Author: Howe; Source: Geek web3
Introduction:On March 9, 2024, the experimental asset protocol BRC-20 celebrates its first anniversary. In this short year, people have witnessed the birth of the Ordinals protocol and the release of the BRC-20 protocol. The subsequent Summer of Inscriptions and the continuous explosion of emerging protocols have brought vitality to the BTC ecosystem that was like a desert.
From a technical perspective, the currentasset issuance scheme in the BTC ecosystem can be divided into UTX< /strong>O-bound typeand non-UTXOBinding typeThe main difference is that, Whether the data of the Inscription asset is directly linked to the UTXO on the Bitcoin chain. According to this distinction, BRC-20 is a non-UTXO-bound asset, while ARC-20 under the Atomics protocol is the first UTXO-bound asset.
This article will mainly focus on the emerging concepts and technologies brought by the Atomicals protocol and the development direction of the entire Atomicals ecosystem. Objectively analyze the history, current situation and future development of the Atomics protocol. Through this article, readers will more easily understand why we call the Atomics protocol a “self-contained BTC ecological revolution.”

Image source: https://twitter.com/okxweb3/status/1765967704282816873
Text:The birth of the Atomicals protocol was quite dramatic. When the Ordinals protocol was first released, founder Arthur wanted to develop a DID project on top of it. However, during the development process, he discovered that the Ordinals protocol There are many limitations that are not conducive to supporting some of the features he wants to achieve.
So, on May 29, 2023, Arthur posted the first tweet about the idea of the Atomics protocol on Twitter. After several months of development Later, the Atomics protocol was launched on September 17, 2023.
Later, the Atomics protocol derived Dmint, Bitwork, ARC-20, RNS, etc.Four major conceptsAVM and split solutions will also be launched in the future. In the following, we will explain the principles of these typical product innovations to help you understand the innovation of Atomics more quickly.
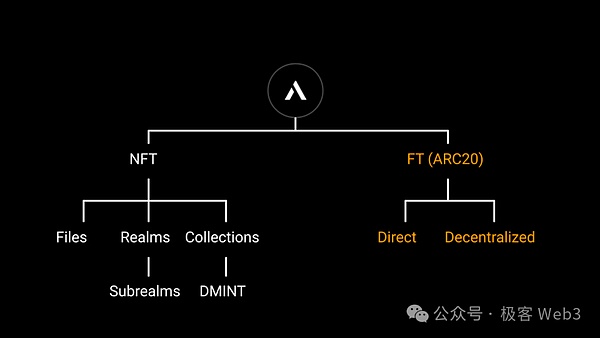
Image source: https://twitter.com/atomicalsxyz/status/1761738325176553535
Bitwork: Non-exclusive PoW
The Atomics protocol adds PoW to the token minting process. This The link is called Bitwork, and the principle is similar to Bitcoin mining.It is set up for current limit and anti-witch.
Let’s first look at the principle of Bitcoin mining: Miners continuously provide different input values to a given algorithm locally, trying to make the output The value complies with the requirements of the Bitcoin protocol. A miner may get lucky and get a result that meets the conditions. At this time, the corresponding output value and input value are written into the block as a "voting certificate" and used as a bargaining chip to obtain mining rewards. Next, as long as the new block is recognized by the vast majority of nodes in the network, miners can obtain BTC rewards.
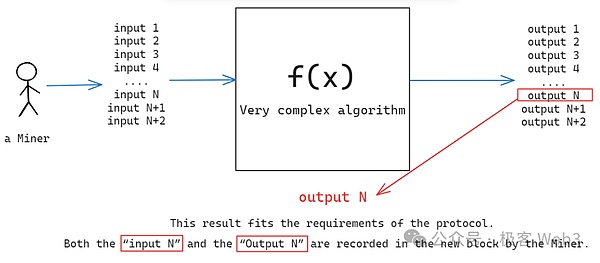
(Simple schematic diagram of Bitcoin mining)
In the Atomics protocol In the solution, you need to perform a similar process and obtain input and output parameters that meet the restrictions before you are eligible to mint tokens. Also similar to Bitcoin, Atomics can also dynamically adjust the mining difficulty. For example, the protocol can be stipulated in advance:
Miners who want to get rewards need to find a set of parameters. After the parameters are input to a given algorithm, the output value meets the following conditions: the first 4 digits are all 6, and the 5th digit is greater than 10 (hexadecimal). At this time, The restrictions are relatively loose. However, the Atomics protocol can periodically change the restrictions, such as requiring that the first five digits of the output value are all 6, which tightens the restrictions and increases the difficulty of mining for miners.
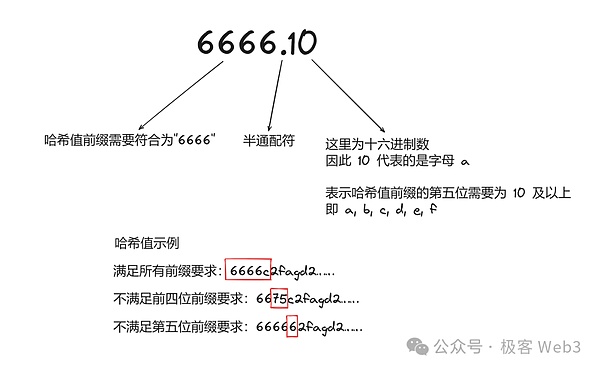
(Bitwork condition example picture)
Bitworkand Bitcoin mining: Bitcoin mining isexclusive and Bitwork mining is non-exclusive. For example, suppose that after blocks No. 99 and No. 100 appear in the Bitcoin network, different mining pools compete for the accounting rights of the 101st block. In the end, only block No. 101 given by one mining pool will be used. The Bitcoin network recognizes that blocks submitted by other mining pools will be "invalidated". This is the exclusivity of Bitcoin mining.
Obviously, cruel exclusive competition is not conducive to the survival of individual miners, and many small miners will eventually contribute their mining machines to large mining pools, the latter will compete with other mining pools as a "whole" that gathers a large amount of computing power. There is no doubt that this will make the computing power in the Bitcoin network tend to be highly centralized. This is even It is clearly mentioned in the Ethereum white paper.
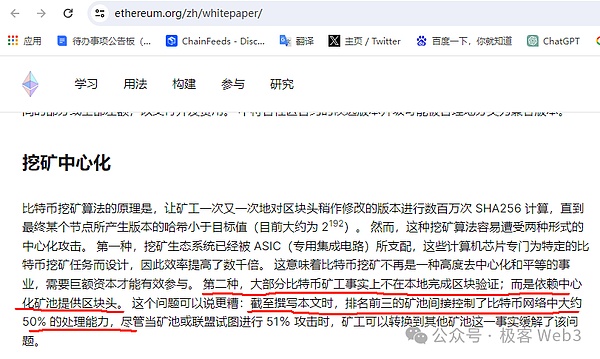
Different from Bitcoin mining, ARC-20 mining under the Bitwork protocol is non-exclusive, that is to say, there is no strict competitive relationship between different miners.As long as the current Atomics AssetsMinting amountdoes notexceedstipulationsGood The total amount,minersgiventhrough the Bitwork mechanismofmining >The result (the token minting statement),will eventually beincluded in the history of the protocol.
Let us imagine the following scenario: Suppose there is an ARC-20 asset that follows the Bitwork protocol and starts to be issued, allowing users to mint in the form of mining, and someone gives The gas is relatively low, but there are many people participating in asset casting, and the gas fee immediately skyrockets. Minting requests with low gas previously given will always be stuck and cannot be uploaded to the chain. But as long as this ARC-20 asset has not been minted, after the gas fee drops, the mint request will still be recognized and the minting action will be triggered.
To explain it in one sentence: Bitwork only looks at the remaining minting amount of the asset, Regardless ofthe order of casting requests,under the Bitcoin mining protocol, miners who submit blocks late will most likely be rejected by other miners. Miners were eliminated.
There is no doubt that Atomics lowersminers/asset minters< strong>The participation threshold,The traditional PoW public chain is subject to huge mining difficulty. The right to produce blocks is basically monopolized by several major mining pools. Individual miners have only a very low probability of successfully mining. Mining, and Bitwork’s improvement measures have greatly weakened the status of centralized mining pools, which is more conducive to the participation of individual miners and asset distribution is more fair.
