Yesterday, the Financial Secretary of Hong Kong officially released the "Policy Declaration on the Development of Virtual Assets in Hong Kong". For a while, from the mainland to Singapore to Canada and Australia, people in the blockchain circle are very concerned. Admittedly, this is a major benefit, but we should not be superficial, and should seriously study practical issues. This article will summarize the legal norms and policies on the regulation of virtual assets in Hong Kong, and provide them to old friends in the circle for your reference.
I also look forward to everyone choosing the Sa Jie team and Dentons Hong Kong office to provide legal services and think tank consulting services.
1. Will Hong Kong’s policies related to virtual assets affect the mainland
I saw in the circle of friends that some people in the industry say that the clarion call for the financialization of virtual assets in Hong Kong is the prelude, and that the mainland will also liberalize the financialization of virtual assets in the future. Sister Sa does not agree with this point of view. In my opinion, Hong Kong and the Mainland are complementary in the development of virtual assets. At the same time, Hong Kong’s open attitude towards the financialization of virtual assets will ease the concerns of some mainland case-handling agencies about virtual asset advocates and occasional transactions.
On the one hand, the wind is blowing in Hong Kong, which shows that my country's legal attitude towards virtual assets is quietly making a strategic layout. The financial innovation of virtual assets and the entry of virtual assets into Web3.0 and the metaverse are major opportunities in the future. As an international financial center, HK will definitely be in place and become a bridge for the financial innovation of virtual assets between the mainland and overseas. It will also attract more projects, personnel and assets to Hong Kong for innovative attempts. Undoubtedly, this news is a great news. Friends in Singapore are still waiting and watching. We believe that Hong Kong’s virtual asset licenses will be gradually liberalized in the future. The number 1 and 9 licenses will increase, which will stimulate more "evangelist "Returned from abroad and "built a nest" in Hong Kong to develop virtual asset business.
On the other hand, the mainland will still treat the legal nature of virtual assets with caution. First of all, we can be sure that mainstream virtual currencies such as Bitcoin will not be classified as "contraband" in the mainland, and mainstream virtual currencies such as Bitcoin will still be protected in accordance with Article 127 of the Civil Code; secondly, based on distribution Consortium chains and private chains based on traditional bookkeeping technology will continue to deepen and gradually iteratively upgrade in areas such as shipping, supply chain finance, power transmission transactions, and bank bookkeeping; again, ICO behaviors based on public chains will still be given " The key point of compliance is the connection point without domestic jurisdiction (for details, please refer to many previous articles on Sister Sa's account); finally, NFT and Web3.0 have relatively high compliance in the mainland and Hong Kong, so pay special attention Anti-money laundering risks and financialization issues will do.
As for the "digital Hong Kong dollar", we also welcome it very much. Similar to it, digital renminbi has gradually been accepted by consumers in online shopping. fun activity.
"Green Bond Tokens" allow the issuance of Hong Kong government green bonds to be tokenized for subscription by institutional investors. The logic behind this attempt is very deep. We expect more institutional investors to be optimistic about green bond tokens, which will contribute to the development of Hong Kong and the economic development of the Mainland.
2. Sorting out the regulatory framework of the blockchain industry in Hong Kong
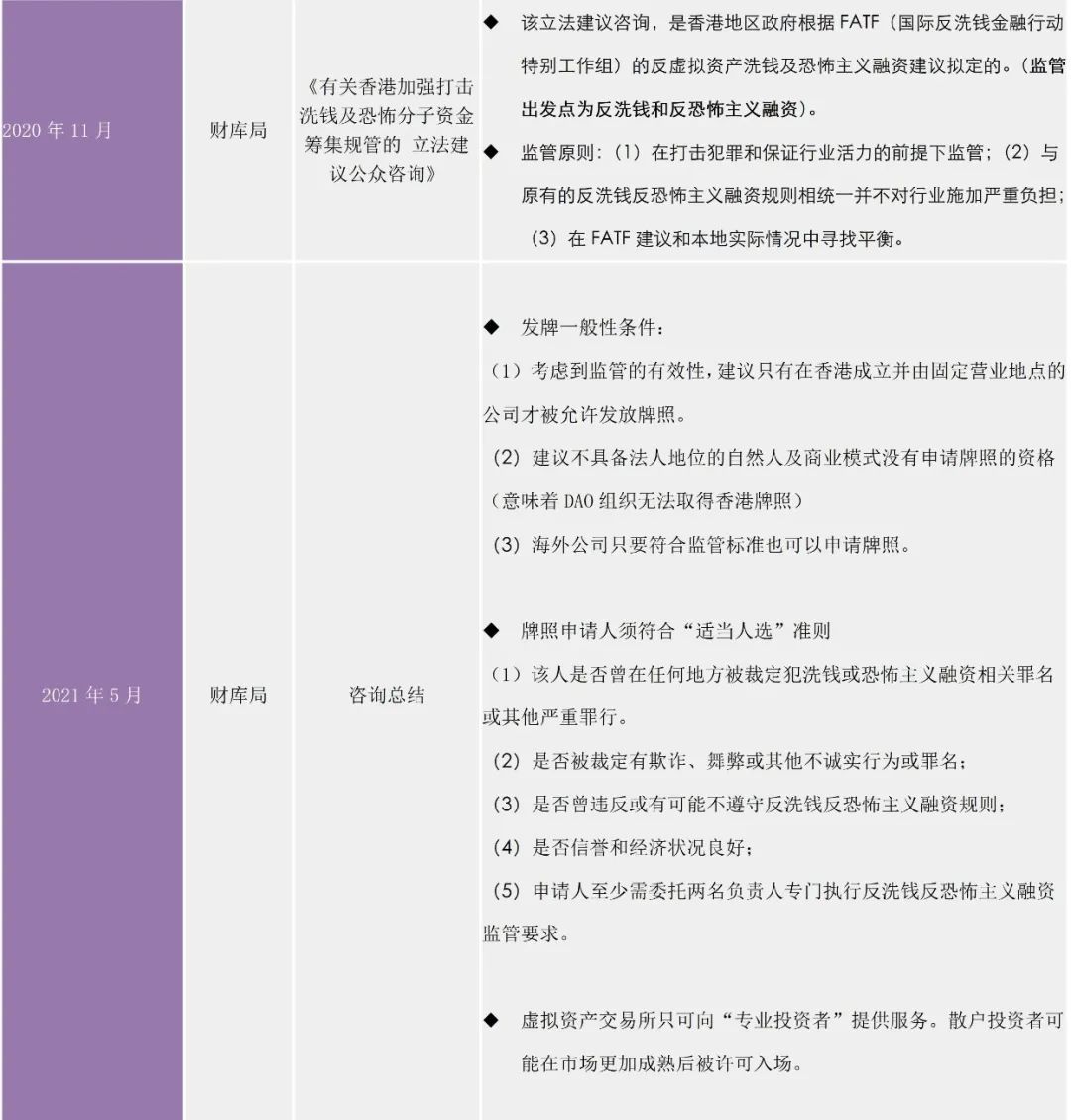
At present, Hong Kong currently has three main regulatory agencies for virtual assets: (1) Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (SCF, hereinafter referred to as "SFC"); (2) Hong Kong Financial Services and Treasury Bureau (hereinafter referred to as "The Treasury") and (3) the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (hereinafter referred to as the "HKMA"). Among them, the China Securities Regulatory Commission is the main regulator, dividing virtual assets into regulated "securities financial assets" and unregulated "non-securities financial assets". Different regulatory perspectives assist supervision (the Treasury Bureau is the second main force of supervision, and its starting point is mainly to combat virtual asset money laundering and terrorist financing activities). Under the planning of the three regulatory agencies, Hong Kong’s virtual asset licensing regulatory system has gradually become clear. Of course, referring to the classification of virtual digital artworks such as NFT by referring to the US "Responsible Financial Innovation Act", it does not rule out that Hong Kong's market supervision and management agencies will join the regulatory army in the future to target "non-financial securitization" virtual assets (pure digital art) products) to issue specific regulatory norms.
The supervision of virtual assets in Hong Kong can be roughly divided into two periods:
The first stage: 2017-2018, centered on regulating ICO behavior. The regulatory idea in this period is to regulate virtual asset activities with financial attributes by analogy with traditional securities and financial products, and the CSRC will mainly regulate ICO behavior.
The second stage: from the end of 2018 to the present. During this period, based on the "2018 Statement" issued by the Securities and Futures Commission in November 2018, Hong Kong's regulatory thinking on virtual assets began to change. The framework system of "box-style licensing supervision" is still refining the licensing rules through various normative documents. Below we will explain in detail the Hong Kong virtual asset regulatory system and implementation rules in the form of charts.
The first stage
During this period, in March 2018, there was a typical landmark ICO incident. A certain group conducted public ICO issuance activities in Hong Kong, which was identified by the China Securities Regulatory Commission as "unapproved sales promotion activities and unlicensed acceptance". Regulatory activities”, the ICO was eventually stopped by the Securities Regulatory Commission and ordered the group to return its tokens to Hong Kong investors, while canceling subsequent related ICO transactions.
second stage
In Hong Kong's current licensing regulatory practice, it is currently relatively cautious. Currently, there are only two virtual asset trading platforms that have successfully obtained trading licenses. One is issued to OSL (Digital Securities Limited, a member company of a technology group) in 2020. OSL DS); one is Hashkey Group, which just obtained a license in the first half of this year. It can be found through public channel information that OSL holds No. 1 license (securities trading) and No. 7 license (automated sales).
It should be noted that according to the "Consultation Summary" of the Treasury Bureau, although the two platforms have obtained licenses, the investors who are allowed to trade can only be Hong Kong professional investors. Hong Kong's requirements for professional investors are: (1) individual investors, including their financial assets (cash, stocks and other highly liquid assets) reaching 8 million Hong Kong dollars or 1 million US dollars; (2) institutional investors, reaching 40 million HKD or USD 5 million. In addition, transactions need to fulfill KYC obligations and investor risk assessment to ensure that customers have sufficient net assets to bear risks and transaction losses.
Sister Sa’s team believes that depending on the specific business types of the platform, if the virtual asset trading platform wants to operate in compliance, it may need to consider obtaining the No. 4 license (providing opinions on securities) and the No. 9 license mentioned in the Hong Kong Securities Regulatory Commission’s 2018 statement. The license (management of virtual assets such as securities or futures contracts) is for reference only. In addition, it is the general trend of Hong Kong to bring all virtual asset trading platforms under the regulatory framework and licensing system in the future. According to the regulatory documents of the Finance and Treasury Bureau and the relevant laws and regulations of Hong Kong securities, anyone who engages in regulated virtual asset activities without a license may be involved in a criminal offense and may be subject to a maximum penalty of 7 years in prison and a fine of 5 million yuan.
3. Complementarity between Hong Kong and Mainland China’s blockchain industry segments
Regarding the supervision of virtual currency, the mainland issued the "Announcement of the People's Bank of China, the Central Cyberspace Administration of China, and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology on Preventing the Risks of Token Issuance and Financing" in 2017, which was later called the announcement of the three associations. This announcement clearly defines token issuance and financing as an act of illegal public financing without approval. In connection with this, any organization and individual is explicitly prohibited from illegally engaging in token issuance financing activities, which basically cuts off the way of token financing in the mainland.
In this regard, Hong Kong's attitude is to allow ICO (Hong Kong subdivides the issuance of securities tokens into STO), but it needs to be strictly licensed and supervised, because the financial attributes of this type of virtual assets constitute a "regulated Financial product". In 2017, the Hong Kong Securities Regulatory Commission issued the "Statement on Initial Coin Offerings". According to the statement, the following three situations will be identified as securitization ICOs and will be subject to special supervision: if the tokens sold represent the equity of a company or own Rights and interests, the purpose of tokens is to enter into or confirm debts or debts borrowed by the issuer, and the proceeds from the sale of tokens are collectively managed by the ICO plan operator and invested in different projects, so that tokens can be held People can participate in sharing the rewards provided by the project.
As far as NFT is concerned, the current supervision of NFT in the mainland is still a relatively extensive overall supervision, which is more to remind investors and consumers of traditional legal risks such as fraud and gambling that may exist in NFT. In April 2022, the mainland issued the "China Internet Finance Association, China Banking Association, and China Securities Association's Initiative on Preventing NFT-related Financial Risks". From this initiative, it can be found that the mainland separates NFT from financial activities. , It is clearly proposed to curb the tendency of NFT financial securitization and prevent NFT financialization. The policy tone for NFT is to affirm its significance in promoting digital cultural creation and industrial digitalization in the real economy, and resolutely stay away from the financialization of NFT.
In this regard, Hong Kong's supervision has carried out a more detailed division. Hong Kong recognizes the existence of financial NFT, and actively divides NFT into two parts: collectible NFT and financial asset NFT. For collectible NFT, its activities are completely outside the scope of the supervision of the China Securities Regulatory Commission, but for financial NFT, its promotion and distribution must be regulated by the China Securities Regulatory Commission, and it can only be carried out after the license is issued. So readers may be wondering, where is the boundary between the two? The Hong Kong Securities Regulatory Commission pointed out that if an NFT constitutes a similar structure of securities or equity under collective investment, it is defined as a financial NFT that needs to be issued with a license.
According to Hong Kong's "Securities and Futures Ordinance", securities are defined as "any group (whether a corporation or not) or government or municipal government authority or issued by him, shares, debentures, bond shares, funds, Bonds or bills", this concept sounds a bit too general, and collective investment interests are also included in securities. Under this definition, a collective investment scheme is defined as comprising four elements: "must involve arrangements in respect of property; the participants have no day-to-day control over the management of the property involved; the property as a whole is managed by or on behalf of the person operating the arrangement the person manages, or the contributions of the participants and the profits or proceeds from which they are paid are pooled; and the purpose or effect of the arrangement is to enable the participants to share in or receive profits arising from the acquisition or management of said property , income or other returns.” Those that meet the above conditions will be defined as financial NFT for license supervision.
Generally speaking, if you only want to make NFT art collections, both the mainland and Hong Kong are fine, but the mainland has a larger potential market and a richer IP background. However, if you want to go through the financialization of NFT, there will be relatively large legal risks in the mainland, and you can consider Hong Kong to get a license to work.
At the underlying technology level of the blockchain, we all know that China and the United States have chosen two completely different directions on this track. China has chosen the metaverse to take the direction of hardware entity empowerment, and the United States has chosen web3.0 to take the direction of software creation. , the direction also determines the policy, and the mainland is relatively friendly to the development policy of the underlying technology of the entire blockchain. In 2020, the Ministry of Education issued a notice of the "Blockchain Technology Innovation Action Plan for Colleges and Universities", and by 2025, a number of blockchain technology innovation bases will be established in colleges and universities, and a group of blockchain technology research teams will be cultivated and brought together.
After this document, notices on the application of blockchain in various specific directions were issued, including the "Guiding Opinions of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the Central Cyberspace Affairs Office on Accelerating the Application of Blockchain Technology and Industrial Development", "The Ministry of Transport's Even in May 2022, the Supreme People's Court issued the "Opinions on Strengthening the Judicial Application of Blockchain", affirming the application prospects of blockchain evidence storage technology in the judicial field. In this regard, Hong Kong does not have too many encouraging norms.
Generally speaking, the mainland encourages the development of virtual technologies that are more closely connected with entities, including NFT that empowers the real economy, and the underlying technology of blockchain that promotes the development of entities; Hong Kong, on the other hand, has more favorable conditions for the financialization of virtual assets. loose.
write at the end
The policies of Hong Kong and the mainland are different, which leads to different directions of future development and completely different positioning of the division of labor. The mainland region will continue to provide Hong Kong with financial tools, digital art IP, and technical tools in the future, and will support Hong Kong in building itself into a world-leading virtual asset economic core area for a long time. Hong Kong, on the other hand, undertakes the great task of developing China's virtual economy, concentrating resources to build a regulated, fast-growing, healthy competition, open and inclusive virtual economic center. Sister Sa's team will continue to pay attention to the virtual asset regulatory policies in Hong Kong in the future, and bring you professional regulatory interpretations as soon as possible.
 Anais
Anais