Last week's events show that despite its growing acceptance by more institutions, Bitcoin remains deeply misunderstood:
-
Jamie Dimon claims Satoshi Nakamoto controls Bitcoin
Vanguard ;Claims that Bitcoin is too volatile to invest
UBS claims that Bitcoin has no application value in the real world
In this article, I will go over the most common misconceptions about Bitcoin.
We are still early.
View: Bitcoin has no support.
Rebuttal: Bitcoin is backed by the most powerful computing network in the world.
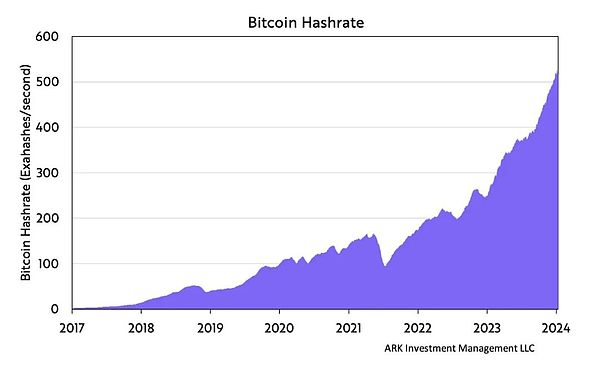
The computing power "supporting" Bitcoin has reached 500 exahashes/second, exceeding the sum of the world's largest computing networks. This computing power is not concentrated in one place or controlled by a single entity. It is distributed across a global network, ensuring decentralization and resistance to attacks or failures.
Miner support > Government support
Opinion: Bitcoin wastes too much electricity.
Rebuttal: The energy consumed by Bitcoin is not a waste. It is purposefully allocated to sustaining a network that will have profound implications for the future of currency.
Bitcoin’s energy consumption is an important design feature that provides the basis for a decentralized, independent, globalized and automated monetary system. necessary security. Bitcoin mining requires a lot of computing power and is very expensiveso the system that Bitcoin is built makes any attempt to attack the network highly infeasible.
In addition, a large portion of Bitcoin’s energy consumption comes from renewable energy. Bitcoin mining’s free market principles provide a strong incentive for miners to seek cheap electricity, inadvertently leading them to adopt more sustainable energy solutions. Many mining sites are strategically located near abundant renewable energy sources. These miners harness energy that might otherwise go unused, especially in regions where renewable energy production varies widely and does not always align with demand. In this case, Bitcoin mining can serve as a stabilizer for the renewable energy grid, providing ongoing energy demand and helping to fund and support the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure.
It is also worth noting that the wasteful nature of Bitcoin depends largely on the directness and unambiguity of its energy consumption,This contrasts with the more hidden and dispersed energy costs of other systems, including traditional financial systems.
The energy consumed by Bitcoin mining should be consistent with a decentralized, global, secure, transparent, and transnational weighed against the intrinsic value of the currency of the political system. In light of this, Bitcoin’s energy consumption is not a waste but an investment in a global financial network where anyone, anywhere can use Bitcoin without discrimination. It symbolizes a collective commitment to support an open global economic system based on free market principles.
Sorry, skeptics, you can only choose one.

Opinion: Bitcoin is slow to process transactions.
Rebuttal: Bitcoin provides strong transaction settlement guarantees.
Bitcoin’s transaction speed reflects its design choices that prioritize security and decentralization.
In a decentralized global monetary system, "transaction speed" is a far less effective measure of performance than "transaction immutability." Although block time will affect the initial confirmation speed of a transaction, it does not guarantee the immutability of the transaction. Bitcoin’s decentralized settlement guarantees are unmatched when compared to “higher throughput” financial settlement networks. Bitcoin is the “fastest” blockchain as measured by the time it takes to ensure a transaction is finalized.
In addition, Bitcoin's "small" block size balances transaction throughput with the ability of individuals to participate in the network without requiring excessive data resources. Its 10-minute block interval is also a deliberate design choice to allow enough time for network synchronization and stable transaction verification.
Opinion: Bitcoin is too unstable.
Rebuttal: Bitcoin’s volatility highlights the credibility of its monetary policy.
Volatility is a natural consequence of Bitcoin’s monetary policy. Unlike modern central banks, Bitcoin does not prioritize exchange rate stability. On the contrary, based on the currency quantity rule, Bitcoin limits the growth of the money supply, allows the free flow of capital, and gives up a stable exchange rate. Thus, the price of Bitcoin is a function of demand relative to supply.
Bitcoin’s volatility is no surprise.
However, Bitcoin's volatility will gradually decrease over time. As Bitcoin adoption increases, the marginal demand for Bitcoin will become a smaller and smaller proportion of its total network value, reducing the magnitude of price fluctuations. For example, all else being equal, a $1 billion new demand for a $10 billion market cap should have a greater impact on the price of Bitcoin than a $1 billion new demand for a $100 billion network value. Bitcoin prices have a greater impact.
Importantly, we believe volatility should not rule out Bitcoin as a store of value, primarily because volatility typically correlates with Bitcoin price consistent with the sharp rise.
Opinion: Bitcoin is exploited by criminals.
Rebuttal: Bitcoin is censorship-resistant.
Criticizing Bitcoin for facilitating criminal activity is criticizing one of Bitcoin’s fundamental value propositions: resistance to censorship. As a neutral technology, Bitcoin allows anyone to conduct transactions without identifying “criminals.” Bitcoin does not rely on a central authority to identify participants by name or IP address, but by encrypting digital keys and addresses, which gives Bitcoin strong censorship resistance. As long as participants pay fees to miners, anyone can conduct transactions anytime and anywhere.
If criminal activity on the Bitcoin network can be censored, then all activity can be censored. In contrast, Bitcoin enables anyone to exchange value on a global scale without any restrictions. This does not mean that Bitcoin is inherently a tool for crime. Compared with Bitcoin, mobile phones, cars and the Internet are no less prohibitible than the facilitation of criminal activity.
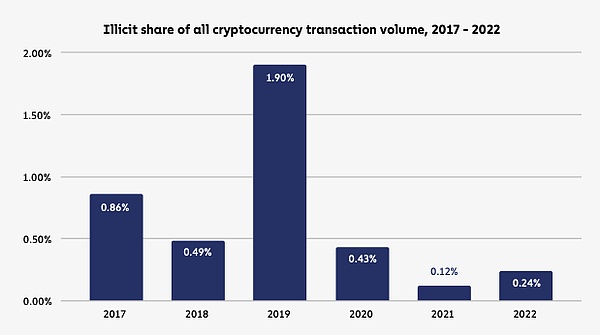
Even so, only a small percentage of Bitcoin transactions are for illegal purposes. According to Chainalysis, 0.24% of cryptocurrency transactions were considered illegal in 2022, with an average of less than 0.7% over the past six years.
OPINION: Governments could easily shut down Bitcoin.
Rebuttal: Governments can’t stop Bitcoin. They can only stop themselves from using Bitcoin.
Bitcoin runs on a global computer network, so it would be extremely challenging for any government or institution to shut it down. The resilience of the Bitcoin network comes from its distributed architecture, with thousands of nodes spread across different jurisdictions maintaining and validating the blockchain. As long as there are at least two nodes running anywhere in the world, Bitcoin will continue to function.
While governments can regulate or restrict the use of Bitcoin within their borders, the global and decentralized nature of Bitcoin makes it impossible to completely shut down Bitcoin. coins is virtually impossible.
Opinion: Satoshi Nakamoto controls Bitcoin.
Rebuttal: Bitcoin contains a unique system of checks and balances that ensures that no one person or entity can control it.
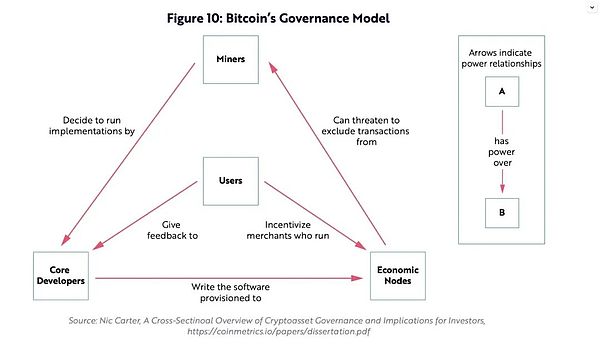
Satoshi Nakamoto does not control Bitcoin. At its core, Bitcoin is software supported by a decentralized network of computer nodes. Its software formalizes its rules. Human beings are not the final arbiters of truth and cannot unilaterally decide to change its rules. Conversely, nodes that validate transactions also enforce the rules.
Every node follows the same set of rules and is only allowed to enter the network if it follows these rules. If a node attempts to break the rules, all other nodes will reject its information. Recommended software changes are meaningless unless various stakeholders choose to accept them. Nodes are spread across the globe and operate independently, and they will not accept any behavior that compromises their integrity. However, nodes are only part of maintaining the integrity of Bitcoin. Bitcoin contains a unique system of checks and balances designed to encourage innovation and maintenance of the protocol while ensuring that any changes are in the interest of stakeholders.
Key to the system of checks and balances is the value of the asset Bitcoin, which provides stakeholders with financial incentives to resolve disputes and maintain the integrity of the system. No stakeholder enjoys preferential rights or treatment, but each stakeholder benefits from Bitcoin's price appreciation, which is the network's primary signaling mechanism. Any changes that threaten the integrity of the system threaten the value of Bitcoin. As a result, stakeholders have little incentive to act maliciously.
This system of checks and balances is also why Bitcoin is able to maintain its predictable monetary policy and limit the supply of Bitcoin to 21 million coins. It is very unlikely to arbitrarily change the rules of Bitcoin.
View: Bitcoin has no intrinsic value.
Rebuttal: Bitcoin is a global currency competitor.
While Bitcoin’s value drivers are different from traditional assets, it would be incorrect to assert that it has no intrinsic value. Bitcoin’s properties as a monetary asset underlie its value and demonstrate that its role in the financial world is sustainable and not merely speculative. Bitcoin’s intrinsic value does not lie in a traditional cash flow-based asset, but in its unique properties that fit both the historical and modern needs of the monetary system.
Bitcoin is often called "digital gold". It not only has many properties of gold, but also improves these properties. Bitcoin is both scarce and durable, while also being divisible, verifiable, portable and transferable. These monetary properties give Bitcoin super utility and are likely to drive demand and make Bitcoin a global digital currency. suitable candidate.
Opinion: No one uses Bitcoin.
Rebuttal: Did you see the numbers?
Cumulative transaction volume: 41.6 trillion US dollars
Cumulative transaction volume Volume: 954 million transactions
Cumulative miner revenue: 58.8 billion US dollars
Addresses with non-zero balance: 51.7 million US dollars
Market cost base: US$440 million
 Brian
Brian







