Author: Coindesk; Compiled by: BitpushNews Mary Liu
Ethereum Dencun upgrade is expected to be around 9:55 AM Eastern Time on March 13 start up. The upgrade involves a new Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) called "proto-danksharding" or EIP-4844, which will usher in a new era of lower fees for auxiliary networks (L2/Rollup) running on Ethereum.
Dencun is taken from the combination of Deneb + Cancun, which means two upgrades that occur simultaneously on the Ethereum consensus layer and execution layer. This will be the biggest update for Ethereum since the Shapella upgrade in April 2023.
Proto-danksharding
Dencun will introduce Proto-Danksharding, which is a theoretical transition A long process into practice (first mentioned by Vitalik Buterin in 2019), it changes the way Ethereum stores data.
Dencun will not store all data directly on the immutable execution layer of the Ethereum mainnet, as this is expensive and computationally intensive. Instead, it introduces a new, temporary way to store "blob" data that is more cost-effective. Although "blobs" may sound unpleasant, they are a common concept in computer science, and there are similar data management mechanisms in programming languages such as Javascript and Python.
Proto-danksharding is Ethereum's first attempt at "sharding" technology, which means breaking the blockchain into mini-shards (or mini-chains) so that Process more transactions cheaper.
Although the final sharded version may take several years to implement, Proto-danksharding can help solve the problems that Ethereum is currently facing by reducing the fees of the L2 network. The problem of high gas charges.
The origin of Proto-Danksharding?
Proto-Danksharding is named after two Ethereum researchers, Dankrad Feist and Proto Lambda, who proposed the change.
Proto-Danksharding is an essential prerequisite for the full rollout of Danksharding, which will further simplify data storage. However, Danksharding was still years away.
In addition, although the word "sharding" is included in the name, Danksharding and Proto-Danksharding are not "sharding" (or splitting) the database in the traditional sense. ) for a smaller portion of what is known in computer science (which was Ethereum’s original scaling plan). In a sense, Dencun's choice to introduce Proto-Danksharding is a serious departure from Ethereum's original roadmap, but this choice was made out of considerations for its easier implementation.
Proto-Danksharding’s first step occurred in 2022, when the largest “trusted setup” ceremony was performed. The ceremony is named after researchers Aniket Kate, Gregory M. Zaverucha, and Ian Goldberg, who created key components of blob storage on Ethereum. Thousands of people participate in the KZG ceremony, which is a way for the Ethereum community to work together to generate the secret string of random data required for the original danks shard.
In the Gas-free era of Ethereum, which sectors will benefit the most?
The launch of Dencun will greatly reduce L2 transaction costs, almost to zero cost. This will prompt almost all activity on Ethereum to move to these networks, and some projects or protocols may incentivize usage by consuming gas fees that users would normally pay (cheaper than paying marketing fees!).
After Dencun launches, L2 will be able to publish data to Ethereum within a dedicated blob space, rather than being forced to pay the higher cost of compressing data into in traditional transactions. In theory, this could help L2 process more data more efficiently, thus reducing costs for end users.
Layer 2 networks such as Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon will benefit the most from Dencun. These networks help scale Ethereum by bundling users’ transactions and then passing them to Ethereum, where they are settled in bulk. Over the past year, they have become the dominant platform for trading on Ethereum, amassing multi-billion dollar pools and consistently boasting higher transaction volumes than the main Ethereum chain.
Proto-danksharding will also enable a new class of blockchains to enter the Ethereum competition market, called data availability (DA) layers. . DA layers such as Celestia, EigenDA, and Avail help networks store large amounts of data; L2 often uses them to store transaction data. Proto-danksharding can reduce the cost of downloading DA data.
Polygon co-founder Jordi Baylina once said, "The cost should be reduced, mainly because it is a matter of supply and demand. Your supply is larger, and on Ethereum The data availability will also be greater, so the cost should be lower. How much? We don’t know, it’s difficult to predict.”
Karl Floersch, CEO of OP Labs, a major development company for the Optimism Network, said: "Scalability is about enabling permissionless collaboration between developers across projects and teams. The fundamental unlocking of . With EIP-4844 and Dencun, developers across the entire Ethereum ecosystem can build together more seamlessly." He said that the upgrade "will enable a loosely coordinated group of developers to truly build something that delivers a holistic experience. systems, these experiences will subvert the top-down, centrally planned platform user experience that we have been accustomed to before."
L2 transaction data
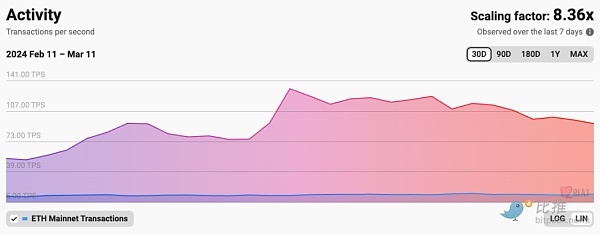
According to L2Beat data, the average per second of the L2 network in the past seven days The transaction volume (TPS) is 93.18, while Ethereum’s average transaction volume per second (TPS) is 14.42, and the L2 Scaling Factor multiple is approximately 8.36.
According to data from L2fees, the average cost of sending ETH using Arbitrum is $0.24, while the cost of exchanging tokens is $0.67. Optimism costs $0.47 and $0.92 respectively, while Polygon costs $0.78 and $2.85.
Fidelity noted in its report on the upgrade that L2 fees account for approximately 10% of total L1 fees. The money manager said it expected this proportion to "decline significantly" following the upgrade.
After Dencun is launched, Ethereum developers will start working on the next upgrade, currently named Electra + Petra.
As of now, the developers have not determined what will be included in the package, but one of the highly regarded upgrades is "Verkle Trees". This is a new type of data structure that helps nodes store large amounts of data efficiently. The development of Verkle Trees is ongoing, and both independent validators and network nodes of Ethereum will benefit from its deployment, which has been confirmed by Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance





