Source: xWhale
I. Introduction
Bitcoin and its unique properties
Bitcoin, as the first and most famous cryptocurrency, has attracted widespread attention around the world since it was created by the mysterious figure Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. The core feature of Bitcoin is its decentralized nature, which does not rely on any central authority, but records transactions through a public ledger - the blockchain. This design not only ensures the transparency of the system, but also enhances security, because the modification of any recorded information requires the consent of the majority of the network's computing power. In addition, the global nature of Bitcoin makes it not directly affected by specific countries or policies, making it a unique international currency.
Bitcoin halving
Bitcoin halving refers to the event in which the reward for generating Bitcoin in the Bitcoin network is halved every four years. This is a pre-set rule in the Bitcoin protocol to control the supply of Bitcoin and mimic the scarcity of gold. The number of new Bitcoins obtained by miners is halved every 210,000 blocks. From the initial reward of 50 bitcoins per block, to 3.125 bitcoins in 2024. This periodic supply reduction will theoretically push up prices while demand remains unchanged, thus having an important impact on the market.
2. Analysis of Bitcoin Halving Mechanism
Definition and Historical Review of Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin halving refers to the event in which the Bitcoin reward for newly generated blocks in the Bitcoin network is reduced by half every 210,000 blocks, approximately once every four years. This is a core part of the Bitcoin algorithm, which is designed to control inflation and imitate the gradual slowdown of mining of scarce resources such as gold. Since the operation of the Bitcoin network in 2009, it has started with an initial reward of 50 bitcoins per block, and now it is 3.125 bitcoins in 2024. After each halving, the mining reward is reduced by 50%, which directly affects the income of miners and the entire Bitcoin economy.
The Role of Miners and Response to Halving
In the Bitcoin network, miners play a key role in maintaining blockchain security and processing transactions. Whenever a halving occurs, miners' rewards are reduced, and many less efficient mining farms may be forced to exit the market due to reduced profits. In response to the halving, miners usually seek more efficient mining equipment and lower-cost electricity supply to remain competitive and profitable.
Analysis of the Impact of Halving on Mining Economics
Halving events usually lead to a major reassessment between mining costs and market value. The profitability of mining is directly affected because the reduction in rewards means that the same mining effort will generate less revenue without an increase in Bitcoin prices. This prompts mining companies to evaluate the efficiency of their operations, invest in more advanced technologies, or look for cost-effective energy solutions around the world.
Adjustments in miner strategies, such as equipment upgrades and changes in geographical distribution
In order to adapt to the challenges brought by halving, miners usually adopt a variety of strategies including upgrading hardware, optimizing mining algorithms, and moving to areas with cheaper electricity. For example, many miners have moved from China to Central Asia, Northern Europe, and even North America to take advantage of lower energy costs and a more stable policy environment.
3. The impact of halving on Bitcoin supply
Halving directly affects the speed of new supply of Bitcoin. In the long run, this reduction in supply may drive up prices while keeping demand stable. In this way, the halving event affects the economic model of Bitcoin, making it more like a "digital gold."
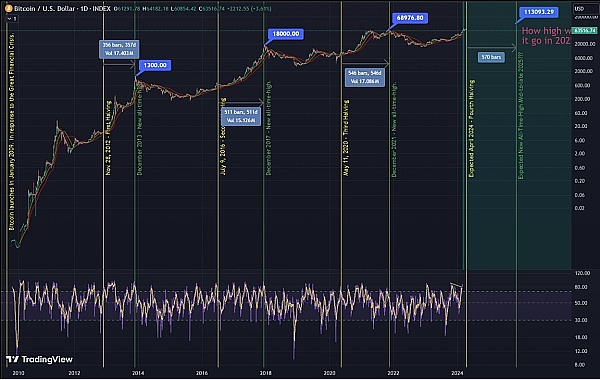
Source: https://www.tradingview.com/chart/BTCUSD/zDs32rdu-BTC-Halving-Cycle-Top-Analysis-2021-2022/
Bitcoin price performance before and after halving:
Halving in 2012: The price of Bitcoin rose from US$12 to US$1,300, an increase of more than 100 times, and it took 357 days.
2016 halving: Bitcoin price rose from $650 to $18,000, an increase of more than 27 times, which took 511 days.
2020 halving: Bitcoin price rose from $9,000 to $69,000, an increase of more than 7 times, which took 546 days.
Short-term volatility: After the past three halvings, Bitcoin price fluctuated within a month after the halving, but then rose sharply in the following year. This phenomenon shows that the market needs time to digest the impact of the halving, but will eventually respond to the reduction in supply brought about by the halving.
Long-term gains: Although there may be volatility in the short term, historical data shows that Bitcoin halvings will bring significant gains in the long term. This is because the halving mechanism will continue to reduce the supply of Bitcoin, and the total supply of Bitcoin is only 21 million, making Bitcoin a scarce asset.
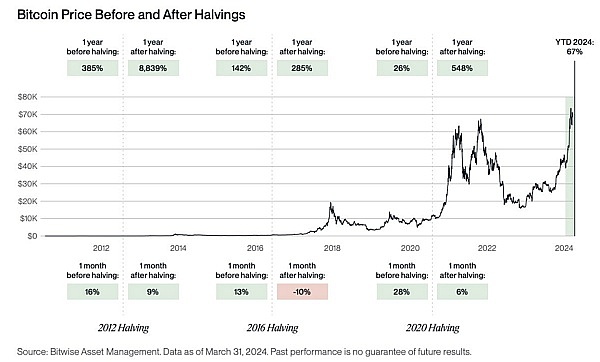
Bitcoin price performance before and after halving
First halving in 2012: One month after the halving, the price of Bitcoin rose by 9%. In the following year, the price of Bitcoin soared by 8,839%.
Second halving in 2016: One month after the halving, the price of Bitcoin fell by 9%. In the following year, the price of Bitcoin soared by 285%.
Third halving in 2020: One month after the halving, the price of Bitcoin rose by 6%. In the following year, the price of Bitcoin soared by 548%.
Miner selling pressure: Miners may sell Bitcoin after the halving, which may cause price pressure in the short term. However, it is important to consider that miners' selling behavior is often affected by market demand. If market demand is strong, miners' selling behavior may be absorbed and will not have a significant impact on prices.
Major Bitcoin Events and Price Impacts (2018 – 2024)
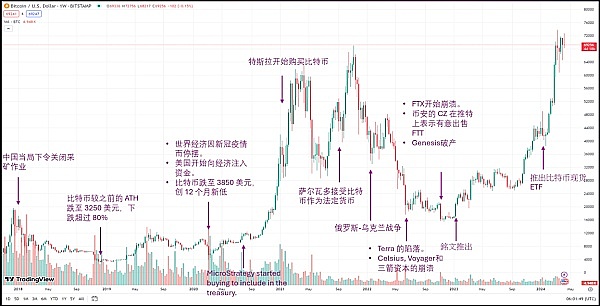
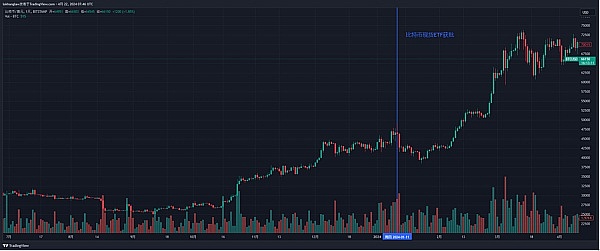
The launch of BTC spot ETF
In January 2024, the first Bitcoin spot ETF was listed in the United States, marking the recognition of digital assets by traditional financial markets. It will further promote institutional investors to enter the cryptocurrency market, increase Bitcoin's liquidity and market depth, and thus have a positive impact on prices.
Fourth, the advantages of Bitcoin as an investment asset
Comparison of Bitcoin with traditional assets (such as gold, stocks)
Bitcoin is often called "digital gold" and has similar non-government control and scarcity characteristics as gold, but it shows advantages different from traditional assets such as gold and stocks in many aspects. First, the globalization and ease of trading of Bitcoin provide advantages beyond geographical restrictions. Compared with gold, the storage and transfer of Bitcoin are more convenient and low-cost. Second, compared with the stock market, the Bitcoin market operates almost around the clock, providing higher liquidity and trading flexibility. In addition, the price of Bitcoin is not directly affected by company performance or economic policies, which provides investors with a potential hedging tool. When global economic uncertainty increases, Bitcoin may show characteristics that are out of sync with traditional markets.
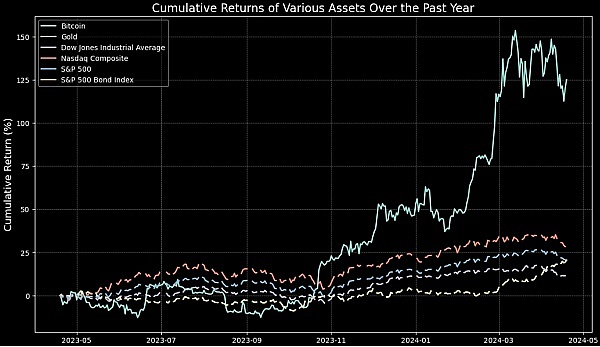
As shown in the figure, the cumulative return of Bitcoin over the past year shows a significant difference compared with other traditional assets. The figure clearly shows the performance of Bitcoin relative to gold, the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the Nasdaq Composite Index, the S&P 500 Index, and the S&P 500 Bond Index. It can be seen that Bitcoin experienced a period of rapid growth in October 2023, and its cumulative return rate rose rapidly in a short period of time, far exceeding other assets.
This sharp growth emphasizes the potential and volatility of Bitcoin as an investment tool, while the growth of traditional assets such as stock and bond indices is relatively stable. In addition, as a traditional safe-haven asset, gold has a relatively mild growth and volatility, which is consistent with the performance of stock and bond indices. When analyzing the returns of these different assets, Bitcoin's uniqueness and high volatility offer a different path for investors seeking non-traditional growth opportunities.
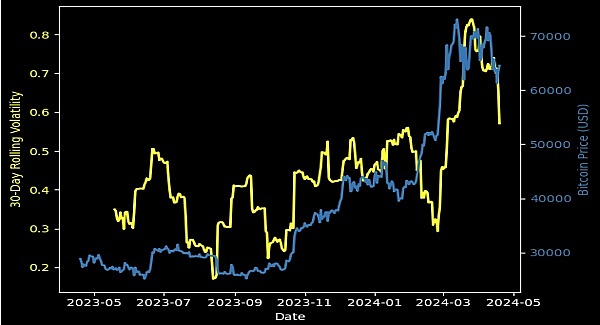
As shown in the figure, there is a significant correlation between Bitcoin's price and its 30-day rolling volatility. For most of the time period, we can see that the rise in Bitcoin's price is accompanied by an increase in volatility. In particular, in early 2024, as marked in the figure, Bitcoin's price reached a peak, and at the same time, volatility also increased significantly, indicating that large price fluctuations and investor uncertainty have increased market volatility. However, in March 2024, Bitcoin's price fell sharply, which is also reflected in the sharp rise in volatility, indicating that when prices change rapidly, the volatility index is an important indicator that reflects market uncertainty and changes in investor sentiment.
In the cryptocurrency market, volatility, as a measure of risk, is closely linked to price, and this should be taken into account when making asset allocations.
