NFTs and Memecoins in the Last Bull Run vs. the Current Bull Run
Explore the market dynamics of memecoins and NFTs in the current bull run vs. previous bull runs.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Author: Huo Huo, Plain Language Blockchain
On August 5, the interest rate hike by the Bank of Japan triggered a violent shock in the global financial market. Japanese and US stocks collapsed, the Bitcoin panic index in the crypto market soared by nearly 70%, and the stock markets of many countries were circuit-breakers several times. Even the European and emerging market stock markets also suffered a significant blow. Under the huge market pressure, people began to seek a good way to alleviate the situation and called on the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates to save the market. The Fed's interest rate hike may come soon, which means that a "bigger" rate hike than the Bank of Japan is coming. Can it pull Bitcoin back to the bull market?
1) What is the Federal Reserve?
Before understanding the concept of the Federal Reserve's interest rate hike and rate cut and its impact, we first need to know what the Federal Reserve is.
The Federal Reserve, or the Federal Reserve Board of the United States, is the central banking system of the United States, consisting of 12 regional Federal Reserve banks. Its goal is to stabilize prices and maximize employment by regulating monetary policy. Inflation rate and employment rate are crucial to economic health, and they are also closely watched by investors and market participants to judge economic prospects and investment risks.
As the central bank of the United States, the Federal Reserve has a huge influence on the financial market. So how does the Federal Reserve exert its influence? It mainly affects the economy by adjusting interest rates through the following monetary policy tools, that is, raising or lowering interest rates:
Raising interest rates means raising the cost of borrowing between banks, thereby raising the interest rates of commercial banks' loans to businesses and individuals:When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, the deposit interest rate of the US dollar rises, and depositors receive higher interest income, which leads to capital inflows into the United States, reduces investment in other countries, worsens the economic environment, and increases unemployment. High interest rates also increase borrowing costs, leading to an increased risk of default for businesses and individuals, which may lead to corporate bankruptcy.
Rate cuts, on the contrary, will reduce deposit rates and borrowing costs:When the Fed cuts interest rates, the US dollar deposit rate falls, capital flows out of banks and flows to other countries, promoting global investment and economic recovery.
So how many times has the Fed cut interest rates before? What impact did they bring?
2) History of rate cuts
Looking back at history, since the 1990s, the Fed has experienced 6 rounds of relatively obvious rate cut cycles. From the perspective of the model, there are 2 preventive rate cuts and 3 relief rate cuts, as well as 1 mixed rate cut that is a combination of preventive rate cuts and relief rate cuts. 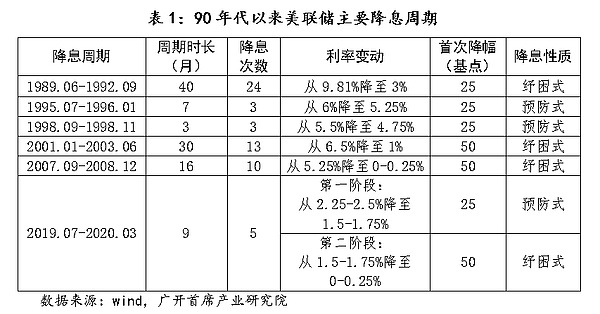
First, let's clarify the differences between these types of interest rate cuts:
Preventive interest rate cuts refer to the monetary authorities taking forward-looking policies to adjust interest rates when the economy shows signs of downturn or faces potential external risks, in order to reduce the risk of recession and promote a "soft landing" of the economy. Features include: a short interest rate cut cycle, a moderate first interest rate cut, a limited number of interest rate cuts, and the federal funds rate will not fall below 2%.
Bailout interest rate cuts refer to continuous and substantial interest rate cuts taken by the monetary authorities when there is a threat of a severe economic recession or a major shock, aimed at helping the real economy and residents avoid a severe recession and promote economic recovery. Features include: a long interest rate cut cycle (may last 2-3 years), a steep interest rate cut (may be continuous and substantial interest rate cuts in the early stage), a strong first interest rate cut (usually more than 50 basis points), and a large total interest rate cut (the final interest rate falls below 2% or close to zero).
In contrast, the hybrid rate cut cycle is more complex. It may appear as a conventional preventive rate cut in the early stage, but due to the rapid change of the situation, it may turn into a relief-style rate cut in the later stage. 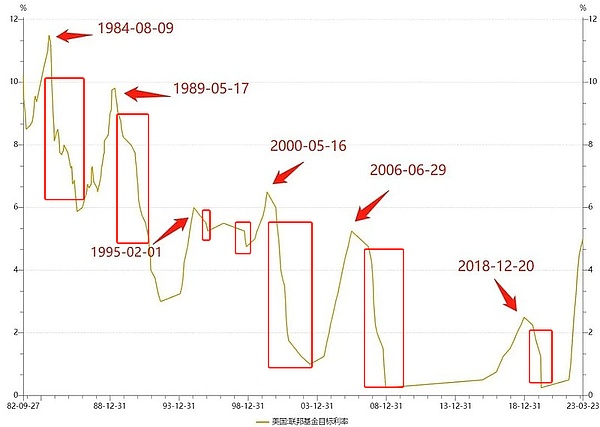
So, what impact have the Fed's several significant rate cut cycles experienced since the 1990s had on the market and the economy?
1990-1992:
Rate cuts:During this cycle, the Fed lowered the federal funds rate from 9.810% to 3.0%.
Market impact:This round of rate cuts helped support the economy's recovery from the 1990 recession. The stock market began to rise during this period, economic growth gradually resumed, and although inflation and unemployment remained under pressure, the overall economic situation gradually improved.
1995-1996:
Rate Cuts: The Federal Reserve began to cut interest rates in 1995, reducing the federal funds rate from 6.0% to 5.25%.
Market Impact: This round of rate cuts was mainly to respond to the slowdown in economic growth and support stock market gains and economic stability. This phase marked a continuation of the economic expansion, with strong stock performance, especially for technology stocks, which then led to the tech boom of the 1990s.
1998 (September-November)
Rate Cuts: The federal funds rate was reduced from 5.50% to 4.75%.
Market Impact: It eased market tensions and supported economic growth. The rate cut had a positive impact on the stock market, especially the strong rebound in technology stocks, and the Nasdaq index rose sharply in 1998, laying the foundation for the subsequent boom in technology stocks.
2001-2003:
Rate Cuts:During this cycle, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates from 6.5% to 1.00%.
Market Impact:This rate cut was made after the 2001 recession. The rate cut helped support the economic recovery and drove the stock market up in 2002 and 2003. However, the excessive relaxation of this round of rate cuts also laid the hidden dangers for the subsequent real estate bubble and financial crisis.
2007-2008:
Rate Cuts: The Fed cut interest rates from 5.25% to near zero (0-0.25%).
Market Impact: This round of rate cuts was in response to the severe impact of the 2008 financial crisis. The low interest rate policy effectively eased the pressure on financial markets, supported the recovery of the economy and financial markets, and promoted a strong rebound in the stock market after 2009.
2019-2020:
Rate Cuts: The Fed cut interest rates from 2.50% to near zero (0-0.25%) in 2019 and 2020.
Market Impact: The rate cuts were initially intended to respond to economic slowdown and global uncertainty. After the outbreak, further rate cuts and large-scale monetary stimulus helped stabilize financial markets and support economic recovery. The stock market experienced a rapid rebound in 2020, and although the epidemic caused a severe economic shock, policy measures alleviated some of the negative impact. This round of rate cuts also indirectly contributed to the occurrence of the Crypto 312 incident.
It can be said that each rate cut cycle has a different impact on the market and the economy, and the policy formulation of rate cuts will also be affected by the economic environment, market conditions and global economic situation at the time.
3) Why is the Fed so influential?
The Fed has a huge impact on global financial markets, so its policies directly affect global liquidity and capital flows. The specific influence is reflected in the following points:
Global reserve currency: The US dollar is the world's main reserve currency, and most international trade and financial transactions are denominated in US dollars. Therefore, changes in the Fed's monetary policy will directly affect global financial markets and the economy.
Interest rate decisions:The Fed’s interest rate policy has a direct impact on the interest rate level of global financial markets. The Fed’s interest rate hikes or cuts will lead other central banks to follow suit and adjust their policies. This interest rate transmission mechanism makes the Fed’s policy decisions have a profound impact on global capital flows and financial market trends.
Market expectations:The Fed’s remarks and actions often trigger fluctuations in global markets. Investors pay close attention to the direction of the Fed’s policies, and the market’s expectations of the Fed’s future policies will directly affect asset prices and market sentiment.
