Author: Arunkumar Krishnakumar, CoinTelegraph; Compiler: Tao Zhu, Golden Finance
1. What is a corporate treasury?
Corporate treasuries are the financial nerve center of a company, tasked with ensuring liquidity, managing risk, and optimizing returns. They are traditionally conservative, relying on fiat currencies, bonds, and other stable investments. However, MicroStrategy has broken this pattern by adopting Bitcoin as its main funding reserve.
The main functions of a company's treasury department include the following.
Liquidity Management: Ensure that the company has enough cash to meet its obligations. This also involves ensuring that there is no liquidity mismatch between assets and liabilities. If short-term debt is expected to be financed by
long-term assets, that is a significant risk.
Risk Mitigation:Manage interest rate fluctuations, currency risk, and credit risk. Typically, there are risk management teams that specialize in market risk, credit risk, operational risk, and liquidity risk. Treasury works closely with these functions to ensure that its financial decisions take all of these risk factors into account.
Short-term Investments:Corporate finance holds the company's assets. It can be equity, debt, or simply the cash flow generated by the business. Treasury is responsible for allocating excess cash to low-risk, liquid assets to generate a return. Their role is to ensure that the rate of return on the company's assets is optimized while risk remains as low as possible.
Debt Management:Handling loans and credits to maintain optimal leverage is an important function of Treasury. This function is often referred to as Asset and Liability Management (ALM). As mentioned earlier, this function is not only responsible for managing the company's liabilities, but it is also crucial to ensure that there is no maturity mismatch between assets and liabilities. A company cannot plan to fund liabilities (debt interest payments) that are due in a week with assets that mature in a month.
Strategic Planning:Supporting long-term goals through efficient capital allocation is one of the strategic functions of corporate finance.
Thus, the goal of money managers is to strike a delicate balance between risk and return. Their primary goal is to protect the company's assets from market downturns or liquidity crises while ensuring the best returns for the remaining funds they manage the company. They should also perform risk management for periods of market volatility and stressed conditions.
This is the point of MicroStrategy's inclusion of Bitcoin in its treasury, challenging traditional norms and adopting a high-risk, high-reward strategy. As a result, this bold strategy has not only transformed its balance sheet, but also its stock performance, cementing the company's position as a pioneer in cryptocurrency adoption.
Other companies that have adopted or are considering Bitcoin as a treasury reserve asset include Metaplanet, Semler Scientific, DeFi Technologies, Solidion Technology, Nano Labs, and Cosmos Health.
2. MicroStrategy: A Visionary Bet on Bitcoin
Once the darling of the Internet bubble, MicroStrategy suffered a major blow after 2000, but achieved a remarkable transformation under the leadership of Michael Saylor, driven by innovative financial management.
By 2002, MicroStrategy's stock price hovered between $1 and $2, reflecting market disillusionment and internal challenges. Over the next two decades, the company regained influence with its data analysis tools. However, its breakthrough transformation began in 2020 when it adopted Bitcoin as a treasury reserve.
Bitcoin Adoption
MicroStrategy co-founder and executive chairman Michael Saylor sees Bitcoin as an antidote to fiat inflation. He believes that the purchasing power of the dollar is rapidly eroding, while Bitcoin has excellent value preservation capabilities due to its limited supply. This strategy transformed MicroStrategy into a hybrid of a software company and a cryptocurrency investment vehicle.
MicroStrategy’s Bitcoin Accumulation Journey
As of November 24, 2024, MicroStrategy holds 226,500 bitcoins, solidifying its position as the world’s largest corporate bitcoin holder.
MicroStrategy uses a variety of financing strategies to fuel its bitcoin purchases. Its strategy needs to be in line with mainstream financial services norms while ensuring it can handle volatile assets such as bitcoin.
Equity Issuance:The company issues new shares to raise funds, benefiting from rising share prices as bitcoin becomes accepted. Rising bitcoin prices mitigate the risk of selling pressure from new share issuances. This strategy must be timed.
Debt Financing:Convertible bonds that offer low interest rates and future conversion options become a key tool. In addition, senior secured notes help fund purchases during periods of Bitcoin decline.
Free Cash Flow:Operating profits are redirected to increase Bitcoin reserves.
Bitcoin-backed loans:Leveraging existing Bitcoin holdings enables the company to access additional liquidity without diluting equity.
By combining the above strategies, MicroStrategy has built a treasury holding $22 billion worth of Bitcoin.
III. MicroStrategy's Bitcoin Acquisition Timeline
MicroStrategy's bold Bitcoin acquisition strategy, using convertible notes and dollar-cost averaging, transformed it from a struggling software company to a Bitcoin proxy company, driving its stock price up more than 1,000 times and redefining its market image.
Here is a timeline of their Bitcoin acquisitions:
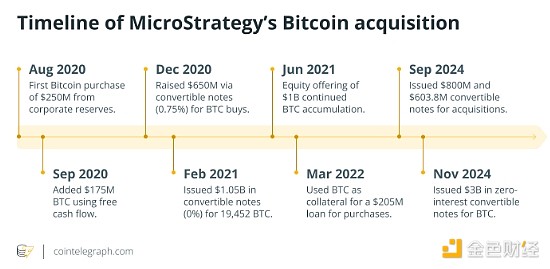
As you can see, MicroStrategy uses a consistent dollar-cost averaging approach to purchase Bitcoin in different market conditions to mitigate price volatility. The company also partners with an institutional-grade custodian to ensure secure storage.
MicroStrategy's transformation from a struggling software company to a Bitcoin broker has seen its stock price soar. Starting at $2 in 2002, the price skyrocketed more than 1,000 times, reaching a peak of over $2,000, largely due to the rapid rise of Bitcoin and investors' perception that MicroStrategy was a way to gain exposure to Bitcoin without having to buy the cryptocurrency directly.
Bitcoin, as an asset, has historically outperformed traditional investments such as bonds or cash equivalents. MicroStrategy has followed this trend and significantly increased its market value, giving it a new position in the technology and financial sectors. While this may seem like a very aggressive money management strategy to many, most moves in the capital markets that achieve exponential growth look like abnormal decisions at first.
Fourth, the return of using Bitcoin as a treasury reserve
MicroStrategy's Bitcoin strategy has significant advantages. While the financial advantages are undoubtedly an important aspect of the strategy, MicroStrategy has also successfully built brand equity through this financial management strategy.
Similar to gold, Bitcoin can hedge against currency depreciation. This bold strategy has attracted visionary investors seeking to participate in Bitcoin's growth. Banks have traditionally relied on fractional reserve banking, which can make businesses vulnerable in times of crisis, as the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank demonstrated.
Unlike banks, Bitcoin provides liquidity at all times through a decentralized global market, allowing businesses to quickly access funds without relying on centralized institutions. By maintaining a Bitcoin vault, companies can reduce operational risk and ensure timely access to liquidity.
MicroStrategy positions itself as a thought leader in financial innovation, often mentioned alongside Tesla and Nvidia—not because of its business fundamentals, but because of its pioneering financial management strategies.
Bitcoin’s limited supply and growing adoption, compared to traditional financial assets, have already generated huge returns for MicroStrategy investors. Despite all of these positives for MicroStrategy, risks remain for them and for those who want to draw inspiration from this strategy.
V. Risks and Challenges of Using Bitcoin as a Treasury Reserve
Despite its many advantages, Bitcoin also presents challenges and potential pitfalls as a financial asset. Building corporate finance on an asset that can drop in value by up to 75% during a bear market requires a lot of planning.
Volatility Risk
Bitcoin's price volatility could significantly impact a company's balance sheet, leading to volatility in reported earnings and shareholder sentiment. As prices and sentiment fall, the company could be forced to sell Bitcoin, which further leads to negative price action and sentiment.
In a market stress scenario, Bitcoin prices fall, causing the company's stock price to fall, and if debt matures at the same time, the company's balance sheet could experience a systemic collapse. In addition, bondholders may not convert bonds into shares, resulting in cash repayments, which could exacerbate MicroStrategy's financial situation.
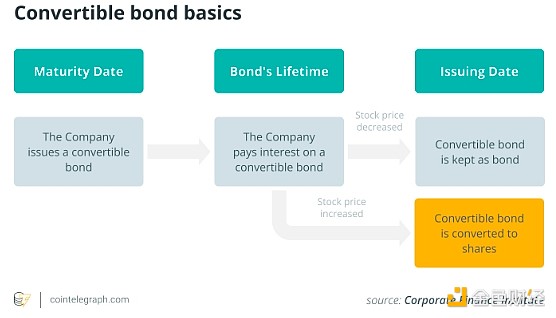
For its part, MicroStrategy has successfully mitigated this risk by having a track record of managing through one of the deepest Bitcoin bear markets. The newly issued debt matures in 2029, providing ample time for its core business to generate additional cash flow, ensuring the Bitcoin-powered vault is resilient during a potential downturn.
MicroStrategy’s last convertible bond, issued in 2020, matures in 2025 and was purchased with additional funds raised by the company in 2024. This suggests a five-year plan.
Liquidity Risk
The need to liquidate Bitcoin during a market downturn could exacerbate losses and destabilize the market. This would create a vicious cycle, as happened with Terra, where the size of the balance sheet shrinks exponentially as Bitcoin must be sold to build a cash position, and the price of Bitcoin keeps falling in the process of acquiring cash.
If the corporate treasury department is caught in this vicious liquidity crisis, it will also find it difficult to raise more funds.
Regulatory Risk
The regulatory risk of cryptocurrencies has been reduced in 2024 with the approval of a Bitcoin exchange-traded fund (ETF). However, there is still a lack of clarity on the accounting treatment of companies holding cryptocurrencies on their balance sheets.
Regulatory shifts such as capital gains taxes or outright bans could devalue Bitcoin holdings.
The example of MicroStrategy could incentivize other companies to overinvest in volatile assets. While diversification is critical, the trend of excessive Bitcoin adoption could destabilize the broader corporate financial ecosystem, amplifying risks during a downturn.
Ultimately, companies considering adding Bitcoin to their vaults must weigh the promise of Bitcoin against its risks to determine if it fits their financial goals and risk appetite.
 Weatherly
Weatherly






