IMF Pushes Pakistan to Tax Crypto Gains Amid Bailout Talks
IMF demands crypto capital gains taxes in exchange for Pakistan bailout funding.
 Weiliang
Weiliang
Author: Gate Research Institute
From 2012 to November 2024, there were 1,740 public security incidents in the blockchain ecosystem, resulting in a loss of approximately US$33.744 billion.
In 2024, there were frequent security incidents in the blockchain industry, with a total of 369 incidents, resulting in a loss of approximately US$2.308 billion, with hacker attacks posing the main threat.
In 2024, private key leaks caused losses of up to US$1.199 billion, accounting for 62.3% of all hacker attack losses, highlighting the importance of private key security in the industry.
In the first three quarters of 2024, contract vulnerability attacks were the most frequent, among which business logic vulnerabilities, reentrancy vulnerabilities and access control vulnerabilities caused the most serious losses.
Centralized exchanges (CEX) suffered the most serious losses, and DeFi was the most vulnerable area.
Ethereum has become the primary target of hackers due to its mature ecosystem and huge capital scale. Rapidly developing emerging ecosystems such as BSC and Arbitrum have also become new choices for hacker attacks.
Of the stolen funds in 2024, about 25.3% were frozen or recovered, but 58.7% remained in the hacker address.
Regulators in various countries are actively responding to money laundering and fraud in the cryptocurrency field and protecting the interests of investors by strengthening KYC and stablecoin supervision.
While Bitcoin broke through $90,000 and set a record high, Meme coins also attracted much attention from the market. The huge wealth effect of Meme coins such as GOAT, PUNT, and BAN ignited market enthusiasm. However, just as investors were immersed in the fantasy of getting rich, a sudden hacker attack broke the market carnival. The decentralized exchange DEXX was hacked, a large number of user assets were stolen, and the prices of many related Meme coins plummeted. This incident once again highlighted the importance of cryptocurrency market security.
The DEXX incident exposed many security issues of decentralized exchanges, and also warned us that while enjoying the convenience brought by cryptocurrencies, we must attach great importance to security issues. In fact, with the rapid development of the cryptocurrency market, security issues have become increasingly prominent. Hackers use various means, such as system vulnerabilities, phishing attacks, smart contract vulnerabilities, etc., to attack crypto assets, causing users to suffer huge losses.
This article will deeply analyze the current situation and trends in the field of cryptocurrency security in 2024. We will review the major security incidents that occurred this year, analyze the attackers' common methods, attack targets, and losses caused. At the same time, we will also explore classic cases in history and summarize the lessons learned. In addition, this article will also look forward to the challenges and opportunities that may be faced in the field of cryptocurrency security in the future, and explore how regulators and industry participants can jointly respond to these challenges and build a more secure and reliable cryptocurrency ecosystem.
According to incomplete statistics from SlowMist Hacked, from 2012 to November 2024, there were 1,740 public crypto security incidents in the entire blockchain ecosystem, with a total loss of approximately US$33.744 billion. From the overall trend, the number of crypto security incidents and the amount of losses caused have shown an upward trend year by year, especially in 2021 and 2022.
The number of crypto security incidents counted each year has increased year by year from 32 in 2012, reaching a peak in 2021, and then slightly falling back, but still reaching 369 in 2024. With the expansion of the cryptocurrency market and the increase in the value of crypto assets, attacks on the blockchain ecosystem have become more frequent. The amount of losses is highly consistent with the number of incidents, surging from $5.97 million in 2012 to $43.98 billion in 2022, an increase of tens of thousands of times. The amount of losses caused by each attack continues to rise. The rapid development of the crypto market has attracted a large number of participants, but it has also become a "treasure pot" for hackers. Especially in 2021 and 2022, when the crypto market was hottest, the price of crypto assets rose sharply, attracting a large number of speculators and hackers. However, data from 2023 showed that the number of security incidents and the amount of losses fell compared to 2022, which may be related to the overall cooling of the crypto market and the industry's increased attention to security.
Figure 1 Statistics of the amount of losses in crypto asset security incidents over the years (2012-2024)
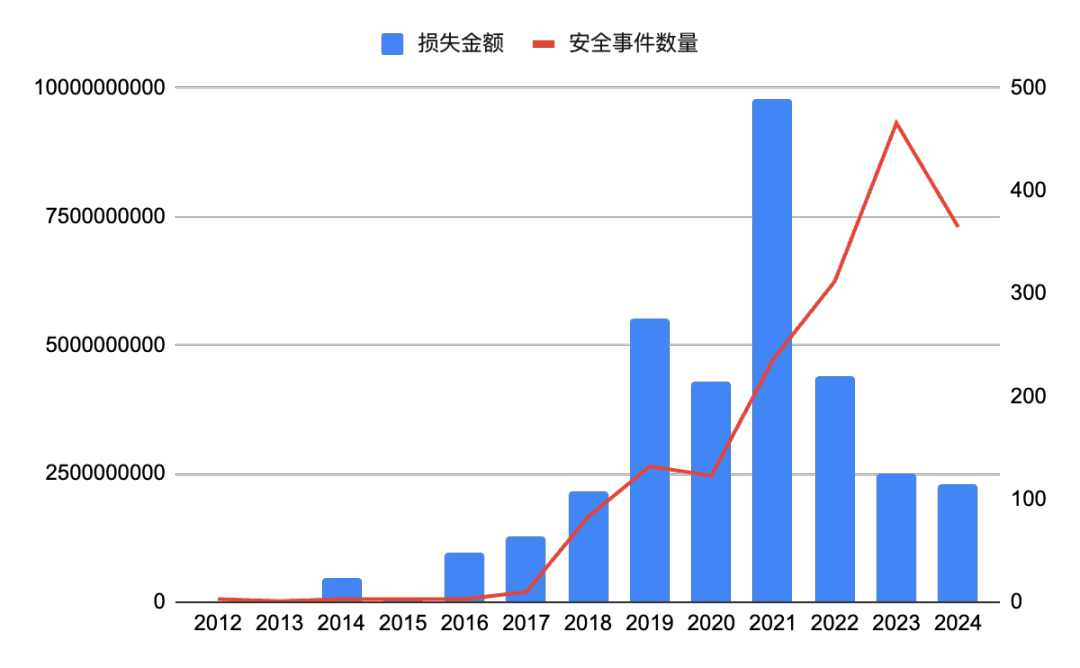
Data: SlowMist Hacked, 2012.01 - 2024.11
From the perspective of attack methods, crypto security incidents over the years are mainly concentrated in ten types, namely: contract loopholes, Rug Pull, flash loan attacks, account hacking, private key leakage, Twitter hacking, price manipulation fraud, wallet theft, information leakage and phishing attacks. Among them, contract loopholes, running away and flash loan attacks are the most common attack methods in recent years, accounting for more than 50% of the total. Specifically, contract loopholes accounted for the highest proportion, reaching 25.7%; followed by running away, accounting for 25.5%; and flash loan attacks accounted for 12.3%. The security of smart contracts, the credibility of project parties, and the design flaws of DeFi protocols are the main risk points in the current encryption field. Rug Pull is a common method of encryption fraud. Scammers create a seemingly promising encryption project by creating a false prosperity to attract investors to invest heavily. Once the funds accumulate to a certain level, the project party will abscond with the money, leaving behind worthless tokens, or directly close the project, causing huge losses to investors.
Thodex, a Turkey-based cryptocurrency exchange, suddenly closed in April 2021. Its founder, Faruk Fatih Özer, absconded with billions of dollars, causing nearly 391,000 users to suffer losses of more than $2 billion, becoming one of the worst runaway incidents in the history of cryptocurrency.
Smart contract vulnerabilities refer to security risks in smart contract codes that hackers can exploit to launch attacks, resulting in losses of user assets.
In June 2016, hackers exploited a reentrancy vulnerability in The DAO smart contract and carried out a reentrancy attack by continuously calling the contract's withdrawal function, successfully stealing about 3.6 million ETH, equivalent to a market value of about $50 million at the time.
A flash loan attack is an attack that uses the instantaneous lending function of the DeFi platform/protocol to borrow a large amount of funds in the same transaction, and then manipulates market prices or uses price differences for arbitrage to obtain improper benefits.
On March 13, 2023, the DeFi lending protocol Euler Finance suffered a flash loan attack. The attacker borrowed a huge flash loan, implemented a high-leverage operation, triggered the liquidation mechanism of the protocol, and eventually stole about $197 million in funds.
Figure 2: Distribution of attack methods in crypto asset security incidents over the years (2012-2024)
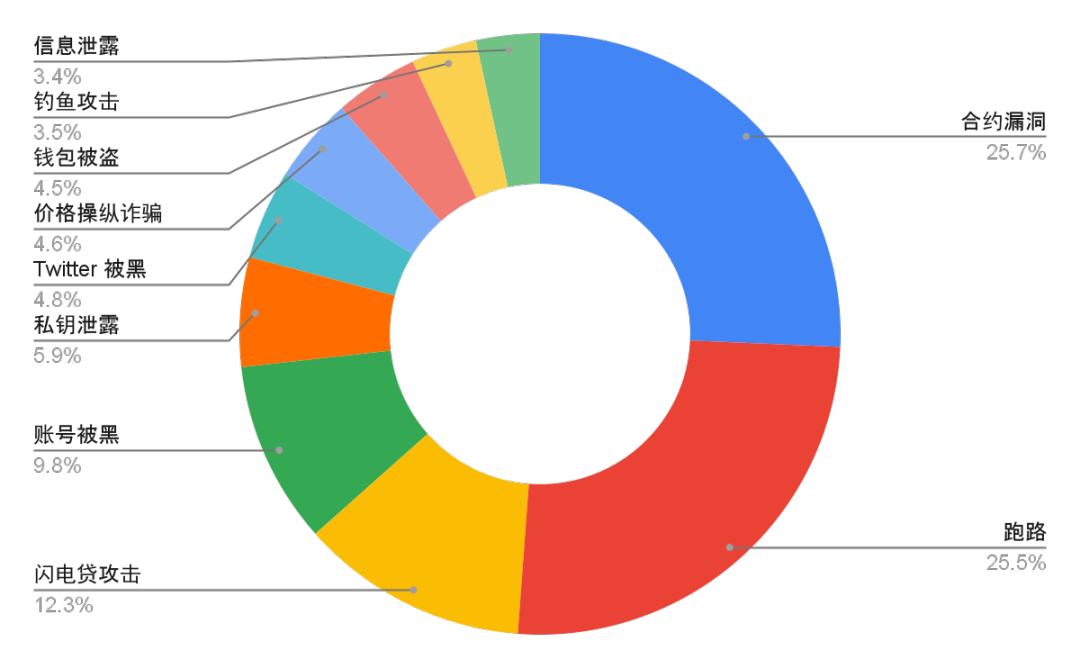
Data: SlowMist Hacked, 2012.01 - 2024.11
From the amount of losses caused by the attack, exchanges are undoubtedly the primary target of hackers. Data shows that the amount of losses in exchanges is as high as 12.374 billion US dollars, far exceeding other categories. This is mainly because exchanges store a large amount of user assets in a centralized manner. Once they are breached, the losses will be extremely heavy. In addition, highly cooperative ecosystems such as the ETH ecosystem and cross-chain bridges, which have frequent capital flows, have also become the focus of hackers. Among them, the ETH ecosystem has a long history of development and many projects, with 379 security incidents, ranking first.
Figure 3 Distribution of attack types of crypto asset security incidents over the years (2012-2024)
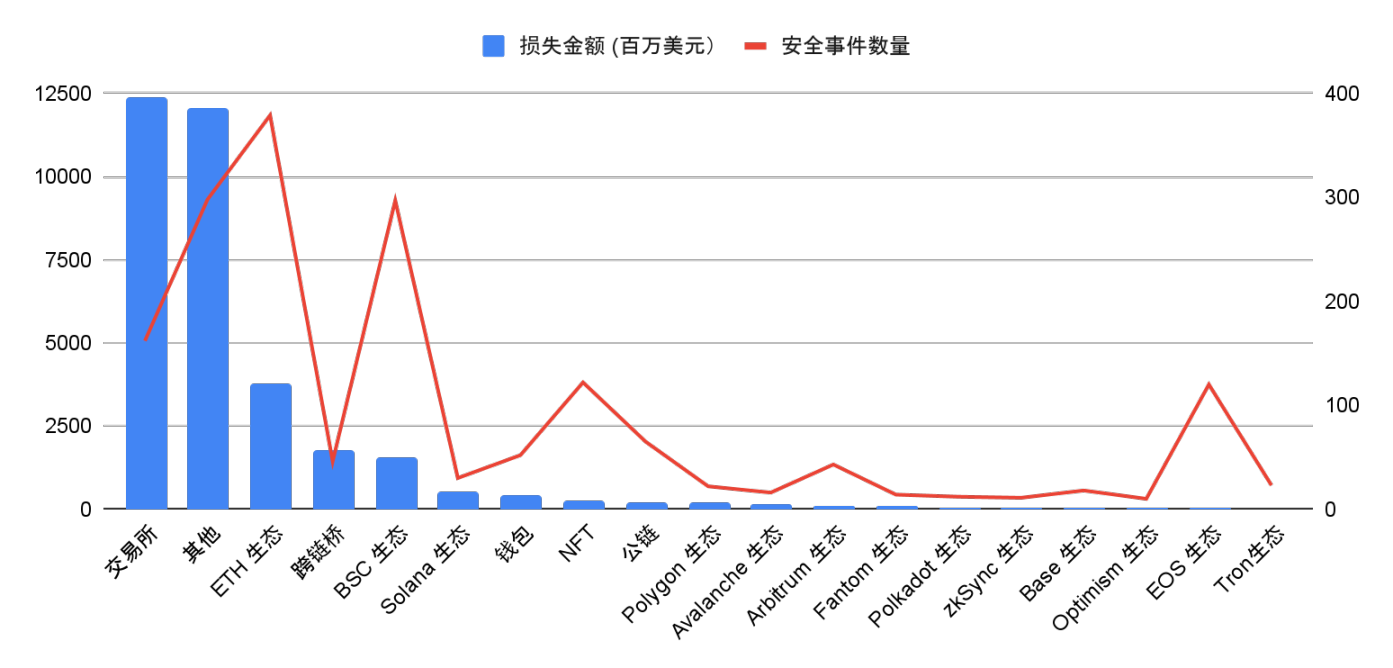
Data: SlowMist Hacked, 2012.01 - 2024.11
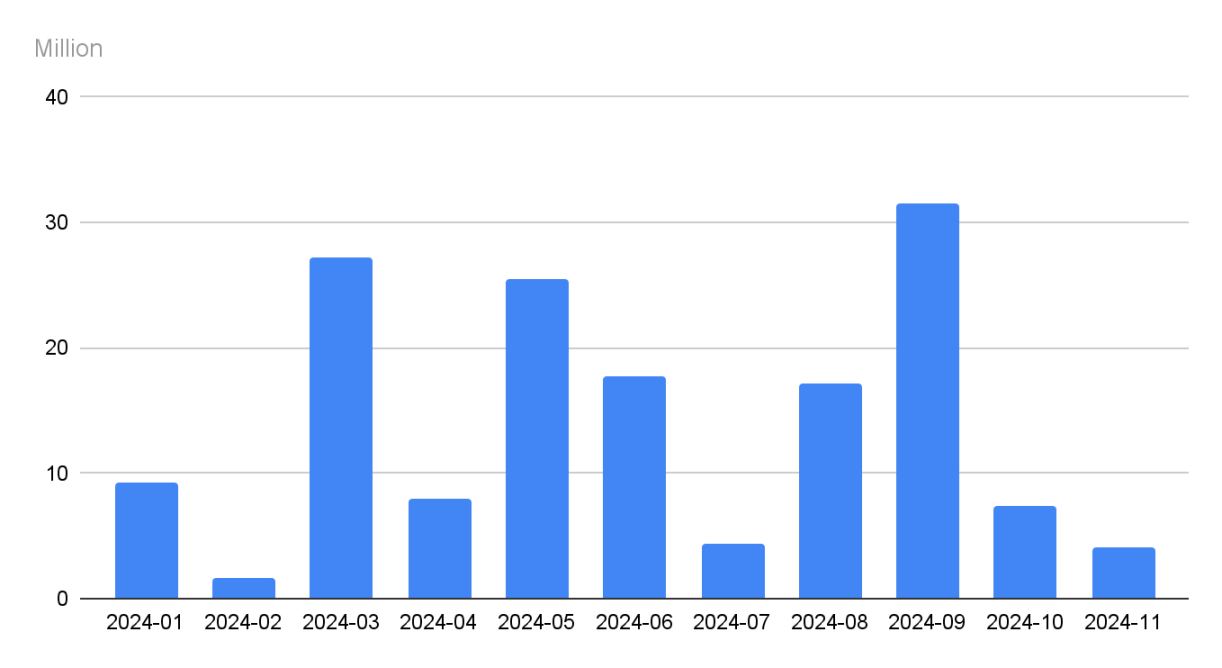
According to incomplete statistics from SlowMist Hacked, there were 369 public crypto security incidents in the entire blockchain ecosystem in 2024, with a total loss of approximately This figure shows that the security issues of encrypted assets cannot be ignored, and frequent security incidents have caused huge economic losses to the industry.
Figure 4 Statistics of the amount of losses caused by crypto asset security incidents in 2024
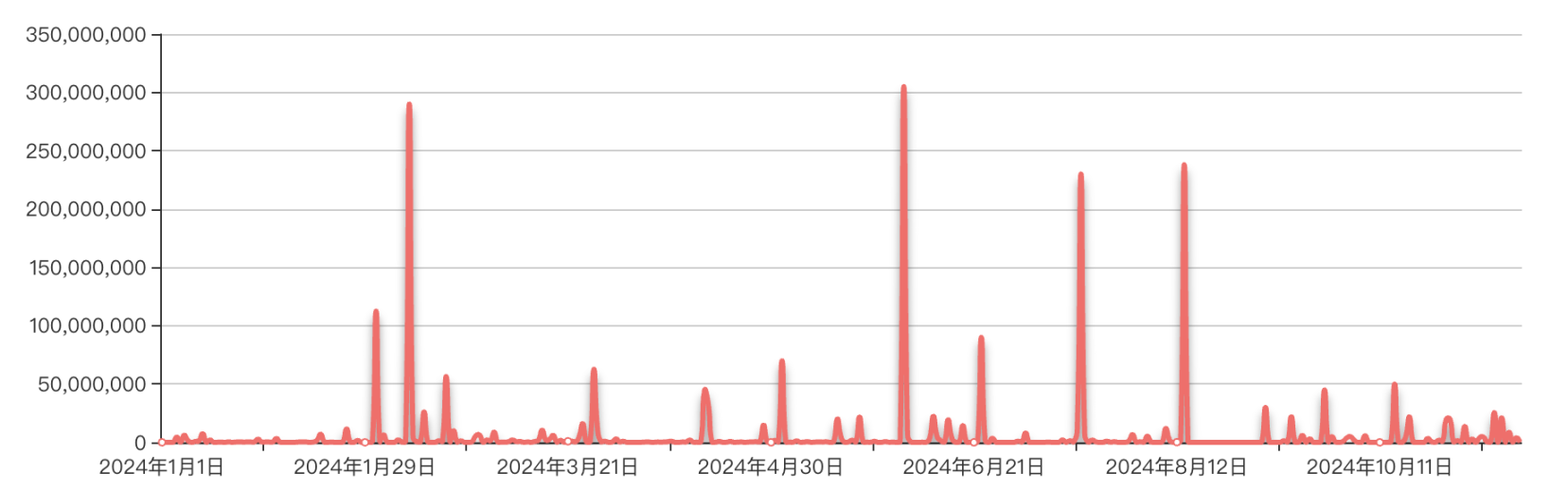
Data: SlowMist Hacked, 2024.01 - 2024.11
We refer to the above-mentioned attack methods over the years, such as contract vulnerabilities, flash loan attacks, account hacking, private key leakage, Twitter hacking, wallet theft, information leakage, etc., as hacker attacks; phishing attacks and price manipulation scams are collectively referred to as phishing scams. Therefore, the attack methods over the years can be roughly divided into three types: hacking, running (Rug Pulls) and phishing.
