, Gmail, X, Discord, etc.
Steal social application permissions: X, Discord, etc.
Induce installation of malicious programs: Fake wallet APP, fake social APP, fake conference APP, etc.
Phishing methods

Next, let's take a look at the common phishing methods:
Account theft/High imitation account
Recently, Web3 project parties/KOLs' X accounts have been frequently stolen. After stealing the accounts, attackers often promote fake tokens, or build similar domain names in the "good news" released to trick users into clicking. Of course, there are also cases where the domain name is real, because the attacker may have taken over the project party's domain name. Once the victim clicks on the phishing link, signs or downloads malware, it will be stolen.
In addition to stealing accounts, attackers often use high-imitation accounts on X to leave messages in the comment area of real accounts to mislead users. The SlowMist security team has conducted targeted analysis and statistics: about 80% of well-known project parties will have the first message in the comment area occupied by fraudulent phishing accounts after posting tweets. Attackers use automated robots to follow the dynamics of well-known project parties. After the project party posts a tweet, the phishing gang's robot will automatically leave a message at the first time to ensure that it occupies the first message position and gets a high number of views. Since the post that the user is browsing is sent by the real project party, and the disguised phishing gang account is highly similar to the project party's account, at this time, as long as the user is not vigilant enough, click on the phishing link in the name of airdrop in the high-imitation account, and then authorize and sign, he will lose assets.
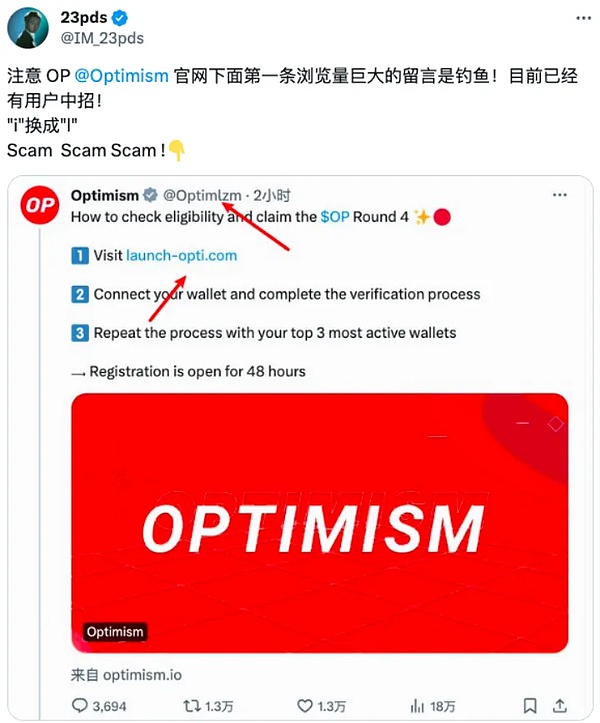
Attackers will also impersonate administrators to post false messages, especially on Discord. Discord supports users to customize nicknames and usernames, so attackers change their avatars and nicknames to match those of administrators, and then post phishing information in the channel or send private messages to users. It is difficult for users to find the problem unless they click on the account information to check the username. In addition, although Discord usernames cannot be repeated, attackers can use names that are highly similar to administrator usernames, such as simply adding an underscore or an English period to the username, making it difficult for users to distinguish between the real and the fake.