Bitcoin Market Acceptance and Growth Potential
In recent years, the market acceptance of Bitcoin has increased significantly, and more and more financial institutions and technology companies have begun to support Bitcoin transactions or accept Bitcoin as a payment method. In the early years, the participation of international payment giants such as PayPal and Square made Bitcoin more mainstream, providing ordinary investors with convenient investment and use channels. In addition, with the development of blockchain technology and the gradual improvement of the regulatory environment for digital currencies, the long-term growth potential of Bitcoin is widely optimistic. As a borderless currency, Bitcoin's potential role in the global economy is gradually expanding, and its growth potential has been recognized by many investors.
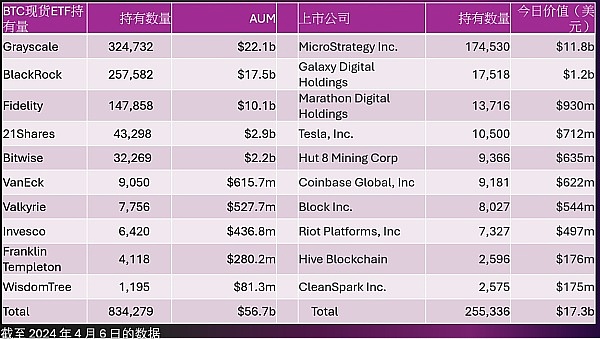
As of April 6, 2024, many well-known ETFs and listed companies hold a large amount of Bitcoin, reflecting the market's acceptance of Bitcoin and its optimistic growth potential. Large asset management institutions such as Grayscale, BlackRock and Fidelity hold hundreds of thousands of Bitcoin spot ETFs, with a total asset value of more than US$50 billion. This data not only shows the positive attitude of institutional investors towards Bitcoin investment, but also implies that Bitcoin, as an emerging asset class, is being recognized by more and more traditional financial market participants.
At the same time, among listed companies, MicroStrategy, Galaxy Digital Holdings, Marathon Digital Holdings and other companies also hold a considerable amount of Bitcoin, totaling more than 250,000 units, with a value of more than US$17 billion. The participation of multinational technology companies such as Tesla further demonstrates the mainstream business sector's affirmation and expectation of the future value of Bitcoin.
Overall, whether it is the asset management industry or major listed companies, the large-scale Bitcoin holdings highlight the market's deep confidence in it and the potential importance of Bitcoin as an investment tool and a means of storing value in global asset allocation. This trend indicates the increasing maturity of the cryptocurrency market and wider market acceptance in the future.
V. Future Outlook and Investment Opportunities
Diversification Effect of Bitcoin Investment and Traditional Investment Portfolios
Including Bitcoin in traditional investment portfolios can provide significant diversification benefits. Due to the low correlation between Bitcoin and traditional financial assets, it provides a means of risk diversification for investment portfolios. In an environment of global economic instability or inflation, Bitcoin even shows the characteristics of a safe-haven asset. By analyzing the performance of Bitcoin under different market conditions, investors can better understand how to use this digital asset to optimize the risk-return ratio of their investment portfolios.
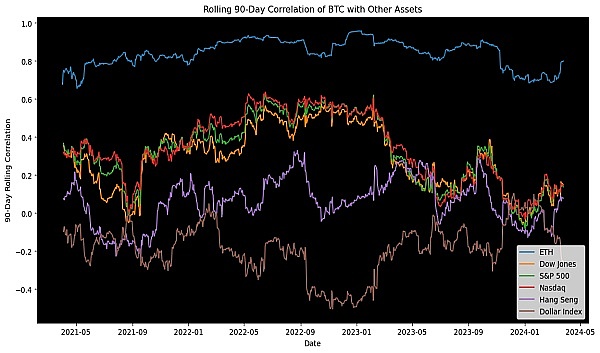
This chart reveals the low correlation between Bitcoin and traditional assets. In addition to maintaining a high correlation with Ethereum, BTC's correlation with mainstream assets such as the Dow Jones, S&P 500, Nasdaq and Hang Seng Index is generally not high. This low correlation shows the advantage of BTC as a diversification tool in the asset portfolio, which helps to diversify the systemic risk of the investment portfolio. Especially when the traditional market is turbulent or facing downward pressure, this feature of BTC may provide investors with a certain degree of protection, thereby reducing the volatility of the overall investment portfolio. Therefore, the addition of BTC can be regarded as a strategic allocation aimed at improving the risk-adjusted return rate of the investment portfolio.
