Author: Kevin He, Co-founder of Bitlayer
Background
Recently, there has been extensive community discussion and attention on the transfer of control of the WBTC project by BitGo.
The author has extensive experience in building blockchain infrastructure, has personally developed centralized wrapped token systems and MPC-based custody platforms, and is currently working on building Bitcoin native verification capabilities.
In this article, the author will review the events, covering multiple actions and feedback to present the facts. Based on the practical experience of system development, the author abstracted a simple architecture and security model for wrapped BTC products. Subsequently, the author classified different technical solutions according to the degree of decentralization, and pointed out that technical solutions based on Bitcoin native verification capabilities represent the future direction.
Event Review
Participants
WBTC: WBTC has wrapped more than 150,000 BTC (worth more than $9 billion) and displayed proof of reserves on its website.
Bitgo (WBTC controller): announced that control of the WBTC project will be transferred from BitGo to an institution associated with Justin Sun’s BiT Global within 60 days.
Related parties
MakerDAO (DAI) risk management team Block Analitica:Expressed concerns about the transfer of control and pointed out that WBTC poses risks, causing them to reduce their risk exposure in related protocols.
Justin Sun (new controller of WBTC):Promised not to move BitGo reserves.
Third party:
Weidai (VC):Suggested that verification bridge would be a better solution.
Liu Feng (media):Questioned the qualifications of BiT Global.
Business model of Wrapped BTC
The business model of Wrapped BTC is relatively simple, as shown in the figure below:
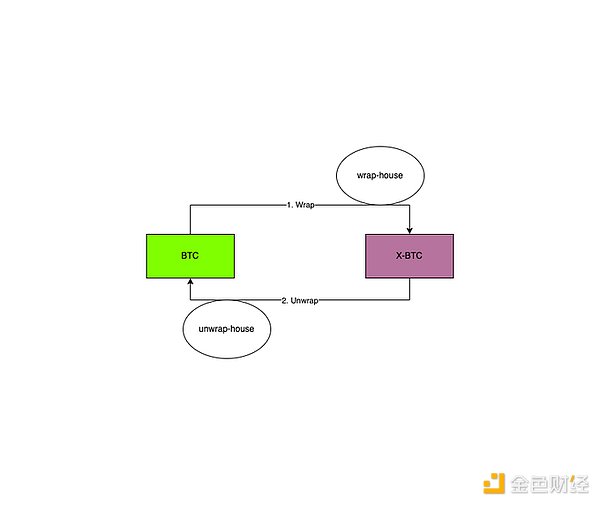
Wrap:
Represents the conversion from BTC to W-BTC.
Wrap-house:
Represents the packaging operation mechanism, ensuring that the BTC deposited by the user is minted into the corresponding W-BTC on the ledger (usually other blockchains, such as ETH), no more and no less.
Unwrap:Represents the conversion from W-BTC to BTC.
Unwrap-house:
Represents the unpacking operation mechanism, ensuring that after the user destroys W-BTC, there is a mechanism for him to obtain BTC on the Bitcoin network, no more and no less.
Comparison of trustlessness
The comparison of the business and technical models mentioned above can be carried out from multiple dimensions. Below, the author will compare the degree of trustlessness from the perspectives of packaging and unpacking.
No trustlessness
A typical example is BitGO's WBTC, where both packaging and unpacking operations are controlled by BitGo Custody.
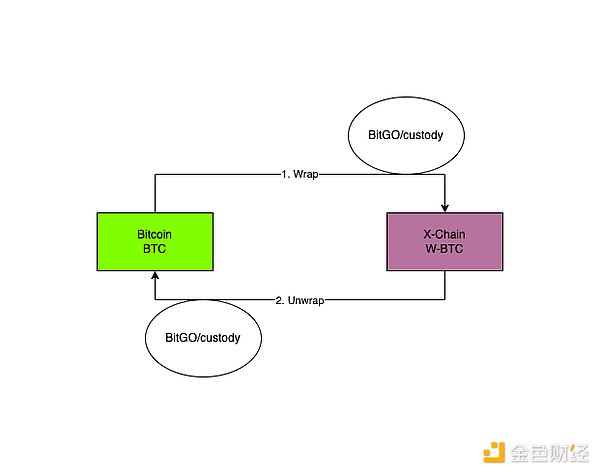
Obviously, users need to trust that the BitGo custodian service provider can always operate correctly.
One-way trust is not required
Next, let's take a look at two representative projects that appeared around 2020: tBTC/renBTC. We can see that on the X chain (for example, with full verification capabilities, such as EVM), wrap-house can more easily achieve a high level of trustlessness, but due to the technical limitations at the time, unwrap-house can only enhance security through threshold signatures, which has nothing to do with the degree of pre-signature.
Two-way trust-free
Fast forward to 2024, thanks to the pioneering attempts of teams such as BitVM/Starkware in Bitcoin's native verification capabilities (including fraud proofs and validity proofs), and the practical implementation of community teams such as BitlayerLabs, unwrap-house is expected to achieve trustlessness.
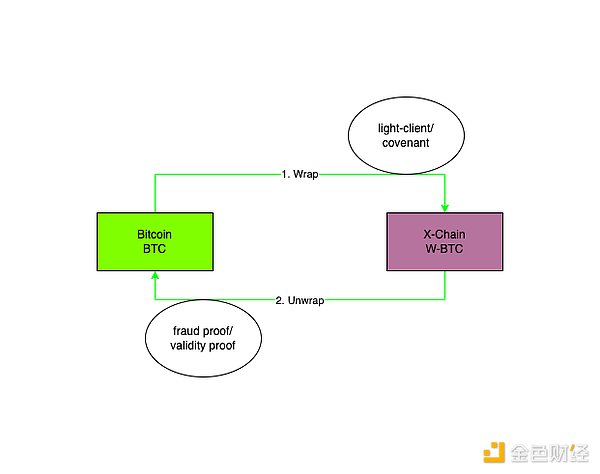
Among them, fraud proof is represented by BitVM and its derivative projects, which realizes optimistic verification without OP_CAT. The mainstream implementation is the commitment and challenge process using zero-knowledge verification.
Validity proof assumes the existence of OP_CAT opcode and directly realizes zero-knowledge verification. With OP_CAT, the locked BTC will be controlled by the so-called contract (a contract-like structure).
Summary of scheme comparison
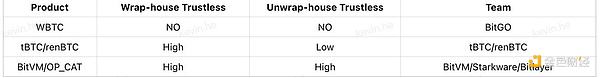
A horizontal comparison of the above various technical solutions shows that the solution based on Bitcoin's validation capability performs better in terms of two-way trustlessness.
Conclusion
The emergence of WBTC in 2018 marked the beginning of bringing BTC liquidity into the DeFi world. The tBTC project in 2020 has made some optimizations and improvements.
Verification technology solutions represented by Bitcoin's native verification capabilities (fraud proof and validity proof) will perform better in terms of two-way trustlessness.
WBTC, it's time to upgrade the technical solution!
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Joy
Joy Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Coinlive
Coinlive  Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Beincrypto
Beincrypto
 链向资讯
链向资讯 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph