Foreword
2023 is an important year for the Bitcoin ecosystem to reach a new peak. In the context of both digital assets and traditional markets facing huge challenges, as the end of the year approaches, the Bitcoin-related ecosystem is sleeping Then came a revival. Although the popularity of Inscription has caused some people to remain opposed, it is undeniable that the market enthusiasm has also brought the return of the "builder culture" to Bitcoin. This development momentum has promoted the innovation wave of Bitcoin, and the most out-of-the-circle It is to draw the market’s enthusiastic narrative about inscriptions to other public chains. This article will discuss the current development direction of the Bitcoin ecosystem. It will only provide an overview of the current Bitcoin ecosystem and does not contain any investment advice.
BTC market hot protocols
The Bitcoin asset issuance protocol has experienced rapid development in the Q1 quarter of 2023, and after one year to the Q4 quarter, the market has shown a booming development. Especially in the Ordinals protocol ecology, multiple tokens represented by BRC20 have caused obvious wealth effects and stimulated FOMO emotions in the market. Even though it is only a JSON script file added to the Bitcoin blockchain, it still gets The market is convinced by rising prices. Over time, more eye-catching protocols have emerged, including Ordinals, Atomics, Taproot Assets, Runes, and PIPE. This trend clearly shows that the Bitcoin ecosystem is developing in a more diversified and innovative direction, and various asset issuance protocols provide the market with a wider range of choices and richer development opportunities.
Ordinals Protocol (BRC-20)

Image source: Hiro
2023 In January, Bitcoin developer Casey Rodarmor released the Ordinals protocol, a Bitcoin-based asset issuance protocol that contains two core components: Ordinals ordinal theory and Inscription. Casey, the author of the Ordinals protocol, carries the content on UTXO through inscription, and the ordinal number assigns a unique identifier to the smallest unit of Bitcoin - 2100 trillion Satoshis. Inscription is the process of associating content with unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs). The asset issuance process of the Ordinals protocol is like writing information into the witness data and recording the token information in JSON format in the form of BRC20.
BRC-20 Token
BRC-20 is a Bitcoin experimental token standard created by Domo on March 8, 2023. The core concept is to leverage JSON data from Ordinal Inscriptions. Through the BRC-20 standard, users can easily implement key functions such as the creation of Token contracts (Deploy), the casting of Tokens (Mint), and the transfer of Tokens (Transfer). Statistics as of December 18, 2023 show that the total market value of the BRC-20 track has reached US$640 million, highlighting the important position of this token standard in the Bitcoin ecosystem and opening up new opportunities for the development of digital assets. New possibilities.
BRC-20 trading volume data source: GeniiData
BRC-100< /p>
BRC-100 is a Bitcoin DeFi protocol built based on Ordinals. In addition to its own token attributes, BRC-100 is also an application protocol. Developers can also design DeFi and other applications based on the BRC-100 protocol. category products. According to developer MikaelBTC, BRC-100 introduces protocol inheritance, application nesting, state machine models and decentralized governance, bringing computing power to the Bitcoin blockchain, making it possible to build AMM DEX, lending and other Bitcoin-native solutions. Centralized applications are possible.
Ordinals NFT
Software engineer Casey Rodarmor launched the Ordinals NFT protocol on the Bitcoin blockchain, which has been officially launched. Users can now create and own their own NFTs on Satoshi (Sat), the smallest unit of Bitcoin, using a random but logical ordering system that makes each Satoshi unique. According to reports, Ordinals NFT has the following three main differences compared with Ethereum NFT:
● Relevant data are stored in the Bitcoin network and do not rely on external storage such as IPFS and AWS S3;
< p>● Permissionless: Transactions can be completed in a decentralized manner through PSBT without the need for "authorization";
● The cost of minting coins is proportional to the transaction volume.
BRC-420
According to the RCSV official Gitbook, BRC-420 focuses on modularizing on-chain inscriptions, including metaverse standards and instant royalty standards These two key parts respectively define an open and flexible format for assets in the Metaverse and set specific on-chain protocols for the creator economy. Unlike other protocols of Ordinals, which are all single inscriptions, the BRC-420 protocol uses a recursive combination of multiple inscriptions.
Atomicals Protocol (ARC-20)

Image source: Atomicals Guidebook
Atomicals , also known as the Atomic Protocol, covers a variety of asset types, including the fungible token ARC20 standard, NFT, Realm and Collection Containers. As a blockchain asset issuance protocol based on UTXO type, Atomics provides two casting methods, namely decentralized casting and direct casting. The decentralized minting method introduces Bitwork Mining, which is a minting method based on the PoW (Proof of Work) model. The protocol uses Satoshi, the smallest unit of Bitcoin, as the smallest unit of issued assets. The current minimum divisible unit of ATOM is 546, and a minimum of 546 ATOM can be sold or transferred.
The difference between the Atomicals protocol and Ordinals in the sorting of asset transactions is that it does not rely on third-party sorters and can be used to create (mint), transfer and upgrade various digital items, including native NFTs, games, Digital identities, domain names and social networks. In addition, the protocol also supports the creation of fungible tokens with the token name ATOM (different from Cosmos’ ATOM, only with the same name).
Recently, founder Arthur shared his views on Meta-Protocols in an interview on December 13. He sees meta-protocols as a completely new approach that allows developers to create their own data structures and rules without being restricted to using pre-existing strict structures. Protocols that represent meta-protocols, such as the Atomics Protocol, are constantly emerging, providing developers with the opportunity to create entirely new structures using smart contracts. This trend allows creators to focus more on Atomicals Virtual Machines (AVMs). The launch of this virtual machine enables developers to build smart contract programs on the Bitcoin network, giving them unprecedented ways to create experiences. This means that creators can focus more on implementing smart contracts in the Bitcoin ecosystem and promoting the process of digital innovation.
Atomics asset type:
● ARC20: It is a token format standard similar to BRC20 on Ordinals;
● Realm: A new concept proposed by Atomicals, which aims to subvert traditional domain names and will be used as a prefix;
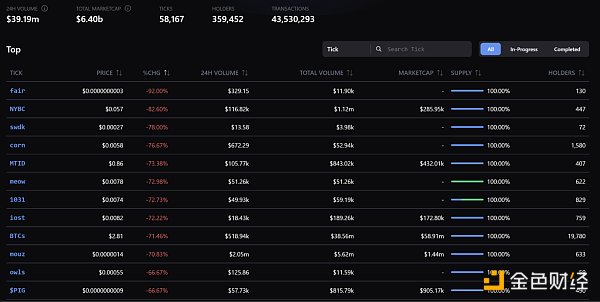
● Collection Containers:This is a data type used to define NFT Collections, mainly used to store readable NFTs and related metadata. According to data on December 20, TOOTHY, which currently ranks first in terms of market value, has a total market value of 46.12 BTC and a seven-day trading volume of 25.74 BTC.
 < span style="font-size: 14px;">Image source: Atomic Market
< span style="font-size: 14px;">Image source: Atomic Market
ARC-20 AVM
December 13 Atomics founder Arthur said in an interview that meta-protocol is a new way for developers to create their own data structures and rules without being restricted by existing strict structures. Meta-protocols such as the Atomics Protocol continue to emerge, enabling developers to create entirely new structures utilizing smart contracts. This allows creators to focus on the Atomicals Virtual Machine (AVM), which enables developers to build smart contract programs on the Bitcoin network.
Runes Protocol (Runes)
Runes was proposed by Ordinals protocol creator Casey Rodarmor to solve BRC-20 There are efficiency issues. Unlike the complexity of some protocols, Runes' design is simple and elegant. By using OP_RETURN in a transaction, Runes causes tokens to be allocated to a specific UTXO, with output index, token amount, and token ID.
The Runes protocol is a Fungible Token protocol based on the Bitcoin UTXO model. It is managed and transferred through simple tuples (ID, OUTPUT, AMOUNT) and OP_RETURN operations. Its main feature is that the protocol is simple, can support some operations without additional off-chain data or native tokens, and optimizes the use of on-chain data.
The Runes protocol was proposed due to Ordinals protocol developer Casey’s dissatisfaction with BRC20’s use of the Ordinals protocol to create a large number of UTXOs, so he proposed a homogeneous token protocol based on the Bitcoin UTXO model. For now, Runes Protocol remains an idea by Casey and does not yet have a complete client and development tools, although it is controversial in some areas.
PIPE protocol

p>
Image source: Trac official
PIPE protocol is developed by developers Benny developed the asset issuance protocol after being inspired by the Runes protocol designed by Casey and the BRC-20 standard based on Ordinals proposed by Domo. The PIPE protocol cleverly combines the characteristics of the Runes protocol and these two protocol standards, and has launched three protocols in the BTC ecosystem: Trac Core, Tap, and Pipe (referred to as TTP, collectively known as Trac Systems).
The main functions of the PIPE protocol include Deploy, Mint and Transfer, referred to as DMT. These features allow PIPE protocol assets to be easily created, distributed and transferred within the Bitcoin network. In addition to supporting fungible tokens, the PIPE protocol also provides a complete data structure and standard for non-fungible tokens.
● Trac Core:The oracle and decentralized indexer for Bitcoin Inscription;
● Tap:It is an expansion of the Ordinals protocol rather than a fork, so it can be seamlessly compatible with BRC20;
● Pipe:It is a new protocol for the Ordinals fork, but the actual process Liquidity needs to be recast;
● Trac Token: Deployed in the Ordinals-BRC20 protocol, it will later be used as the governance token of the Tap protocol;
● TAP Token: Deployed on the Ordinals-Tap protocol.
Stamps (SRC-20)
On December 6, Bitcoin core developer Luke Dashjr revealed on social platforms that Inscriptions is using the Bitcoin core client Bitcoin A vulnerability in Core spams the blockchain. This vulnerability allowed users to set additional data size limits on transactions when forwarding or mining, and Inscription circumvented this limit by disguising its data as program code. Dashjr stated that this vulnerability will be fixed when the v27 version is released next year. However, he later said in response to Ordinals-related questions that the inscription itself did not exist and was a hoax.
This statement poured "cold water" on the Ordinals ecosystem, causing the price of BRC-20 tokens to fluctuate violently, with the price of ORDI falling by more than 25% in a single day. Critics of Dashjr argue that the Bitcoin network belongs to the community and developers have no right to decide the fate of the Ordinals protocol based on personal preferences. Even if Dashjr completes the update of the Bitcoin program, as long as miners do not adopt the updated program, the entire Bitcoin network will not be able to complete the upgrade.
Although the controversy about the inscription has not yet been finalized, the controversy has triggered people's reflection on the nature of Ordinals and blockchain, and also attracted people's attention to another token standard SRC-20 and Bitcoin Stamps protocol. The Ordinals protocol is a derivative protocol that uses Bitcoin UTXO as a data storage medium and stores arbitrary data through Bitcoin's OP_RETURN function. The protocol results in larger Bitcoin blocks, which introduces centralization risks and increases the cost of running the network. The Bitcoin Stamps protocol was created by Mike In Space and is based on the Counterparty (XCP) protocol. It is the first NFT token protocol standard on the Bitcoin chain. Stamps encode image data into Base64 strings and store them in Bitcoin UTXO. Compared with Ordinals, Stamps pays more attention to the reliability of data and cannot be permanently removed from the Bitcoin public ledger.
This controversy has promoted people's thinking about the nature of Ordinals and blockchain, and has drawn attention to the SRC-20 standard and the Bitcoin Stamps protocol. The SRC-20 is similar to the BRC-20, but avoids the controversy brought by Ordinals. Bitcoin Stamps uses the method of directly writing image data into Bitcoin UTXO, emphasizing the reliability of the data and the fact that it cannot be removed.
Turing completeness extension:
Alan Turing
Graphics machine It is an abstract computing model proposed by Alan Turing in 1936 to define the concept of computability. Turing completeness is a concept related to computing theory. It refers to whether a computing system can simulate the calculation process of any Turing machine. The key point is that if a computing system is Turing complete, then it has the ability to perform any Turing machine calculation. process capabilities. It is worth noting that the Bitcoin blockchain itself does not possess Turing completeness. In the impossible triangle of blockchain, decentralization and security are achieved by completely abandoning scalability. So this design choice helps prevent malicious code from running on the Bitcoin network, thus ensuring the security and stability of the network.
