Has the technological myth of the new digital wave fallen from the altar so quickly? Since breaking into the public eye and trading market at a rocket speed in August last year, NFT (Non Fungible Token, non-homogeneous token) has become a new star in the art collection market, a social currency in the trend circle, and a new favorite in the investment community. But in May, NFT became a hot topic again, accompanied by keywords such as "trading volume dive", "IQ tax shattered", and "sell". According to data from Opensea, the world's largest NFT trading platform, the global NFT transaction volume on May 19 was approximately US$37.67 million, a decrease of approximately 92% from the data on May 1.
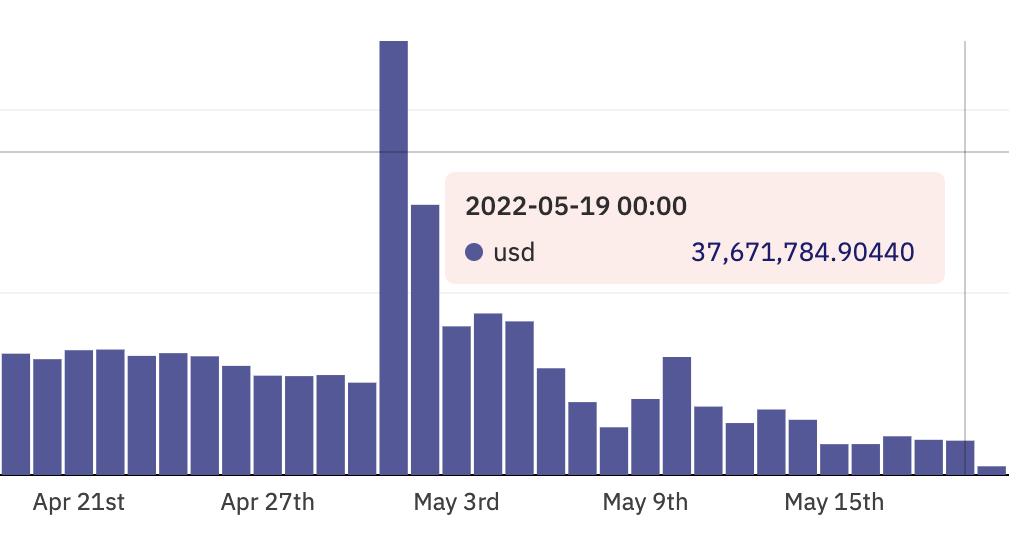
Global NFT transaction volume on May 18 on Opensea. Image source: NFT data platform DuneAnalytics
According to Google data, the global popularity index of NFT has gradually declined since mid-January this year , and the NFT global popularity index in the second week of May has dropped by nearly 70% compared with mid-January.
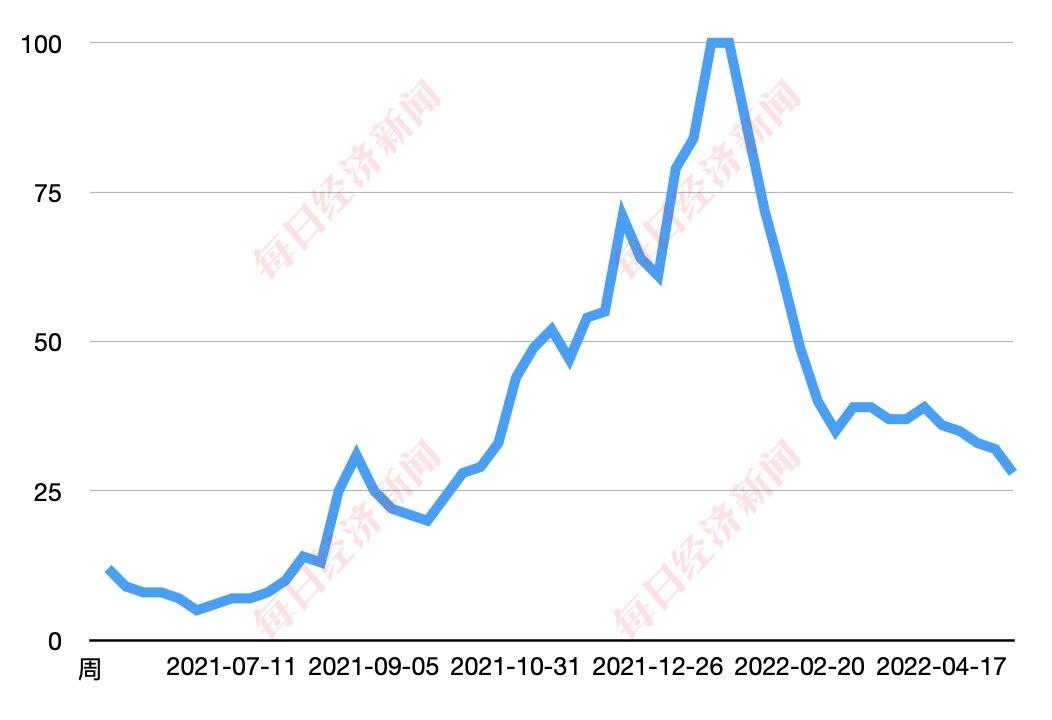
NFT Global Heat Index Data Source: Google Trends
Some people firmly believe in the value of NFT, while others question the illusory coat of its technology; some people think that the bubble has burst, and some people think that it is only a cyclical fluctuation. The current NFT industry is like a complex of contradictions. Even among practitioners, the answers about the value and future of NFTs are not conclusive. For a new industry born in a new era, the speed and frequency of change are unpredictable. And if NFT is indeed valuable, how does it face the uncertain market environment? And how to maintain its own value after experiencing exponential growth? And for the general public, where is its true value? On May 17, when the NFT industry continued to be affected by the turmoil in the currency circle, a reporter from "National Economic News" (hereinafter referred to as "NBD") interviewed Ran Ran, the co-founder of Shanghai Ningfengtian Technology Co., Ltd. Wei (hereinafter referred to as Michael). Before