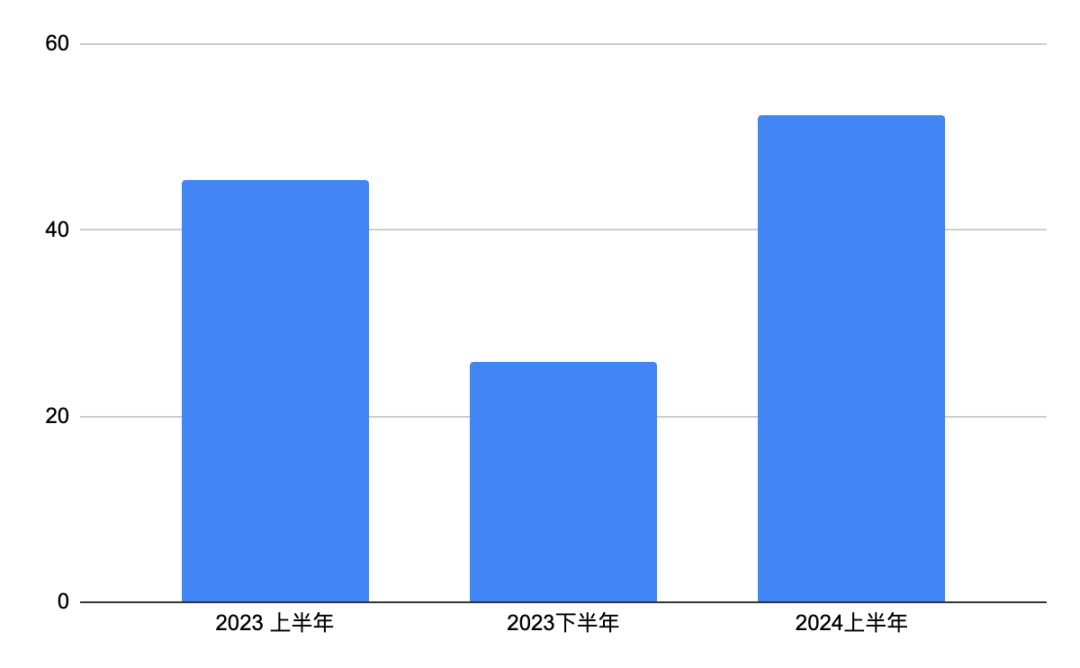
Beosin Alert data shows that in the first three quarters of 2024, security incidents in the Web3 field occurred frequently, resulting in a total loss of up to US$2.276 billion, a year-on-year increase of 45%. Among them, the loss of hacker attacks was the most serious, reaching US$1.624 billion, a year-on-year increase of 59.18%. Hacker attack methods are becoming increasingly complex, posing a serious threat to the security of the Web3 ecosystem. Phishing losses also increased by 191.26% year-on-year to US$528 million. In the first half of 2024, phishing losses increased significantly, indicating that hackers are becoming more and more adept at exploiting users' psychological weaknesses and tricking users into leaking private keys or transferring money through forged websites or information. In contrast, the loss of Rug Pull incidents in 2024 decreased to only US$122 million, a year-on-year decrease of 66.54%. This may be related to the community's increased vigilance against Rug Pull incidents and the strengthening of relevant regulatory measures.
Figure 5 Quarterly loss amounts of different types of crypto asset security incidents from 2023 to 2024
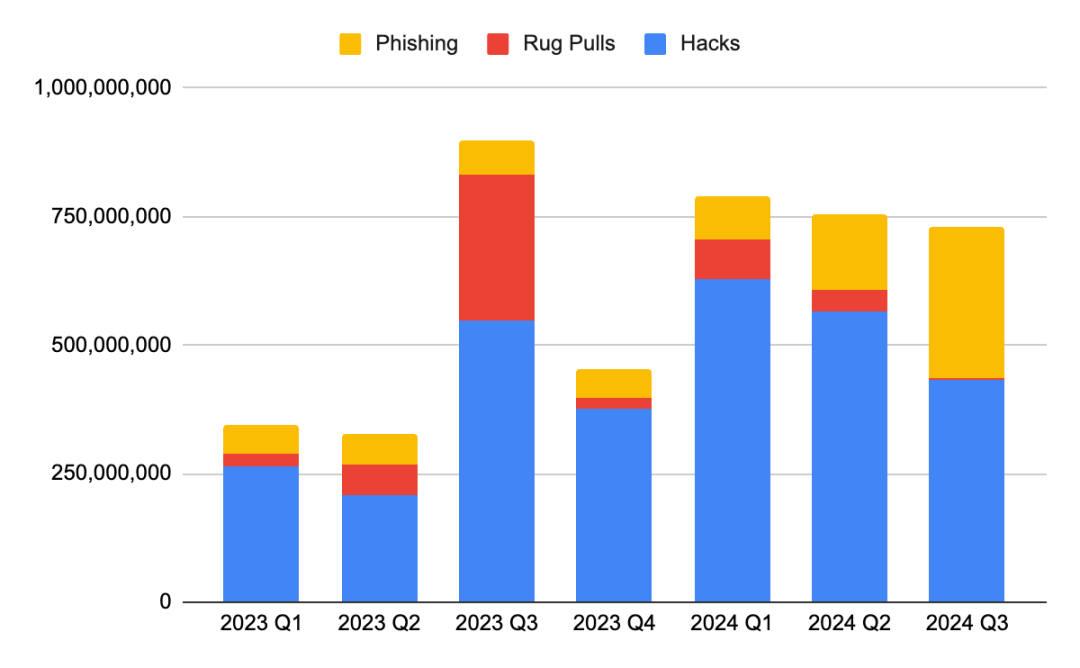
Data: Footprint Analytics, @Beosin
In the first three quarters of 2024, private key leakage incidents caused losses of US$1.199 billion, accounting for 62.3% of all hacker attack losses. Similar to 2023, private key leakage incidents are still the most damaging of all hacker attack types. The second largest loss was caused by attacking social account information, and contract vulnerability exploitation ranked third, accounting for 13.7%.
In 2024, multiple platforms and individuals such as DMM Bitcoin ($308 million), PlayDapp ($290 million), WazirX ($230 million), Ripple co-founder Chris Larsen ($112 million), BtcTurk ($55 million), BingX ($45 million), and Indodax ($22 million) suffered significant losses due to private key leaks. These incidents show that private key security remains one of the biggest challenges facing the cryptocurrency industry.
Figure 6: Proportion of loss amount from different hacker attack methods in 2024
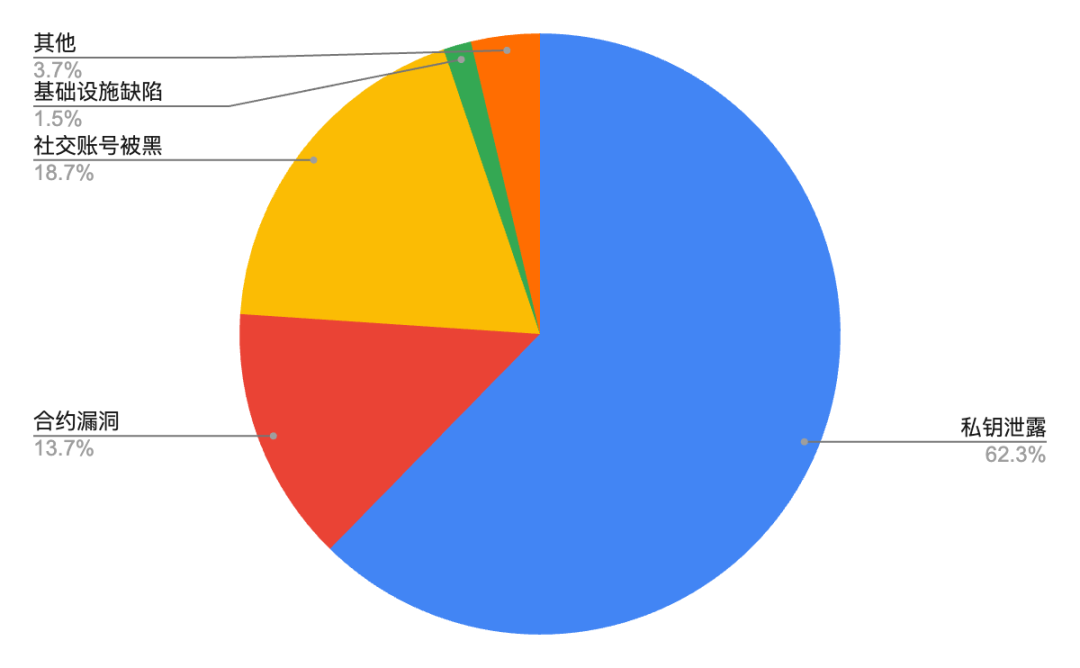
Data: Footprint Analytics, @Beosin, 2024.Q1-2024.Q3
From the number of security incidents, in the first three quarters of 2024, contract vulnerability attacks were the most rampant, accounting for as high as 51.8%. Hackers exploit vulnerabilities in smart contract codes to implement various attack methods to steal user assets. Although the direct economic losses caused by contract vulnerabilities (accounting for 13.7%) are not as serious as private key leaks, their high incidence cannot be ignored. Some projects are easily targeted by hackers due to many defects in their contract design.
Figure 7: Percentage of security incidents caused by different hacker attack methods in 2024
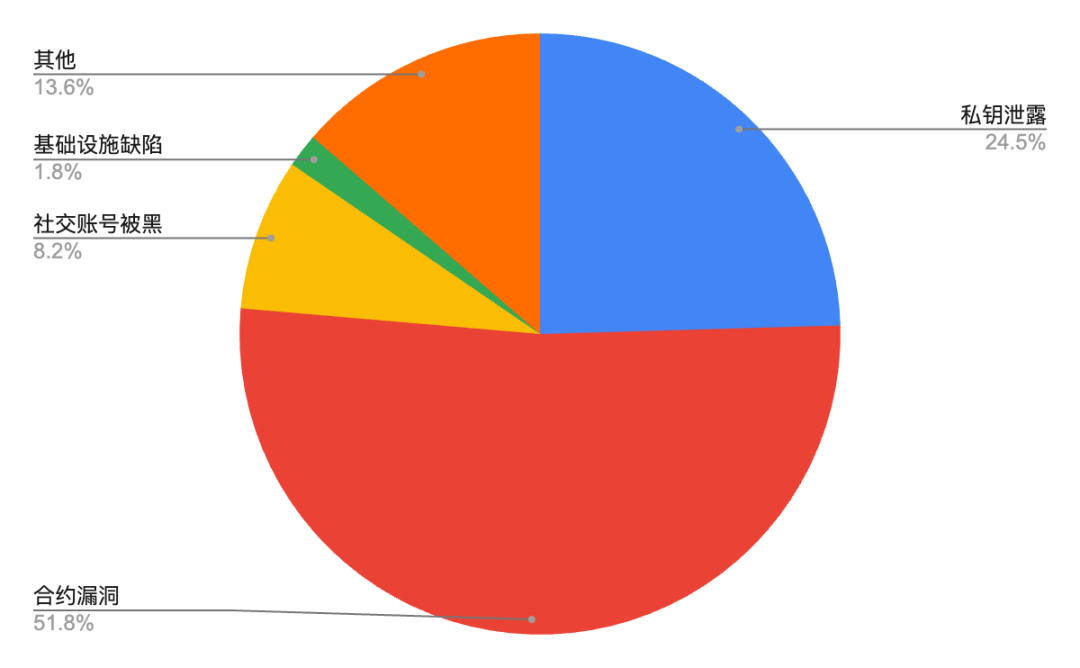
Data: Footprint Analytics, @Beosin, 2024.Q1-2024.Q3
In terms of vulnerability types, the top three vulnerabilities that caused the most losses in the first three quarters of 2024 were business logic flaws, reentrancy vulnerabilities, and access control vulnerabilities, accounting for 34.7%, 34.6%, and 10%, respectively. The most frequently occurring vulnerabilities are also business logic vulnerabilities, followed by validation issues.
