Author: Stacy Muur; Translated by: TechFlow
In just 30 days, 89 projects on 9 blockchains completed more than 2 million gas-free transactions, saving up to $117,000 in gas fees.
This wave of gas-free transactions shows that solutions like Paymaster in ERC-4337 smart wallets can quickly increase on-chain activity by paying fees for users.
Paymaster-driven usage may mask real user demand
A surge in transaction volume does not necessarily reflect real user interest, especially when a small number of wallets (such as traders, robots) repeatedly call contracts.
For example, a one-time airdrop, free minting or claiming event will lead to a surge in the number of wallets in the short term, but subsequent usage may be minimal.
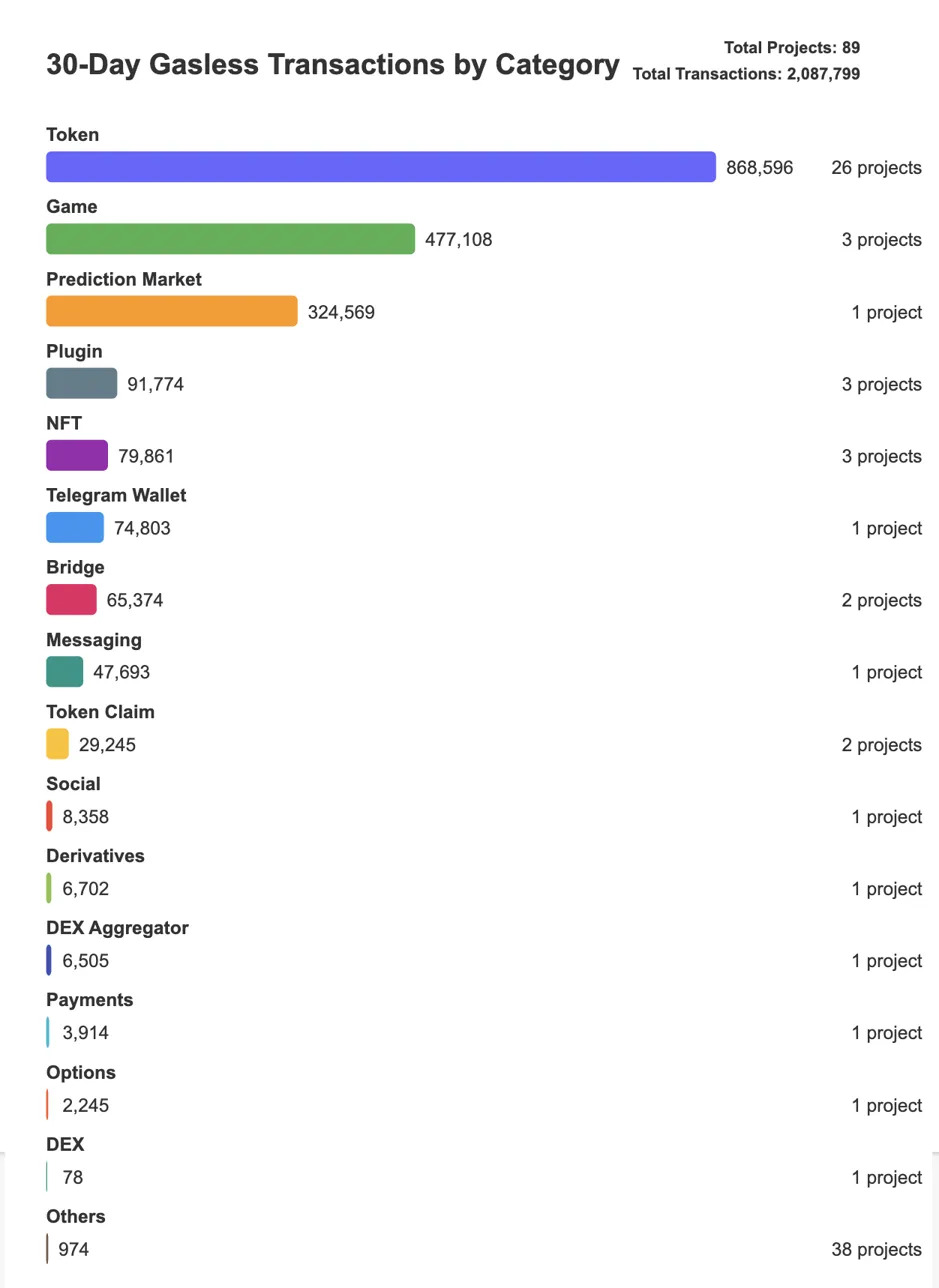
Currently, NFT, game, and token-related projects have indeed attracted a large number of new wallets, but many of them are only used for one-time operations (such as minting or claiming rewards) and there is no sustained user participation.
On the other hand, some applications demonstrate deeper reuse, which is usually due to more attractive gameplay loops, regular DeFi operations, or infrastructure-level services.
These findings show that ERC-4337 smart wallets are reshaping on-chain activities. On the one hand, the sponsorship of Gas fees effectively attracts users; on the other hand, only applications that are attractive and can encourage users to use them repeatedly can truly retain them.
@0xKofi created the definitive dashboard tracking this growth, powered by @base:
https://www.gogasless.io/leaderboard/all
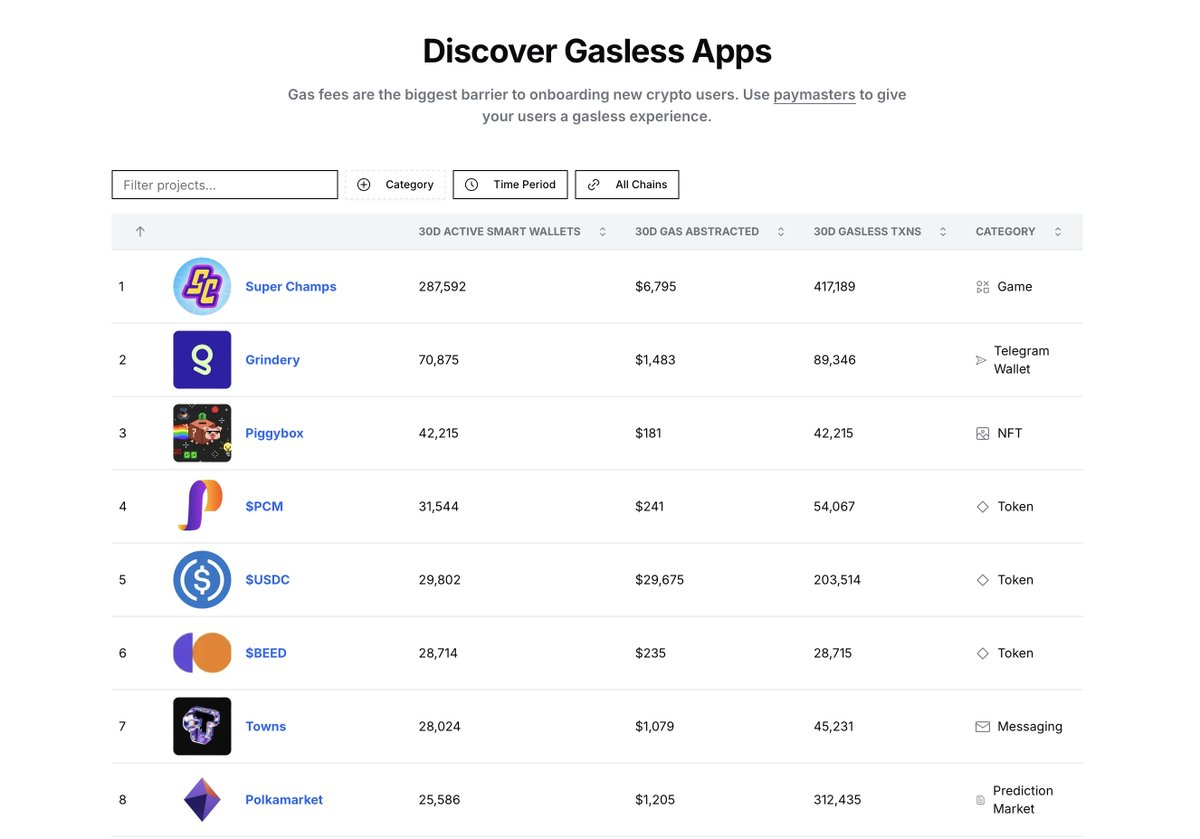
Core Data
89 independent applications/protocols
~724,000 active smart wallets
~$117,000 Gas fees are abstracted
~2.08 million gas-free transactions
The bigger picture of ERC-4337 evolution
The rapid growth of gas-free transactions is part of a larger trend. In 2024, more than 103 million user operations (UserOps) were performed through ERC-4337 accounts, up more than 10x from 2023 (8.3 million). Of these, 87% of transactions were paid by Paymaster, providing a gas-free experience.
Looking at the monthly Paymaster Gas spending chart, an interesting trajectory of this evolution can be seen:
Early Adoption Phase (2023): Spending is low until mid-2023, with Optimism taking the lead.
Growth Phase (Late 2023): Monthly spending grows steadily to ~$400K by October 2023.
Peak Activity (April 2024): Spending surges to ~$700K, driven primarily by Base.
Recent Trends (Late 2024-Early 2025): New highs are reached in November-December 2024 (~$630K), but spending drops significantly in early 2025 to ~$150K in February 2025.
Peak Activity (April 2024): Spending surges to ~$700K, driven primarily by Base.
Recent Trends (Late 2024-Early 2025): New highs are reached in November-December 2024 (~$630K), but spending drops significantly in early 2025 to ~$150K in February 2025.
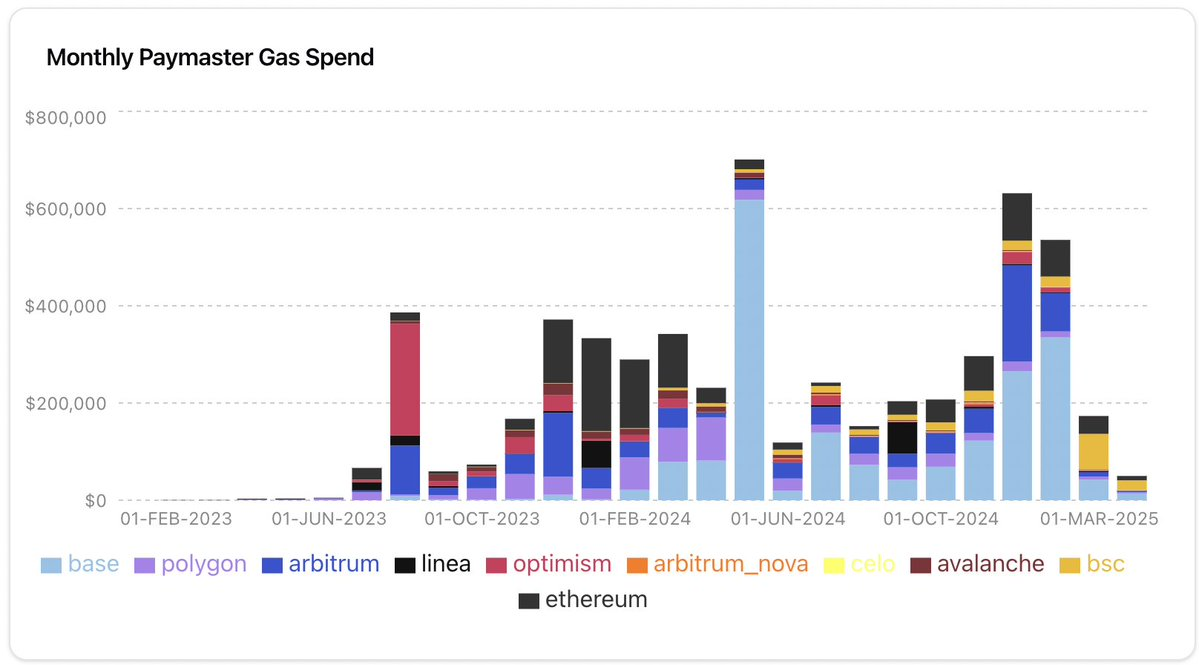
UserOps fees paid by apps and users through Paymaster have exceeded $3.4 million, with major providers including @biconomy, @pimlicoHQ, @coinbase and @Alchemy. Despite the market contraction, total spending in the first quarter of 2025 showed a downward trend, but @base ($391,000), @ethereum ($121,000) and @BNBCHAIN (about $112,000) are still the leaders.
Data source: https://www.bundlebear.com/
Developer: @0xKofi
Chain activity ranking
Base(43.2%): Entertainment and social center, leading the gaming sector (76.8%).
Polygon (21.4%): Community interaction layer, focusing on NFT (50.7%) and Telegram wallet (42.3%).
Optimism (8.5%): Focus on security and emphasize recovery infrastructure.
Celo (7.4%): Expert in niche areas, focusing on prediction markets.
BSC(4.2%): Value transfer layer, with the highest gas cost and a focus on token transactions.
Key insights from the data
Before diving into the data, there are two key metrics to understand:
1️⃣Tx/Wallet (Transactions per Wallet) – Measures the average number of transactions per wallet. Low values (such as 1.0) indicate one-time use, such as minting NFTs or claiming airdrops. High values (such as 25) indicate repeated participation, such as active trading, gameplay, or bot operations.
2️⃣Cost/Tx (Cost per Transaction) – Represents the average cost per transaction. In a gas-free system, this reflects the abstracted fees per transaction, not the actual payment by the user.
1.NFTProjects: Large wallet counts usually mean one-time accounts
Piggybox: ~1 transaction/wallet, ~$0.004/transaction.
Somon Badge: ~1.4 transactions/wallet, ~$0.007/transaction.
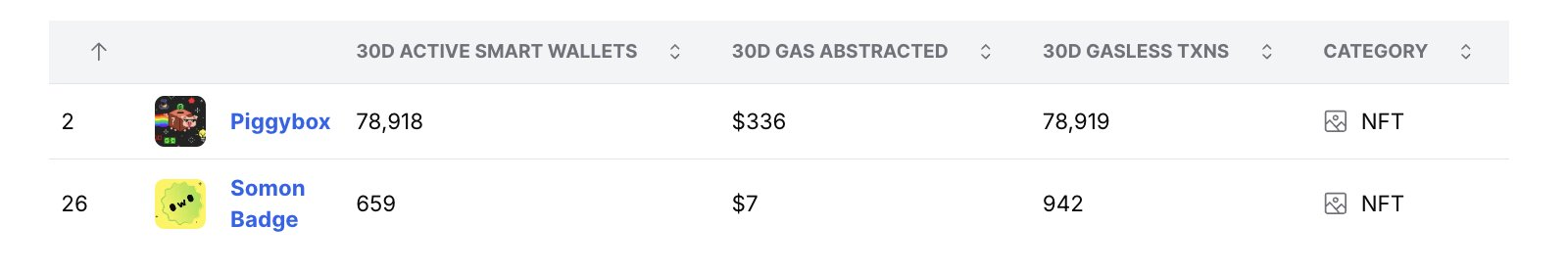
Interpretation: Piggybox’s 1:1 ratio of wallets to transactions strongly suggests that it is mainly driven by minting or claiming activities. Piggybox is an NFT that users receive when they sign up for EARN’M, and comes with a raffle box that may contain EARNM tokens.
One-time surge: Many wallets only make one transaction (initial minting or claiming) and then never use it again, resulting in an almost perfect 1:1 ratio.
Ranking distortion: Due to the large number of new wallets participating in minting, Piggybox ranks at the top of the wallet number/transaction volume ranking. However, if one-time wallets are filtered out, its ranking may fall from the top five, and user retention rate is also very low.
2. Token transactions: A few projects dominate
Data analysis: The total number of token transactions (868,000) seems to dominate, but there are 26 token projects in the list, far more than other categories. However, only two tokens ($BVRP and $USDC) have more than 667,000 transactions, accounting for the vast majority of transactions.

**$BVRP**: An average of about 25 transactions per wallet, with a cost of $0.012 per transaction.
**$USDC**: An average of about 4.6 transactions per wallet, with a cost of $0.21 per transaction.
Interpretation:
This concentration of trading volume shows that not all token projects are equally active, but rather that a few head projects are driving the growth of total trading volume.
$BVRP shows extremely high transaction activity compared to the number of wallets, which may indicate high user engagement on the platform, frequent transactions, and possible automated or repetitive operations.
3. Games: A "hit" and the difference in wallet/transaction ratio
Data analysis:
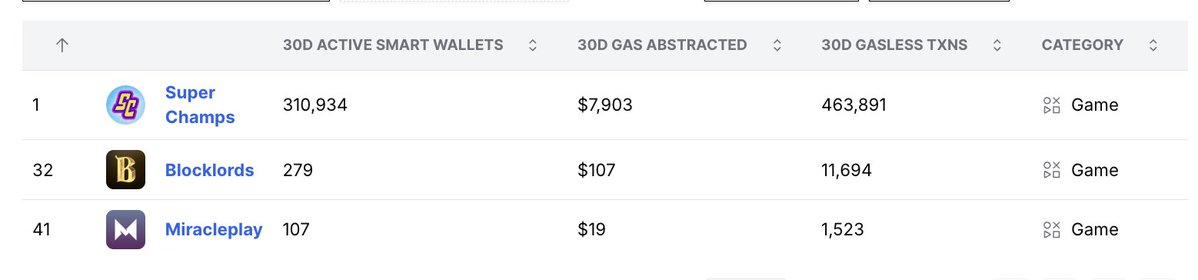
@SuperChampsHQ: ~1.49 transactions per wallet, cost $0.017 per transaction.
@BLOCKLORDS: About 42 transactions per wallet, each transaction costs $0.009.
@miracleplay_cn: About 14 transactions per wallet, each transaction costs $0.012.
Interpretation:
Although Super Champs' total transaction volume (463,000) far exceeds other games (about 13,000 in total), it only completes about 1-2 transactions per wallet, indicating low user engagement.
Although Blocklords has a small number of wallets, the transaction volume per wallet is extremely high (about 42 transactions), which is usually associated with repetitive behavior that may be operated by robots. As David Johansson of Blocklords said: “They are fighting robots.”
https://www.blockchaingamer.biz/features/interviews/33860/blocklords-david-johansson-podcast/
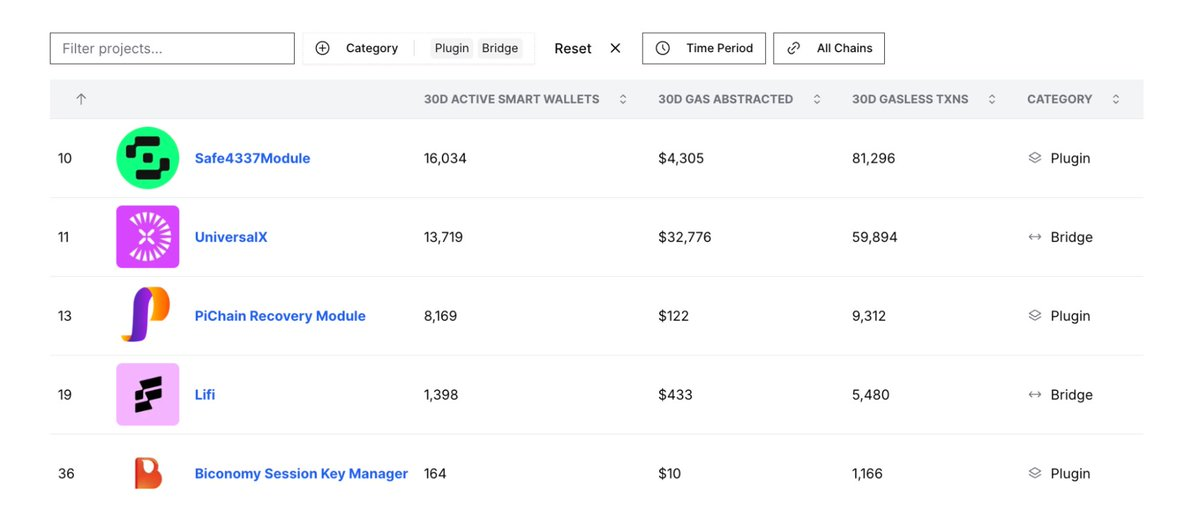
4. Cross-chainBridges and Plugins: Stable Use and Higher Gas Costs
UniversalX: About 4.4 transactions per wallet, costing $0.55 per transaction.
Safe4337Module: About 5.1 transactions per wallet, costing $0.053 per transaction.
Interpretation:
Behind-the-scenes tools: Cross-chain bridges and plugins are not as eye-catching as tokens or games, but their usage remains stable because multiple dApps rely on them.
Ecosystem health indicators: The continued moderate usage of infrastructure services indicates that they provide real practical value, rather than a short-term surge driven by hype.
5. Professionalization trend of on-chain activities
@base: 99.5% of gaming wallet activity (312,361 out of 310,934 wallets).
@0xPolygon: Dominates NFT and social activity, accounting for 87% of the ecosystem’s NFT wallets.
@BNBCHAIN: Leads in high-value cross-chain bridge transactions, accounting for 23.2% of all Gas abstract transactions.
@Celo: Strong performance in prediction markets (25,574 wallets, 12.7 transactions per wallet on average).
6. Cost differences between chains
Gasless transaction costs vary by up to 100x on different chains, driving different application categories to choose specific chains:
Ethereum: $2.41 per Gasless transaction (highest).
BSC: $0.50 per Gasless transaction.
Base: $0.02 per Gasless transaction (lowest among major chains).
Polygon: $0.03 per Gasless transaction.
Conclusion: This huge difference in cost structure will drive specific application categories to choose specific blockchains regardless of technical similarity. For example, high-cost chains are not suitable for games and social applications with high economic requirements.
Overall Observations
NFTAdoption: Although NFT activity may show tens of thousands of wallets minted once (such as Piggybox), subsequent usage is extremely low.
Infrastructure: Cross-chain bridges and plugins have stable usage, with higher transaction costs (cross-chain bridges) or lower volatility as background tools (plugins).
Transaction Pattern Differences: The transaction volume per wallet varies significantly between categories, some are highly repeated operations, and some are "one-time" behaviors.
Long tail of projects: Many projects have little to no user engagement, suggesting that free gas alone is not enough to spark demand; dApps need to offer a real value proposition to retain users.
Key points
Account abstraction and gas sponsorship do drive transactions and user registrations, but the real test is repeat engagement. Combining data on wallet counts, gas abstraction, and gas-free transactions shows that usage in each category tends to be concentrated in a few star dApps or large-scale one-off campaigns. Projects like Piggybox can quickly climb the charts with an almost 1:1 wallet-to-transaction ratio, but quickly drop in the rankings when one-off accounts are filtered out. Cross-chain bridge and plugin solutions, on the other hand, show more stable medium usage, reflecting real needs of the ecosystem rather than short-term hype.
The Role of ERC-4337 Smart Wallets
All of these trends - Gas-free gaming, seamless DeFi, on-chain professionalization - are driven by ERC-4337 Smart Wallets.
Unlike traditional external accounts (EOAs), smart wallets significantly improve the user experience through automation, security, and flexibility.
What is an ERC-4337 Smart Wallet?
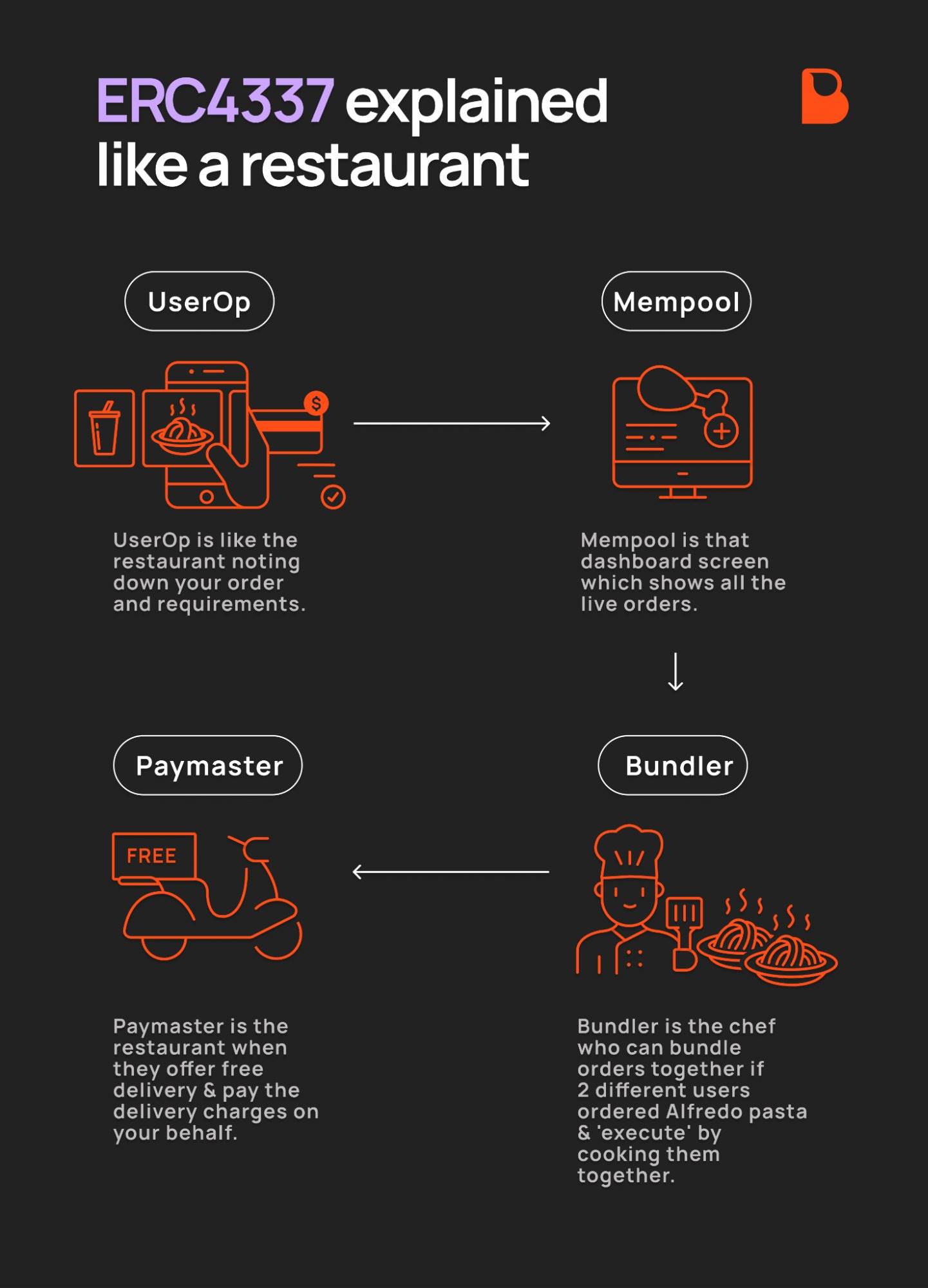
A smart contract wallet (or smart wallet) is a programmable Ethereum account that provides the following features:
✅ Batch transactions: Users can combine multiple operations (such as authorization + trading on DEX) into a single transaction.
✅ Gas fee abstraction: Users do not need to hold ETH to pay Gas fees; fees can be paid by sponsors or paid in other tokens.
✅ Mnemonic-free security: Users can authenticate through keys, social recovery, or multi-factor authentication instead of relying on high-risk mnemonics.
How do Gas-free transactions work?
When a user initiates a transaction, Paymaster (a dedicated smart contract) can pay the Gas fee on their behalf or allow the user to pay with any ERC-20 token. This greatly reduces the entry barrier for new users and makes blockchain applications as smooth as Web2 applications.
Challenges of ERC-4337 and Solutions of EIP-7702
Although ERC-4337 promotes Gasless transactions, it also faces significant adoption challenges, which directly lead to the retention rate issues mentioned above:
Technical barriers: Complex components such as UserOperations, Bundlers, and EntryPoint contracts set high barriers for ordinary users and developers.
Cost issues: Although Gasless transactions are beneficial to users, the cost of implementing a full technology stack is high, and the profitability of packagers will also be affected during Gas fluctuations.
Reliability issues: Network congestion can cause transaction delays, and complex verification logic increases potential security vulnerabilities.
User Experience Defects: Multi-chain fragmentation leads to inconsistent wallet experiences, hindering seamless cross-chain management.
Key Points
Account Abstraction and Gas Sponsorship have indeed effectively increased transaction volume and the number of new wallet registrations, but the real challenge lies in how to maintain continuous user engagement. Data shows:
Many dApps only see a surge in usage during one-time events (such as NFT casting, airdrops), while long-term retention rates are low.
A few star projects drive most of the on-chain activities, while most projects face the dilemma of insufficient actual user demand.
Cross-chain bridges and infrastructure solutions show more stable usage, indicating that they provide real practical value rather than short-term hype.
While ERC-4337 facilitates gas-free transactions and improves user experience, its complexity and cost barriers limit widespread adoption by mainstream users. EIP-7702 fills these gaps by:
As mentioned in the community post, this is particularly beneficial for users who love their external accounts (EOA) and find it too cumbersome to migrate their assets to a new account.
ERC-4337 laid the foundation, but EIP-7702 will make smart wallets cheaper, simpler, and easier to use, accelerating the next wave of Web3 adoption.
 Miyuki
Miyuki