that, he worked in the social field and the payment industry for many years. After that, he served as the chief technology officer of TR Lab, an NFT art platform, and launched the artist Cai Guoqiang's first NFT work. Now he is turning to the metaverse to start a business. Ran Wei, co-founder of Shanghai Ningfengtian Technology Co., Ltd. The interviewee provided that in the two conversations, he talked about the bubble, value and application of NFT, the current dilemma, the future of the industry and other topics, and gave his own thinking.


The decline in the currency circle implicated NFT "but it does not mean that the industry itself is wrong." From the perspective of the external environment, the three major US stock indexes have all fallen recently, and the spread of cryptocurrencies is undoubtedly an important factor causing the recent turbulence of NFT. Among them, the "value unanchoring" of the third largest stablecoin UST in the cryptocurrency market and its sister token Luna announced the intensity of this round of turmoil. According to Coindesk data, since May 10, UST and Luna have seen a significant decline. On May 16, UST, which was supposed to anchor the value of 1 dollar, once fell to a historical low of 6 cents per coin, a drop of 94%. As of 5:45 pm on May 20, Luna fell to a single coin of $0.000152, almost zero. NBD: What do you think of the current turmoil in the NFT trading market? Michael: First of all, the monthly periodic fluctuation of NFT has actually happened several times. The decline in the cryptocurrency market this time has indeed had a great impact on NFT. Usually, when retail investors have excess idle encrypted assets and the secondary market is in a bull market, everyone tends to buy NFTs with relatively stable encrypted assets. But when the entire cryptocurrency market shrinks, everyone will panic sell the NFT in their hands and replace it with a more stable cryptocurrency. So I think that as long as the overall cryptocurrency market picks up, the NFT industry will pick up accordingly. But now the price of Bitcoin is also affected, so the entire NFT market is in panic.