BitVM
On October 9, ZeroSync project leader Robin Linus published a white paper called "BitVM: Compute Anything On Bitcoin", which triggered everyone's concern about improving Bitcoin. Thinking about programmability, BitVM is the abbreviation of "Bitcoin Virtual Machine". It proposes a Turing-complete Bitcoin contract solution without changing the Bitcoin network consensus, allowing any computable function to be verified on Bitcoin, allowing developers to run on Bitcoin Complex contracts without changing the fundamental rules of Bitcoin.
BitVM is a new Optimistic Rollup + Fraudproof + Taproot Leaf + Bitcoin Script computing paradigm. It is the abbreviation of "Bitcoin Virtual Machine". This allows developers to simulate program behavior without imposing any load or changes on the actual Bitcoin network. BitVM uses its unique solution to do this extension. Its main roles are:
●Certifier and verifier:The former will use the information input by a certain system to create Proof, the latter needs to verify the calculation result of this proof, but it cannot know the specific content of the information to ensure the accuracy of the calculation result;
● Off-chain calculation and on-chain proof: Without changing the Bitcoin consensus, BitVM will undoubtedly need to transfer a large amount of calculations and expansion off-chain to improve flexibility.
RGB
RGB is the LNP/BP Standards Association (Lightning Network Protocol/Bitcoin Protocol: Bitcoin Protocol/Lightning Network Protocol), which is an organization that oversees the development of all layers of Bitcoin. Non-profit organization covering smart contracts such as Bitcoin protocol, Lightning Network protocol and RGB. The RGB protocol is suitable for scalable and private Bitcoin and Lightning Network smart contract systems. Its purpose is to run complex smart contracts on UTXO and introduce it into the Bitcoin ecosystem. The official description is: A scalable and confidential smart contract protocol suite for Bitcoin and the Lightning Network that can be used to issue and transfer assets and rights more broadly.
Layer2 extension solution:

Image source: Bitcoin Layer 2: Your Complete Guide
Stacks
Stacks is a Bitcoin Layer 2 that can use smart contracts. It aims to link itself to the Bitcoin chain through its unique "Proof of Transfer" consensus mechanism Proof of Transfer (PoX), thereby Achieve a high degree of decentralization and scalability without adding additional environmental impact. Stacks is an open source Bitcoin second-layer blockchain that brings smart contracts and decentralized applications to Bitcoin. Stacks was originally named Blockstack, and its groundwork began as early as 2013. Stacks’ technical architecture includes a core layer and a subnet. Developers and users can choose between the two. The difference is that the mainnet is highly decentralized but has low throughput, while the subnet is less decentralized but has higher throughput. high. The Nakamoto upgrade carried out by Stacks will comprehensively improve network performance and introduce an important product - SBTC.
● Stacks has updated a version called Nakamoto, which allows Stacks not only to settle Bitcoin transactions, but also to upgrade to 100% Bitcoin reorganization resistance, and to increase the speed of the stack so that the block time can be predetermined. Estimated to be 5 seconds;
● SBTC has introduced a decentralized and native anchoring method to increase the total locked value (TVL) and the number of users of the Stacks network, by issuing stablecoins based on SBTC .
Lightning Network
Lightning Network is a second-layer scaling solution for the Bitcoin network, designed to solve the scalability and transaction speed issues of the Bitcoin network. It is a smart contract-based payment protocol that allows participants to make fast, low-cost micropayments without having to record every transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain.
In the Lightning Network, participants can open a multi-signature payment channel. By conducting transactions directly within the channel, almost instant payments can be achieved and avoid having to perform each transaction on the Bitcoin main chain. transaction needs. Actual settlement with the Bitcoin main chain only occurs when channels are opened and closed. This allows the Lightning Network to greatly increase the processing power of the Bitcoin network, reduce transaction fees, and speed up transaction confirmation.
The Lightning Network uses a delivery method similar to that in the network, passing payments from one node to another through multiple payment channels, thus forming a payment network covering the entire network. This design allows participants to make cross-node and cross-channel payments through links, thereby achieving a high degree of interconnectivity. Its core functions include:
● Issue stable currency: Use the value of Bitcoin to provide users with stable currency in a borderless financial world, for example, you can use it to create a The new stablecoin taUSD, and a single Bitcoin transaction can be used to transfer BTC and taUSD into the Lightning Network channel for DeFi operations;
● Multiple Universe mode:Universes are Repository that holds all the information needed to initialize the Taproot Asset wallet and synchronize the state of a specific Taproot Asset;
● Asset Issuance and Redemption API: Users on Bitcoin Trading various assets is as easy as investing in stocks and bonds in the real world, which maps to the issuance of real-world assets;
● Asynchronous reception function: for development Provides tools for adding Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) to on-chain addresses;
● Extensibility: New feature build-loadtest command to allow developers to test software Conduct a stress test.
MVC
MVC is a revolutionary public chain that integrates multiple innovations. On December 8, Jason, the chief operating officer of the Bitcoin side chain MVC. Kwok announced the MVC roadmap for the first quarter of next year and said it will complete the development of the Bitcoin cross-chain bridge. Based on the UTXO and PoW models, MVC achieves breakthrough features of high performance, low cost and powerful decentralization. With the help of Layer1 DID and smart contract technology, it provides the Bitcoin virtual machine MVC, and its goal is to become the top blockchain that leads 8 billion users into the Web3 era.
MVC has updated 9 major sections in the roadmap for the first quarter of next year: building a trustless asset bridge; releasing two Bitcoin-compatible wallets; launching a new block browser; built-in support for Ordinals and BRC- 20; Metacontract integrated development environment; MetaID Bitcoin version; MVC/BTC compatible with DEX Orders.Exchange; opening the first phase of Proof of Building; and launching MVC node V0.2.
BEVM
BEVM is a completely decentralized BTC Layer2 project that uses Musig2 aggregation multi-signature technology and Bitcoin light nodes to achieve BTC decentralization and cross-chain to BTC Layer2. By being compatible with EVM to expand the smart contract scenario of Bitcoin, BTC can get rid of the limitations of the Bitcoin blockchain that is not Turing complete and does not support smart contracts, and can build decentralized applications with BTC as the native Gas.
BEVM implements decentralized BTC cross-chain with 1000+ Bitcoin light nodes based on Schnorr signature and Mast contract brought by Taproot upgrade. In its network, BTC can circulate freely between L1 and L2 without trust. At the same time, BTC is used as Gas and is compatible with EVM. It is quickly supported by the Bitcoin community and attracts the participation of developers and users to the greatest extent, thereby quickly realizing the implementation of BTC. L2’s business closed loop.
Since BEVM is Layer2 compatible with EVM, various decentralized applications that can be deployed on ETH EVM can also be deployed on BEVM. The only difference is that BTC Layer2 uses BTC as Gas. Every transaction on BTC Layer2 will be packaged into BTC Layer1 in the form of a sequencer at a ratio of 10:1 to achieve the security of BTC Layer2 sharing BTC Layer1. In the long term, BEVM's BTC Layer2 solution will enhance Bitcoin's scalability, reduce fees, and cultivate a more secure and decentralized financial ecosystem, which is of great significance to the long-term development of Bitcoin.
Side chain expansion solution:
Image source: DCX Learn: What is a Sidechain
< h3>RSK
RSK is the first EVM-compatible side chain on the Bitcoin network, a stateful smart contract platform guaranteed by Bitcoin miners. Miners receive rewards through joint mining, allowing them to actively participate in the smart contract revolution. RSK's goal is to enable smart contracts, instant payments, and greater scalability to enhance value and utility for the Bitcoin ecosystem. A distinctive feature of the RSK smart contract is the use of Bitcoin’s mining mechanism to maintain its network and security. This means that the RSK smart contract blockchain is more secure and decentralized than Ethereum, while avoiding some of the scalability and performance issues in the Ethereum network.
RIF is a network based on RSK smart contracts. It provides a series of infrastructure services (DeFi, storage, domain name services, payment solutions) to solve the technical complexity and user experience faced by the second-layer network. There are many problems such as insufficient security, lack of unified standard ecosystem, etc.
Spiderchains
Spacechain is the latest proposal for Bitcoin sidechain design, which merges mining and requires miners to run both the Bitcoin node and the sidechain node they want to mine. The transaction chain starts with a UTXO, and each transaction creates two outputs. The first output is a token UTXO, indicating that this transaction chain is related to a certain Spacechain; while the second output is a small denomination UTXO that anyone can spend, although due to its small denomination, additional inputs and outputs are required. Starting with the second transaction of the chain, anyone can spend the second output from the Spacechain transaction chain and use it to commit their own sidechain block header. Spiderchain, meanwhile, sits on top of the main chain base layer and was created by Botanix Labs in September this year to port the Ethereum Virtual Machine to a platform anchored to the Bitcoin network. It is unique in that it does not directly involve the role of miners in the consensus, nor does it use any form of merged mining. Spiderchain uses multi-signature and escrow margins to create a second layer of proof-of-stake system on top of Bitcoin and can be deployed without any changes to Bitcoin.
Softchains
Ruben Somsen proposed a side chain mechanism called Softchain in January 2021. This concept originated from Somsen's earlier "PoW Fraud Proof" proposal, whose original intention was to improve the security of Simple Payment Verification (SPV). In Softchain, the main chain node needs to download and verify the block header of each Softchain side chain. When a chain split occurs, the main chain nodes must download the relevant blocks and verify these blocks using the UTXO set commitment, which forms the basis of the two-way anchoring mechanism.
Other protocols:
 < /p>
< /p>
Image source: What is a Network Protocol and How Does it Work
Omni (stable currency)
JR Willett proposed the Omni protocol in January 2012. It is a digital currency and communication protocol based on the Bitcoin blockchain. It uses Bitcoin The currency blockchain implements functions such as smart contracts, user assets, and decentralized peer-to-peer exchange. In 2014, USDT was first issued on the Bitcoin blockchain based on the Omni Layer protocol. Since then, it has gained the first-mover advantage and captured most of the cryptocurrency stablecoin market in one round. It is Omni-USDT based on the Bitcoin network. The deposit address is the BTC address, and the deposit and withdrawal are through the BTC network;
< strong>Colored coins (asset issuance)
Chia is a more efficient and environmentally friendly cryptocurrency platform provided by Bram Cohen, the founder of the BitTorrent protocol. Chia introduces a new consensus mechanism called Proof of Space and Time (PoST), which is an alternative to the traditional Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. The script protocol that has been hot in the market recently has the concept of using Bitcoin for asset issuance as early as 2012.
DLCs (Extensible Smart Contracts)
On November 4, according to official news, DLC.Link announced the launch of dlcBTC, a project designed to An innovative solution to securely enable Bitcoin for DeFi operations. It is reported that dIcBTC is scheduled to be released in February 2024, which will allow Bitcoin holders to seamlessly participate in DeFi protocols like Curve and AAVE without the need for a custodian or third party.
Ethscriptions (an inscription protocol for creating and transferring content on Ethereum)
The earliest Ethscriptions protocol was created in 2016, but Tom Lehman was Related products were developed for the protocol on June 17 this year. Ethscriptions is an inscription protocol that uses transaction call data (Call Data) to create and transfer digital content on Ethereum. It bypasses the use of smart contract storage. and execution to implement the application of deterministic protocol rules to Ethereum calling data to calculate the state, and to trust each other to determine the results of the contract without informing the oracle and trusting a third party.
Multibit (cross-chain bridge)
Aims to complete the connection between the Bitcoin network and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) network through the Multibit cross-chain bridge Bridging is currently used between the three networks of ETH, BNB and BTC. Its main purpose is to provide DeFi services for BRC-20 assets.
Conclusion:
2023 can be said to be the pioneering year of the Bitcoin ecology. Although its ecological development is difficult due to its natural lack of Turing completeness, but with the The emergence of Inscription not only shifted the market's attention to the Bitcoin ecosystem, but also attracted many developers to join. Perhaps we are on the eve of an ecological explosion, and just like the last round of public chain disputes in early 2021, a situation of "a hundred flowers blooming" will erupt.
Protocols that can stand out under the current situation are also worthy of our expectation and discussion. The circulation and delivery of digital gold are still to be continued.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance




 < span style="font-size: 14px;">Image source: Atomic Market
< span style="font-size: 14px;">Image source: Atomic Market



 < /p>
< /p>