Figure 8 The proportion of security incidents with different hacker attack methods in 2024
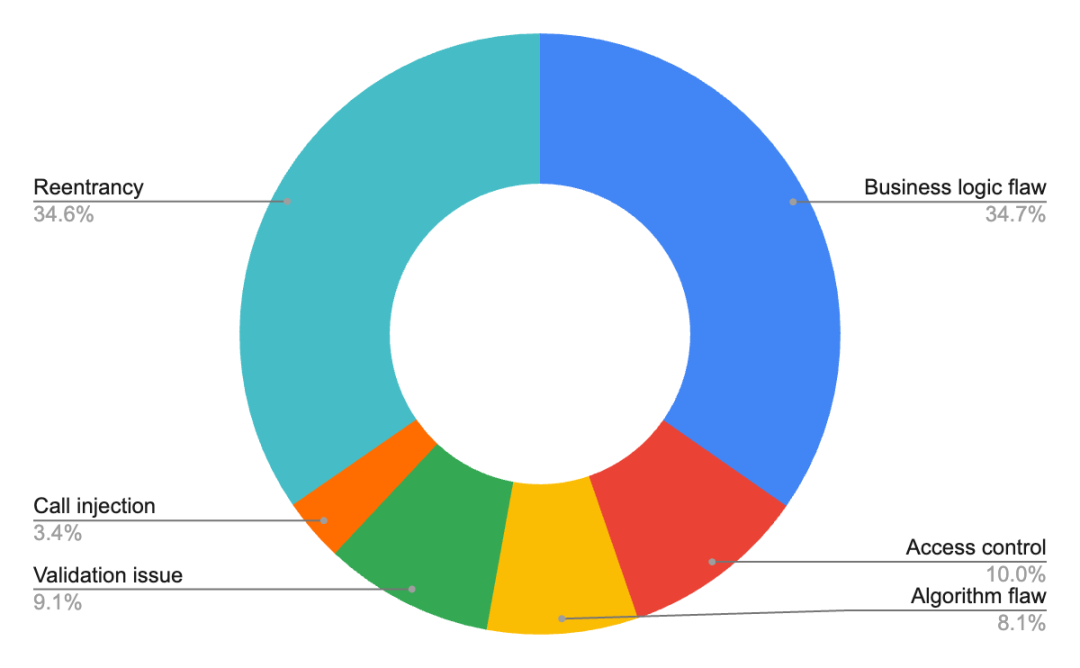
Data: Footprint Analytics, @Beosin, 2024.Q1-2024.Q3
From the perspective of project track, in the first three quarters of 2024, centralized exchanges (CEX) suffered the most serious losses, accounting for as high as 35.8%, with cumulative losses reaching US$688 million. Among them, the DMM Bitcoin incident was the most serious, with a loss of up to $308 million. It is the seventh largest security incident in the history of cryptocurrency hacker attacks and the security incident with the largest loss in 2024. The DMM Bitcoin incident is the third largest cryptocurrency exchange theft in Japan after the Mt.Gox incident in 2014 and the Coincheck incident in 2018. Because CEX concentrates a large number of user assets, it is easier to become a key target for hackers. Although the frequency of security incidents in CEX is relatively low, the losses caused by a single incident are often huge, posing a great threat to the security of the entire exchange ecosystem.
Secondly, wallets and game projects also suffered large losses, accounting for 21.8% and 20.2% respectively. Wallets are the first choice for users to store encrypted assets. Once they are hacked, the losses are often heavy. Game projects have also become high-risk areas for hacker attacks due to their large user base and a large number of virtual asset transactions. Take the attack on Gala Games on May 20 as an example. The attacker minted a large number of tokens and then quickly exchanged them for other mainstream cryptocurrencies, causing huge losses to the platform.
Figure 9: Proportion of loss amount of attacked project types in crypto asset security incidents in 2024
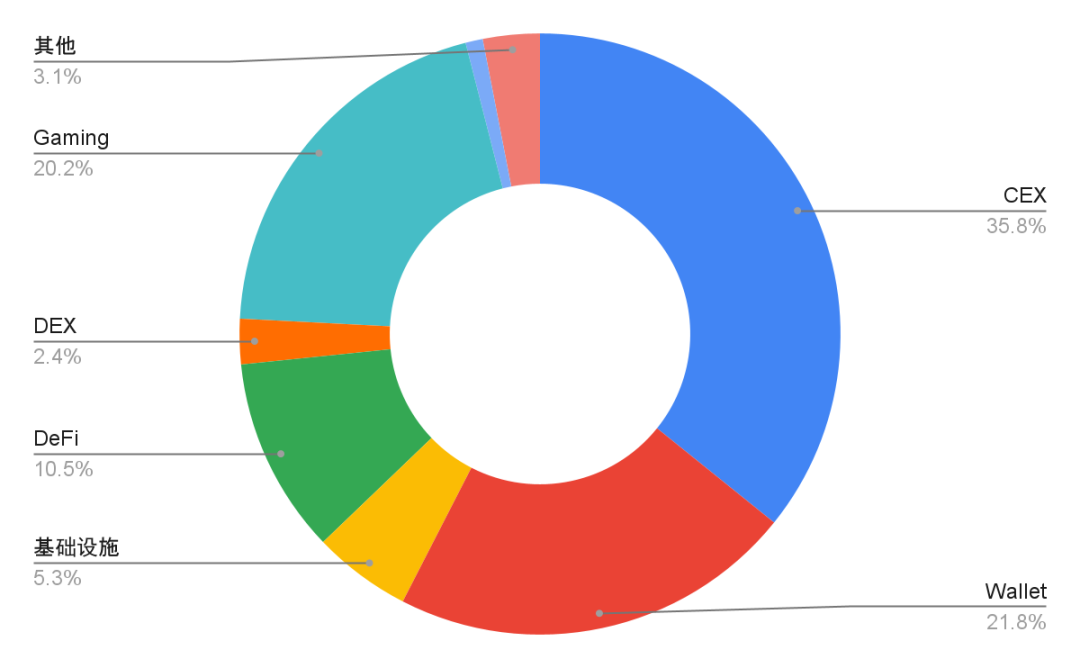
Data: Footprint Analytics, @Beosin; 2024.Q1-2024.Q3
From the number of attacked projects, DeFi is the most vulnerable field. According to Beosin Alert data, in the first three quarters of 2024, the number of attacks on DeFi projects accounted for as high as 45.5%, becoming the main target of hackers. The complexity of the DeFi protocol, the high concentration of funds, and the frequent security vulnerabilities are the main reasons for its repeated attacks. In contrast, although centralized exchanges (CEX) and wallet projects have also been attacked, the number of attacks is relatively small due to the use of multiple security measures. However, DeFi projects are attacked most frequently, but due to the relatively small amount of a single transaction, the direct economic losses caused may be lower than CEX. This is because CEX stores a large amount of user assets, and once it is breached, the losses caused are often more serious.
Figure 10. Percentage of attacked projects in crypto asset security incidents in 2024
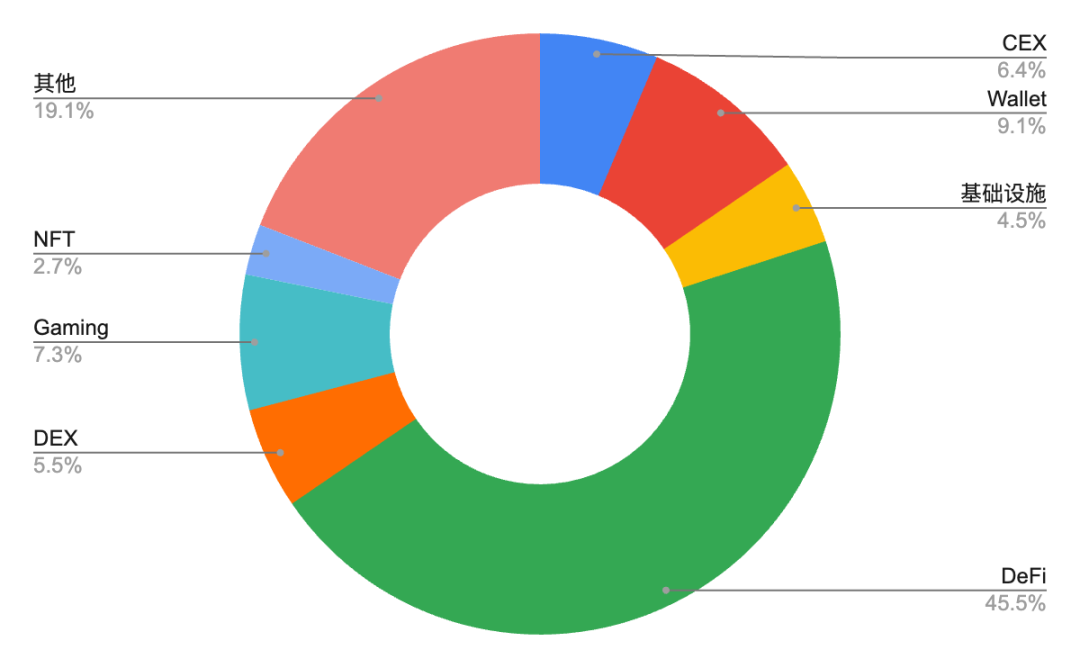
Data: Footprint Analytics, @Beosin, 2024.Q1-2024.Q3
From the perspective of attacked ecosystem, in 2024, Ethereum is still the public chain with the highest loss, reaching US$460 million; followed by BSC, with a loss of approximately US$86.08 million, followed by Arbitrum, with approximately US$83.23 100 million US dollars. Ethereum has become the preferred target of hacker attacks mainly because it is currently the largest smart contract platform with a rich ecosystem and a huge amount of funds. BSC, as a competitor of Ethereum, has also faced a large number of attacks, and the amount of losses is second only to Ethereum.
It is worth noting that the rapid development of the Solana ecosystem in 2024 has also made it the focus of hackers. For example, on May 16, the Solana-based token launcher pump.fun suffered an attack using flash loans, with losses of up to 80 million US dollars. This incident highlights that the Solana ecosystem still has great challenges in security.
In addition, with the rise of Layer2 solutions such as Arbitrum and Optimism, the security of these ecosystems has also received increasing attention. Although these ecosystems have made many technical optimizations, they are still inevitably subject to hacker attacks.
Figure 11 Number of security incidents and loss amount of crypto assets in each ecosystem in 2024
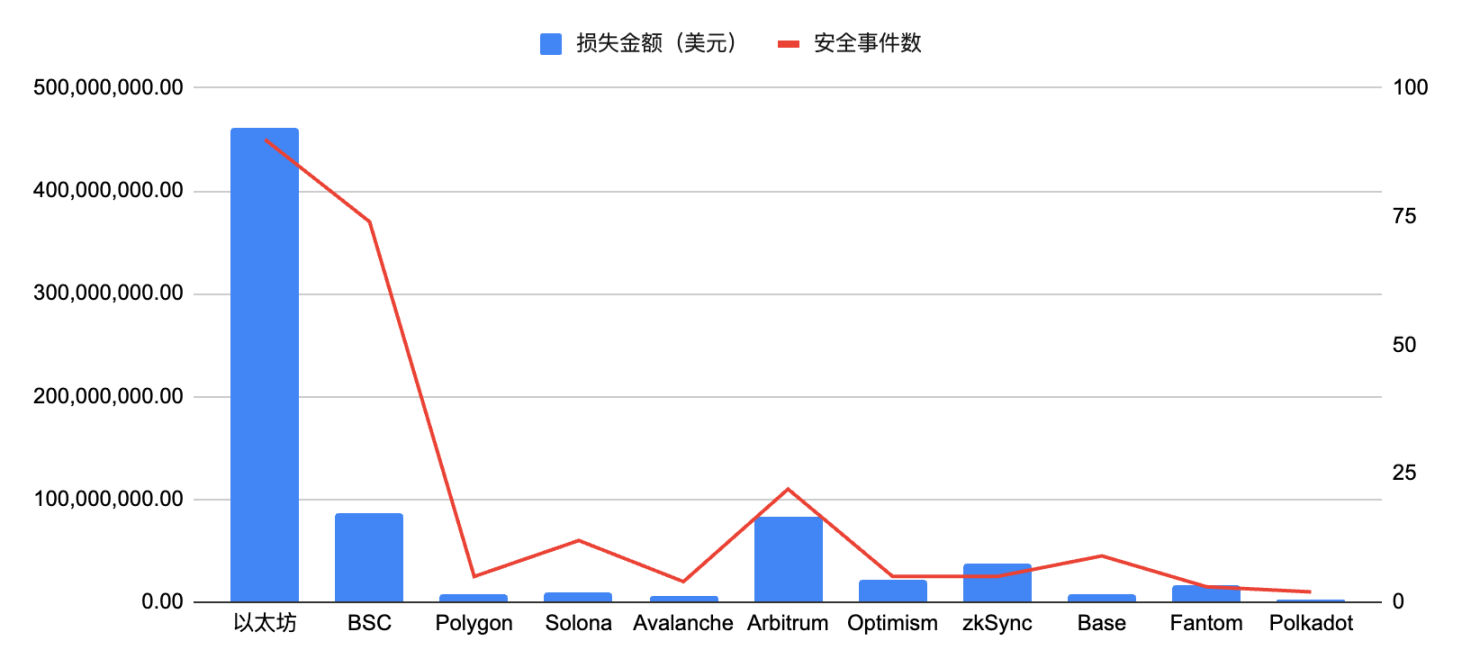
Data: SlowMist Hacked, 2024.01 - 2024.11
In addition, by comparing the loss amount and the proportion of the number of incidents of crypto asset security incidents in each ecosystem in 2024, we can find that the loss amount of the Ethereum ecosystem accounts for as high as 62.6%, which is much higher than other ecosystems. Although the number of security incidents accounts for only 39%, the loss caused by a single attack is much higher than that of other ecosystems. This may be related to its status as the largest smart contract platform, with a rich DeFi ecosystem and a huge amount of locked funds. Once attacked, the losses are often more severe. In contrast, the number of security incidents in the BSC ecosystem is comparable to that of Ethereum, accounting for 32%, but the amount of losses accounts for only 11.7%, indicating that although the incidents are frequent, the losses caused by a single attack are relatively small.
Figure 12: The proportion of security incidents and losses of each ecological crypto asset in 2024
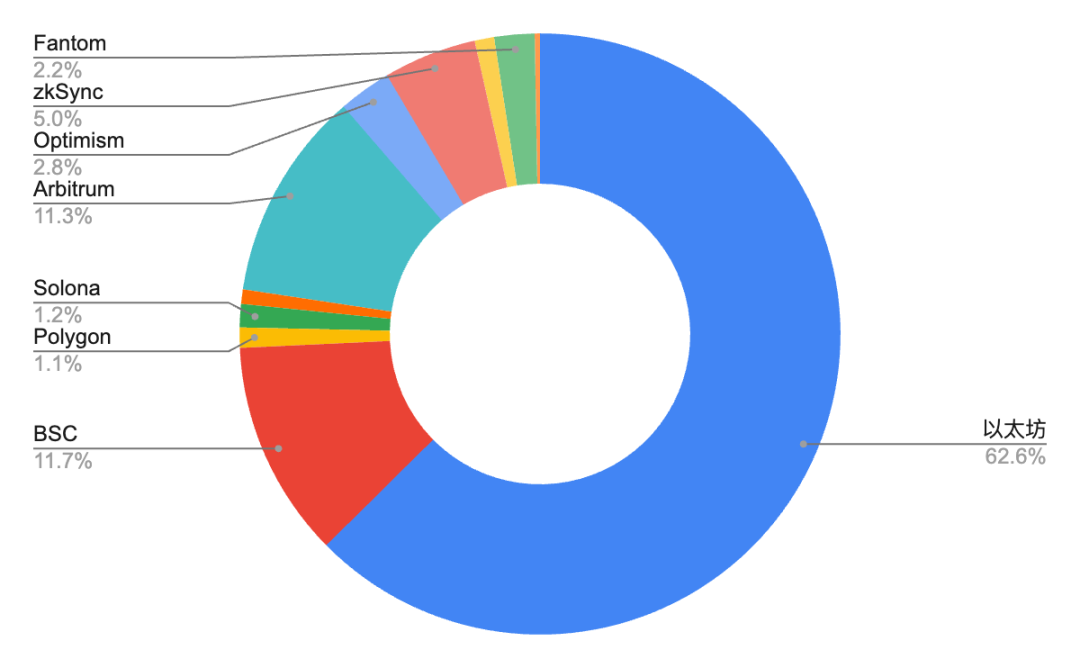
Data: SlowMist Hacked, 2024.01 - 2024.11
Figure 13: The proportion of security incidents of each ecological crypto asset in 2024
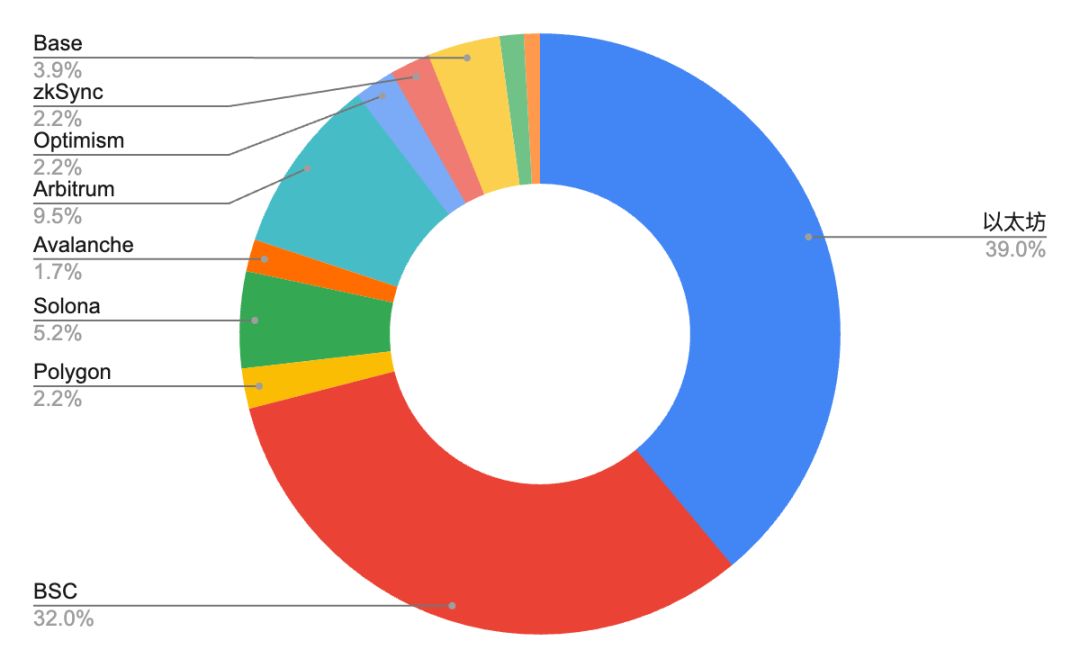
Data: SlowMist Hacked, 2024.01 - 2024.11
In 2024, the cryptocurrency industry faced a severe security situation, and hacker attacks occurred frequently, causing huge economic losses to the industry. The following summarizes some major security incidents in the first three quarters of 2024, covering different attack methods and significant loss amounts.
Figure 14: Some typical attacks on encryption security in 2024
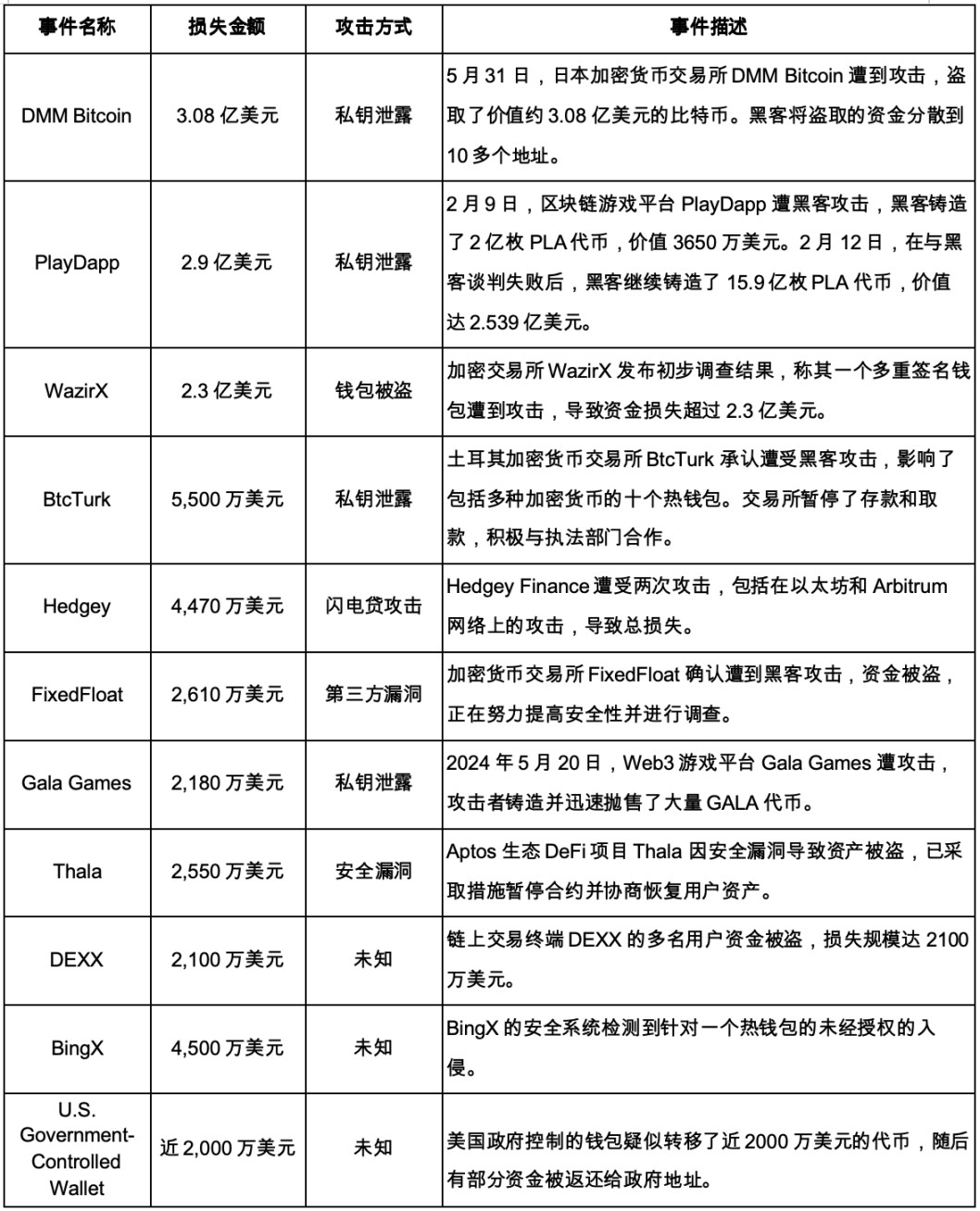
Data: SlowMist Hacked
According to Beosin KYT data, about 25.3% (4.86%) of the funds stolen in 2024 were stolen. In 2020, about 10.9% (US$209 million) of the stolen funds were transferred to exchanges, a higher proportion than in 2023. Only 5.1% (about US$98 million) were transferred to mixers, and the amount of stolen funds cleaned through mixers has been greatly reduced.
Figure 15 Funds flow of crypto security incidents in 2024 (million US dollars)
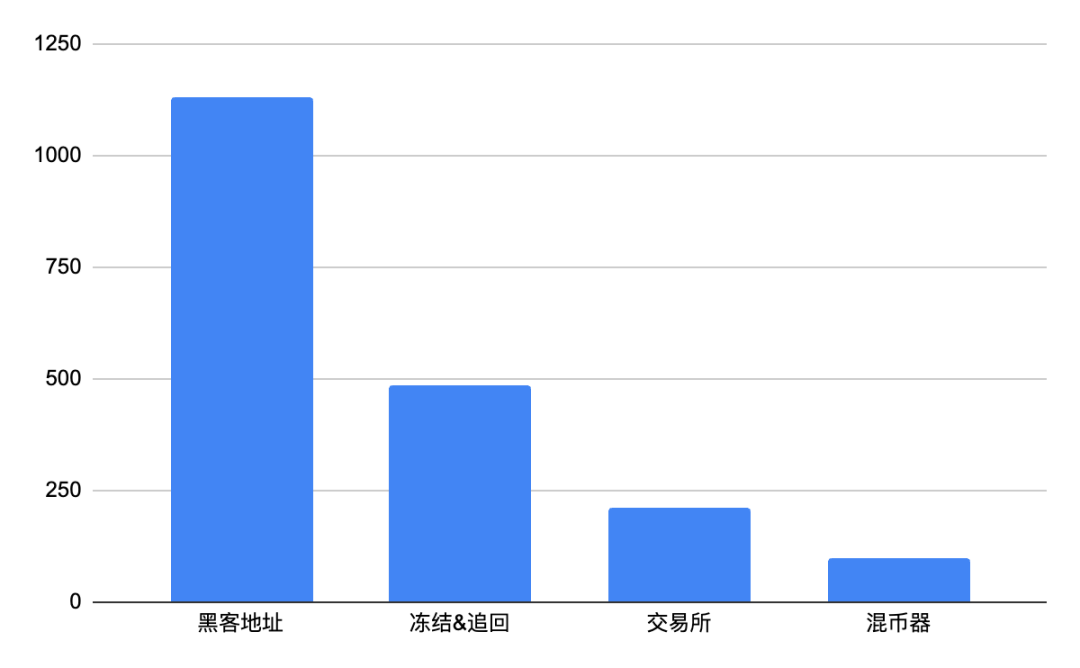
Data: Footprint Analytics, @Beosin, 2024.Q1-2024.Q3
From the above data, it can be seen that there are four main destinations for hackers to steal funds: frozen or recovered, kept in the hacker's address, transferred to the exchange, and cleaned through the mixer. Among them, Tornado Cash is one of the most commonly used mixers. It allows users to improve transaction privacy through mixed transactions, but it may also be used for illegal activities such as money laundering. Beosin KYT data shows that in the first half of 2024, the amount of money laundered by hackers using Tornado Cash increased significantly compared with 2023, an increase of 15.42% compared with the first half of the year and 103.42% compared with the second half of the year, indicating that hackers are increasingly relying on Tornado Cash to conceal the source of their funds.
Figure 16 Amount of funds stolen by hackers flowing to Tornado Cash (million US dollars)
Data: Footprint Analytics, @Beosin, 2024.Q1-2024.Q3
As criminals use mixers such as Tornado Cash to launder money, regulators are paying more and more attention to cryptocurrency mixing services. In August 2022, the U.S. Treasury Department's move to impose sanctions on Tornado Cash marked the regulator's tough attitude towards the balance between cryptocurrency privacy and anti-money laundering. This incident has attracted widespread attention from the entire industry, and compliance and risk management have become the top priorities for crypto platforms. Governments around the world have stepped up their supervision of cryptocurrency mixing services to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
In recent years, the money laundering methods for stolen cryptocurrency funds have become increasingly complex and diverse. Hackers continue to innovate and try their best to conceal the source of funds through multi-layer transfers, mixing services, DEX transactions, and anonymous coins. Among them, the North Korean hacker group Lazarus Group is particularly active, launching cyber attacks on financial institutions and cryptocurrency exchanges many times, causing huge losses. For example, the Axie Infinity Ronin attack and the DMM Bitcoin attack are closely related to the Lazarus Group, and both incidents are among the largest attacks in the history of cryptocurrency.
The money laundering strategy of the Lazarus Group has evolved over the years and has formed a mature and complex system. They usually take the following steps:
1. Initial obfuscation: Deposit the stolen cryptocurrency into a mixer such as Tornado Cash to cut off the transaction chain and achieve initial anonymization.
2. Cross-chain transfer: Use cross-chain protocols such as Thorchain to convert funds into different cryptocurrencies to increase the difficulty of tracing.
3. Fund obfuscation: Lazarus Group obfuscated funds through multiple addresses. For example, part of the funds were transferred to the Bitcoin chain through a cross-chain, and then the tBTC protocol was used to transfer the funds to Ethereum, further increasing the complexity of money laundering.
4. Distributed storage: Distribute the funds to multiple addresses and transfer them to chains with less supervision, such as the TRON chain.
5. Over-the-counter transactions: Conduct over-the-counter transactions through platforms such as Paxful and Noones to convert crypto assets into fiat currency or other cryptocurrencies to circumvent KYC review.
Industry analysts generally believe that the inflow of funds from Lazarus Group to Tornado Cash is closely related, indicating that Tornado Cash plays an indispensable role in hacker money laundering activities. Data shows that the amount of ETH deposited by Lazarus Group through Tornado.Cash has shown a fluctuating upward trend, indicating that its money laundering activities continue to be active. Although regulators continue to strengthen supervision of Tornado Cash, Lazarus Group has successfully circumvented supervision by continuously innovating money laundering methods, such as multi-layer transfers and cross-chain transfers, which has increased the difficulty of law enforcement. In response to the money laundering activities of hacker organizations, regulators need to keep pace with the times and strengthen international cooperation to more effectively combat cryptocurrency crimes.
Figure 17. Amount of money deposited by Lazarus Group in Tornado Cash
Data: DUNE, @tornado_cash
4.3.1 Tracking the stolen funds from DMM Bitcoin: suspected to be the work of Lazarus Group
On May 31, 2024, hackers hacked into the DMM Bitcoin platform and stole 4,502.9 Bitcoins, worth approximately US$308 million. As of December 2, the value of these stolen Bitcoins had risen to more than US$429 million. After the incident, DMM Bitcoin restricted withdrawals and cryptocurrency purchases on the platform to mitigate losses. However, these measures failed to prevent the expansion of losses, but instead had a negative impact on user services.