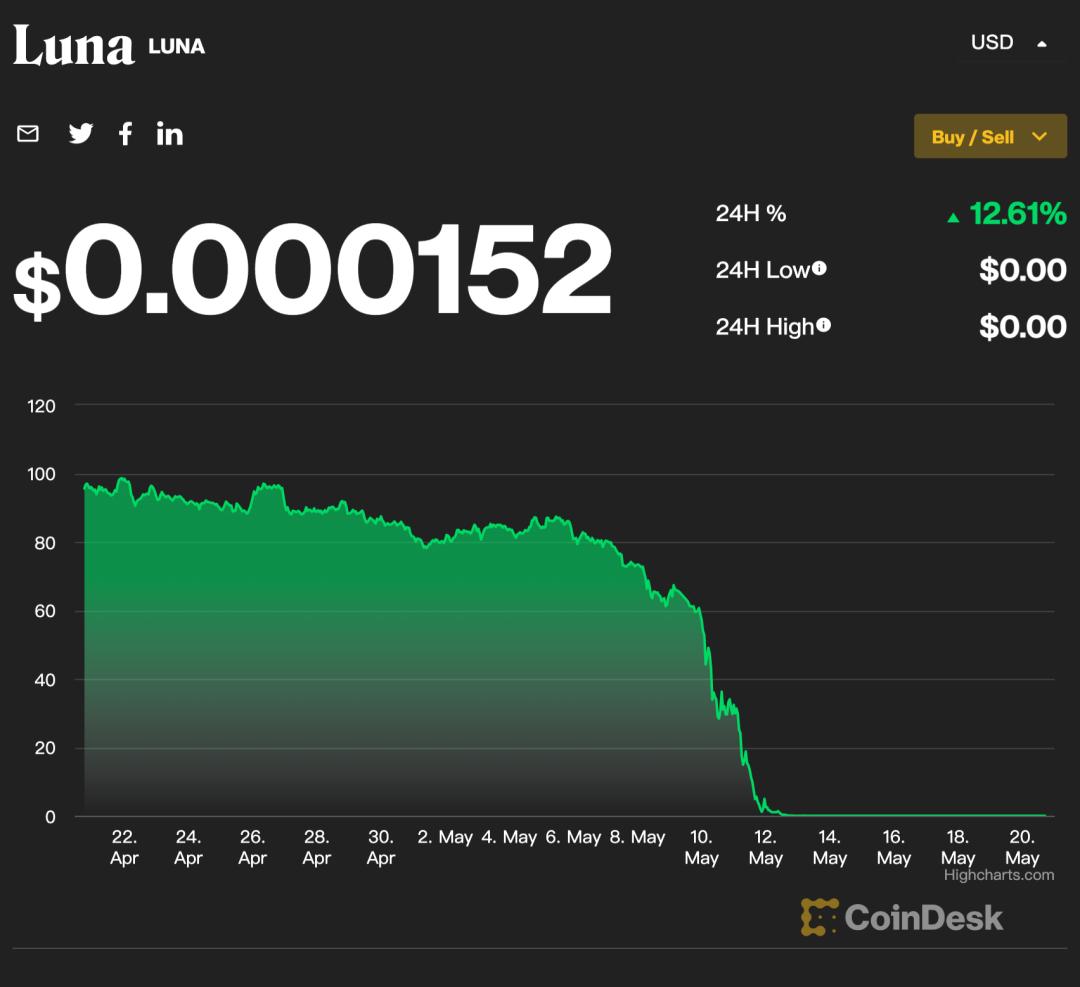
As of 17:45 on May 20, the market value of a single Luna coin. Image source: screenshot of Coindesk official website
NBD: Even stablecoins are currently falling. With the credit of cryptocurrency damaged, will players have concerns about its value and stability in the future? Michael: I think we can use the stock market analogy. Before 2018, many people believed that the stock market was more stable than cryptocurrencies, but in the past two years, at least in the U.S. stock market, the cryptocurrency market dominated by Bitcoin has been more stable than U.S. stocks. Judging from past experience, every time the encryption market experiences fluctuations, whether it is regulatory level, capital regulation or market stability, its performance will be more standardized. For example, after the cyclical fluctuations in 2011, 2015, 2017, and 2021, the bitcoin market has performed better, and now some countries have begun to accept cryptocurrencies as legal payment currencies. This round of shocks actually originated from some newer tracks, such as decentralized finance and the algorithmic stablecoin market. The large-scale growth of these tracks started a year or two ago. But for bitcoin and stablecoins, which have long established consensus for many years, I think it can be restored. It's like the Internet crash 20 years ago, but the Internet itself is not completely dead. Looking back now, the Internet market in 1999 and the cryptocurrency market in 2017 actually had irrational rises, which would lead to retaliatory falls. But this does not mean that the industry itself is wrong, nor does it mean that the new technology itself is wrong.
Most of the current NFTs are financial hype, liquidity illusions, extremely fraudulent pixel avatars with over 20 million US dollars, and works of art with over 90 million US dollars. The ceiling of NFT has been continuously raised in the wave of frenzy. Even at the lower end of the pyramid, the popularity of mass consumer NFT is still unabated. For example, during this year's Winter Olympics, the Bingdundun NFT with a unit price of $99 once skyrocketed hundreds of times in the secondary market. Today, the value of the once-popular IP series NFT has declined to varying degrees. In the face of crisis, the IP aura is not protective.