Global economic linkage:As the global economy is highly interconnected, the economic conditions of the United States, as the world’s largest economy, also have an important impact on the economies of other countries. The Fed regulates the U.S. economy through monetary policy, which will also affect the trend of the global economy.
Risk asset price fluctuations:The Fed’s policy measures have an important impact on the prices of risky assets (such as stocks, bonds, and commodities). The market’s interpretation and expectations of the Fed’s policies will directly affect the volatility of the global risk asset market.
In general, due to the importance of the US economy and the global status of the US dollar, the Fed's policy measures have a profound and direct impact on the global financial market, so its decisions have attracted much attention from the global market.
So what will be the intensity, speed and frequency of the upcoming Fed rate cut cycle? How long will the entire rate cut cycle last? How will it affect the global financial market?
1) Expectations for this round of rate cuts
Entering the third quarter of 2024, there are signs in the US domestic market that monetary policy may need to be adjusted. Data such as unemployment rate, employment, and salary growth show that market activity has declined, the decline in technology stocks shows that economic growth has slowed, and the United States still has a huge amount of outstanding debt interest. All signs indicate that the Fed needs to cut interest rates to promote consumption, revitalize the economy, and over-issue currency. Before Black Monday, the market generally predicted that the Fed might start cutting interest rates as early as September this year.
According to market expectations, Goldman Sachs had previously predicted that the Fed would cut interest rates by 25 basis points in September, November and December, and pointed out that if the August employment report was weak, a 50 basis point cut in September was possible. Citigroup also predicted that interest rates might be cut by 50 basis points in September and November. Economists at JPMorgan Chase adjusted their forecasts, believing that the Fed might cut interest rates by 50 basis points in September and November, and mentioned that emergency rate cuts might be made between meetings.
After Black Monday, some radical analysts believed that the Fed might take action before the September meeting, with a probability of 60% for a 25 basis point cut, which is extremely rare and is generally used to deal with serious risks. The last emergency rate cut occurred at the beginning of the epidemic.
However, the uncertainty of the global economic trend, including the US economy, is still very large. Whether this round of rate cuts is a preventive rate cut or a relief rate cut, major institutions have different conclusions, and the impact of the two on the market is also very different, which needs further observation.
2) Possible impact of this round of Fed rate cuts
The Fed's rate cut expectations have begun to affect global financial markets and capital flows. In order to cope with the downward pressure on the economy, the interest rate cut bets of the Bank of England and the European Central Bank are also heating up. Previously, some investors believed that the probability of the Bank of England cutting interest rates in September is now more than 50%. For the European Central Bank, traders expect two rate cuts by October, and it is not far from the expectation of a sharp rate cut in September.
Next, let's take a look at some of the possible impacts of this round of rate cuts:
A. Impact on global markets
This Fed rate cut is expected to have a significant impact on global financial markets.
First, the reduction in US dollar interest rates may prompt funds to flow to markets and assets with higher yields, leading to an increase in global capital flows.
The rate cut may also depreciate the US dollar, which may trigger exchange rate fluctuations and push up the prices of dollar-denominated commodities such as crude oil and gold. In addition, the depreciation of the US dollar may enhance the competitiveness of US exports, but it may also exacerbate international trade tensions.
At the same time, interest rate cuts may reduce the borrowing costs of global stock markets, boost corporate profit expectations, and thus drive stock markets up.
The reduction in international capital costs will encourage more investment, but the impact on countries and companies that are already highly indebted will be limited.
Because although the reduction in international capital costs will encourage investment, highly indebted countries and companies may find it difficult to use these low-cost funds for new investments due to debt pressure and strict borrowing conditions.
Finally, interest rate cuts may bring global inflationary pressures, especially when currencies depreciate and commodity prices rise, which will have an impact on economic stability and central bank policies.
B. Will interest rate cuts directly benefit the crypto market?
Although many people believe that interest rate cuts increase market liquidity, reduce borrowing costs, and may push up cryptocurrency prices, and in an interest rate cut environment, economic uncertainty increases, and investors may turn to safe-haven assets such as Bitcoin, there are also reserved views that we need to be vigilant about the potential risk of economic recession.