Blockchain security experts found that the stolen bitcoins were quickly dispersed to multiple wallets and laundered through suspicious platforms such as Huione Guarantee. The attack method and money laundering model are highly suspected to be the work of the North Korean state-backed hacker organization Lazarus Group.
Beosin Trace's tracking shows that the stolen 4,502.9 bitcoins have been dispersed to 10 new addresses. Blockchain detective ZachXBT's investigation shows that Lazarus Group has laundered more than $35 million of DMM Bitcoin stolen funds through Huione Guarantee in Cambodia.
Figure 18 DMM Bitcoin stolen funds path
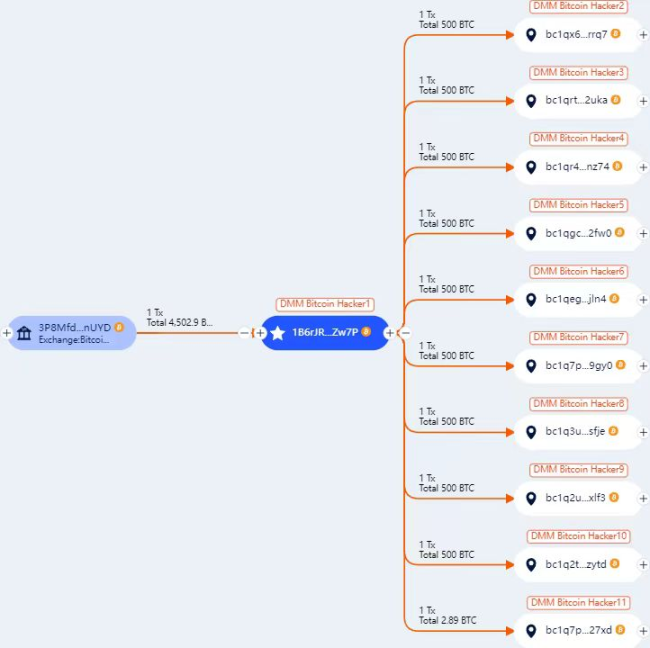
Data: BEOSIN
This incident has aroused widespread market concern about the security of cryptocurrency exchanges. The suspension of DMM Bitcoin highlights the severe security challenges faced by exchanges and has attracted close attention from regulators. The results of the investigation by the Financial Services Agency (FSA) of Japan showed that the company had serious deficiencies in risk management, including the lack of independent audits, the centralization of security functions, and violations of cryptocurrency trading regulations.
The investigation found that DMM Bitcoin had not established a sound risk management system, and its internal audit was non-existent, which failed to effectively prevent the loss of crypto assets. The company did not assign a dedicated person to be responsible for risk management, and the relevant responsibilities were concentrated in the hands of a few people. In addition, the company did not keep key logs that would help investigate the theft, which violated relevant regulations. The FSA has issued a "business improvement order" to the company and emphasized that the company has serious problems in system risk management and responding to the risk of crypto asset leakage.
This incident is one of the most important cryptocurrency thefts in 2024 and the second largest illegal cryptocurrency outflow in Japanese history. It highlights the escalating cybersecurity threats in the digital asset field and has aroused widespread concern about the regulation of cryptocurrency exchanges. The experience of DMM Bitcoin once again reminds us that cryptocurrency exchanges are facing huge security risks. In order to protect user assets, exchanges must continuously strengthen security measures. At the same time, regulators should also strengthen supervision of the cryptocurrency market to maintain market order and prevent similar incidents from happening again.
4.3.2 Turkish Crypto Ponzi Scheme: Stolen Funds Tracking
On May 30, 2024, Turkish police conducted a large-scale raid on a cryptocurrency project called Smart Trade Coin (STC), arrested 127 suspects of fraud, and seized a large number of assets and guns.
Since its launch in 2021, the STC project has attracted a large number of Turkish investors with its promise of high returns that can connect multiple cryptocurrency exchanges and manage multiple trading accounts in a unified manner. However, as time goes by, more and more investors begin to suspect that the project is a Ponzi scheme. Victims' lawyers said that up to 50,000 Turkish investors are deeply involved, and the total loss amount may exceed US$2 billion. Many users reported losing 95% of their savings and were unable to verify whether these funds were misappropriated by the STC team.
Beosin KYT's on-chain fund tracking analysis based on the project name Smart Trade Coin shows that the STC token contract transferred most of the funds through the 0x5f45 address and eventually flowed into the 0xc12c address. Further tracking found that the 0xc12c address conducted a large number of one-way ETH transfer transactions, with a huge amount of transfers, close to the published estimated loss amount. Moreover, all transaction fees involving ETH transfers were paid by the 0xc12c address, which further proves that the address was used to distribute stolen funds.
The figure below only shows part of the fund flow, and the 0xc12c address involved more than 20,000 transfer transactions. According to the tracked transaction data, after the stolen funds were distributed, part of them were directly transferred to major exchanges, while the other part eventually flowed into the exchanges through complex operations such as splitting, merging, and obfuscation.
Figure 19 Smart Trade Coin on-chain fund path
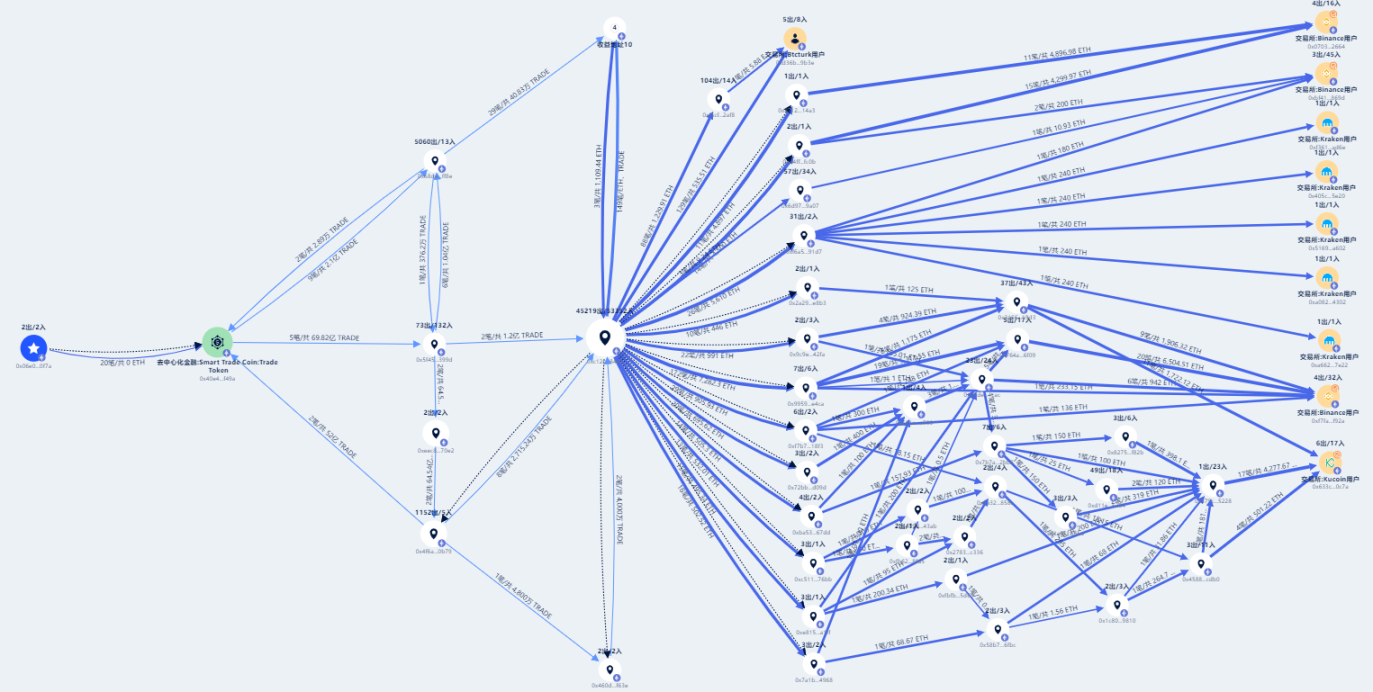
Data: BEOSIN
This incident highlights the serious lack of regulation in the Turkish cryptocurrency market. Although the government has been encouraging innovation, the lack of an effective regulatory framework has allowed criminals to take advantage of the situation and harmed the interests of the majority of investors. Local governments should establish a sound regulatory system as soon as possible to protect the rights and interests of investors and promote the healthy development of the cryptocurrency industry.
Turkey's experience shows that it is not advisable to simply pursue cryptocurrency freedom. While encouraging innovation and development, it is necessary to strengthen supervision and establish a compliant and transparent market environment. Only in this way can cryptocurrency truly play its value and become an effective tool to promote economic development and hedge risks. The government and the industry should work together to formulate sound regulatory laws and regulations, strengthen market supervision, improve industry transparency, and jointly create a safe and reliable cryptocurrency investment environment.
Money laundering activities in the cryptocurrency field are intensifying, posing a serious threat to financial security. Since 2024, in response to this challenge, the global regulatory efforts on cryptocurrencies have been continuously strengthened. Regulators in various countries require virtual asset service providers to strengthen KYC/AML compliance and actively participate in international regulatory cooperation. However, how to protect the interests of investors without stifling innovation is a major problem facing regulators. The cryptocurrency industry also needs to actively adapt to the regulatory environment and seek a balance between compliance and business development.
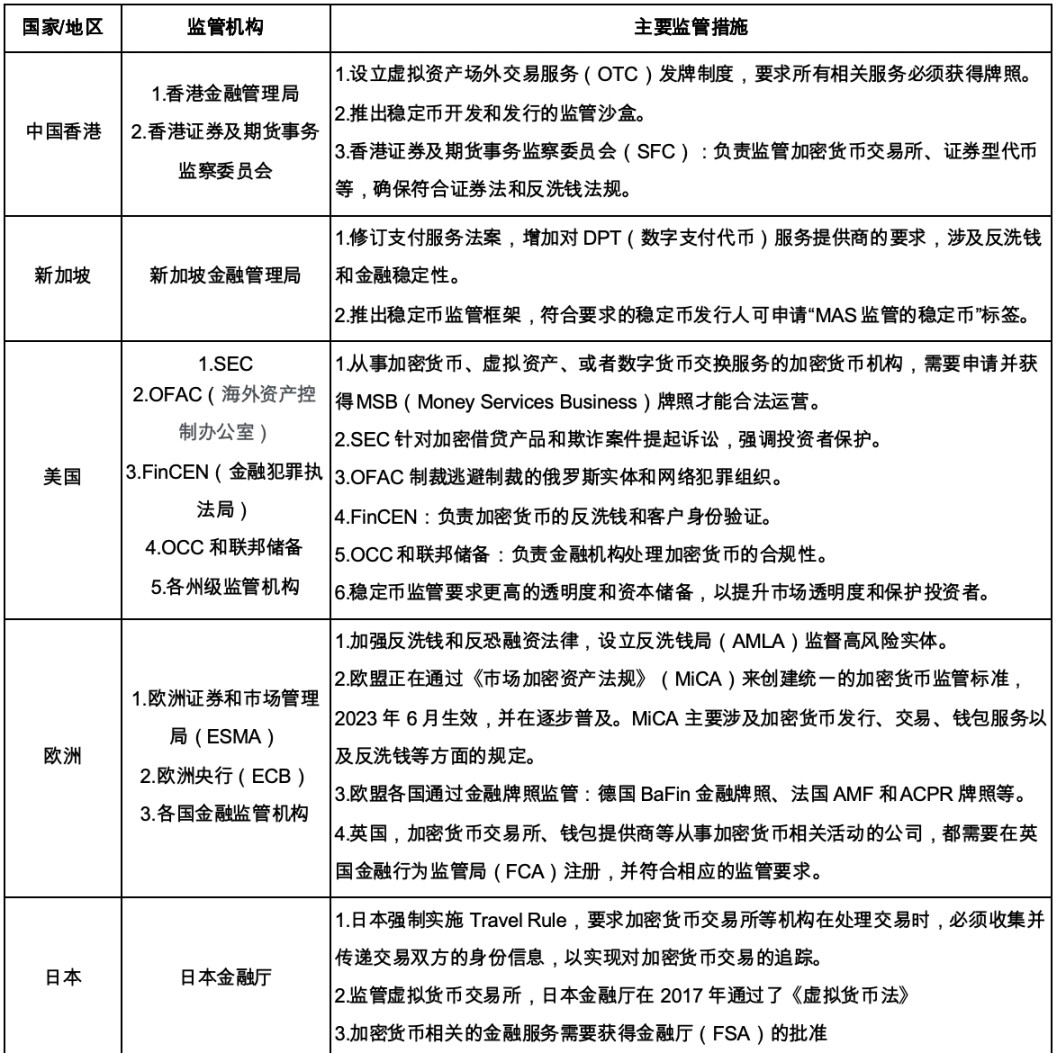
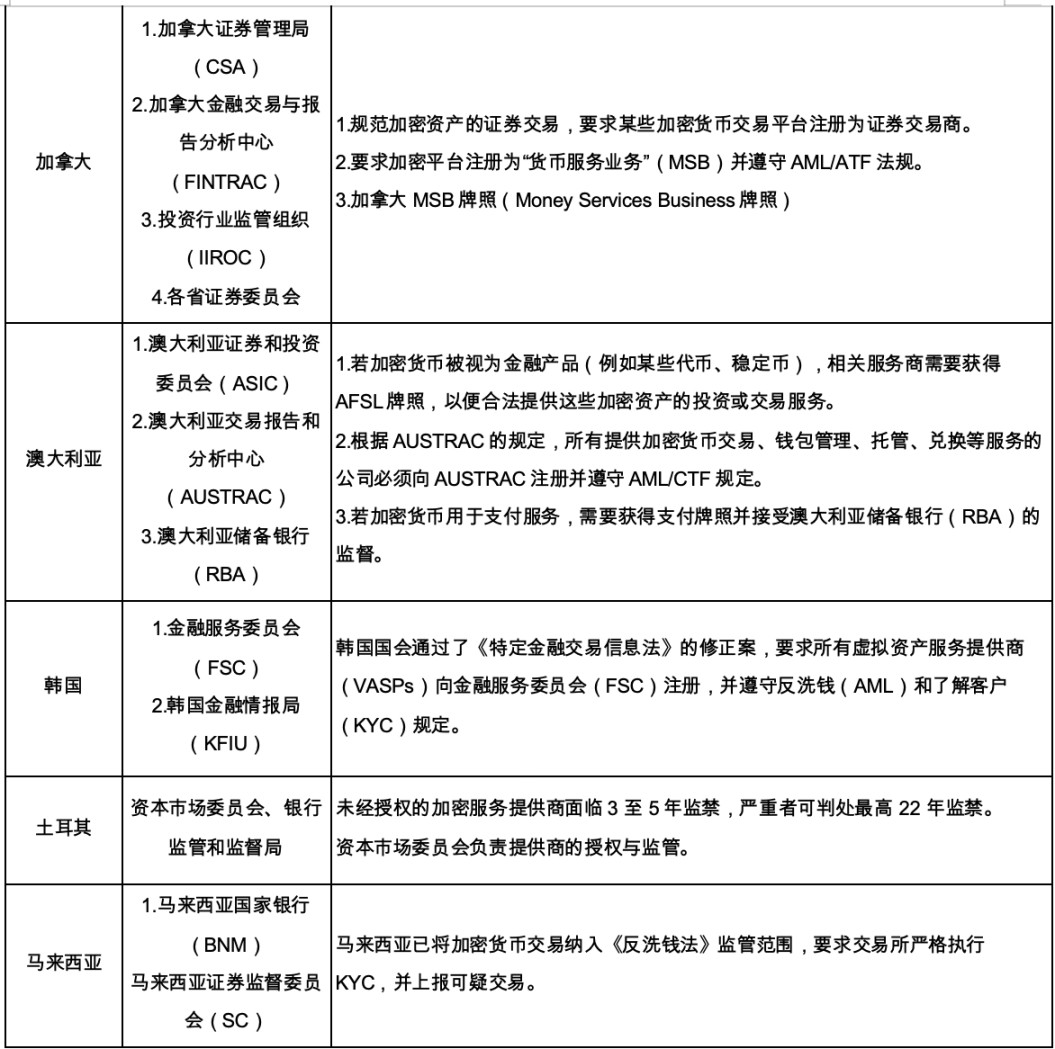
Countries have shown diversity in their practices in anti-money laundering regulation. Taking Hong Kong, Singapore, the United States, Europe, Japan, Canada, Australia, South Korea, Turkey and Malaysia as examples, these regions have all introduced corresponding regulatory policies, mainly focusing on the following aspects: First, strengthen the supervision of virtual asset trading platforms and require relevant licenses; second, strengthen anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing measures, such as implementing the Travel Rule (fund movement rules: This rule requires financial institutions that handle the transfer of encrypted assets to pass customer information to the next institution, which should include the name and address of the sender and recipient), and strengthen KYC certification; third, pay attention to the supervision of stablecoins, requiring improved transparency and capital reserves; fourth, protect the rights and interests of investors and combat fraud and cybercrime. These regulatory measures show that a consensus is forming globally that the supervision of the cryptocurrency market needs to be strengthened to maintain financial stability and protect the interests of investors.
Figure 20 Anti-money laundering regulatory measures for cryptocurrency in various countries
In 2024, the security situation of crypto assets remains severe. Hacker attack methods are constantly updated, which brings significant challenges to the development of the industry. Although old problems such as rug pull, smart contract vulnerabilities and private key leaks still exist, the weak security awareness of users and the emergence of new attack methods have made the security protection of crypto assets more complicated. A number of major security incidents have revealed the vulnerability of decentralized exchanges and other platforms in asset protection, highlighting the urgent need to strengthen security measures.
Security incidents such as the DMM Bitcoin incident and the Turkish crypto Ponzi scheme sounded the alarm, forcing regulators in various countries to accelerate the pace of regulation of the cryptocurrency market. By strengthening anti-money laundering and KYC measures, regulators aim to protect the rights and interests of investors, combat financial crimes, and maintain market stability. At present, countries around the world have taken measures such as issuing licenses, strengthening anti-money laundering, protecting investors, and regulating stablecoins. For example, Hong Kong, China, has introduced a virtual asset OTC licensing system, and Singapore has strengthened supervision of digital payment token service providers. The US SEC has strengthened supervision of crypto lending products, and Europe has passed the Market Crypto Assets Regulation (MiCA), which provides a unified regulatory standard for the cryptocurrency market. These regulatory measures are aimed at balancing innovation and risk, and building a safer, more transparent and compliant ecosystem for the cryptocurrency industry.
In the future, the cryptocurrency industry will still need to find a balance between innovation and security. Only by improving technical means, strengthening security protection and improving the legal framework can we effectively deal with increasingly complex cyber threats. In addition, international cooperation between regulatory authorities of various countries is crucial, which will promote information sharing and coordinated regulatory strategies, and jointly build a safer and more transparent cryptocurrency ecosystem. Only in this way can we achieve long-term sustainable development and create a safer investment environment for investors.
IMF demands crypto capital gains taxes in exchange for Pakistan bailout funding.
 Weiliang
WeiliangBakkt stock jumps as leadership transition aims to capitalize on custody firm's turnaround.
 Alex
AlexAvalanche memecoin Sender's implosion amid suspicious fund movements reignites exit scam fears.
 Alex
AlexBlackRock's $100M tokenized Ethereum fund paves institutional DeFi path amid regulatory vetting.
 Miyuki
MiyukiGenesis Global, a bankrupt crypto lender, agrees to a $21 million penalty tied to Gemini Earn, settling SEC charges of securities law violations.
 Weiliang
WeiliangThe UK's FCA aims to recover $8 million for supervising stablecoins and crypto, part of a broader regulatory agenda.
 Alex
AlexStarknet has adjusted its airdrop schedule for eligible Immutable X users and pooled Ether stakers, resolving technical issues and allowing users to claim their STRK tokens in April. However, the process has faced criticism and challenges, impacting the price of STRK.
 Miyuki
MiyukiThe Nigerian High Court has ordered Binance to provide user data to the EFCC amidst allegations of criminality, impacting the cryptocurrency landscape in Nigeria.
 Weiliang
WeiliangNotcoin, a popular Telegram clicker game, is preparing for a token airdrop, attracting millions of players and introducing NFT vouchers for trading.
 Alex
AlexAethir sold $60 million of Checkers nodes in under 30 minutes, aiming for decentralization. Its low-barrier approach includes NFT licenses and easy software operation.
 Miyuki
Miyuki