Considering that PoW itself is a fairer asset distribution solution than PoS and ID0, the Atomics protocol further increases the fairness of asset distribution. , there is both the value injection of material resources and the presence of random elements of luck (mining is a process of getting lucky). This further fueled the development of the Fair Launch concept.
ARC-20: More like a colored coin than an inscription
In fact, many people have misunderstandings about the ARC-20 concept included in the Atomics protocol, thinking that it is also an inscription protocol. But in fact, ARC-20 is closer to a colored coin. It uses sat, the smallest division unit of Bitcoin, as the basic "atom". The number of Sats corresponding to each Bitcoin UTXO is Represents the amount of ARC-20 assets bound to it, 1 sat=1 Token.
Here we take an ARC-20 called "TEST" as a case to explain its operating principle.
First of all, TEST’s token issuer must determine which block of Bitcoin will be used as the “genesis block” of TEST and initialize The information is recorded in a Bitcoin UTXO transaction script in the genesis block. This initialization information includes token symbols, total supply, etc. This process is actually equivalent to dyeing, converting existing bits The Sats in the currency UTXO are dyed in a form that is bound to ARC-20. The number of sats balance this Bitcoin UTXO has is equivalent to the number of ARC-20 assets.
The above-mentioned TEST token issuer can use the function of Taproot lock script to set some restrictions. Only those who meet the restrictions can control it from the above lock script. Of the Bitcoin Sats, some Sats are transferred. We mentioned earlier that these Sats are dyed. If you take part of the Sats locked by the issuer, it is equivalent to acquiring the same amount of TEST tokens.
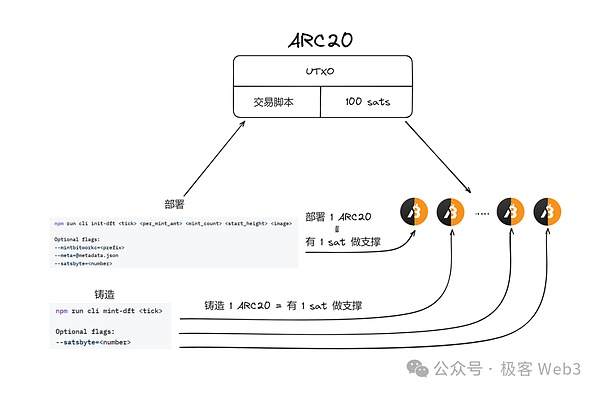
After the aboveasset minters successfully obtain TEST tokens, they can directly transfer these ARC-20 tokens to others. This process is almost the same as normal transfers on the Bitcoin chain. It is to divide the Bitcoin UTXO on your hand, and transfer one or more of them to others. The number of Sats balance corresponding to each of these divided Bitcoin UTXOs corresponds to the number of ARC-20 tokens.
Based on this feature,the transfer of ARC-20 tokens does not need to be inscribed with the inscription information related to the Transfer command like BRC-20, which saves money. Transfer costs also reduce the size of additional data generated on the BTC network.
To summarize, ARC-20 assets mainly include deployment and casting , three types of transferoperations:
When deploying ARC-20, the asset issuer needs to set the token name, total amount, difficulty setting, genesis block and other information, and configure the corresponding Taproot lock script.
When users mint ARC-20, they will submit the Claim information (data that needs to be submitted for minting tokens) ) is written into the locking script of the aforementioned UTXO, and then the corresponding ARC-20 asset (dyed sats) is taken out.
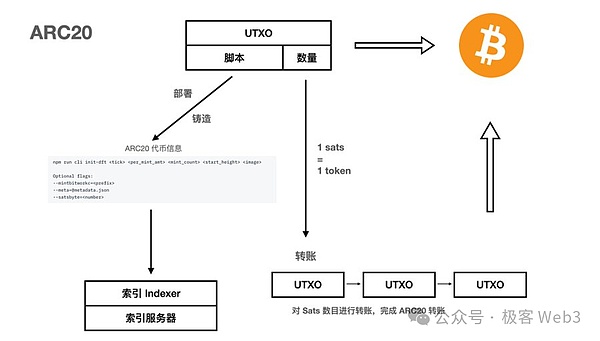
When transferring ARC-20 later, users do not need to deposit any data to BTC, only When the aforementioned UXTO is transferred to another person, the recipient can confirm that it is associated with the ARC-20 asset by tracing the source of the Bitcoin UTXO.
Similar to the "one-time seal" featured in the RGB protocol,ARC- 20The security of transactions is completely guaranteed by the BTC main network. When anyone tracks historical transaction records and calculates the current ARC-20 asset balance, there is no need for additional off-chain transactions. To read data from the storage module, you only need to check those Bitcoin UTXOs related to ARC-20 dyeing. This is the biggest difference between it and the BRC-20 protocol. The latter often has a strong dependence on off-chain indexers and off-chain storagelayers.
Source: https://twitter.com/blockpunk2077/status/1725513817982136617
For ARC-20, we only need a lightweight indexer (or wallet client) to help us identify which ARC-20 assets are minted and transferred on the Bitcoin chain.
Of course, the one-coin-one-satoshi design has flaws that cannot be ignored, because the Bitcoin main network has restrictions to prevent "dust attacks". The transfer requires at least 546 Sats to be transferred to the recipient at one time. In other words, every time you transfer the dyed Bitcoin Sats, you have to transfer at least 546 Sats, which may not be acceptable to most people. In addition, since each ARC-20 token is bound to a Sats, the minimum split precision of ARC-20 asset balance is 1 and cannot be subdivided to a smaller level.
At the same time, we have noticed that many people are still vague about the difference between the ARC-20 indexer and the BRC-20 indexer. Here is a detailed explanation:
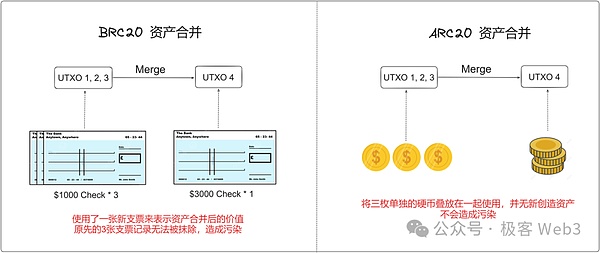
ARC-20 indexer is more concise than BRC-20 indexer light. We can think of BRC-20 as a paper check and ARC-20 as a hard coin. The BRC-20 standard allows users to fill in any number of BRC-20 assets in this check, which is why the BRC-20 protocol uses 3 different index transactions to ensure the accuracy and security of BRC-20 assets; No matter how ARC-20 is traded, it is like directly transferring ready-made coins. When we calculate the balance of ARC-20 assets, it will be much easier than calculating the balance of BRC-20 assets. The ARC-20 indexer The workload will be much less than that of the BRC-20 indexer.
ARC-20 transaction index is more convenient than BRC-20 transaction index in asset merging. We can simply understand it as: BRC-20's asset merger is to replace three checks with a value of $1,000 by writing a new check with a value of $3,000. However, the original three checks should theoretically be destroyed, but because they have been It is recorded on the chain and cannot be erased directly, thus causing data pollution; many times when withdrawing coins from the exchange, you will encounter some inexplicable inscriptions.
The asset merger of ARC-20 is to package 3 coins into one transaction and send them out. In many cases, from the exchange You will always encounter some inexplicable inscriptions when withdrawing coins, but the ARC-20 transaction index will not pollute the sats data because its workflow is different.
Dmint: A new way to issue NFT
In the Atomics protocol, NFT collections are They are called "Containers" and are issued using a decentralized method called "Dmint". For NFT issuance that follows the Dmint protocol,the specific process is divided into four steps: NFT data preparation, container configuration, verification of NFT projects, and casting of NFT.
For NFT project parties, the focus can be on the preparations before NFT issuance, which requires collecting all NFT data and configuring Dmint Data etc. At the same time, NFT issuers that follow the Dmint protocol will summarize all NFT data and build it into a Merkle Tree. The Merkle root of this tree will be published on the chain, and the complete NFT metadata will be stored off-chain.
When the NFT minter selects the NFT to be minted, it will learn its off-chain metadata, and then the minter will provide Merkle Proof to the outside world. Prove that the NFT data you have learned is indeed associated with the Merkle Tree originally built by the issuer, which means it exists in the NFT data set declared by the NFT issuer.
In the process of minting NFT, theAtomics protocol provides advanced options for the project’s founding team,such as setting mint payment rules, allowing NFT minters mint some limited edition NFTs, which not only need to be minted through the aforementioned Bitwork method, but also must pay some tokens to the designated address to take effect.

Source: https://docs.atomicals.xyz/collection-containers/dmint-guide
It can be said that after combining with Bitwork, Dmint has introduced a decentralized casting mechanism for NFTs on the Bitcoin chain. At this time, all minters need to "mining" to draw lottery tickets. In the form of continuous participation in the NFT minting process, it is difficult for script scientists to rely on automated code to initiate flood transactions.
With the combination of Bitwork and Dmint protocols, whether it is a homogeneous token or a non-fungible token in the Bitcoin ecosystem Tokens are all ripe for Fair Launch.
Through Dmint, the Atomics protocol strengthens the security and uniqueness of NFT, provides flexible management options, and allows project parties to freely control it on the Bitcoin blockchain Its NFT collection. This not only opens up customized options for creators to meet diverse creative needs, but also provides convenient on-chain operation solutions for the casting, transfer and update of digital assets, greatly enhancing the flexibility of static and dynamic digital assets. .
In addition, the Bitwork mining mechanism introduced by Dmint , is < strong>Everyoneprovides equal one-time casting opportunities, fundamentally eliminating the possibility of script-automated casting and market competition related to gas fees.
RNS: Infinite expansion of domain names
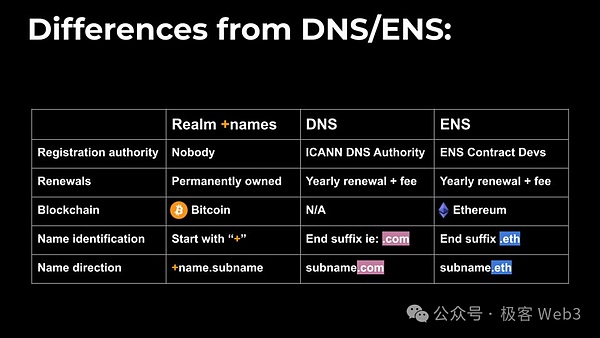
This article has been published before Mentioned that Arthur originally wanted to do a DID project in the Ordinals ecosystem. This project was RNS — Realm Name System, also known as Realm.
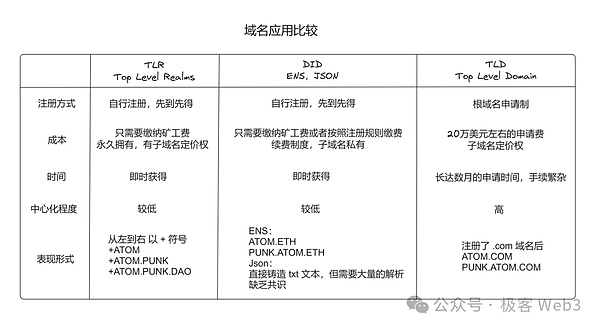
Realm's name starts with a plus sign + and has at least one alphabetic character, such as +alice and +agent007, which are all valid DID identifiers. Compared with traditional domain names and ENS, Realm has higher scalability and flexibility while retaining decentralization.
Today’s domain name services or DID projects have great limitations. Most of the domain names provided are used to refer to a single object (i.e. website/wallet address, etc.) , the user cannot extend it deeper. For example, Alice owns the Alice.com domain name. The role of this domain name is limited to adding different prefixes such as blog.Alice.com to represent links to different websites or personal information. The domain name cannot be continuously extended downwards, such as Alice.com. .blog.text is a domain name form with more scenarios.
Here we will make a more in-depth comparison of two different domain names: Alice.com/blog/text and Alice.com.blog.text. For example, Alice.com/blog/text1 and Alice.com/blog/text2, single finger opens the first/second page of the blog diary in Alice's room;
And Alice.com.blog.text1 and Alice.com.blog.text2 can correspond to two understanding methods:
1. Open two different rooms Two different blog notes in the book
2. Open two different pages of the blog diary in Alice's room.
We can find thatthe traditional "/" mode limits the operating space very narrowly from the beginning, while the sub-domain mode used by Realm domain names, There is no such restriction.
Realm Domain Name Agreement allows any user to issue subdomain names (SubRealm) under any Realm domain name, manage the domain name ecology in a hierarchical/graded manner, and tokenize it. The specific rules are as follows:
Any Realm or SubRealm All can publish SubRealm
All SubRealm can inherit the same characteristics and publish their SubRealm based on SubRealm
Everyone is the registrant of the Realm they own, and there is no centralized domain name management agency
Theoretically, there is no limit to the number of extensions of SubRealm, which makes the imagination space of the Realm domain name system extremely huge. For example, we can treat the top-level Realm domain name as a Tieba community, the first-level SubRealm can be various types of posts, and the subsequent second-level SubRealm is the reply under the corresponding post... In this way, the Realm domain name The system may bring about a revolution in domain name applications, which will empower domain name applications and bring higher scalability.
Source: https://twitter.com/atomicalsxyz/status/1761744365448274371
AVM: A potential dark horse
Since its inception, the Atomics protocol has had ambitions beyond asset issuance. After about half a year of development, more and more assets are compliant with the Atomics protocol, which has led to a new question - how to provide richer usage scenarios for assets to enhance their liquidity and do more in terms of functionality. expand.
As we all know, Bitcoin does not support Turing-complete programming languages, and it is difficult to build complex DAPPs on top of it. Inspired by the ideas of BitVM and concerns about the development of the Atomics protocol, Arthur proposed the idea of AVM. Although the specific details of AVM have not yet been announced, the market has high expectations for it.
According to Arthur's view, AVM is mainly to support the implementation of complex logic in the Bitcoin network, such as solving the problem that ARC-20 "one coin, one satoshi" cannot be split, etc. question. In addition, there are basically various problems with the current Bitcoin expansion plans on the market. We hope that the release of AVM can bring more vitality to the BTC ecosystem.
According to Arthur, under optimistic circumstances, the first beta version of AVM can be released before the Bitcoin halving, and we will conduct it at that time Further detailed explanation.
Atomics Protocol Ecological Summary: Opportunities are about to emerge
No matter Whether it is the Inscription Protocol such as BRC-20 or the Atomics ecology, they have all fallen into a cooling-off period after experiencing several waves of climax. But we found that the asset issuance on BTC is very different from the previous asset issuance on Ethereum. The two ecosystems are more about the difference between decentralization and centralization.
Existing assets onBTC make the concept of "Fair Launch" popular , the Atomics protocol increases market users’ access to the market through Bitwork, Dmint,no pre-mining, no distribution Thetrust of the project assetsreduces the project party’sdirectness towards the assets strong>Manipulation. To a certain extent, this is actually the love-hate relationship between centralization and decentralization.
Centralized projects are more efficient and responsive in the early stage of development. If they are manipulated properly, they can easily succeed; while decentralized projects pursue higher The fairness and decentralization require more spontaneous actions from the community in terms of project promotion and marketing. There may be great resistance to early development, but once the difficult period is overcome, centralized projects will soon be left behind.
The same is true for the Atomicals ecosystem. The picture below shows the Atomicals ecological projects that are currently online and under development. Even though the entire BTC asset market is relatively deserted now, the development of the Atomics protocol is still in its early stages, and many projects still choose to actively connect to the Atomics ecosystem. This stems from the strong confidence of community members in the Atomics ecosystem.
The source of these strong confidence comes from the "Fair Launch" craze caused by the Ordinals protocol and the BRC-20 protocol on the one hand, and from this The vision of decentralized experimentation in the wild.

We believe that with the subsequent release of AVM, the Atomics protocol can achieve programmability on Bitcoin Layer1, develop more AVM-based applications, and write a new chapter for the entire Bitcoin ecosystem.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance

