The NFT "Merge" project created by NFT artist Pak reached a turnover of 91.8 million US dollars. Image source: Screenshot from Nifty Gateway
NBD: What kind of NFT is considered a valuable NFT? Michael: To be honest, I don't quite understand it now. Let's go back 20 years and look at the millennium crash of the US stock market. In that stock market crash, 90% of Internet companies died, and the stocks of Amazon, Google, and Oracle that survived were also cut in half, but in the end, these companies that insisted on value interconnection survived and became today’s industry standard . The experience of these companies can give us an inspiration, that is, if NFT itself is valuable, the companies in it need to do technological innovation, underlying infrastructure, and broaden application scenarios. Rather than like now, a large number of financial players operate NFT in a financial way, so it is really difficult for us to see its value. If you want to simply treat NFT as a financial tool, then I am more optimistic about homogenized assets such as Bitcoin and Ethereum , because the liquidity illusion of non-homogeneous assets will give people a very strong sense of fraud. NBD: Compared with homogeneous tokens such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are non-homogeneous tokens more prone to bubbles? Michael: Yes, there is a term in the NFT industry called "liquidity illusion". If I have a bitcoin, I don't have to worry about whether the market recognizes its value or whether it has enough liquidity in the secondary market. But if I have a blue-chip NFT, and the company has a scandal the next day, then even if the value of the NFT in my hand does not drop immediately, its liquidity will become very poor. It is difficult for me to cash out, this is the invisible loss of assets.
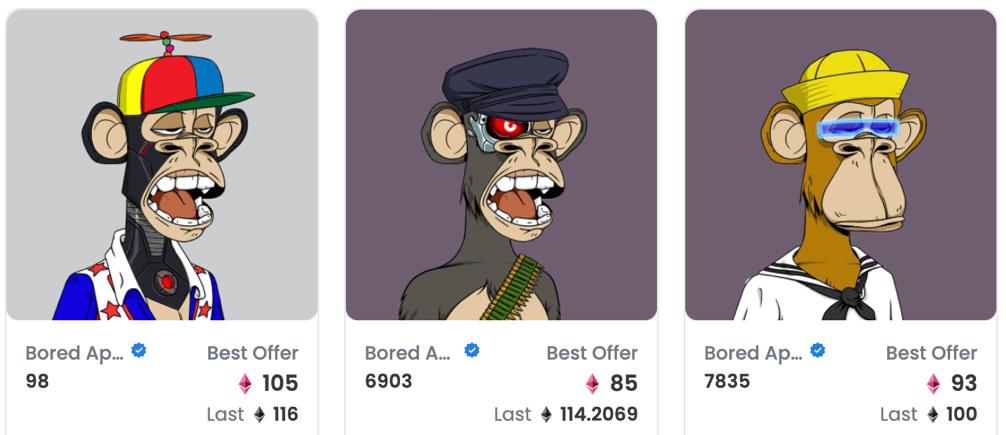
The recent transactions of the "Boring Ape Yacht Club" series of NFTs. Image source: Screenshot of Opensea official website
"Boring Ape" is just an IP being operated, and its value is not supported by a financial system. This is actually the same as buying a sky-high price painting in an art gallery. It is difficult for you to judge whether its true value is reflected on paper. To give an inappropriate example, when a person can choose between a painting worth 100 million and RMB 100 million in cash, most people will choose cash, because RMB is a homogeneous token, and its value is more certain . Let me give another non-"boring ape" example, Azuki, a Japanese-style NFT, was also very popular some time ago. Later, a reverse marketing by its founder caused great negative effects, and its liquidity plummeted. An NFT project with a market value of over 100 million is so easily influenced by a certain person. In this market turmoil, Azuki was also greatly affected. It once fell to six or seven ethers, and now it has risen back to about 13 (note: many NFTs in the Azuki series have been sold at prices of 1,000 ethers). This is a very typical example. What used to be a high-quality project has now become a second-rate project. So I think the value of most NFTs is actually derived from the myth of creating wealth in the industry that started two years ago. Their intrinsic value is primarily financial rather than use value.
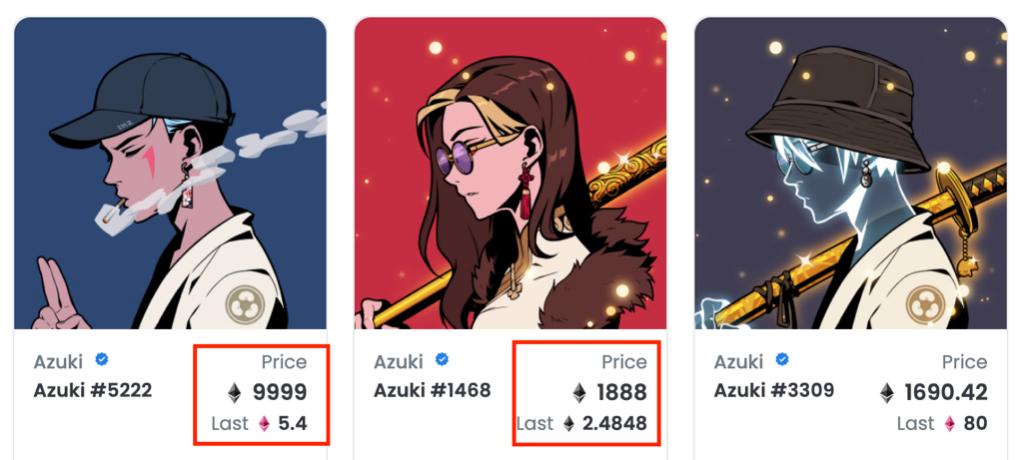
Azuki series NFT price changes. Image source: Screenshot of Opensea official website

Finding practical application scenarios for NFT is like finding e-commerce on the Internet. Looking at the NFT myths in the past period of time, most of them appeared in the field of auction collections. Mass consumer NFTs are mostly co-branded. The lack of use value has always been the point of attack for NFT to be questioned as an "IQ tax". No matter how revolutionary a technology is, it will be like a castle in the air if it cannot land in the consumer market and bring about definite industrial upgrading. The next major industry turmoil will definitely occur again. NBD: How can we better demonstrate the value of NFT? Michael: This market fluctuation actually exposed some problems accumulated in the NFT industry, such as not yet finding a practical application scenario. Like Otherdeed, a new NFT project that was popular before, the floor price has dropped by 70 to 80%. It was developed for a Metaverse game, but the game actually didn’t bring too many surprises to the market after it went live. Since its birth, the explosion of the NFT industry has been mainly based on its strong financial attributes, that is, the attributes of wealth creation, which is one of the reasons why it is difficult to get rid of financial risks in the early stage. As for when NFT will usher in a big explosion in value, that is when NFT technology is really applied in fields such as decentralized identity verification, metaverse games, metaverse asset management, virtual asset management, and physical asset mapping services, as well as those I am now Even in unimaginable scenes. Just like Internet technology is to e-commerce, if you go back to 1999 and tell people at that time that you can use your mobile phone to order food in the future, they will not believe it. In the same way, the NFT application scenarios we think of today may be rudimentary in 20 years. I still firmly believe that this industry will find its value, but this requires a lot of excellent engineers and a large number of people with business acumen to work together. This is difficult, so everyone is also very confused now. NBD: There are various NFTs on the market, such as IP co-branded NFTs. Is this a valuable NFT? Michael: I don’t think so, but I think the emergence of this type of NFT has a positive effect. The first is to allow more ordinary people to start experiencing NFT. The problem is, how do museums and brands that launch these NFTs empower relevant rights and interests to those who hold NFTs, and now they buy them and put them in their mobile phones. When I say empowerment, I don’t mean selling the salted fish. Then it is still a pure financial product. As an entrepreneur, if I give all the content financial attributes, will those artists who don’t understand finance and NFT suffer instead? So did I do a good thing or a bad thing? So at present, I am not sure that adding financial attributes to an NFT and combining culture, art, and trendy brands must be a good direction.
