Author: Shailey Singh, CoinTelegraph; Compiler: Deng Tong, Golden Finance
1. What is Bitcoin halving, and how does it relate to cross-chain interoperability?
The Bitcoin protocol reduces the supply of new Bitcoins by 50% through the quadrennial Bitcoin halving. This means a 50% reduction in revenue for Bitcoin miners (in BTC) and has an indirect impact on cross-chain interoperability.
The Bitcoin halving event, which occurs approximately every four years, reduces the block rewards for Bitcoin miners. The halving process is hard-coded into the Bitcoin protocol by its elusive creator Satoshi Nakamoto, and the supply of 21 million Bitcoins (BTC) is also limited.
The last three halvings occurred in 2012, 2016 and 2020. The first Bitcoin halving in 2012 reduced the reward for mining a block from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. The next Bitcoin halving impact is expected to occur in April 2024, with the halving cycle continuing until 2140, when the last Bitcoin will be mined.
Cross-chain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to seamlessly share information and value. It allows users and assets to move smoothly, promoting the integration of blockchain into a more integrated and efficient financial ecosystem.
In the cryptocurrency market, Bitcoin is known for its impact on scarcity and value, becoming a behemoth with unparalleled market dominance. However, due to its proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism and inherent design as a highly non-interoperable chain, the Bitcoin blockchain is disconnected from discussions of cross-chain collaboration. Bitcoin’s prominence and market dominance still make it worthy of consideration in discussions about interoperability, albeit more indirectly.
2. The impact of Bitcoin halving on network congestion and transaction fees
As mining rewards decrease, miners may compete more actively to verify transactions, which may lead to Network congestion.
The Bitcoin halving is intended to control the issuance of new Bitcoins and maintain the scarcity that supports their value. One notable consequence of the incident was its impact on Bitcoin blockchain network congestion and transaction fees.
After the halving event, the block reward is reduced, and miners may need Adjust strategies to maintain profitability. As miners become more picky about block transactions, users offering higher fees gain priority, creating a competitive environment. The overall decrease in block rewards, combined with the increase in user activity often observed during halving events, has resulted in a surge in transaction numbers, exacerbating network congestion.
This surge, coupled with a market-driven response to increased transaction fees during periods of high demand, could prompt users to consider alternative blockchains that may have greater Advantages such as lower fees, faster transactions or better cross-chain compatibility. This trend, while difficult to measure accurately, reflects the dynamic and evolving nature of the cryptocurrency industry.
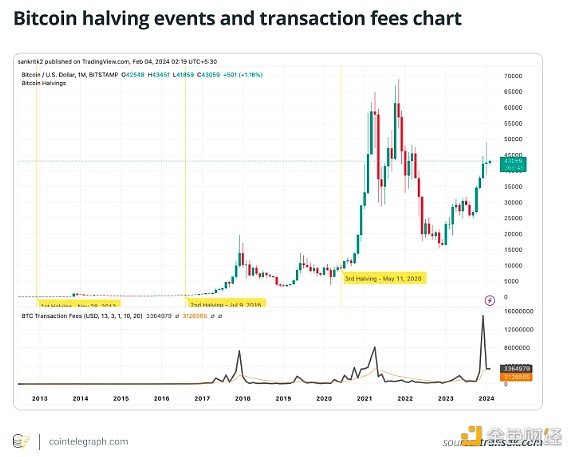
Bitcoin Halving The incident triggered a chain reaction, affecting network congestion and transaction fees. Reducing block rewards, changing miner behavior, and increased user activity create an environment where transaction fees become more competitive.
3. As the Bitcoin issuance rate declines, investors seek alternatives
As the Bitcoin issuance rate declines, investors seek alternatives on other blockchains choose.
The Bitcoin halving period has prompted a reassessment of risk and reward dynamics among investors who have traditionally viewed Bitcoin as a lucrative investment, in part due to its deflationary nature. As the Bitcoin halving event causes the creation rate of new Bitcoins to slow down, its increasing scarcity enhances its appeal as "digital gold."
However, investment dynamics in the cryptocurrency space are complex and multifaceted. In the pursuit of portfolio diversification and risk reduction, investors often explore alternative blockchain projects that offer different functionality, utility, or potential returns.
Enhanced cross-chain interoperability is needed as investors seek to invest in diverse blockchain projects and fluidly transfer value and assets between these platforms. An interoperable multi-chain ecosystem has also become crucial, enabling seamless transactions and transactions between different blockchains interact to expand the scope of investment strategies and risk management.
Cross-chain interoperability acts as a bridge, allowing assets and value to be exchanged between different Seamlessly move between blockchains. As more and more capital flows into alternative blockchains, the demand for efficient, secure, and user-friendly cross-chain interaction mechanisms continues to grow. This in turn has spurred innovation in the space, creating complex multi-chain platforms and interoperability protocols that can accommodate a wide range of financial services and products.
The interplay between Bitcoin issuance rates and investor behavior highlights broader decentralization trends and creates an environment for cryptocurrency markets to mature.
4. The significance of cross-chain interoperability solutions
Cross-chain interoperability solutions add a layer of meaning to the Bitcoin cycle by improving market efficiency and capital allocation.
Cross-chain interoperability solutions address fragmentation and enhance cross-blockchain liquidity. Crucial to changing the cryptocurrency landscape. The context of the Bitcoin halving event adds an additional layer of significance to the role these solutions play in improving market efficiency.
Cross-chain interoperability solutions may help reduce the number of Arbitrage opportunities arising from price differences between blockchains. As assets move seamlessly across the interconnected network, price differences between the same assets on different chains shrink, thereby improving market efficiency. This is especially important during periods of heightened volatility, such as the Bitcoin halving event, where price differences can be even more pronounced.
The Bitcoin halving event has led to market volatility and increased cryptocurrency trading activity as investors react to changing supply dynamics. During this period, efficient capital allocation is critical to optimizing returns and managing risk. Cross-chain interoperability solutions facilitate this process by enabling the seamless movement of assets between different blockchains. Investors can quickly reallocate funds to take advantage of emerging opportunities or mitigate potential losses.
A wrapped token that is tied to the value of an asset on a blockchain It reflects the impact of cross-chain interoperability on liquidity and market efficiency. For example, Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is an Ethereum-based token pegged to the value of Bitcoin. The token allows users to participate in the value of Bitcoin within the Ethereum ecosystem, unlocking opportunities for decentralized finance applications. Users can leverage their Bitcoin value in a variety of financial instruments, such as lending and trading, without interacting directly with the Bitcoin blockchain.
The relationship between the Bitcoin halving event, market volatility and cross-chain interoperability solutions is indirect but complex. As the cryptocurrency landscape evolves, interoperability becomes increasingly important, shaping a more connected and efficient financial future for blockchain networks and users.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance






