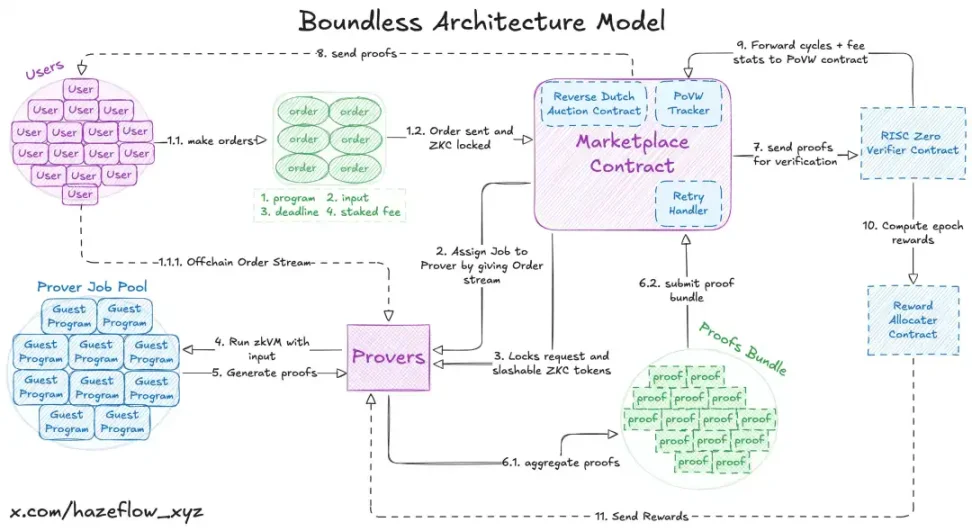
Boundless has built a marketplace that facilitates secure zk-computations, enabling efficient collaboration between developers and Provers. As zk-technology grows, it's becoming modular. Layers are emerging: some handle computations, others optimize, and marketplaces like Boundless allow anyone with hardware to join. To illustrate this concept, we'll think of Boundless as a global courier company. Instead of shipping packages, Boundless can be best understood as a global delivery marketplace, except it handles any type of zk-computation. The customer is the developer or application that needs work done. The courier is the Prover with the hardware to do the heavy lifting. The central hub is a system of smart contracts that ensures every package (computation) is delivered on time, couriers are paid fairly, and cheaters are punished. 1. Marketplace Imagine a busy market square: Customers (users/requesters) walk in with jobs: "I need this package delivered, here's the destination, here's my budget, and I'll lock up some funds upfront." They post these requests on the market bulletin board (market contract). Couriers (provers) gather around the board. Jobs are announced using a Dutch reverse auction: prices don't fall like on eBay, but rather rise over time. Early adopters can get it at a low price, but if they wait too long, the price will become more attractive, attracting competition. When the courier accepts it, they also leave a security deposit at the counter (deposited ZKC). This proves they are serious. If they abandon it, they will lose the deposit. Once locked, the courier takes the package (zk program + inputs) back to their truck (hardware). They run the delivery route (zkVM calculations, or mathematical calculators that don't lie) and return a sealed envelope (proof) indicating that the package was delivered exactly as requested, without tampering.
Back to the hub:
The verifier (RISC Zero, an instant double-check machine) double-checks the seal in seconds.
If valid, the courier gets paid, their deposit is refunded, and the customer receives a verified delivery.
2. What if the courier fails?
Now, imagine a courier picked up a package but never delivered it. The Hub can't let its customers down. Here's what happens:
The courier loses their deposit (slashing): part goes into the Hub's coffers, and part is reserved as a reward for anyone who rescues the job.
The job is reposted on the notice board, but this time without exclusive bookings, any courier can compete to deliver it.
This retry pattern creates a sense of urgency. Other couriers see not only the original payment but also part of the failed courier's deposit. Suddenly, the job becomes extra valuable, so someone quickly picks it up and delivers it.
This ensures the market keeps functioning. Even bad actors can't stop it: at worst, they just pay a fine. 3. How can we support the marketplace over the long term? Behind the bustling plaza is a treasury where investors and couriers can deposit the marketplace's token (ZKC). Here's how it works: When you lock ZKC in the treasury, you earn non-transferable points, like a loyalty card. Over time, as the marketplace collects fees from each delivery, treasury participants can spend their points to withdraw a pro-rata share of revenue or unlock their tokens. Couriers can also stake their tokens here. The tokens they stake not only earn them points but also serve as a security deposit when accepting jobs. This system ensures that both workers (couriers) and backers (investors) share in the market's success. The busier the market, the greater the rewards. 4. Boundless as a global courier company. Boundless becomes easier to imagine through this analogy: Market contracts are the job board in the town square. Reverse auctions are how jobs are fairly priced. Provers do the heavy lifting, backed by a deposit. Provers are sealed envelopes: easy to check, impossible to forge. Slashing and retries keep deliveries reliable. A vault + points system keeps long-term backers and couriers invested. All of this is powered by underlying cryptography, but for users and developers, it feels like a self-regulating, always-on gig economy. The only difference is that instead of moving boxes, it's providing computation for the blockchain. 5. Applications on Boundless. Boundless transforms light clients into zk-stateless clients, making them more secure and trustless by outsourcing their verification work to a network of Prover nodes. These clients can verify multiple chain states in parallel and broadcast the results globally via Boundless Signal, effectively acting as universal light clients for all chains. This architecture unlocks new types of deliverables in the blockchain world. For cross-chain communication, Signal acts like a global bulletin board, where each delivery is stamped and published.
Any chain can simply check the bulletin board and see a certified receipt indicating that a package from another chain has arrived, without sending a courier (bridge, multisig, custodian) that you must trust.
For developers, Steel is like renting a private workshop within a courier network. You hand over the raw materials, it builds the product offsite, and in return you get a sealed report (zk-proof) that anyone can trust without having to re-do the work.
In this way, Boundless transforms computing into a shared courier economy, where packages move faster, receipts can be trusted by anyone, and every station in the network becomes part of a verifiable delivery system.
 XingChi
XingChi