However, many institutions generally believe that in the complex and changing market environment, the market may also experience significant fluctuations during the interest rate cut period. During the 2008 financial crisis, even though the Federal Reserve took interest rate cuts in the early stage, the market still fell sharply after a brief high point. Although the Federal Reserve quickly and significantly reduced interest rates, it failed to effectively contain the spread of the crisis. The roots of this crisis can be traced back to the successive bursts of the Internet bubble and the real estate bubble, which had a profound recessionary impact on the economy.
Whether the current interest rate cut policy will repeat the same mistakes and trigger outbreaks such as the artificial intelligence bubble or the US debt crisis, which will in turn drag down the crypto market, remains to be seen.
However, in the short term, the interest rate cuts by global central banks represented by the Federal Reserve are a shot in the arm for the global financial market and the crypto market. There is no doubt that the expectation of interest rate cuts will directly promote the increase of market liquidity, trigger market optimism, and is expected to prompt the cryptocurrency market to usher in a wave of rising prices in the short term, bringing investors opportunities for quick profits.
In the long run, the trend of the cryptocurrency market will be affected by more complex and changeable factors, and price fluctuations are not only driven by a single factor, which requires a comprehensive analysis:
First, the market trend mainly depends on the strength of economic recovery.If interest rate cuts can promote economic growth, the cryptocurrency market may benefit; conversely, if the economic recovery is weak and market confidence weakens, cryptocurrencies will inevitably be affected. During the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, Bitcoin was also affected by the stock market and commodities and crashed on March 12.
Markus Thielen of 10x Research recently pointed out that the US economy is weaker than the Federal Reserve expected. If the stock market follows the decline of the ISM manufacturing index, the price of Bitcoin may continue to fall. In addition, investors may sell Bitcoin when the economy is in recession.
Second, inflation factors need to be considered.The central bank cuts interest rates to stimulate the economy and promote consumption, but it may also lead to inflation risks such as rising prices. Then rising inflation will in turn lead to central banks raising interest rates, which will bring new pressure to the crypto market.
Third, the US election and global regulatory changes also have far-reaching impacts.Who will be the new president of the United States? It is still unknown what policy the new president will adopt towards cryptocurrencies.
In short, the prelude to interest rate cuts by global central banks has undoubtedly brought new opportunities and challenges to the crypto market. The interest rate cuts are likely to provide liquidity support for crypto assets in the short term, which includes factors such as increased liquidity and increased risk aversion.But it also faces the lessons of historical financial crises and challenges from other complex factors. It is difficult to guarantee that it will be beneficial to the development of cryptocurrencies for the time being.
In general, this Black Monday is a result of concerns about the US economic recession, which led to the collapse of the market. In addition, industry giants are not optimistic about US economic expectations and global geopolitical turmoil. In the short term, these will keep the market in a period of policy fluctuations.
Through the cyclical laws of finance in the past, crises and opportunities are born together. Generally, economic downturns, market fluctuations and investment losses may bring about anxiety and panic, but they also provide investors and companies with an opportunity to regroup and find opportunities for innovation. At the same time, crises force companies to improve their business models and increase efficiency, so as to develop more steadily in the future.
Explore the market dynamics of memecoins and NFTs in the current bull run vs. previous bull runs.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceCrypto market liquidity has increased, BTC has performed strongly, and altcoins are competing with ETH due to macro influences.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceIn the current cycle, Bitcoin is up 2.8x and altcoins are up 1.7x.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceArmstrong predicts XRP to lead the 2024 crypto bull run, citing its strong team, marketing, community, and technological advancements.
 Alex
AlexIndustry experts believe Asian countries like Hong Kong will lead the new crypto bull run.
 Beincrypto
BeincryptoCrypto prices took a hike recently but while some are optimistic that the crypto bulls are returning, others feel that it is just a bull trap in a bull market. What is your perspective on this?
 Catherine
CatherineBitcoin may be close to reaching a bottom or has already bottomed out, but it still faces several months of consolidation in Q4.
 Beincrypto
BeincryptoCompared to previous bull runs, the next Bitcoin rally will have to be more focused on utility and less on the story.
 Others
OthersMessari named the seven trends most likely to fuel the next bull run.
 Beincrypto
BeincryptoWith all the recent turbulence in the crypto space, the question of the moment is: What will drive the next crypto bull run?
 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph