The current status of the three blockchain abstraction giants: Axelar, Wormhole, and LayerZero
“Interoperability is the future” — Vitalik Buterin.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Author: Metrics Ventures
Axelar belongs to the two major narratives of the full chain and the Cosmos ecology. The full-chain track will gain more room for growth and market attention as the bull market transaction volume increases and the number of public chains increases. A more direct catalyst may come from the issuance of tokens by Layerzero and Wormhole, which will bring market growth to the entire full-chain track. Boom
TL;DR:
Axelar belongs to the two major narratives of the whole chain and the Cosmos ecology. The full-chain track will gain more room for growth and market attention as the bull market transaction volume increases and the number of public chains increases. The more direct catalyst may come from the issuance of coins by Layerzero and Wormhole; the Cosmos ecosystem is developing healthily, and the ecosystem at the end of 2023 The general rise has also attracted the market’s attention to the Cosmos ecosystem.
Axelar has profound accumulation of technical advantages in the whole chain track and will become the core target in the whole chain narrative. Axelar has achieved interoperability between 56 chains, surpassing competitors such as Layerzero; GMP and AVM simplify the multi-chain development process for developers and help developers achieve full-chain contract deployment and liquidity integration.
In this cycle, the cross-chain protocol that can achieve full-chain cross-chain deployment can basically only be an external verification bridge. Compared with similar cross-chain protocols, Axelar has satisfactory performance in terms of security, number of cross-chains, and number of integrated dApps. Compared with direct competitors Layerzero and Wormhole, Axelar is far below its first-tier valuation.
Axelar is the main channel connecting the Cosmos ecosystem and the EVM chain, especially the connection between Osmosis and the EVM chain. As the liquidity portal of the Cosmos ecosystem and the EVM chain, it will directly benefit from the growth of the Cosmos ecosystem.
Axelar is developed based on Cosmos SDK and is compatible with all EVM chains. It is an application chain designed to connect all blockchains to achieve true mutuality. Operational, supports bridging any information/assets. From the perspective of implementation, Axelar is an externally verified cross-chain protocol. It is a complete PoS public chain with an independent decentralized network and verifiers.
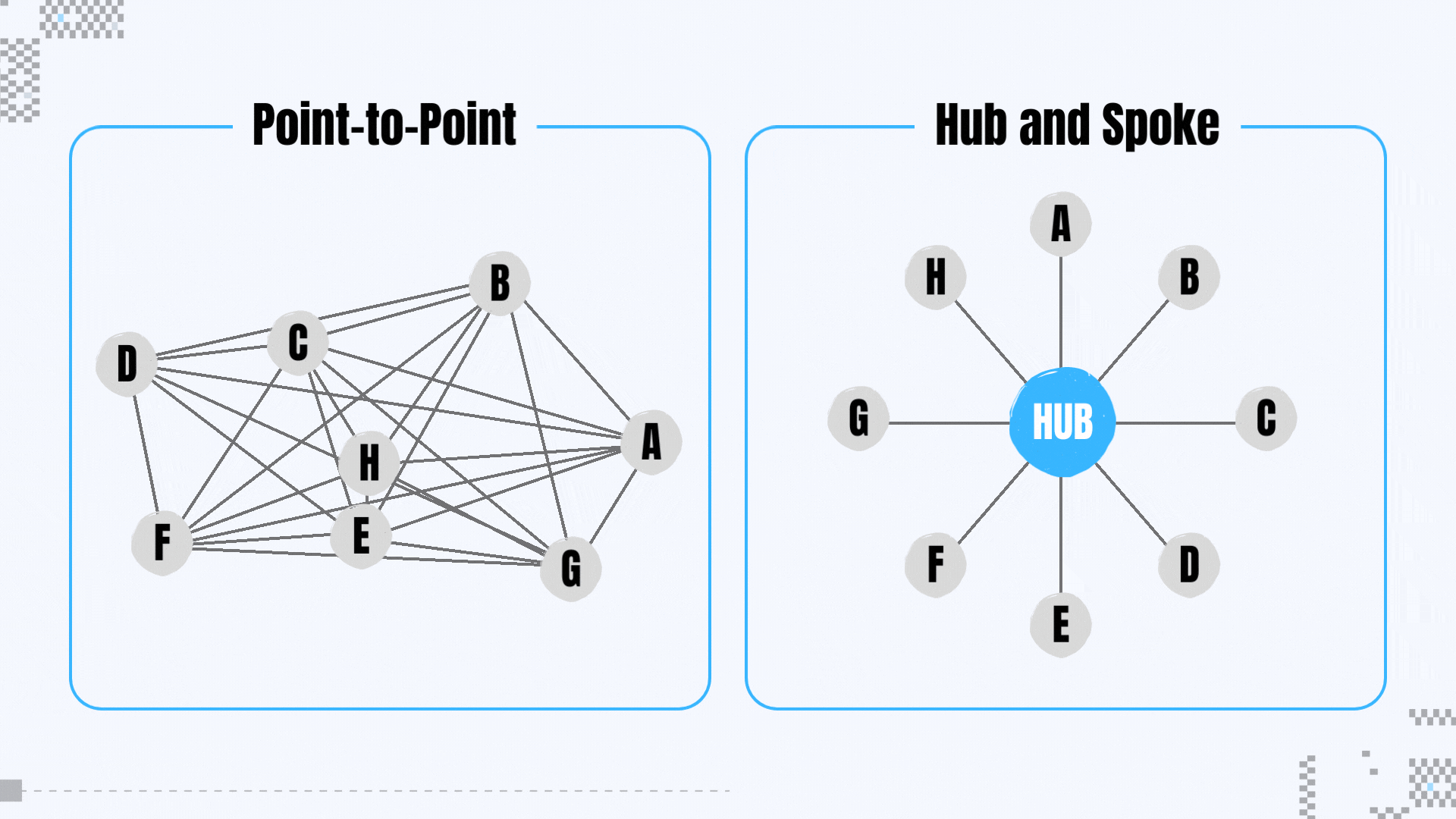
Axelar is built using a hub-and-spoke topology, which is similar to the Hub-Zone topology of the Cosmos ecosystem. Each public chain is directly connected to Axelar (the hub). This achieves indirect connections instead of point-to-point connections, reducing the number and complexity of connections and improving the scalability of the number of connections.
In terms of the specific implementation of Axelar, Axelar’s technology stack mainly includes three Key components: decentralized network/gateway smart contract/API and developer tools. The decentralized network is the trust layer and transport layer of Axelar's cross-chain. It is composed of a group of dynamic, decentralized verifiers, responsible for verifying events on the chain and executing readings on the gateway smart contracts deployed on the connected public chains. write operation. The gateway smart contract is on top of the connected blockchain and together with the decentralized network forms the core infrastructure layer. The validator monitors the gateway smart contract of the source chain and reads the transaction. The validator then reaches a consensus on the validity of the transaction and writes to the gateway of the target chain to execute the cross-chain transaction. APIs and developer tools are the application development layer, allowing developers to easily add universal interoperability to their blockchains and applications.
For cross-chain protocols, security is the core requirement. Axelar mainly ensures the security of the system through 3 mechanisms:
First, the Proof of Stake consensus (PoS) guaranteed by $AXL, which is an external validator A mechanism for reaching consensus on cross-chain transactions. The security of Axelar's cross-chain essentially depends on the security of the Axelar public chain under PoS consensus. It relies on a dynamic and permissionless set of validators, providing higher security than relying on external verification bridges such as PoA or multi-signatures.
Second, Quadratic Voting further improves the decentralized nature of the consensus mechanism. Quadratic voting is: voting cost = number of votes^2, which is used to alleviate the threat posed by oligopoly to network security and avoid the monopoly party that accumulates the majority of tokens from reviewing transactions. Axelar implemented quadratic voting to verify and process cross-chain transactions in the Maeve upgrade at the end of August 2022.
Third, other security measures besides the consensus mechanism mainly include rate limiting and network key rotation. The Axelar gateway has a rate limiting feature that limits the amount of each asset that can be transferred within a given time interval. Validators are also encouraged to rotate keys every two months to protect the network from persistent attackers. In addition, the Axelar network and contracts are 100% open source, and the bug bounty program will encourage the inspection and submission of possible vulnerabilities.
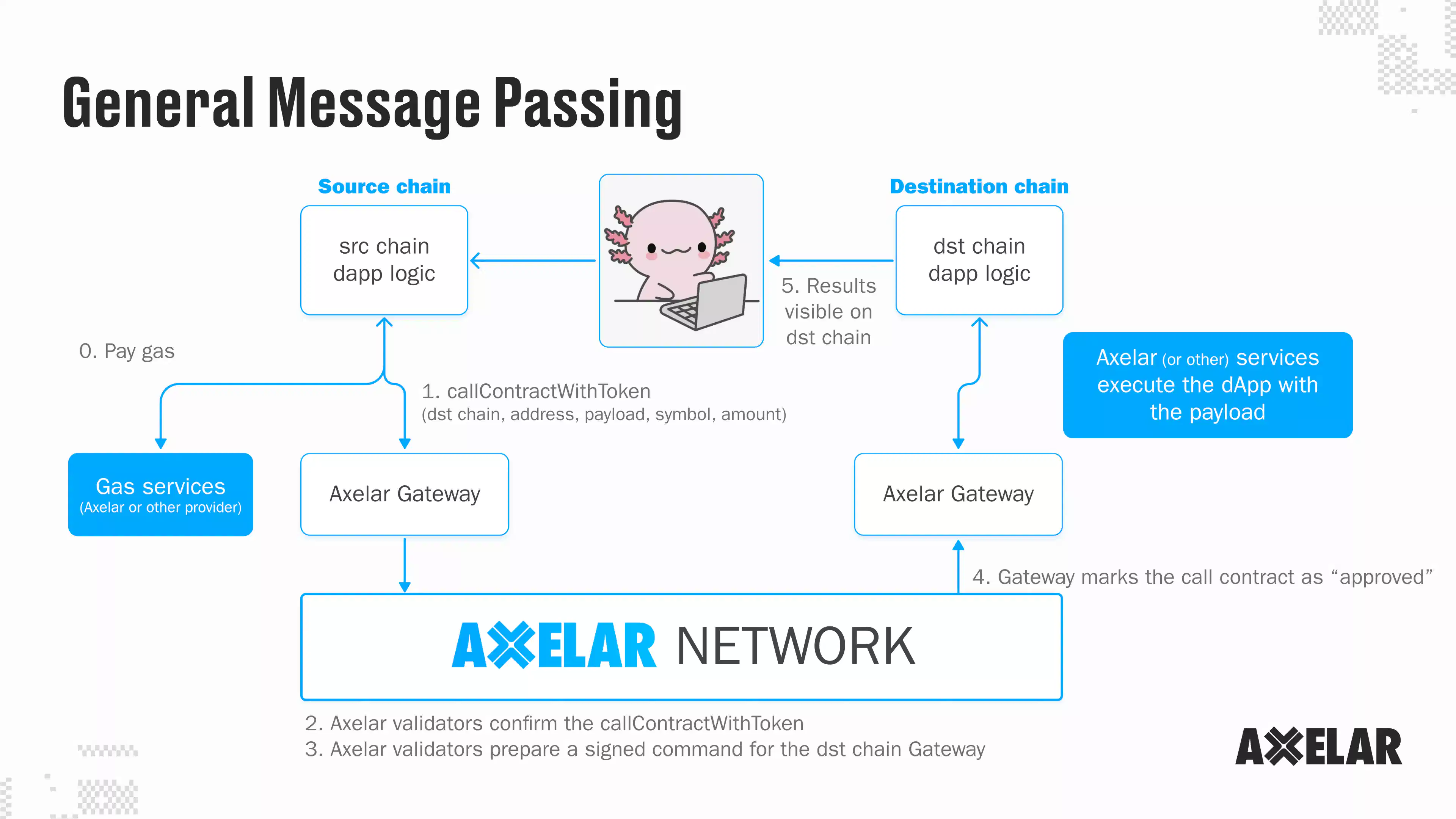
General Messaging goes beyond the concept of bridging assets , enabling developers to build native cross-chain applications and implement chain abstraction for users to perform cross-chain function calls and status synchronization. The implementation process and working principle of Axelar GMP are as follows:
The user initiates a call on the source chain, and the call will enter the Axelar gateway contract from the source chain and be passed to Axelar. In the centralized network, Axelar's verifier confirms the call, deducts the usage fee, and prepares to initiate a transaction on the target chain. When this call is approved, it will enter the target chain through the gateway on the target chain and finally be executed. This Gateway-to-Gateway process takes only about 120 seconds to complete and is verified and secured by Axelar’s PoS mechanism.
Based on universal messaging, Axelar is becoming the cross-chain underlying protocol developed by Dapps. In order to improve customization and simplify the multi-chain development process, Axelar developed AVM, with the support of Cosmwasm, turning interoperability into a programmable layer, allowing developers to write smart contracts on Axelar, and smart contracts can abstract away cross-chain tasks, thereby simplifying the user experience. Currently, three functions are implemented based on AVM:
AXL has three main uses:
AXL token will be issued in September 2022, with an initial supply of 1B and no maximum supply. . The token distribution and unlocking schedule is as follows. The current circulating supply is 535,564,229, the total supply is 1,128,220,669 (according to Coingecko data), the pledged amount is 761M (according to Axelarscan data), and the token inflation rate is 6.1%.


Rewards: Token holders can pledge AXL and delegate AXL to validators of the staking pool to receive rewards. Network validators stake AXL to generate blocks and validate and vote messages to earn commissions.
Fees: used to pay cross-chain fees for using the Axelar network.
Governance: Allow token holders to participate in governance of proposals such as parameter changes or protocol upgrades.
Interchain Amplifier: allowed to develop People can establish a connection to the Axelar network without permission and connect to all chains in the Axelar ecosystem by paying the cost of developing a connection, that is, "amplifying" resources. Permissionless connectivity will facilitate the rapid expansion of the ecosystem that Axelar connects to.
Interchain Maestro: If developers want to deploy contracts on multiple chains, they need to repeat the deployment process multiple times , consuming a lot of time and cost. Interchain Master allows developers to build a contract once and run it on multiple chains, reducing the cost for developers to extend or clone the contract to other chains.
Interchain Token Service: It is a component of Interchain Master and has been released in July 2023 to the testnet. It allows developers to issue cross-chain tokens with one click, reducing the cost of developers repeatedly deploying tokens on multiple chains. At the same time, these tokens can achieve interoperability and solve the problem of multi-chain liquidity fragmentation. Based on this, it can improve DeFi liquidity, simplify cross-chain liquidity mining and staking, allow cross-chain staking, create chain-independent wallets, etc. Sushi is one of the first applications to adopt inter-chain token services.
In December 2023, the community passed a A proposal to reduce AXL’s inflation rate. AXL's inflation rate is mainly composed of three parts: TM (Tendermint) consensus, MSigs inflation and external chain inflation. The first two constitute the basic inflation rate. External chain inflation is the reward for nodes to verify public chain information outside the Cosmos ecosystem. It ranges from 0- For 1 year, it is 1% for each chain, for 1-2 years it is 0.75%, and for 2-3 years it is 0.5%.
There are two main ways to reduce inflation this time: reducing the inflation rate of external links and implementing a gas burning mechanism.
First of all, before the proposal was passed, the external link inflation rate was 0.75%, and the total inflation rate was 11.5% (1% basic inflation rate + 0.75% *14). The proposal decides to change the external chain inflation rate to 0.3%, reducing the total inflation rate to 5.2%. Considering the five EVM chains that will be included, the inflation rate will reach 6.7%. This proposal reduces overall inflation levels and increases the Axelar system's ability to accommodate external link connections.
The second is the gas burning mechanism. When users conduct cross-chain transactions, they need to pay gas to Axelar, and then Axelar will redistribute it to the pledgers. This proposal decides to burn this gas and remove it from the supply.
Since the second half of 2023 , Axelar has reached partnerships with multiple blue-chip projects, rapidly increasing its share of the interoperability market:
On June 16, the Uniswap Foundation released a cross-chain bridge evaluation report, and the committee approved Axelar’s specific use cases for Uniswap’s protocol. Uniswap’s evaluation is: Axelar is the only decentralized cross-chain platform with 75 nodes, strong security practices, and a universal information transfer mechanism that allows users to interact with any contract function on any chain with one click.
On June 23, Axelar became the official cross-chain bridge on Filecoin. Bringing liquidity to DEX and AMM on FVM: Axelar wrapped assets will become the standard cross-chain assets of the Filecoin ecosystem.
On July 11, Microsoft and Axelar reached a partnership. Axelar provides cross-chain services to Microsoft customers through the Azure Marketplace.
On September 12, Squid implemented direct tokens between Ethereum, various EVM compatible chains and the Cosmos ecosystem Swap currently supports 14 EVM chains and 48 Cosmos chains.
On September 14, Lido selected Axelar and Neutron to launch wstETH on Cosmos. Neutron and Axelar provide liquidity.
On November 13, Ondo Finance cooperated with Axelar to launch the Ondo Bridge. Any chain integrated by Axelar can issue Ondo’s USDY.
On November 15, JPMorgan Chase, Apollo and Axelar reached a partnership.
On November 21, Frax passed a proposal to use Axelar to expand new chains.
On December 14, it was announced that Vertex would be integrated. Vertex became another leading DEX project integrating Axelar after dYdX, Uniswap and Pancakeswap. .
"Interoperability is the future". Axelar has a profound accumulation of technical advantages in the whole chain track and will become the core target in the whole chain narrative. The Omnichain actually includes two dimensions. One is to achieve interoperability with as many blockchains as possible and realize the connection between EVM chains and non-EVM chains; the other is to transcend asset cross-chains and realize any message and data of transmission. Based on the Cosmos Liquidity Center, Axelar has achieved interoperability between 56 chains, which has surpassed competitors such as Layerzero. At the same time, Axelar supports any message delivery, and the establishment of AVM has further upgraded the message delivery function. It simplifies the multi-chain development process for developers and helps developers achieve full-chain contract deployment and liquidity integration. In summary, the product delivery progress and partnership expansion fully demonstrate Axelar’s technology accumulation in the entire chain and confirm the solidity of Axelar’s fundamentals.
Before analyzing Axelar’s competitors, it is necessary for us to review the entire cross-chain track: why cross-chain protocols are still a growing industry track? What kind of cross-chain protocol do we need? What types of cross-chain protocols are currently on the market?
Why is cross-chain protocol still a growth track?
First of all, as the demand for blockchain expansion and customization increases, more and more public chains are being developed, including dYdX Many Dapps in the blockchain choose to migrate to application chains. The growth of modular blockchains, universal rollups and application chains has led to the rapid expansion of the number and diversity of blockchains. Blockchain operability is particularly important in the multi-chain era, and cross-chain Protocols are the most important underlying infrastructure for achieving blockchain interoperability.
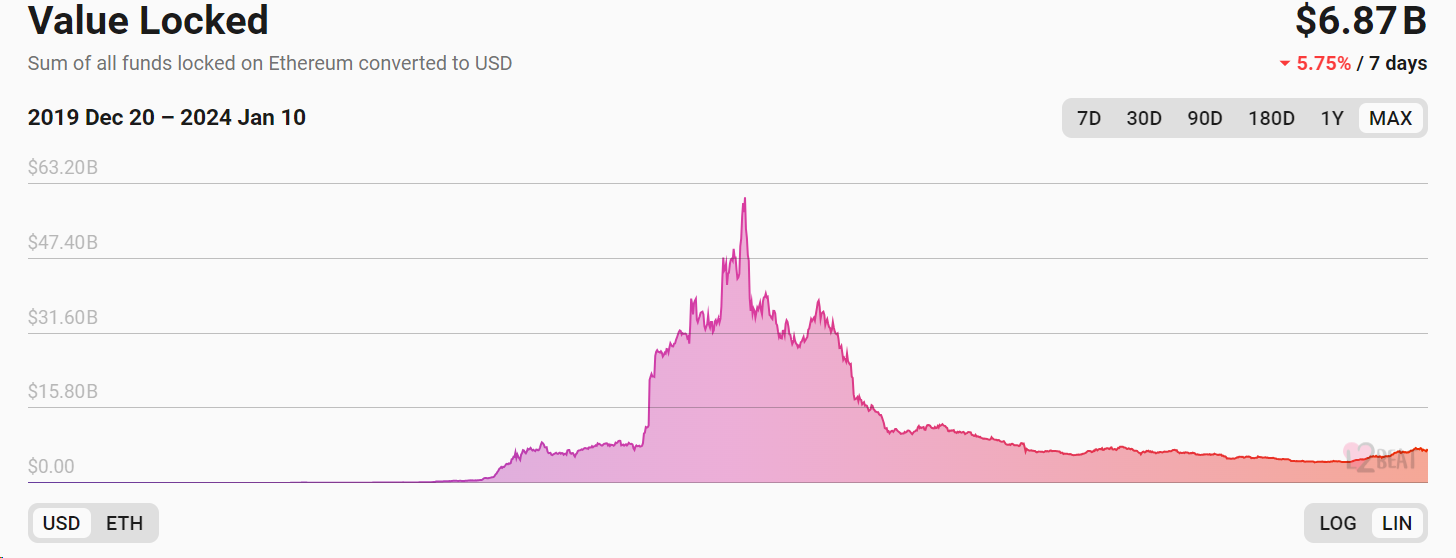
Secondly, according to L2beat data, the TVL of the cross-chain bridge track is US$6.7 billion, which has shrunk by nearly 90% from the previous peak of US$56 billion. %, the coming of the bull market will bring about an increase in the number of on-chain interactions and cross-chain demand. The increase in the number of blockchains will also increase reliance on cross-chain technology. With the emergence of new technologies and new architecture cross-chain bridges, the cross-chain track The scale of the industry still has extremely high room for growth.
Third, although blockchain interoperability and cross-chain protocols are crucial to the industry Important, but the development situation of the cross-chain track is actually unsatisfactory. On the one hand, cross-chain bridges are still one of the most serious targets of hacker attacks and losses, and their security is worrying; on the other hand, cross-chain protocols in the market are still dominated by asset cross-chain bridges, which can make applications seamless. Cross-chain protocols for cross-chain development are still in their early stages of development. Therefore, for such an important underlying technology, cross-chain protocols still have a lot of room for technological progress.
What kind of cross-chain protocol do we need?
According to the cross-chain analysis framework proposed by Arjun Bhuptani, founder of Connext, there is also the impossible triangle in cross-chain interoperability: security (Trustlessness), Generalizability and Extensibility, these three points just summarize the market’s core needs for cross-chain protocols.
The first is security. The highest security is to not add any trust assumptions outside the underlying chain, and have the same security as the underlying chain. Security is still the most important issue for cross-chain protocols. The most recent cross-chain bridge attack was the hacker attack on Orbit Chain on January 1, with the damage amount reaching US$81.5 million.
The second is versatility, which supports the transmission of arbitrary messages between different blockchains. The cross-chain track is still dominated by asset bridges, which support cross-chain asset transfer or asset exchange, but this is not enough for cross-chain protocols. On the one hand, although cross-chain assets can be transferred or exchanged, the liquidity (funds, users, traffic, etc.) between different chains is still scattered; on the other hand, this requires users to still It requires complex cross-chain behavior and increases the user threshold. Therefore, cross-chain protocols are exploring the cross-chain of any message, based on which cross-chain contract calls, liquidity aggregation, and cross-chain applications can be built.
The third is scalability, which can easily adapt to more blockchains, especially the realization of heterogeneous chains with lower development time and cost. cross-chain. Connecting more blockchains will bring a wider user base, funds and traffic.
With the evolution of cross-chain protocols, our expectations for cross-chain protocols have ranged from multi-chain (Multi-Chain) to cross-chain (Cross-Chain). Then go to Omnichain, Interchain, Chain Abstraction or Chain-Agnostic.
Specifically, Multi-Chain refers to deploying Dapps in multiple blockchains, resulting in the same Dapp operating in different blockchain ecosystems. There are multiple instances or versions in the Dapp, and the same Dapp is separated between different chains. Users realize interactions on different chains through asset bridging, which corresponds to the era of cross-chain assets. Cross-Chain represents any process of mutual communication and transactions between blockchains. It consists of multiple smart contracts deployed on multiple chains to form a unified application. Smart contracts on different chains can perform different tasks and maintain Synchronization constitutes a complete dapp instance without requiring developers to repeatedly deploy the same function on different networks. Cross-chain Dapps need to rely on the universal information transfer of cross-chain protocols. Omnichain further enhances the scalability and breadth of cross-chain protocols and enables interoperability between various heterogeneous chains. Inter-chain operations, chain abstraction and chain-independence further hide cross-chain, gas, native assets and other information from users, further optimizing user experience. Cross-chain protocols will be the core technology for chain abstraction implementation.

(Source: Chainlink)
p>Therefore, the market is looking forward to a cross-chain protocol that has security guarantees, can realize cross-chain deployment and chain abstraction, and expands the depth and breadth of cross-chains as much as possible. .
What types of cross-chain protocols are currently on the market?
Of course, the ideal is very rich and the reality is very backbone. Cross-chain technology is still in its early stages, and existing technology cannot break through the inadequacies of cross-chain interoperability protocols. Maybe the triangle can only sacrifice some characteristics to achieve the best possible balance. What types of cross-chain protocols are currently on the market? Which cross-chain protocols are closest to our needs for cross-chain protocols?
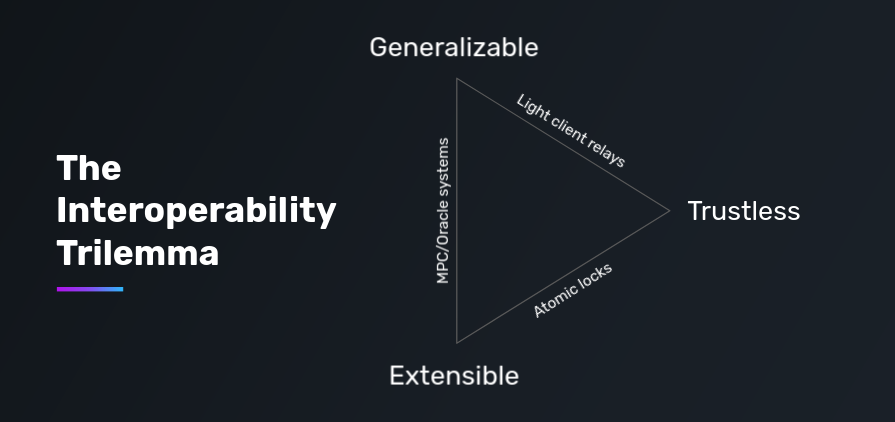
According to the trust layer division, existing cross-chain protocols can be divided into native verification, external verification and local verification Three major types of verification. Native verification refers to deploying light nodes of the source chain on the target chain to verify messages from the source chain. The relay is only responsible for passing the block header of the source chain to the light node contract on the target chain and is not responsible for verification. Native verification has the highest security and does not introduce new trust assumptions, but the verification cost is too high, the development difficulty of establishing light nodes is also too high, and the scalability is weak.
External verification refers to the introduction of a group of external witnesses to verify cross-chain messages, and the witnesses reach consensus through some internal mechanism. External validators may take many forms, including MPC network, PoS/PoA network, TEE network, multi-signature group, etc. External authentication is highly scalable and can deliver arbitrary messages, but its security has been criticized.
Local verification means that the counterparty directly verifies the transaction. The typical paradigm is atomic swap based on hash time lock, but it can only be used for cross-chain assets. .
In addition, there are also many cross-chain protocols using new technologies being developed. The most anticipated one is ZK Bridge, which uses ZK technology for light node expansion. The cross-chain solution will generate block verification certificates off-chain and then submit them to the target chain, saving block verification costs. However, this technology is currently in the research and development stage. It is difficult to develop, has a long development cycle, and is difficult to use directly in the short term. It still needs to deal with different consensus mechanisms and signature schemes, and its scalability is limited.
In summary, although the light client-based bridge has higher security, it can currently only be developed for specific chains, and external verification is still the current cross-chain protocol. main program. In this cycle, the cross-chain protocol that can achieve full-chain cross-chain deployment can basically only be an external verification bridge. The more decentralized the external verifier network is and the stronger the security of the consensus mechanism, the more it can meet the market’s requirements for cross-chain deployment. expectations of the chain protocol.
According to the analysis of the cross-chain track, cross-chain protocols that use external verification and support universal messaging are still the main players in this cycle and are direct competitors of Axelar. Representative protocols include Wormhole and Layerzero , Chainlink CCIP, Celer. After comparison, we believe that Axelar is the most comprehensively competitive cross-chain solution in terms of security, universal messaging and ecosystem growth.
2.2.1 The most important factor: security
Cross-chain The security of the protocol first depends on the consensus mechanism of the trust layer, that is, the method used to verify information. Among the above projects, Axelar adopts the DPoS mechanism, Wormhole adopts the PoA mechanism, Layerzero adopts the dual guarantee mechanism of separation of Oracle and Relayer, CCIP adopts its own oracle network verification, and Celer adopts the dual guarantee mechanism of DPoS and optimistic verification.
Wormhole:
Cross-chain protocol using PoA mechanism It is the subject that has experienced theft incidents: In July 2023, the Multichain security incident caused more than 265 million US dollars in capital outflows, and it has basically lost its competitiveness. Wormhole was hacked in February 2022, with a loss of approximately 226 million US dollars. Under the PoA mechanism, inter-chain messages are verified by a group of trusted entities, but the number of verifiers is small, no pledge is required, and there is a lack of economic incentives. Many verification nodes are controlled by subjects with strong interests, or even the same entity. , the cost of doing evil and the safety are lower.
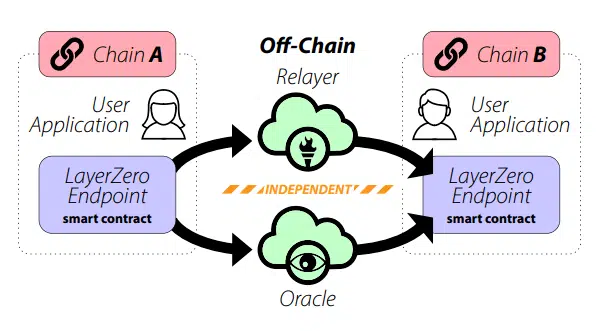
Layerzero:
Layerzero V1 uses double verification Mechanism, the protocol consists of three core components, namely Oracle, Relayer and Endpoint. The Relayer is responsible for delivering messages and message proofs. The Oracle is responsible for obtaining and delivering the block header based on the block where the message is located. The Endpoint of the target chain will verify the message based on the block header. Its core design lies in the separation of Relayer and Oracle to avoid collusion between the two. The security of Layerzero relies on trust in Oracle and Relayer to ensure that the two do not collude. However, Layerzero allows the project party to configure and run its own Relayer and Oracle. In this case, the project party entity still needs to be trusted, making Layerzero's security It has always been criticized.
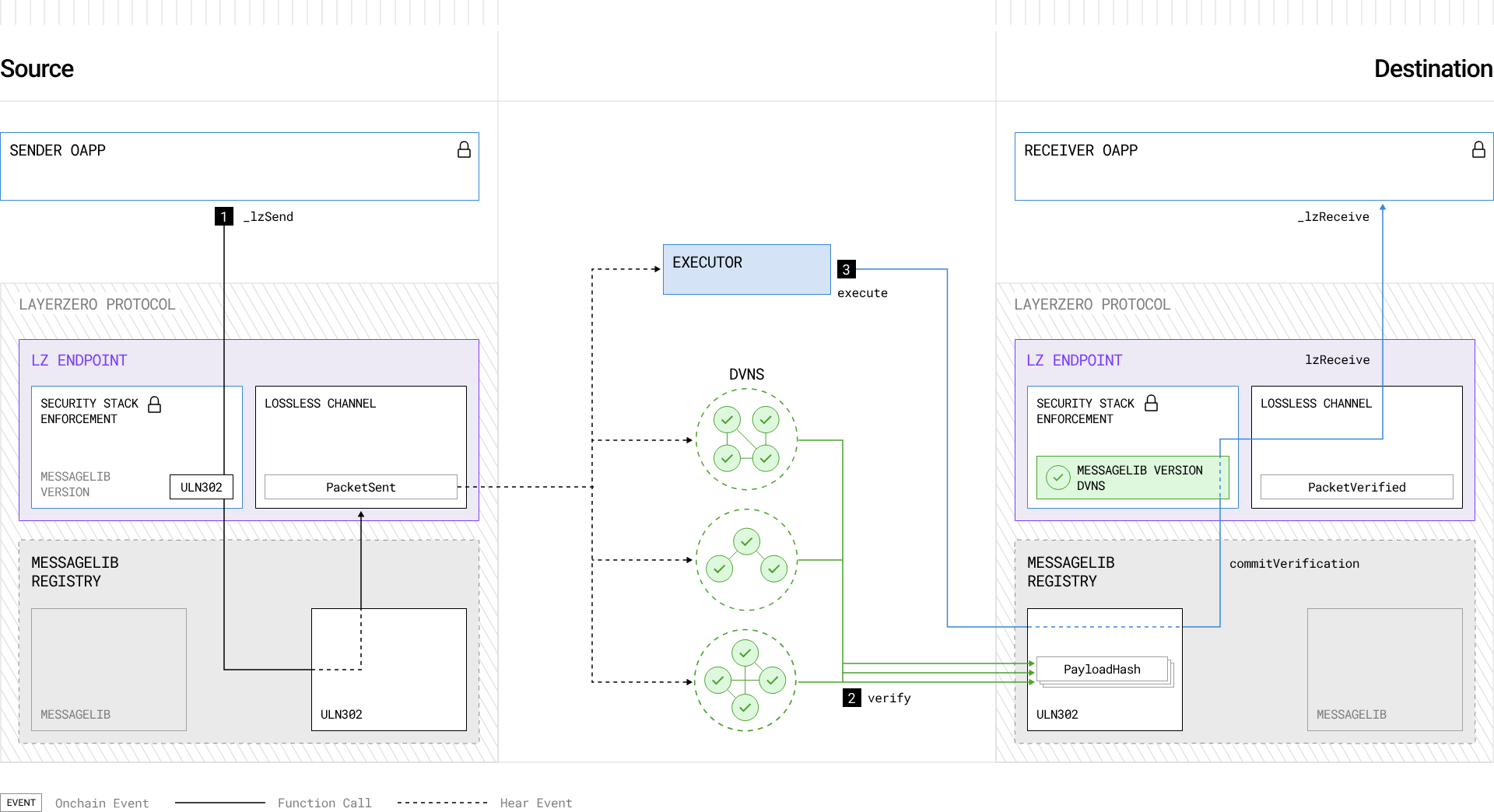
Recently, Layerzero released a technical white paper on V2, and the message is verified by DVN (Decentralized Verification) network) is completed, the Executor is responsible for delivering verified messages and triggering transactions on the target chain. Message verification is performed using an Other DVNs complete the verification together. The entities that can currently run DVN are major entities in the industry, including Blockdaemon, Google Cloud, Animoca, Delegate, Gitcoin, Nethermind, P2P, StableLab, Switchboard, Tapioca, LayerZero Labs, and Polyhedra, but trust in these entities is still required, especially in DVN When the number is small, it actually introduces more trust assumptions than the PoS mechanism like the PoA mechanism. It is worth mentioning that Layerzero introduced Axelar and CCIP as DVN Adapter, which also proves the security of Axelar.
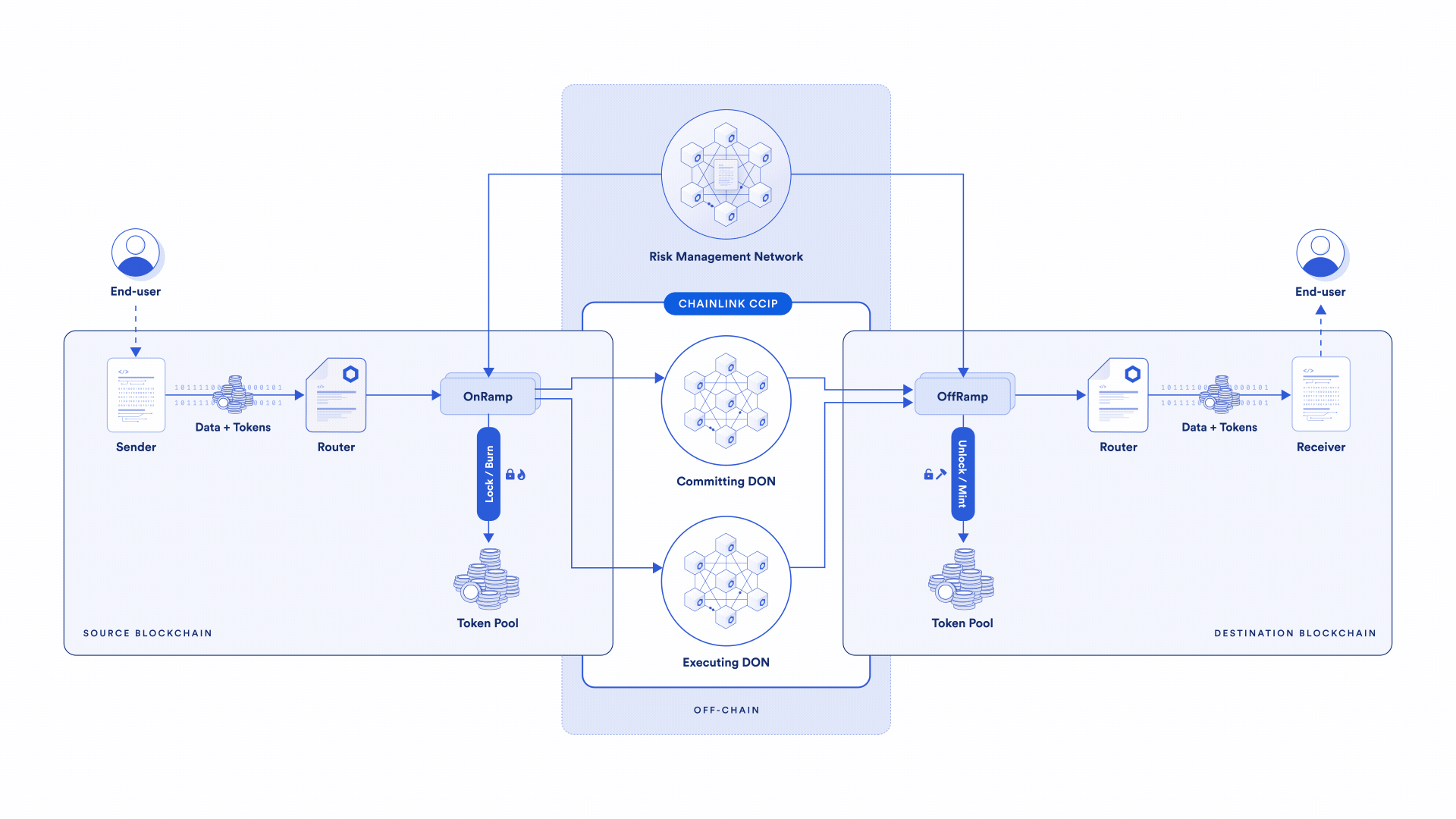
Chainlink CCIP:
Chainlink CCIP's information transmission is monitored and signed by Chainlink DONs, and then passed to the target chain by Relayer to complete transaction execution. In addition, Chainlink CCIP also introduces a risk management system, which is independent of the oracle network and serves as a new verification layer. The risk management node will monitor all Merkle roots of submitted messages on each target chain, and obtain all messages on the source chain to independently reconstruct the Merkle tree, check whether there is a match between the Merkle root submitted by DON and the root of the reconstructed Merkle tree, and detect abnormalities. Afterwards, the risk management nodes can vote to stop CCIP. The security of CCIP is mainly guaranteed by DON. DON has protected tens of billions of dollars in assets and achieved trillions of dollars in on-chain transaction value. Therefore, its security is trustworthy, but the overall development progress of CCIP is relatively slow. Slowly, after its launch in 2021, it will not enter the early access stage of the mainnet until mid-2023.
Celer IM:
Celer IM is monitored, routed and verified by SGN (State Guardian Network). SGN is a PoS blockchain built on Cosmos SDK and becomes a verifier by pledging $CELR. In addition, Celer also provides a second security model, namely optimistic verification. Before the transaction is executed, SGN submits the transmitted message to the chain and enters the "isolation zone". After a period of time, the message is confirmed and is finally Execution,During the quarantine period, the Dapp can run the,App Guardian service to verify the authenticity of submitted,messages.
But it should be noted that Celer’s validator network currently only has 22 validators, including IOSG, Hashkey, Binance, Ankr, InfStones and other industry authorities Entity, Uniswap’s cross-chain bridge evaluation expressed concerns about the same entity operating multiple validators, and the conditions for becoming a validator cannot currently be determined based on official documentation. The optimistic verification mechanism mainly relies on the Dapp itself to run the App Guardian to verify transactions, requires the spontaneous maintenance of the Dapp, and relies on trust in the Dapp. It does not actually reduce the trust assumption to the 1/N level.
In summary, in terms of security, we have reason to believe that Axelar stands out among the solutions. Axelar’s security was recognized by Uniswap in June, believing that it “has a complete crypto-economic mechanism to ensure the security of the protocol.”
From a mechanism design perspective, relying on a dynamic, decentralized, permissionless PoS network for verification is trust. Solution with the lowest sexual assumptions.
From the specific data, we can further compare the verifier data of Axelar and Celer, which also focuses on the PoS mechanism. Comparative data can be divided into two major categories: (1) Verifier related; (2) Token locked value related.
(1) Validator related: The number of Axelar validators (75) exceeds the number of Celer (22) three times; the verifier decentralization passes the top 10% The sum of Validators' voting weights is evaluated. The lower the value, the more dispersed it is. The more dispersed it is, the easier it is to avoid a small number of individuals concentrating a large amount of voting power and colluding to do evil, reducing the risk of centralization. Axelar's validators are more dispersed than Celer.
(2) Related to token locked value: Axelar’s locked token value is as high as $795,420,281, which is approximately 15 times that of Celer; based on the pledged token value/TVL It can be seen that Celer's ratio is less than 1, which makes the value of the mortgage assets used to ensure security lower than the value of the assets being protected, and has a higher risk of evil, while Axelar's ratio is 3.72, which is at a relatively healthy level.
| Number of validators | Verification Dispersion (%) | Staking token value | TVL | Pledged token value/TVL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| https://sgn.celer.network/#/staking | 22 | < td style="border-width: 1px; border-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);">24.9%$54,373,903 | https://devillama.com/protocol/cbridge< /td> | 0.54 | |
| https://axelarscan.io/validators | 75 | 17.2% | $795,420,281 | https://axelarscan.io/tvl | 3.72 |
2.2.2 Scalability and ecosystem development
First of all, for Dapp Said that choosing a protocol that connects to a larger number of public chains to develop native cross-chain applications means having richer funds, users and markets. Currently, Axelar is connected to the largest number of public chains. It is promoting the integration of L1 such as Solana, Ripple, Sui, etc., and has developed the function of automatically integrating L2. The Hub-Spoke architecture is also more scalable than the point-to-point architecture; Layerzero, Celer and Wormhole have relatively high scalability, and CCIP is also in its infancy and currently only supports the interoperability of a small number of public chains within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Secondly, judging from the number of integrated Dapps, Axelar’s ecosystem has expanded rapidly and is in a leading position in capturing the interoperability market, with nearly 100 Dapps. It is integrating Axelar, integrating more blue-chip projects than any cross-chain bridge, and reaching partnerships with Microsoft, JP Morgan and other companies. In terms of integrated Dapp, Axelar spans a wide range of business fields and has a particularly outstanding performance in cross-chain DEX. dYdX, Uniswap, Pancakeswap and Vertex all use Axelar as a cross-chain solution. Axelar’s market share in cross-chain DEX has exceeded 50% (calculated based on market trading volume).
| Number of supported public chains | The number of integrated dApps | The number of dApps planned to be integrated | Blue chip project representative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axelar | 56 | 62 | 30 | dYdX, Lido, Uniswap, Pancake, Squid, Sushiswap, Frax, Metamask, Decentraland |
| Wormhole | 30 | 68 | 15 | Frax, Lido, Raydium |
| Layerzero | 48 | 87 | / | Curve, AAVE, Pancake, Radiant, Balancer | < /tr>
| CCIP | 7 | No official data | / | / |
| Celer | 45 | No official data | / | / |
2.2.3 Summary: Axelar is the most comprehensive and mature cross-chain solution
Based on the above analysis, Axelar is currently the most comprehensive and mature cross-chain solution on the market. The best solution for security, scalability, and arbitrary messaging needs. Wormhole and Layerzero are currently becoming the two most anticipated projects on the cross-chain track with airdrop expectations. Axelar’s fundamentals are comparable to Wormhole and Layerzero, but FDV is currently only less than half of the first-level valuation of the two. To, it is undervalued in the cross-chain field.
| Verification mechanism | Connection public Number of chains | Ecosystem | MC | FDV or first-level estimate Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axelar | DPoS+quadratic voting | 56 | 62+30 | < td style="border-width: 1px; border-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);">$501,347,130$1,016,772,630 | |
| Wormhole | < td style="border-width: 1px; border-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);">PoA30 | 68+15 | / | https://www.theblockbeats.info/flash/200438?search=1 | |
| Layerzero | Dual verification of Oracle and Relayer separation | 48 | 87 | / | https://www.theblockbeats.info/flash/135165?search=1 |
| CCIP | DON message verification + risk control management | 7 | / | $11,256,847,756 | $19,173,647,260 |
| Celer | DPoS+optimistic witness hybrid verification | 45 | / | $91,352,633 | $161,816,247 |
Another reason why Axelar deserves attention is the Cosmos ecology narrative. We focus on two Questions: First, why the Cosmos ecosystem deserves attention; second, if the Cosmos ecosystem is deployed, why Axelar is a target that cannot be missed.
The first question, why is the Cosmos ecosystem worthy of attention?
First of all, the application chain narrative will be an important narrative in this cycle. Cosmos itself is built around the application chain topic, and each chain is dedicated to Designed for hosting applications, and all chains are seamlessly connected through a shared communication standard. Of course, the Cosmos ecosystem faces challenges from the Ethereum Rollup ecosystem, but the technical standards of Cosmos itself give it unique advantages: First, Cosmos allows developers to build a Layer 1 with higher sovereignty, both in terms of token economy and technology. Higher autonomy, rather than being attached to Ethereum’s L2/L3; second, Cosmos achieves interoperability between multiple chains through the inter-chain communication standard IBC protocol, enabling seamless transfer of assets and data between different blockchains. Seam transfer has advantages in cross-chain that other ecosystems cannot match. In addition, dYdX moved from the Ethereum ecosystem to the Cosmos ecosystem to build an application chain, which can be said to have attracted enough attention to the narrative of Cosmos on the application chain. Therefore, whether in terms of technology or market attention, Cosmos will occupy a place in the application chain narrative.
Secondly, the recent upgrade of Cosmos will enable the Cosmos ecosystem to develop more healthily. Two important upgrades: One is Replication Security, launched on March 15, 2023, which allows blockchains in the Cosmos ecosystem to give up their own validator sets and use Cosmos Hub’s validators to ensure security and improve ATOM empowerment and reduces the difficulty of application chain development. Second, Noble announced its cooperation with Circle to introduce native USDC into the Cosmos ecosystem. After the collapse of UST, the Cosmos ecosystem has been lacking native stablecoins and can only use cross-chain mapped stablecoins, which increases systemic risks.
