USDe is primarily used as a savings and yield-generating tool. Its integration with DeFi protocols such as Aave and Pendle improves funding efficiency and composability, while tying stability to on-chain leverage. Market stress events such as the Bybit hack and the October flash crash tested Ethena's design and risk management, highlighting how funding, exchange, pricing, and liquidity dynamics influence the stability of synthetic dollars like USDe. The Rise of Ethena's Synthetic Dollar, USDe, launched in 2024 and quickly became the third-largest stablecoin by market capitalization. Currently, USDe's market capitalization exceeds $10.5 billion, making it a strong competitor and differentiated alternative to the long-dominant USDT and USDC. USDe's appeal stems from its unique design: a yield-generating "synthetic dollar" backed not by cash or Treasury bonds, but by a delta-neutral hedging strategy in crypto assets and perpetual swaps. However, these characteristics have also made it a focal point in discussions about systemic risk in cryptocurrencies, with comparisons often made to the death spiral of Terra’s UST. While fundamentally different from UST’s algorithmic design, the Bybit hack in early 2025 and the market flash crash on October 11th highlighted the vulnerability of synthetic dollars like USDE during periods of market stress. This rapid rise, coupled with recent market volatility, provides an opportunity to examine how the Ethena synthetic dollar system actually operates. In this CoinMetrics State of the Network report, we’ll break down:
How USDe and its staking-yielding version, sUSDe, work
Ethena’s support and yield generation principles
The use of USDe and sUSDe on exchanges and in decentralized finance (DeFi)
The risks of synthetic stablecoins revealed by recent volatility
Support, stability, and sources of yield
A long contract on a spot crypto asset held as collateral at an over-the-counter custodian (primarily BTC, ETH, or staked ETH).
An equal and opposite short contract in the perpetual futures market on exchanges like Binance, Bybit, and OKX.
This combination allows Ethena's risk exposure to remain market neutral while benefiting from the funding rates of perpetual futures. Simply put, perpetual futures are derivatives that allow for hedging or speculation on crypto assets, similar to traditional futures contracts, but without an expiration date. To keep prices close to the spot price of the underlying asset, exchanges implement funding fees—fees charged for periodic transactions between long and short traders. When the funding rate is positive, short contracts will earn a profit, allowing Ethena to pass this profit on to sUSDe holders.
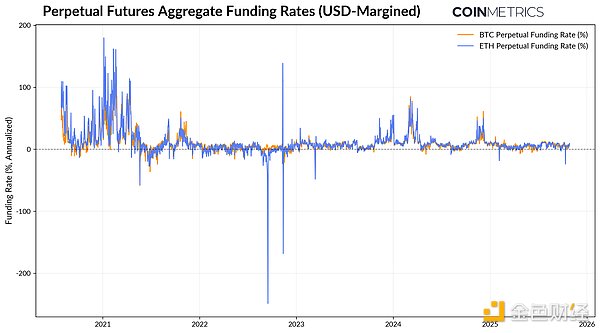
Source: Coin Metrics Market Data Pro
As shown in the above figure, the futures funding rates for BTC and ETH have been positive during the bull market, averaging an annualized rate of approximately 11% in 2024 and approximately 5% in 2025. Sustained high fees indicate that the market is paying for long positions, enabling Ethena to capture this spread through its delta-neutral strategy. However, during periods of market stress, such as the Luna and 3AC incidents, the FTX crash in November 2022, and the flash crash in October 2025, funding rates have turned negative, severely testing the protocol's stability and yield generation capabilities. Where Does Revenue Come From? While perpetual swap funding is the primary source of Ethena's revenue, the protocol supplements this income with two additional revenue streams: Perpetual Futures Funding: Yield generated from the price difference between long spot and short futures. Staking Revenue: Revenue earned from staking ETH on the Ethereum consensus and execution layers. Interest on liquid stablecoins: Coinbase's USDC fixed rate or short-term US Treasury bond investment income through BlackRock's BUIDL fund. The income generated by these sources is distributed to holders of staked USDe (sUSDe). sUSDe automatically accrues income through the ERC-4626 treasury standard, and its value will exceed that of USDe. Therefore, the growth of Ethena's synthetic USD supply and yield is driven by the interaction of these yield sources, enhancing its appeal in a bull market. Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro Ethena Reserve Fund To manage risk in an adverse environment, Ethena has established a reserve fund as an insurance buffer against negative funding rates or unexpected losses. When funding rates are high, the protocol prefers a delta-neutral strategy; when funding rates are low, it turns to holding stablecoins to maintain support and provide benchmark treasury bond interest rates. The assets in the reserve fund are held by this contract and consist of highly liquid stablecoins (currently $41.8 million in USDtb, the Ethena stablecoin backed by BlackRock’s BUIDL tokenized treasury bonds). Ethena’s USDe and sUSDe Usage After understanding Ethena’s underlying operating mechanisms, understanding the scenarios and methods of using its assets (USDe and sUSDe) helps to understand their unique uses and risk profiles. Unlike stablecoins such as USDT or USDC, which are used for transactions and more frequently for payments or settlements, USDe is a savings and income tool rather than a medium of exchange. Source: Coin Metrics ATLAS Looking at the snapshot of major holders' account balances (as of October 2025) in the table above, we see that approximately half ($5.1 billion) of the USDe supply is staked to obtain yield-generating sUSDe. Approximately 13% ($1.3 billion) of USDe is held in LayerZero's OFT bridge to facilitate cross-chain liquidity, while two Binance wallets hold approximately 14% of the USDe supply. Since Binance integrated USDe as a collateral asset for futures trading and Binance Earn in September, over $4 billion worth of USDe quickly flowed into Binance. However, USDe soon de-pegged on Binance, causing its price to plummet to $0.67, resulting in a $2.9 billion outflow. On the other hand, a large portion of sUSDe's supply resides in DeFi protocols. Aave (lending) and Pendle (yield tokenization) together account for over a third of all sUSDe in circulation, as users use the token for collateralized lending and on-chain yield strategies. This creates a "yield amplification" loop, where users stake USDe to mint sUSDe, which is then deposited and tokenized on Pendle and reused as collateral on Aave. This improves capital efficiency and composability, while also establishing deeper connections to on-chain leverage and liquidity dynamics. The 2025 market stress event provides a realistic perspective on how the Ethena synthetic dollar system performs under market volatility. We can observe this through the Bybit hack in February and the flash crash on October 11th, both of which occurred on weekends when traditional markets were suspended. Source: Coin Metrics Reference Rates Despite the outage, funding rates across major exchanges remained positive, allowing Ethena’s short futures positions to continue generating income and providing a buffer for the protocol along with its reserve fund. The incident highlights exchange and custodial risks: while Ethena’s collateral in over-the-counter custody remains safe, protecting it from Bybit’s potential insolvency, the incident also highlights the importance of diversifying trading and custodial platforms and reducing single points of failure. The October 11 flash crash resulted in a more dramatic but shorter-lived decoupling. On Binance, USDe briefly plummeted to approximately $0.65 as liquidity dried up, cascading liquidations, and the auto-deleveraging mechanism (ADL) exacerbated the price decline. Funding rates across exchanges turned sharply negative, but the decoupling remained localized due to sparse order books and pricing discrepancies between centralized exchanges and DeFi platforms. This incident highlights the sensitivity of USDe's peg to platform-specific liquidity conditions and the challenges of maintaining price consistency across interconnected markets. While Ethena remains resilient and continues to operate, these events reveal the dynamics and risks of synthetic dollars like USDe. Negative funding rates can put pressure on protocol revenues and test reserves, while exchange outages highlight the importance of diversified trading venues and liquidity conditions. OTC custody can protect collateral, but pricing and arbitrage still rely on functioning markets. As Ethena's assets become increasingly integrated into the DeFi space, its stability increasingly reflects broader leverage and liquidity cycles, closely tying its growth and resilience to the health of centralized and on-chain markets.
 Catherine
Catherine






