Source: FT Chinese
In 2016, Trump was elected as the President of the United States for the first time, becoming the first president in American history without any government or military experience. How could Trump, a political "novice", be elected?
On May 30, 2024, the jury of the Manhattan Criminal Court in New York in the "hush money" case unanimously ruled that Trump was guilty of all 34 criminal charges brought by the prosecution. How could Trump, who was "guilty", be re-elected?
Most of the so-called "uncertainty" people think that Trump will win, but in fact, Trump is certain. In his first term, Trump has defined China as the main competitor of the United States and launched a "trade war", which will only be strengthened in his second term. Compared with other countries, China should not have a fluke mentality with Trump and should seriously deal with his second term.
In 2016, how could Trump, a political "novice", be elected?
Trump's campaign in the 2016 presidential election was based on the core slogan of "Make America Great Again" (MAGA), focusing on economic, immigration, trade, diplomacy and anti-establishment issues. His campaign strategy successfully attracted a wide but specific group of voters, winning the US election for Trump, who had no experience in governing.
First, the economic policy was mainly to revitalize the manufacturing industry and give priority to the domestic economy, including: promising a comprehensive tax cut policy, especially for the middle class and enterprises to stimulate economic growth; promising to create more jobs for American workers by restricting outsourcing, increasing infrastructure investment, and cracking down on illegal immigration; emphasizing the restoration of manufacturing, criticizing globalization for causing unemployment among American workers, and calling for "Bring Jobs Back".
Second, the immigration policy was to strengthen border security and restrict illegal immigration. Trump proposed building a "border wall" on the US-Mexico border to prevent illegal immigrants and drugs from entering the country, and asked Mexico to pay for the wall. He advocated strict restrictions on immigration, especially immigrants from the Middle East and other "high-risk" countries. He promised to take tough measures against illegal immigrants, including accelerating deportations and cracking down on sanctuary cities.
The third is the "America First" trade policy, which emphasizes reshaping fair trade rules and protecting American interests. Trump called the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) "disastrous" and threatened to withdraw from the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement (TPP); criticized China's trade practices and promised to impose tariffs on Chinese products to protect American companies and workers.
In addition, there are anti-establishment policies that fight corruption and challenge political elites, as well as a foreign policy that prioritizes American interests and re-examines alliances.
Trump's campaign appeal first attracted working-class white voters, especially those living in the "Rust Belt" in the Midwest (such as Ohio, Michigan, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin) who were severely affected by globalization and the decline of manufacturing. These voters strongly resonated with Trump's policy of reviving manufacturing and creating jobs.
Secondly, voters living in rural areas and small towns, especially conservative whites, supported Trump's immigration policy and cultural conservatism. They were generally disappointed with the "establishment" and sought leaders who could change the status quo.
Third, the Republican Party's base, conservative voters, especially Christian evangelicals, were satisfied with Trump's positions, including abortion, religious freedom and gun policies. Although Trump's personal style is controversial in the eyes of some people, he caters to conservative needs on key policies.
Finally, Trump's anti-traditional campaign style and "outsider" image attracted some independent voters and anti-establishment voters who were tired of political elites. They hoped to promote "reforms" in Washington through Trump and break the existing political ecology.
In 2016, white voters accounted for about 70% of the total number of voters in the United States. Judging from the election results, more than 80% of Trump's voters are white. In the face of immigration growth, racial equality movements and the expansion of diversified culture, most white voters feel that their cultural status and economic interests are threatened.
Trump's support rate among African-American voters is about 8%. Most African-American voters support the Democratic Party, but the African-American voting rate in 2016 was lower than in 2012, partly due to lack of enthusiasm for Hillary. Although Trump's immigration policy is believed to weaken Latino support, he still won 28% of the Latino vote. Asian voters generally tend to favor the Democratic Party, but Trump has won some support among some conservative Asian groups.
Trump's main campaign propositions revolve around the "America First" economic and trade policy, strict immigration control and anti-establishment sentiment, capturing the psychology of voters who are disappointed with globalization, immigration and traditional politics. Through his outspoken personal style and strong populist propositions, he successfully attracted working-class, conservative and anti-establishment voters, laying the foundation for his victory in the 2016 election.