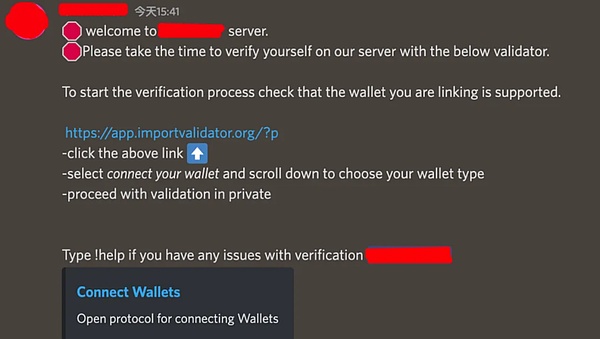
Invitation Phishing
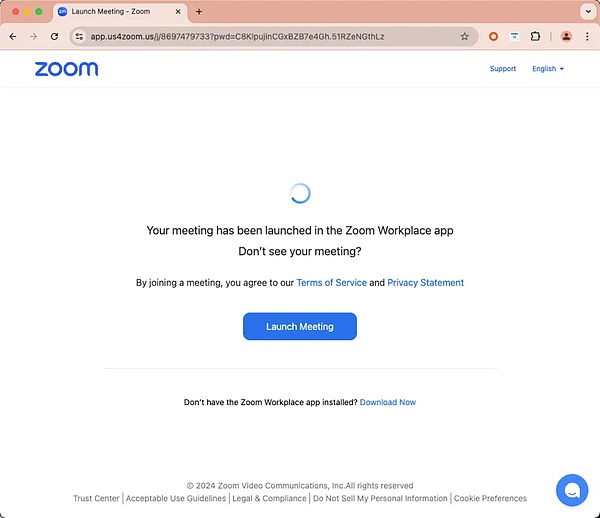
Attackers often establish connections with victims on social platforms, recommend "high-quality" projects to users or invite users to attend meetings, and guide victims to visit malicious phishing sites and download malicious applications. Previously, there were cases where users were stolen because they downloaded fake Zoom. Attackers use domain names such as "app[.]us4zoom[.]us" to disguise as normal Zoom meeting links, and the page is highly similar to the real Zoom. When the user clicks the "Start Meeting" button, it triggers the download of a malicious installation package instead of launching the local Zoom client or downloading Zoom's official client. Since the malicious program induces users to enter passwords when it is running, and the subsequent malicious scripts will also collect plug-in wallet data and KeyChain data in the computer (which may include various passwords saved by the user on the computer), the attacker will try to decrypt the data after collection to obtain sensitive information such as the user's wallet mnemonics/private keys, thereby stealing the user's assets.
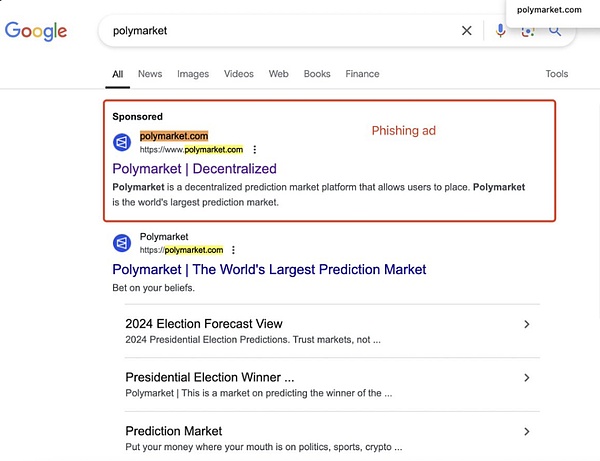
Use search engine rankings
Since search engine rankings can be improved by purchasing ad promotions, this may lead to the situation where phishing websites are ranked higher than the real official website. Without knowing the official website URL, it is difficult for users to judge whether it is a phishing website based on the website display page alone. In addition, phishing websites can customize the URL displayed in the ad in the Google Ads promotion function. The URL displayed in Sponsored may be exactly the same as the official URL, but when users click on the ad URL, they will jump to the phishing website built by the attacker. Since the phishing website created by the attacker is very similar to the real official website and can be mistaken for the real one, it is not recommended that users directly search for the official website through search engines, as this is likely to lead to a phishing website.
TG Advertisement
Recently, the number of users who have been harmed by fake TG Bot has increased significantly. Many users reported that when they were using trading robots, a new robot appeared at the top of the channel. They thought it was a new official launch, so they clicked on the new robot to import the private key to bind the wallet, but their money was stolen. The attacker used Telegram to precisely deliver advertisements to the official channel to lure users to click. This type of phishing method is highly concealed. Since this advertisement appears in the official channel, users can easily subconsciously think that it is an official robot. Once they are not vigilant enough, they click on the phishing Bot and upload the private key for binding, and their money will be stolen.
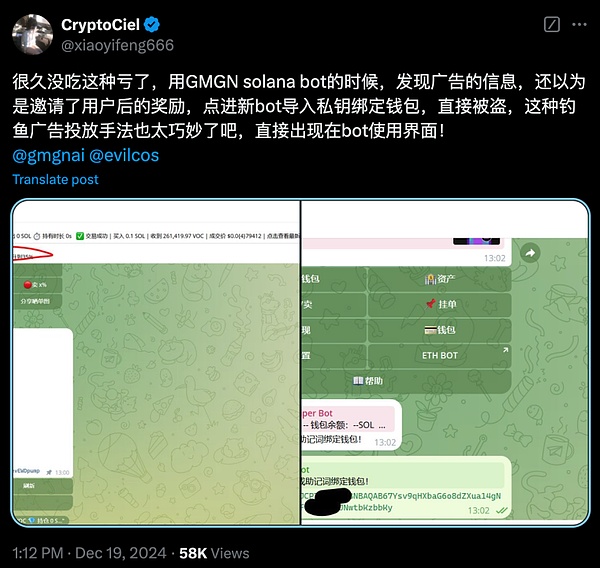
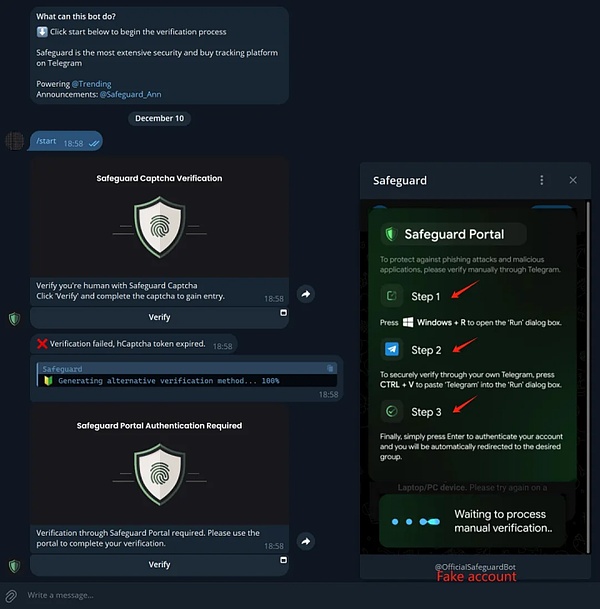
In addition, we recently disclosed a new method|Telegram fake Safeguard scam, many users were stolen because they ran malicious code according to the attacker's tutorial.
APP Store
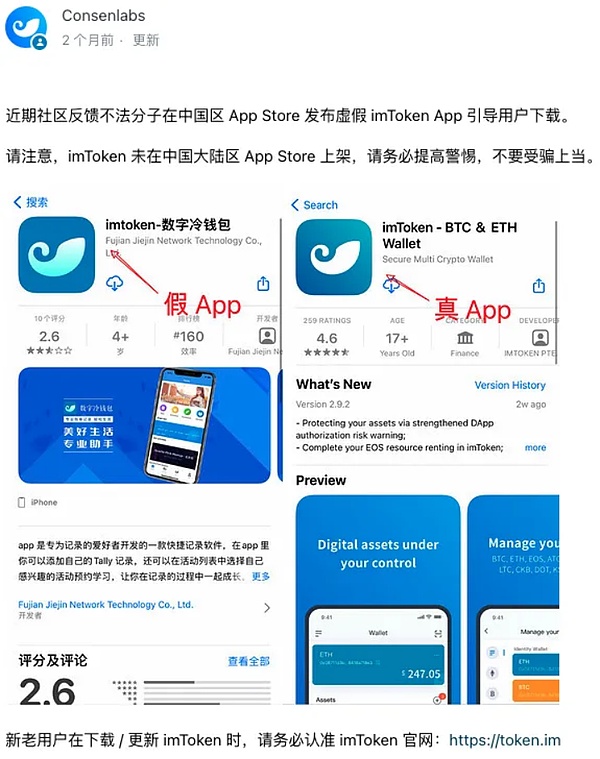
The software on the application store (Google Play, Chrome Store, App Store, APKCombo, etc.) is not all genuine, and in many cases the store has no way to fully review the software. Some attackers induce users to download fraudulent apps by purchasing keyword rankings and other methods. Please be careful to identify them. Before downloading, be sure to check the application developer information to ensure that it is consistent with the official developer identity. You can also refer to the application rating, download volume and other information.
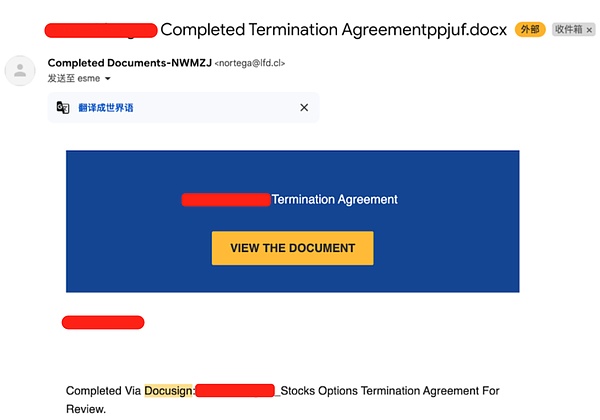
Phishing Email
Email phishing is the most classic routine, which can be said to be "plain and unpretentious". Attackers use phishing templates and Evilngins reverse proxy to build emails similar to the following figure: After the user clicks "VIEW THE DOCUMENT", it will jump to the fake DocuSign interface (now unable to open). Then if the user clicks Google login on the interface, it will jump to the reverse proxy Google login window. Once the account, password, and 2FA are entered, the account will be taken over by the attacker.
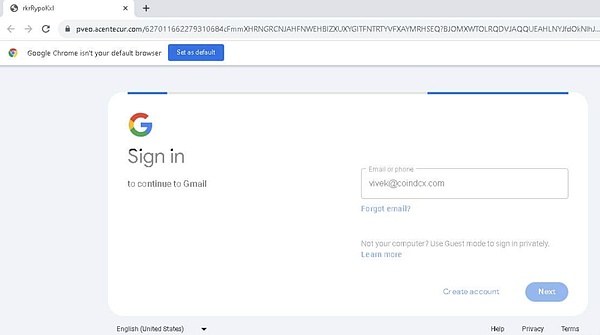
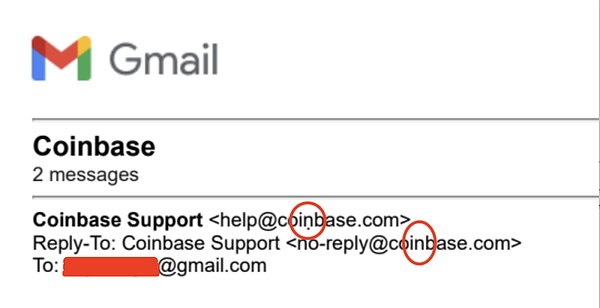
The phishing email in the above picture is obviously not processed carefully enough, because the sender's email address is not disguised. Let's see how the attacker in the picture below disguises himself: the attacker's email address only has a small dot more than the official address. The attacker can find special characters supported by Gmail through DNSTwist. If you don't look carefully, you might think it's a dirty computer screen.
Exploiting browser features
For details, see SlowMist: Exposing how malicious browser bookmarks steal your Discord Token.
Defense challenges

The attacker's methods are constantly evolving, and are generally moving towards refinement and templateization. Previously, we found that attackers can not only create web pages that are highly similar to the official websites of well-known project parties and take over the domain names of project parties, but also a whole set of projects are fictitious. Fake projects not only have many fans (bought) on social media, but also have GitHub repositories, which brings greater challenges to users to identify phishing threats. In addition, the attackers' proficiency in using anonymous tools also makes it more difficult and complicated to track their traces. In order to hide their identities, attackers often use VPN, Tor, and even control hacked hosts to carry out malicious behaviors.

After having an anonymous identity, attackers need to purchase basic service facilities to build a phishing network, such as Namecheap, which supports cryptocurrency payments. Some services only require an email address to register, and no KYC verification is required, so attackers can avoid being tracked.

After the above foundations are prepared, the attacker can launch a phishing attack. The profited funds are then used to confuse the fund path using services such as Wasabi and Tornado. To further enhance anonymity, the funds may also be exchanged for highly anonymous cryptocurrencies such as Monero.

To avoid leaving samples and evidence, the attacker will clear the traces and delete related domain name resolution, malicious programs, GitHub repositories, platform accounts, etc. This also leads to security personnel often encountering situations where phishing websites can no longer be opened and malicious programs can no longer be downloaded when analyzing accidents, which increases the difficulty of analysis and tracking.
Defense Strategy


Users can identify phishing threats based on the features in the above picture, and master the basic methods to verify the authenticity of information. They can also use some defense tools to improve anti-phishing capabilities:
Phishing risk blocking plug-ins: For example, Scam Sniffer can detect risks in multiple dimensions. When users open a suspicious phishing page, the tool will pop up a risk prompt in time.
Wallets with high interactive security:Such as Rabby's observation wallet (no private key required), phishing website identification, WYSIWYG, high-risk signature identification, historical record Scam identification and other functions.
Internationally renowned antivirus software:Such as AVG, Bitdefender, Kaspersky, etc.
Hardware wallet:Hardware wallet provides a way to store private keys offline. When using hardware wallets to interact with DApps, private keys will not be exposed online, effectively reducing the risk of asset theft.
Written at the end

In the blockchain dark forest, phishing attacks are everywhere. Practice is in the mind and thoughts, you need to watch your own thoughts and avoid unconsciously "having thoughts and thoughts" in the environment. When walking in the blockchain dark forest, the most fundamental thing is to develop the habit of maintaining zero trust and continuous verification. It is recommended that you read in depth and gradually master the "Blockchain Dark Forest Self-help Handbook": https://github.com/slowmist/Blockchain-dark-forest-selfguard-handbook/.
 Weatherly
Weatherly























