Source: Coin Metrics; Compiled by: Golden Finance
Key Points
Demand for Bitcoin Exposure: Continued inflows into spot Bitcoin ETFs and the performance of digital asset treasury tools like "Strategy" demonstrate investor demand for Bitcoin (BTC) exposure. While this may lead to a concentration of holdings among a small number of institutions, such products broaden investment channels for traditional investors.
Lagged Activity: Despite record-high Bitcoin prices, its blocks have not consistently been at full capacity. While this allows low-value transactions to be included in blocks, improving network accessibility, it also raises concerns about miner profitability—limited transaction fee revenue reduces miners' incentive to maintain network security.
Ever-Expanding Bitcoin Use Cases: Wrapped Bitcoin (BTC) products and emerging native Bitcoin applications are creating new income opportunities for holders and driving network activity. However, transaction fees have remained subdued since August 2024, never exceeding $150. Over the long term, fee revenue will need to play a greater role in maintaining miner incentives and network security. The development of regulated Bitcoin investment vehicles and a wave of pro-cryptocurrency legislation have driven a significant rise in Bitcoin prices. While investor security has improved, the sustainability of the underlying network has been overlooked. Without considering network activity, the long-term investment case for Bitcoin is incomplete. In September 2024, our inaugural Bitcoin Asset Analysis highlighted Bitcoin's increasing scarcity, its advantages within Modern Portfolio Theory, and the rise of Bitcoin ETFs. Today, Bitcoin's price has surpassed $124,000, and ETF inflows are on the rise. In this updated report, we delve into the recent demand for Bitcoin exposure through ETFs and treasury firms, the impact of this demand on network activity, and emerging trends in the Bitcoin ecosystem in 2025 and beyond. II. Factors Driving Bitcoin Interest (I) Continued Inflows into US Spot Bitcoin ETFs Since the approval of US spot Bitcoin ETFs in January 2024, market interest in them has fluctuated. Currently, the total amount of Bitcoin held in Bitcoin ETFs exceeds 1 million, representing over 5% of the current Bitcoin supply. As Bitcoin prices reach record highs, institutional investors and traditional portfolios are returning to ETFs, eager to increase their Bitcoin exposure. The increase in inflows into Bitcoin ETFs can be explained by the following: 1. Support from Modern Portfolio Theory: This theory suggests that investing in Bitcoin can help improve risk-adjusted returns. Bitcoin's low correlation with gold and stocks can help diversify portfolios and hedge against market downside risks. 2. Simplified Custody: Self-custody of Bitcoin requires significant resources for seed phrase management and multi-signature wallet security, while ETFs avoid these custodial complexities. 3. Convenient Access: Investors can participate in ETFs through traditional brokerage platforms, without having to connect to new cryptocurrency exchanges or engage in peer-to-peer trading, which aligns with their existing investment practices.
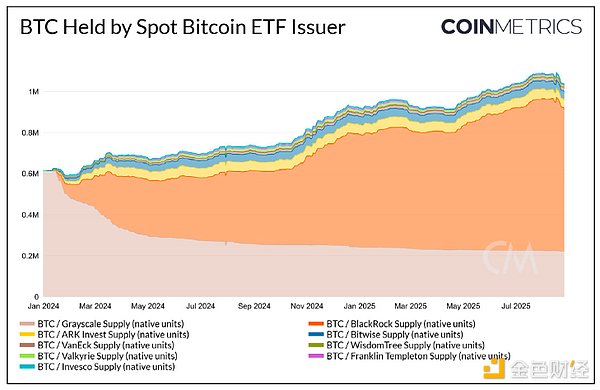
(II) The Rise of Strategy: A Leveraged Bitcoin Investment Tool
Investors seeking greater Bitcoin exposure are turning to publicly traded companies focused on building Bitcoin treasuries, such as Strategy (NASDAQ: MSTR).
Compared to Bitcoin ETFs, Strategy shares offer greater volatility, thus offering investors higher potential returns. This is due to Strategy's model of increasing Bitcoin holdings through recursive leverage: the volatility of its shares enables it to consistently issue low-interest convertible bonds (which experienced investors can use for hedging) and use the proceeds to purchase Bitcoin. The Strategy's core objective is to increase the number of Bitcoins per outstanding common share ("BTC Yield"). Investors expect that Strategy will continue to increase its Bitcoin holdings, which drives its stock price to a premium relative to the value of its underlying treasury. Currently, Strategy holds over 628,000 Bitcoins, representing 3% of the current Bitcoin supply. For reference, this amount is only 100,000 less than the total Bitcoin held by BlackRock's Bitcoin ETF for millions of investors. Strategy uses the concept of "BTC Risk" to measure the probability that the value of the Bitcoin backing its issued bonds will fall to the bond's par value. If Bitcoin prices decline over a long period of time, this risk, if realized, could weaken Strategy's ability to finance future Bitcoin purchases and even force it to repeatedly reduce its Bitcoin holdings to meet debt obligations.
III. Is Network Activity Correlated with Bitcoin Demand?
Just as company revenue determines stock price value, transaction fees are considered a key factor in determining token prices. Transaction fees not only reflect network usage but also serve as the core reward that incentivizes miners to maintain network security.
Passive Bitcoin holdings reduce network activity and fee revenue, thereby threatening network security. If miners cannot generate sufficient Bitcoin revenue from block rewards and transaction fees, they may cease operations to avoid losses, leading to the concentration of hashing power in a small number of operators. By analyzing changes in transaction fee activity, we can clearly determine whether it is driving Bitcoin prices higher.
(I) Mining Pool Dominance Continues
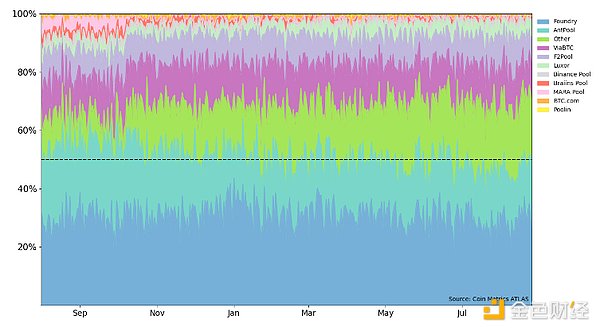
Since the release of our first "Bitcoin Asset Analysis Report," the control of total hashing power by the top mining pools has remained stable. The US mining pool Foundry controls approximately 30% of the hash rate, followed closely by the Chinese mining pool Antpool, which holds 18%. To maximize profits, miners continuously compete for control of hash rate and network dominance. The current block generation difficulty is at an all-time high, indicating that mining pools are continuously investing in new mining machines to maintain their position in the network.
Bitcoin Mining Pool Share Chart (August 2024 to Present)
(II) Miner Income is Unsustainable
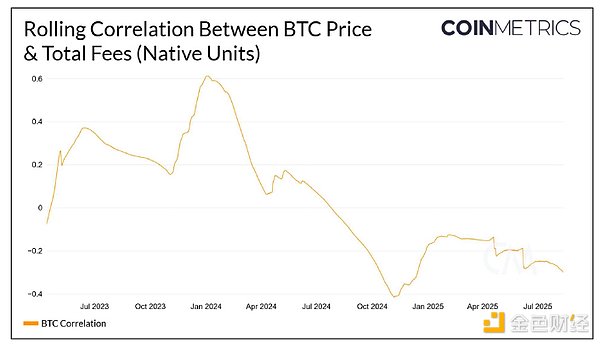
Despite mining pools' control of the network, individual miners' income is increasingly dependent on Bitcoin's price. After Bitcoin's fourth halving in April 2024, the proportion of transaction fees has continued to decline, currently accounting for less than 1% of miners' total revenue. Individual miners are reducing their holdings of Bitcoin, partly due to operational security concerns and partly due to the need to sell Bitcoin to cover operating costs. Bitcoin is expected to undergo its fifth halving in 2028, at which point miners will only receive 1.5625 new bitcoins per block. This significant drop in revenue could cause some miners to exit the market due to the inability to maintain profitability. This miner exit would pose a threat to Bitcoin's decentralization and network security. Against this backdrop, transaction fee revenue will become increasingly important in incentivizing miners to maintain network security and prevent the concentration of computing power. The revenue gap caused by the reduction in Bitcoin's block rewards can be offset in two ways: first, a surge in network activity driving up transaction fees, and second, the development of new applications creating additional demand for block space. Since January 2025, the available Bitcoin block space has increased significantly compared to the 2024 average. Block weight measures the size of transactions included in a block—complex transactions carry a higher weight and occupy more block space than simpler ones. Currently, there is ample space in the blocks to accommodate more transactions, provided there is demand. Low demand for block space has kept transaction fees low, enabling many fee-sensitive users to participate in network transactions. While low fees increase the inclusiveness of value transfer on a censorship-resistant network, there is little correlation between demand for Bitcoin assets and institutional investor demand for block space. Bitcoin is increasingly being viewed as "digital gold" and a store of value. Its appeal stems not from the fees generated by the network but rather from its ability to hedge against fiat currency inflation and serve as an alternative means of storing or transferring value.
V. Bitcoin Use Case Development in 2025
(I) Emerging Wrapped Bitcoin Alternatives
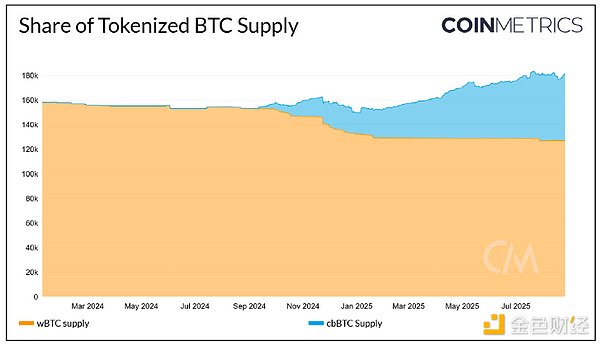
Coinbase's cbBTC supply saw a significant increase as BitGo's wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) underwent custody adjustments. Users locked up their Bitcoin and obtained tokens like cbBTC and wBTC representing the underlying asset, thereby seeking yield opportunities on other networks.
While BitGo previously held a majority share of the tokenized Bitcoin market, its announcement in August 2024 of a partnership with BitGo Singapore Pte. Ltd. and BiTGlobal to adjust its custody model sparked market concerns about its reserve management. As a result, the supply of Bitcoin in BitGo custody has stagnated, with the wBTC supply stabilizing at approximately 127,000, down from a total supply of 153,000 last year. Meanwhile, the cbBTC supply has grown to over 52,000 since its launch in August 2024. While BitGo still holds the majority of Bitcoin for its users, Coinbase is steadily gaining market share.
(II) Native Bitcoin Applications Continue to Evolve
Developers are actively developing applications to reduce users' reliance on custodians and cross-chain bridges when earning returns using Bitcoin. Holders can interact with these applications using native Bitcoin without having to hold tokenized Bitcoin.
The Babylon Genesis Chain provides security for external Proof-of-Stake (PoS) networks by incentivizing miners to stake Bitcoin to operators. Leveraging the Bitcoin network to verify state changes in the PoS network not only enhances the security of the PoS chain but also generates additional transaction fee income for Bitcoin miners. While Bitcoin stakers retain Bitcoin ownership, they also receive rewards from the PoS network, which requires the operator's assistance in verifying the network's status. On August 22, 2024, when the Babylon staking service initially opened for deposits, block space demand increased significantly, and network fees briefly exceeded $150, setting a new high for single-block fees since OKX's unspent transaction output (UTXO) integration in June 2024. This phenomenon fully demonstrates the market's expectations for the Babylon staking service. Since the Babylon staking service triggered a fee increase, Bitcoin transaction fees have never peaked above $150. Unless new factors emerge to incentivize users to include their transactions in the next block, transaction fees will continue to account for a low proportion of miners' revenue. The instability of fee revenue forces miners to rely more heavily on newly minted Bitcoin block rewards to maintain operations. Sixth: Outlook The increased demand for Bitcoin generated through ETFs and digital asset treasuries (DATs) is a primary reason for Bitcoin's recent strong performance. However, this demand has not translated into increased network activity. Continued low fee revenue casts uncertainty over the health of the Bitcoin network. As the number of newly minted Bitcoins decreases, transaction fees will become increasingly important in incentivizing miners to maintain network security. If miners are forced to exit the network due to prolonged losses, Bitcoin's decentralization and censorship resistance will be at risk, and its core value proposition will be lost.
The emergence of more native Bitcoin applications is expected to return transaction fee income to miners, rather than allowing related activities to flow to other blockchains. If Bitcoin is to match its high valuation, network activity and miner incentives must be improved as soon as possible.
 Catherine
Catherine