Why can Trump, who is "guilty", be re-elected in 2024?
The 2024 US presidential election has come to an end, and Trump has successfully defeated the Democratic candidate and current Vice President Harris to win the presidency. Trump won 312 electoral votes and Harris won 226 electoral votes. In this election, Trump won all key swing states including Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, and Georgia. It can be said that Trump won a crushing victory.
The jury in the "hush money" case unanimously ruled that Trump was guilty of all 34 criminal charges brought by the prosecution. Trump thus became the first former president in American history to be found guilty in a criminal case. In addition, during the 2024 campaign, Trump was also troubled by multiple criminal and civil cases, including: election interference cases (controversies related to the results of the 2020 election, especially allegations of election interference in Georgia), confidential documents cases (confidential documents were found in Mar-a-Lago, Florida), and other legal disputes (cases related to business practices and personal life). Why was Trump elected with an absolute advantage despite having criminal cases on his hands?
What are the similarities and differences between the 2024 campaign propositions and those in 2016?
In 2024, Trump continued to emphasize the "America First" economic, trade and foreign policies, including protecting domestic jobs, reducing outsourcing and being tough on China. As in 2016, Trump regarded illegal immigration as a major issue and continued to advocate the construction of a border wall and restrictive immigration policies. He continued to portray himself as an "anti-establishment" fighter, criticizing the "Washington swamp" and special interest groups, and catering to the dissatisfaction of grassroots voters.
The 2024 campaign will focus more on economic issues, especially controlling inflation and energy prices, which did not become a core issue in 2016. The 2024 campaign will also focus more on "culture war" issues, such as "woke culture", gender education, LGBTQ+ rights and anti-tech censorship, which did not become a focus in 2016.
Grassroots white voters, especially working-class and lower-middle-class white voters, are the groups most affected by globalization and immigration issues. They are anxious about inflation, rising energy prices and cultural changes, and support "America First" economic and social policies, which remain an important support base for Trump. Trump's emphasis on conservative values and religious freedom continues to attract evangelical Christians and cultural conservatives, who are particularly concerned about culture wars and education issues.
An obvious change in the 2024 presidential election process is that technology giants such as Musk, Bezos, and Zuckerberg have expressed their support for Trump during or after the election, and these people have traditionally been hardcore supporters of the Democratic Party. The shift of the tech giants is due to factors such as the economy (Trump will continue to lower tax rates or provide other corporate tax incentives after his election), regulation (Trump and the Republican Party emphasize "freedom of speech" and criticize big tech companies for excessive content censorship), energy and environmental policies (Trump's energy policy tends to support fossil fuels, while not overly restricting the new energy industry, which may provide a more balanced market environment for companies such as Tesla), and another factor that cannot be ignored is their aversion to "woke culture". Musk has publicly criticized "woke culture" and "political correctness" many times in recent years, believing that these cultures have become obstacles to innovation and corporate development. Trump's tit-for-tat stance against this culture is consistent with Musk's views.
Trump's 2024 campaign propositions, while continuing his 2016 "America First" concept, incorporate new economic and cultural issues to respond to current political and social realities. These propositions are aimed at consolidating his core voter base while winning over voters affected by inflation and energy prices, as well as independent voters who are dissatisfied with the Biden administration. By focusing on economic, immigration and cultural issues, he seeks to reshape himself as a "spokesman for the people" in the 2024 election.
Challenges and divisions within the Democratic Party
In 2024, the political climate and social divisions in the United States remain serious. The Democratic Party faces many challenges, especially the divisions between different factions within the party. Some supporters of the Democratic Party tend to be radical left-wing ideas, while others are more center-right.
In terms of the economy, although the Biden administration has implemented large-scale fiscal stimulus measures, the US economy still faces problems such as inflation, unstable job market, and declining purchasing power of the people. In particular, for some working-class and middle-class voters, the economic recovery has not been significant. People's dissatisfaction with rising prices, high housing prices and stagnant income growth has caused some voters to lose confidence in the Democratic Party.
Trump's "victim" image and political mobilization
Trump is very good at shaping and using the image of a "victim", which enables him to turn his predicament into political capital when facing legal proceedings. He constantly emphasized through social media, campaign rallies and public speeches that he was the target of attacks by the deep government and political enemies, especially the so-called "left-wing conspiracy" and "political persecution." Trump described these legal issues as the sacrifices he faced as an anti-establishment candidate, thereby inspiring sympathy and support for him among voters.
During the 2024 presidential campaign, Trump suffered two assassination attempts. The assassination attempts enabled Trump to portray himself as a victim of political violence and reinforce his previously claimed image of "political persecution." He used this in his campaign to claim that he "took the bullet" for democracy and national interests to inspire voters' sympathy and support.
In general, Trump's re-election in 2024 is due to the interweaving of multiple factors such as his strong voter base, effective campaign strategy, efficient use of media operations, accurate grasp of economic and cultural issues, and the characteristics of the two-party system and the electoral college system in the United States.
Globalization, Immigration and MAGA
Globalization has brought profound economic, social and cultural impacts to the United States, especially to the middle and lower class white groups. Many aspects are negative, which has led to their strong dissatisfaction with globalization.
Globalization has led to the decline of manufacturing and the outflow of jobs. With the advancement of globalization, many American companies have moved their manufacturing to countries with lower labor costs in order to reduce costs, especially China, Mexico and other Asian countries. This has led to the loss of a large number of jobs for the middle and lower class white groups in the United States, especially in traditional industrial states (such as Ohio, Michigan, Pennsylvania, etc.). These areas were originally the center of the US manufacturing industry and had a large number of blue-collar workers. They have lost a large number of job opportunities in the context of globalization.
In many industries, with the outsourcing of manufacturing, the remaining positions are usually lower-paid and require fewer skills. This has forced many workers who used to work in factories, steel mills, auto plants and other fields to accept lower-paid and poorly treated positions, resulting in a decline in their quality of life.
The direct consequence is the shrinking of local economies and the decline of communities. Many cities and towns that rely on manufacturing as their mainstay have been severely impacted by globalization. When these factories and enterprises moved abroad, the economy of many places fell into trouble, unemployment rates rose, and living standards fell. Residents of these cities and towns, especially lower-middle-class whites, face higher poverty rates and social problems, such as rising crime rates and increased demand for social welfare. With fewer job opportunities and stagnant income levels, many people find it difficult to get upward mobility economically, social classes solidify, and the phenomenon of intergenerational transmission of poverty becomes more serious.
The gap between the rich and the poor has widened. Although globalization has promoted the flow of technology, capital, and information, helping some high-skilled workers and large companies to gain huge benefits, it has not benefited all Americans. The lower-middle-class white groups, especially low-skilled workers, often fail to benefit from the economic growth brought about by globalization. Instead, they face stagnant wages, rising costs of living, and difficulty finding competitive positions in the labor market.
On the one hand, high-skilled technical workers, financial industry practitioners, managers, etc. have gained more opportunities due to globalization, and their salary levels have gradually increased; on the other hand, low-skilled traditional workers have lost their security, resulting in a further widening of the gap between the rich and the poor. Many lower-middle-class whites feel marginalized in this change.
Globalization has not only changed the economic structure of the United States, but also brought about cultural changes. With the increase in immigration and the integration of global cultures, American society has become more diverse. Many middle- and lower-class white voters feel that their culture, traditions and lifestyles are threatened. In particular, when they see their communities gradually changing and the influence of foreign cultures, languages and religions increasing, they have strong cultural anxiety and identity crises.
As globalization has caused the economic status of the middle- and lower-class white groups in the United States to decline, many people believe that the "American Dream" they once believed in has been shattered. They believe that they could live a better life by working hard in the past, but now they are facing problems such as job outflows, stagnant incomes and family instability, which makes them disappointed with the fairness and future of American society.
In addition to the economy, the racial structure of the population is also an important factor affecting the US presidential election. According to 2024 estimates, among the major ethnic groups, white Americans (non-Hispanic) account for 58.4%, Latinos (i.e. Hispanics) account for 19.5%, African Americans account for 13.7%, and Asian Americans account for 6.4%. The chart shows the racial distribution of the US population since 1990.