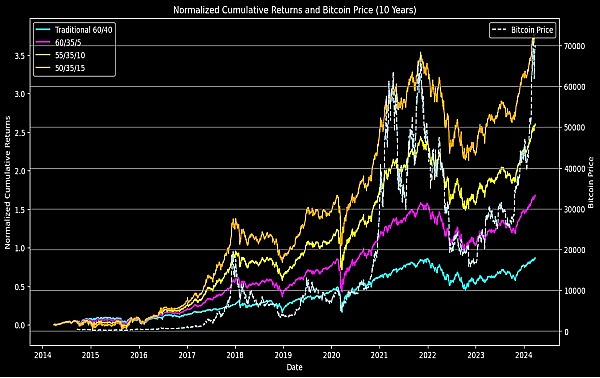
This figure shows the standardized cumulative returns of the traditional 60/40 portfolio (60% stocks, 40% bonds) and portfolios with different proportions of Bitcoin allocation over the past decade, as well as the changing trend of Bitcoin prices. 60/35/5, 55/35/10 and 50/35/15 represent the proportions of stocks, bonds and Bitcoin in the portfolio. As the proportion of Bitcoin increases, the volatility of the portfolio's return rate also increases.
It can be observed that during the period of Bitcoin price increases, the return rate of the portfolio containing Bitcoin allocation is significantly higher than that of the traditional 60/40 portfolio. Especially after 2020, as the price of Bitcoin has risen significantly, the portfolio containing Bitcoin has shown stronger growth momentum.
However, this is also accompanied by higher volatility, especially during Bitcoin price peaks and pullbacks. This shows that while including Bitcoin in an investment portfolio has the potential to increase returns, it also increases the portfolio's risk exposure.
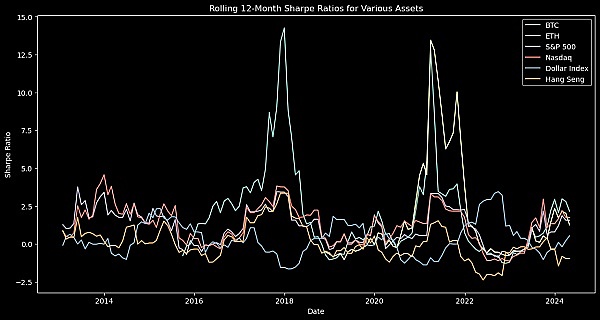
This graph depicts the rolling 12-month Sharpe Ratio of Bitcoin and a variety of assets. The Sharpe Ratio measures the excess return per unit of risk, and a higher Sharpe Ratio means a higher risk-adjusted return.
As can be seen from the figure, Bitcoin's Sharpe Ratio is much higher than other assets in certain periods, indicating that it brings the largest excess return per unit of risk. In particular, during 2017 and 2021, Bitcoin's Sharpe Ratio spiked, reflecting its excellent ratio between investment returns and risks during these time periods. However, it can also be observed that Bitcoin's Sharpe ratio exhibits great volatility, corresponding to the sharp fluctuations in its price.
In contrast, traditional stock indices such as the S&P 500 and Nasdaq have lower Sharpe ratios but less volatility, reflecting more stable risk-adjusted return performance.
 Kikyo
Kikyo
 Kikyo
Kikyo Huang Bo
Huang Bo Cheng Yuan
Cheng Yuan JinseFinance
JinseFinance Kikyo
Kikyo Coindesk
Coindesk Others
Others Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph