1. Scam project risks
In the current Bitcoin protocol, for the project Identification relies primarily on the project name specified in the deploy operation and identified in the indexer by a unique ID. However, for ordinary users, they can often only remember the name of the project and use it as a basis for transactions. There is a certain risk in this name-dependent transaction method, because there are a large number of similar but different strings in the ASCII code, which provides opportunities for visual fraud. Malicious parties can use these similar but different strings to trick users into thinking they are transacting with a well-known project and issue tokens from similar projects in large quantities.
This kind of fraud often occurs during the project mint process. Malicious parties may induce users to pay fees in order to obtain tokens or other virtual assets that may have no real value. This kind of fraudulent behavior not only harms the interests of users, but may also cause instability in the entire ecosystem.
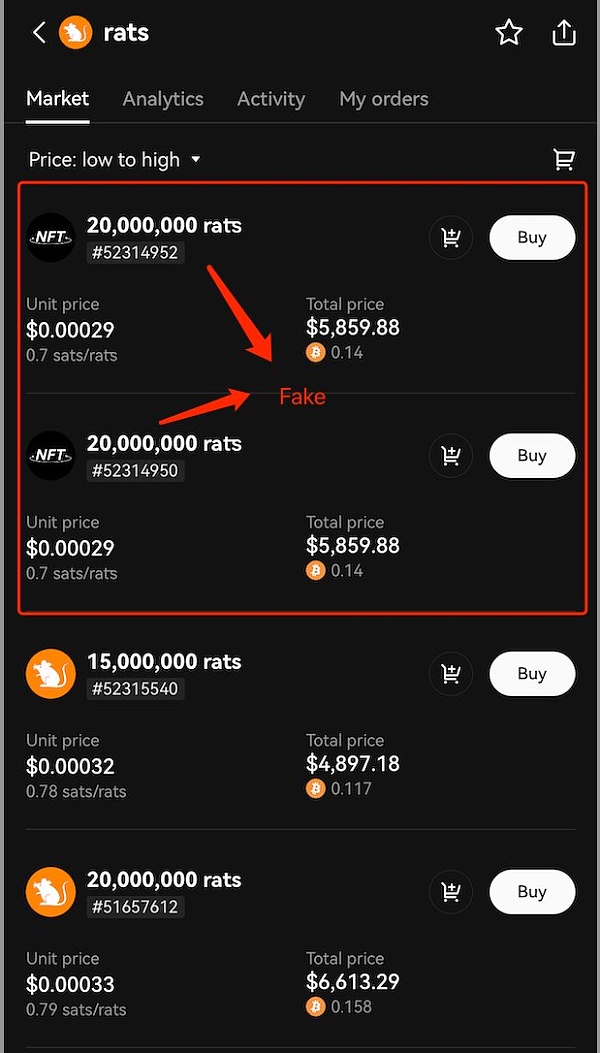
Here we give an example of fake rats. The names of the fake rats and the real rats are very similar because they use similar ASCII codes. If users do not carefully identify the name (note the "t" in rats), they will be mistakenly guided to purchase fake rats tokens, causing financial losses.
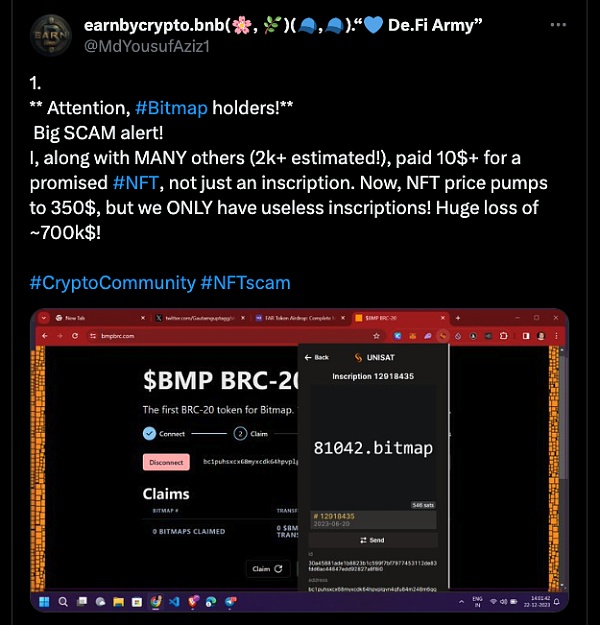
In addition to the false inscription, Some scam inscriptions even defraud users of additional funds during the mint process.
For example, as shown in the picture, when casting the inscription on the bitmap, the fraudulent webpage additionally requires the user to pay to an address. If the user does not notice the amount of the payment, he or she will suffer significant losses.
Countermeasures: Avoid casting inscriptions from unknown sources
Nowadays, the channels for casting inscriptions are very diverse, and the types we are currently exposed to include:
The project's own issuance website
Auxiliary tools for wallets such as Unisat
Other third parties The auxiliary tools provided
These different types of inscription casting channels will make users confused and unable to distinguish the correctness and safety of the channels, thus falling into the fraud trap of scam inscriptions. . Here werecommend users to use the wallet and the project’s official issuance website to cast inscriptions. Try to confirm the correctness of the website before casting inscriptions, and carefully observe the required casting amount. If it is a large-scale batch mint, werecommendthe use of wallet auxiliary tools to further increase fund security.
2. Risk of mistaken transfer and misburn
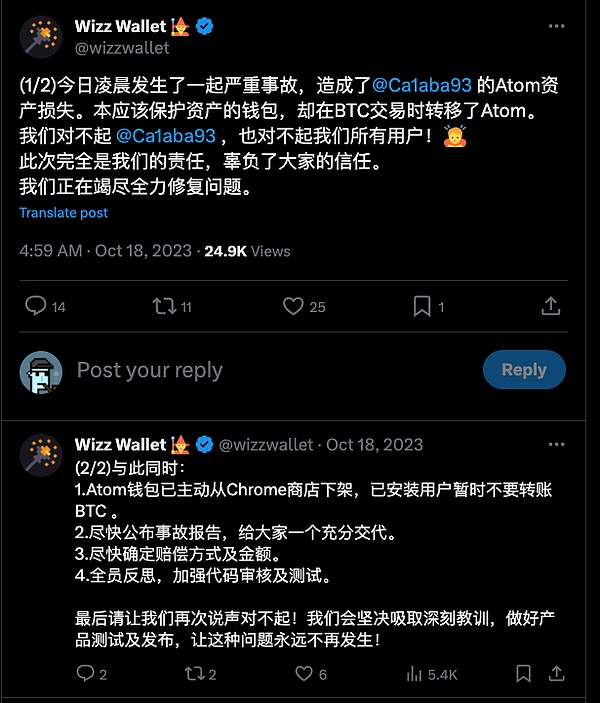
First of all, mistaken transfer refers to transferring the inscription carrier as a normal Bitcoin. Case. Since the inscription is attached to the Bitcoin transaction, for a traditional BTC wallet, it will not consider the additional value brought by the inscription, and will only display the value of the satoshi locked in the UTXO model. Some users may perform traditional transfer operations without fully understanding the inscription. This may cause the wallet to mistake the inscription for an ordinary Bitcoin asset, merge it with other UTXOs, split them and send them to the wrong address, resulting in irreversible losses.
Secondly, accidental burning refers to burning or deleting inscriptions as worthless or meaningless information. Since inscriptions do not directly affect the ownership or value of Bitcoin in the split model, some users may mistakenly believe that these inscribed Bitcoin paper assets are of lower value, unimportant, or invalid, and choose to combine them with others. UTXO model fusion. This may result in the permanent loss of important information or assets associated with the inscription.
For example, as shown in the picture, in a BTC transaction that should have protected the inscription, the wallet mistakenly did not recognize the inscription, thus transferring it as dust, causing losses.
Countermeasures: Prepare a dedicated Inscription address and wallet
In the split model, in order to prevent users from mistakenly transferring or burning high-value Inscription assets, it is recommended that users prepare a dedicated Inscription address and wallet. Such an approach can effectively reduce the risk of misoperation and ensure the safety of inscribed assets. This address should be distinguished from other regular transaction addresses to avoid confusion with ordinary Bitcoin transaction addresses. By isolating Inscription transactions from other transactions, users can better control and manage Inscription assets.
3. Risks of centralized tools
The decentralized design of the blockchain allows users to directly participate in the block However, since it is too complicated to directly use the complex RPC protocol to join the blockchain ecosystem, the vast majority of users choose to rely on auxiliary tools to participate in the casting and transaction process of the inscription ecosystem.
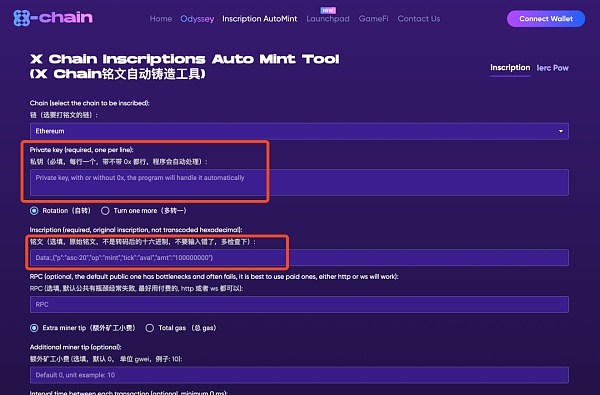
Since inscription is a new concept, its ecology is still in its infancy compared to the mature ERC20 system. Although auxiliary tools are springing up like mushrooms after a rain, most of them focus on functional implementation, and there are still some gaps in security considerations. For example, users can directly import their private keys for signing, and allow users to entrust assets to the platform to implement transactions, etc. These operations expose the user's private key, and the centralized tool essentially controls all the user's assets, which is prone to centralization risks such as rugs. This kind of risk is similar to that of some wallet companies. After mastering the user's private key, they privately took away all the user's assets and declared the company bankrupt.
For example, the following payment tool directly steals the money in the wallet by obtaining the user's private key.
Countermeasures: Use safe inscription auxiliary tools
In order to improve the security of inscription assets,users should trade and operate in well-known inscription markets.
This type of widely recognized inscription exploration and market platform provides a safe trading environment and reliable inscription information. Minting, trading, and other operations of inscriptions on these well-known platforms can increase user security. In addition, users should remain vigilant and not blindly trust inscription casting and trading services provided by unknown websites. The credibility and safety of the website should be carefully researched and confirmed before taking any action. Additionally, users should ensure that they do not reveal their private keys or other sensitive information to any untrusted third parties to prevent phishing or theft.
Summary
After having an in-depth understanding of the risks of Inscription Scam, the risks of mistransfers and misburns, and the potential threats of centralized tools, We can find that although the inscription ecology is full of prospects and possibilities, it is also accompanied by many risks and challenges. Users must maintain a high degree of vigilance and caution in the transaction and storage of inscriptions. From using official channels to cast inscriptions, preparing dedicated inscription addresses and wallets, to choosing safe inscription auxiliary tools, these precautions can reduce risks to a great extent and protect users' asset security. Finally, we encourage all users to be cautious when participating in the Inscription market. In the world of digital assets, safety always comes first.