In 1990, whites accounted for 75.6% of the U.S. population, Latinos accounted for 9%, African Americans accounted for 11.7%, and Asian Americans accounted for 2.7%. Over the past 35 years, the proportion of whites has continued to decline, from 75.6% in 1990 to 58.4% in 2024; the Hispanic population has grown significantly, from 9% to 19.5% in 2024, becoming the most important minority group; the African American population has grown steadily, and its proportion has remained between 12% and 13%; while Asian Americans have risen rapidly, with their proportion increasing from 2.8% to 6.4%, mainly due to high education and skilled immigration policies. The U.S. Census Bureau predicts that by 2045, whites will no longer be the majority (i.e., less than 50% of the population).
Chart 1: Racial Proportion in the United States
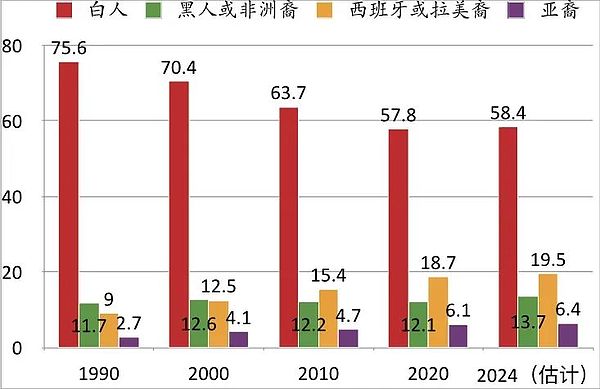 Data source: U.S. Census Bureau
Data source: U.S. Census Bureau
The main drivers of changes in the racial composition of the population are immigration and birth rates. The United States is a country of immigrants, and changes in the source of immigrants directly affect the racial composition. Historically, European immigrants in the 19th century laid the foundation for the proportion of whites; in the second half of the 20th century, immigrants from Latin America and Asia increased significantly. The birth rates of Latino and some Asian groups are significantly higher than those of white and African groups, which has driven their share of the overall population to rise.
Globalization has generally had a negative impact on the middle and lower class white groups in the United States, especially in terms of job losses in manufacturing, increased economic inequality, shrinking local economies, and a crisis of cultural identity. The decreasing proportion of white Americans in the population has intensified their aversion to globalization and modern social change, and promoted support for protectionism, populism and "America First" policies.
Trump's MAGA campaign platform caters to the emotions and needs of middle- and lower-class white voters, promising to restore their lost economic and cultural status by canceling trade agreements, restricting immigration, and promoting the return of manufacturing.
In addition, abolishing affirmative action is also an important part of Trump's 2016 campaign platform. During the campaign, Trump made it clear that he opposed affirmative action, especially racial quota policies in higher education and employment; affirmative action is essentially "reverse discrimination", advocating that everyone should have equal opportunities by abolishing such policies, and that certain groups should not be favored or discriminated against because of race or gender. He believes that such policies "kill opportunities" and do not actually help minority groups such as African Americans and Latinos, but instead cause unfair treatment to white and Asian groups. For Trump's conservative supporters and lower-middle-class white voters, this position is consistent with their understanding of fair competition and racial equality.
The impact of Trump 2.0 on China and how China should respond
In Trump's core 2024 campaign platform, policies such as immigration and tax cuts have no direct impact or little impact on China, while tariffs and trade policies have a direct impact on China.
Trump, who is re-elected, may impose higher tariffs on imported goods, especially those from China. He once said that he was considering imposing a comprehensive tariff of 10% on all imported goods and a tariff of 60% or higher on Chinese goods. He even exaggeratedly mentioned in his speech in Detroit that he might impose tariffs of up to 100% and 200% on Chinese automakers' factories in Mexico to ensure that the products of such factories could not flow into the United States.
Trump emphasizes America first and toughness on China. Judging from his resume and previous public remarks, the cabinet members he nominated have a prominent feature: they are a group of young anti-China hawks who are both loyal to Trump. The composition of this group of confidants shows that Trump has emphasized the continuity and depth of his tough stance on China in his personnel layout. It is reasonable to predict that in the next term, the Trump administration's China policy will obviously tend to a tough line, and this overall tone may be clearly reflected in future policy formulation and implementation.
During Trump's last term, the Office of the United States Trade Representative included China in the "Priority Watch List" through the "2017 Special 301 Report" and launched a "301" investigation against China. From June 2018 to December 2019, the Trump administration imposed a wide range of tariff policies on China, and carried out 5 rounds of actions, imposing tariffs on a total of US$550 billion in Chinese goods.
According to the Peterson Institute for International Economics (PIIE), this has led to a sharp increase in the average US tariff rate on Chinese imports from 3% in early 2018 to a high of around 21% in September 2019; it has since dropped to around 19.3% in March 2020, still at a high level.
Drawing on historical experience, the last round of Sino-US trade friction dragged down the growth rate of total exports to around 0% in 2019. However, the overall impact on economic growth is relatively controllable, with economic growth in 2019 falling 0.9% to 6.0% from 2017. Considering that China's export structure has been significantly adjusted and its dependence on exports to the United States has dropped from 19% in 2017 to 14.7% at present, the marginal impact of the US tariff increase on China will be weakened.
Trump is very sensitive to trade deficits, and the goal of his trade policy is to reduce the US trade deficit to zero. Figure 2 shows the trade gap between China and the world's major economies. In 2024, China's trade surplus with the United States is US$361.032 billion, accounting for 36.4% of China's total trade surplus of US$992.155 billion and 1.97% of China's GDP in 2024 (estimated by the IMF to be US$18.3 trillion). If the trade surplus with the United States really drops to zero, it will have a significant impact on China's exports and economy.
Chart 2: China's trade deficit with major economies in the world (US$ billion)
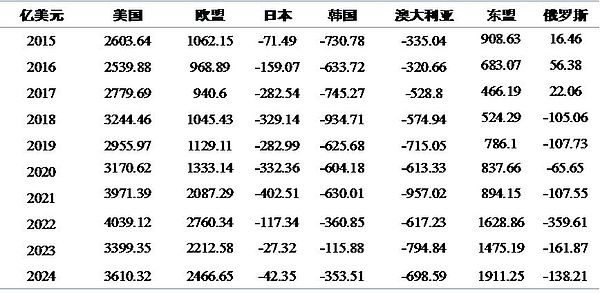 Data source: General Administration of Customs of China, iFind
Data source: General Administration of Customs of China, iFind
According to PIIE calculations, Trump's current round of tariffs will drag down China's real GDP growth by an average of 0.2%-1%, drag down the US real GDP growth by an average of 0.1%-0.4%, and increase US inflation by an average of 0.25%-0.6%.
As China's response to the US tariff increase, the first is to expand diversified export markets. Deepen trade cooperation with markets such as ASEAN and the EU, and reduce dependence on exports to the US. Accelerate the "Belt and Road" initiative and expand the export share of emerging markets (such as Africa, the Middle East, and Latin America). Strengthen economic and trade cooperation with RCEP and CPTPP member countries, and use regional trade agreements to reduce tariff barriers.
The second is to broaden the re-export trade channels. During the last round of Sino-US trade frictions, the re-export trade from China to ASEAN and Mexico, and from ASEAN and Mexico to the United States showed a clear growth trend. China re-exports to the United States through ASEAN and Mexico to circumvent the restrictions on direct trade in Sino-US trade frictions. The rise of this re-export trade model has also provided new development opportunities for economies around China and Mexico.
Then Chinese companies go global and optimize the layout of the global supply chain. By directly investing in and building factories in countries such as Vietnam and Mexico to reduce production costs, improve product quality and expand overseas markets, the diversified layout of the global supply chain can be achieved, the tariffs and trade barriers imposed by the United States can be avoided, and the overall risk resistance can be improved.
The main goal of Trump's tariff increase is to bring manufacturing back to the United States, thereby increasing the employment rate of middle and lower-class white people in the United States. Pragmatic cooperation can be carried out under the premise of reducing tariffs on China, and Chinese companies can directly invest and build factories in the United States to drive the recovery of the US manufacturing industry. China can promote the development of the US manufacturing industry through investment, technical cooperation and other means, create jobs for the United States and help it revive its local economy. China's manufacturing advantages can supplement the US supply chain and help the two sides achieve a mutually beneficial and win-win situation on economic issues.
 Weiliang
Weiliang