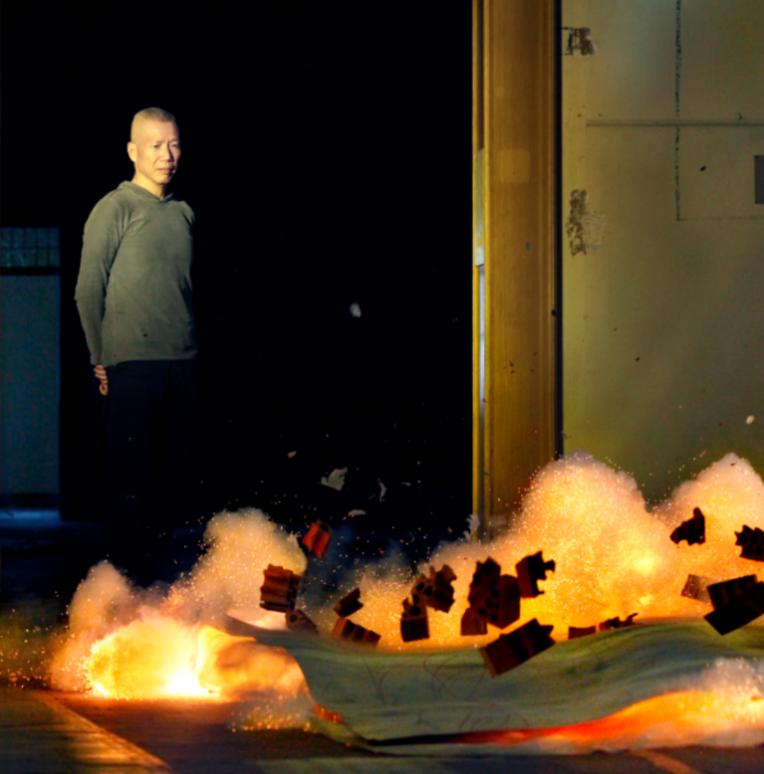

TR Lab launched Cai Guoqiang's first NFT project "Eternal Moments: The Explosion of 101 Gunpowder Paintings" in July last year. Image source: TR Lab official website project introduction
"The industry has to go through 2 to 3 times of skyrocketing or returning to zero." The capital market based on "expectations" and "consensus" is often keen and sensitive. The stock market goes up and down in rotation, and the birth and demise of industries also have a process. Companies that can provide value in use will be left by the market. How to judge the future of the NFT industry? Perhaps it is necessary to clarify a major premise first, that is to determine whether it has value or not. NBD: This market turmoil has a great impact on NFT. How can the NFT industry itself improve its stability in the future? Michael: I dare not make predictions now. But I think it is necessary to continue to attract capital and high-quality talents to enter this industry, and then continue to try and make mistakes. Trial and error means that new projects continue to grow rapidly or fall rapidly, and then the market continues to iterate, low-quality projects disappear, and high-quality projects surface. For now, NFT has not yet developed in a direction that can be seen clearly by people and can truly create real value, so it still needs more funds and talents, and then it is more closely linked to the real world. The reference object is Bitcoin. Bitcoin used to be the same as today's NFT, and could not find any real value. However, after several rounds of reincarnation, when Bitcoin is applied to more and more scenarios, there will be more users, and the entire industry will become larger. In fact, it is more closely linked to the financial system, and its price is less likely to experience large-scale growth or decline. But NFT has nothing yet, and only a small group of people are playing it now. I think the NFT industry may still go through 2 to 3 big rounds, that is, the industry will skyrocket or return to zero, so that we can see what the real value of this industry is. NBD: For an industry with unclear direction and cyclical fluctuations, how to attract capital and talents? Michael: In the early days, we had to rely on financial means to let a certain batch of NFT projects go out of the circle first. In fact, "Boring Ape" has almost done it, and a large number of celebrities have bought it. The next step is financial hype to create wealth, which attracts a large number of practitioners to enter the industry, and then undergoes a wave of reshuffle. 99% of the projects will die, some unsteady practitioners will leave, and the rest will continue to do it, and then recycle. After several waves of reshuffle, this industry will gradually become an industry that can continue to attract high-quality talents and funds. Bitcoin has gone through this process before. NBD: But all this is based on the valuable potential of NFT itself? Michael: Right. Our assumption is that NFT can create value for the metaverse, or it can create actual value for future games and future decentralized financial markets. I personally think that the future of NFT still has unlimited possibilities, and the market is still very early. But the future I'm talking about is not the next 12 months or 24 months, it may be the next 20 years. How long it will take in the future is hard to say, but the future value will definitely exist.
 Anais
Anais