Finally, the Cosmos ecosystem is thriving. The Cosmos ecosystem is growing rapidly, and many projects will have extremely high growth rates in 2023, including Celestia, Injective, Osmosis, Kujira, and Neutron. The general ecological growth has caused the Cosmos ecosystem to regain market attention, and the market sentiment towards Cosmos is generally positive.
The second question is to lay out the Cosmos ecosystem. Why is Axelar one of the best targets?
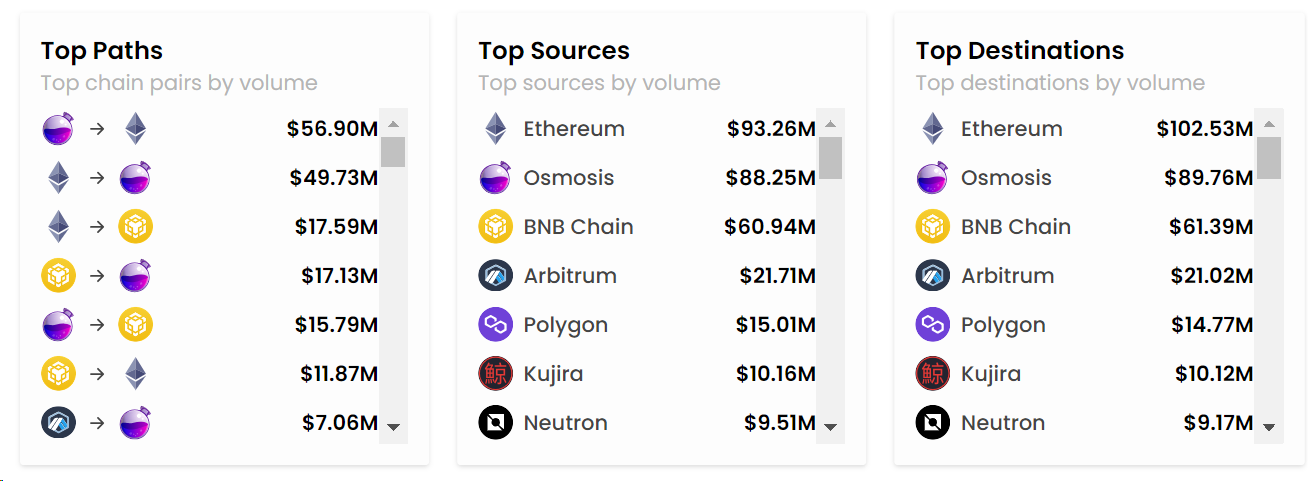
Axelar is the main channel connecting the Cosmos ecosystem and the EVM chain, especially the connection between Osmosis and the EVM chain. In the past 30 days, the total cross-chain volume between Osmosis and Ethereum achieved through Axelar was 106.63M. Axelar is the main cross-chain path from Osmosis to the EVM ecosystem. As more applications are built on the Cosmos ecosystem, the need to connect the Cosmos ecosystem with other ecologies will gradually increase. Axelar is the most important channel connecting the Cosmos ecosystem with other ecologies and will directly capture the value of the expansion of the Cosmos ecosystem.
To sum up the above analysis, at this stage we believe that Axelar is a worthy target. The reasons can be summarized as two points: the fundamentals are mature; the timing is right.
First of all, from a fundamental point of view, Axelar has obvious technical advantages in the full-chain track and profound technical accumulation. From the cross-chain quantity, message and data transmission and full-chain It has significant advantages in chain application development and is currently the cross-chain protocol that best meets market demand. As a general information cross-chain protocol, Axelar has satisfactory performance in terms of security and scalability.
In terms of security, Axelar uses a dynamic, permissionless set of validators for message passing for verification, a quadratic voting mechanism and sufficient validators. Quantity, token locked value and validator decentralization make it one of the most secure solutions among external verification protocols.
In terms of scalability, Axelar currently has the highest number of integrated public chains and is the most important channel connecting the Cosmos ecosystem and the EVM chain. The Hub-Spoke architecture saves the cost of connecting more public chains, and AVM reduces the difficulty for developers to access Axelar Network and build cross-chain Dapps. Recently, Axelar has reached cooperative relationships with a number of blue-chip projects and enterprises, and its ecological development is booming, which has verified its ability and potential in ecological expansion.
Secondly, from the perspective of timing, Axelar’s track and narrative are expected to have greater growth space and potential for attention in the future.
Axelar belongs to the two major narratives of the whole chain and the Cosmos ecology. The full-chain track will gain more room for growth and market attention as the bull market transaction volume increases and the number of public chains increases. A more direct catalyst may come from the issuance of tokens by Layerzero and Wormhole, which will bring market growth to the entire full-chain track. Recently, Layerzero has made it clear that it expects to complete token distribution in the first half of 2024. As a direct competitor of the two, Axelar's current FDV is significantly lower than the first-level valuation of the two, and may complete value discovery with this incident. The Cosmos ecosystem is developing healthily. The general ecological growth at the end of 2023 has attracted the market's attention to the Cosmos ecosystem. Axelar is the liquidity portal of the Cosmos ecosystem and the EVM chain and will directly benefit from the growth of the Cosmos ecosystem.
“Interoperability is the future” — Vitalik Buterin.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAxelar is a cross-chain interoperability project based on cross-chain technology. On top of the concepts of cross-chain and multi-chain, it also proposes an inter-chain concept and is committed to providing a unified development environment for all Web3 applications. .
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAxelar is a cross-chain interoperability project based on cross-chain technology. On top of the concepts of cross-chain and multi-chain, it also proposes an inter-chain concept and is committed to providing a unified development environment for all Web3 applications. .
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceBinance listing propels Axelar's AXL token up 81%, reflecting market excitement for its Web3 interoperability role. Partnership with Ripple further boosts prospects.
 Xu Lin
Xu LinAXELAR, cross-chain bridge, why is Axelar said to be a dark horse in the cross-chain track? Golden Finance, what does the future of cross-chain look like?
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceAxelar and Microsoft have teamed up to develop and offer blockchain interoperability products. As part of the deal, Axelar’s cross-chain stack will be available to Microsoft customers via the Azure cloud marketplace.
 TheBlock
TheBlockThe hacker exploited a vulnerability in the IAVL TREE to forge a malicious withdrawal message.
 Numen Cyber Labs
Numen Cyber LabsAxelar is partnering with leading infrastructure company Mysten Labs to enable decentralized applications built on Mysten’s Sui blockchain.
 Others
OthersThe main layer-one blockchain bridge between ethereum, Binance Chain and bitcoin has been stolen for nine figures, but said its BTC bridge was not affected.
 Cointelegraph
CointelegraphThe layer-1 blockchain’s main bridge between Ethereum, Binance Chain, and Bitcoin has been exploited for nine figures, but says its BTC bridge has not been affected.
 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph