Source: Bing Ventures
The rise of Bitcoin has triggered financial changes on a global scale and brought important concerns about personal privacy and security. This Bing Ventures research will explore the protection and challenges of Bitcoin privacy from an independent perspective, providing readers with in-depth enlightenment. We will explore current privacy challenges and related solutions, and look towards the future direction of Bitcoin privacy protection.
Bitcoin Lightning Network is a second-layer solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain, designed to enable faster and cheaper transactions through off-chain payment channels. While the Lightning Network has advantages in scalability and efficiency, it also raises some privacy concerns. We believe that in the future, the development of the Lightning Network privacy protection mechanism will continue to focus on the balance of user experience, security and privacy protection. In order to enhance privacy protection, you can also consider integrating other Layer 2 networks and security enhancement measures such as zero-knowledge proofs to further improve users' anonymity and privacy protection levels.
Routing privacy
First of all, the routing privacy of Lightning Network is a key issue. When using the Lightning Network, payment channels need to be established for participants to conduct transactions. The process of finding and establishing these channels can compromise privacy by revealing information about participants and their associates. Routing privacy issues mainly involve router nodes being able to observe transaction paths in the Lightning Network. When a participant initiates a payment request, router nodes in the network need to select the best routing path based on factors such as channel availability and cost. However, these nodes have the ability to observe the identities of senders, receivers, and intermediate nodes of transactions, which may reveal transaction relationships between participants.
For example, suppose Alice wants to send a Bitcoin payment to Bob, and there is no direct payment channel between them. To complete this transaction, Alice's payment request may be routed through a series of intermediate nodes until it reaches Bob. During this process, intermediate nodes can observe the path of the payment request, and they may learn the connection between Alice and Bob, which will reveal their transaction relationship.
To solve this problem, some solutions have been proposed to protect the routing privacy of the Lightning Network. One of them is to use Zero-Knowledge Proofs technology to hide the path of the transaction and the identity of the participants. Zero-knowledge proofs allow participants to prove that a certain statement is true without revealing any specific information about the statement. By applying zero-knowledge proofs, participants can prove that they have valid payment paths without revealing the details of those paths, thereby protecting routing privacy.
In addition, the Lightning Network can also use Multi-Path Payments to enhance routing privacy. Multipath payments allow a payment to be split and transmitted through multiple different channels, making the relationship between participants more ambiguous and difficult to track. By using multiple channels, router nodes are unable to determine exactly which path a particular payment was transmitted through, increasing privacy protection.
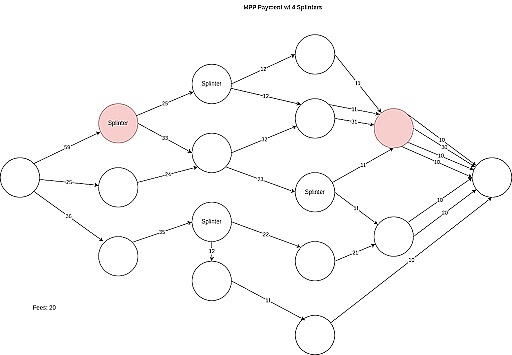
Source: LN Capital
Transaction Privacy
The transaction privacy of the Lightning Network is also worthy of attention. Although Lightning Network transactions will not appear explicitly on the Bitcoin blockchain, the opening and closing of payment channels will still leave traces on the blockchain. Transactions on these blockchains can provide a certain level of information about the participants and their activities. In order to solve this problem, CoinJoin technology came into being.
CoinJoin technology is an innovative solution designed to improve the privacy of Bitcoin transactions. The principle is to combine multiple transactions into a single transaction, thereby confusing the input and output of the transaction, increasing the complexity of the transaction, and making it difficult for external observers to determine the sender and receiver of the transaction. Specifically, CoinJoin technology combines transactions from multiple Bitcoin users into one batch transaction. In this way, it is impossible to accurately track which input corresponds to which output, thereby protecting the user's transaction privacy.
As time goes by, CoinJoin technology continues to evolve. Currently, there are some Bitcoin wallets and exchanges that have implemented CoinJoin, such as Wasabi Wallet and JoinMarket. These platforms allow users to participate in CoinJoin transactions, improving the privacy of their transactions. However, CoinJoin technology also faces some challenges. One of them is that the merging of transactions can lead to delays in transactions. Transaction confirmation times may be relatively long due to the need to wait for enough participants to merge. Additionally, the size of CoinJoin transactions may also be limited, as larger transactions are more likely to attract the attention of observers. While CoinJoin technology can increase the complexity of transactions, it is still possible to perform transaction analysis through other means to reveal the true sender and receiver of the transaction. Therefore, CoinJoin technology needs to be combined with other privacy-enhancing technologies to provide a higher level of transaction privacy protection.
Network Analysis
Network analysis of the Lightning Network is also a potential privacy issue. Because Lightning Network transactions occur off-chain and are not recorded directly on the Bitcoin blockchain, network analysis becomes more difficult. However, it is worth noting that with appropriate monitoring and analysis techniques, it is still possible to collect information about transactions and possibly associate Lightning Network activity with specific users.
To understand this problem, we need to understand the basic principles of the Lightning Network. The Lightning Network utilizes payment channels and skip payments to enable fast, low-cost transactions. Participants can establish multiple payment channels in the Lightning Network and conduct transactions through these channels. Since transactions are not directly recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain, network analysts may not be able to directly obtain complete transaction data, but they can still collect some information by monitoring network traffic and node behavior.
For example, suppose Eve is a network analyst and she wants to track Alice's Lightning Network activities. Although Eve cannot directly obtain specific transaction records on the Lightning Network, she can monitor node behavior in the network. By observing the communication patterns and frequencies between different nodes, Eve can infer something about transaction activity. For example, if Eve notices that a specific node frequently communicates with other nodes, and these nodes are related to Alice's payment channel, then she can reasonably speculate that this node may be Alice's intermediate node, thus revealing Receives some information about Lightning Network activities.
In order to deal with this problem, the Lightning Network can also adopt random routing and payment path selection strategies to increase the difficulty of network analysis. By randomly selecting payment paths and routing nodes, it can improve privacy protection by making it more difficult for network analysts to track a specific user’s transaction activity.
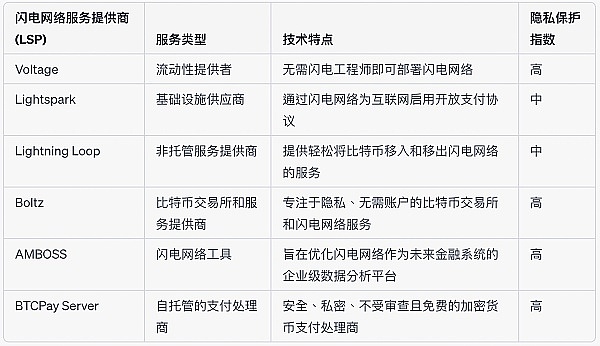
Source: GWEI Research
Privacy Potential and Challenges of Lightning Network
Privacy Potential and Challenges of Lightning Network It has always been the center of attention. While the Lightning Network has great potential to improve the privacy of Bitcoin transactions, there are some technical challenges and feasibility issues that need to be overcome. We believe that projects in the following directions are expected to further improve the privacy protection level of the Lightning Network and provide users with a safer and more private payment experience.
Improving the routing algorithm of the Lightning Network is an important part of improving privacy. Current routing algorithms may leak information about participants because the process of finding and establishing payment channels requires exposing the relationships between nodes. To reduce this risk of information leakage, more privacy-preserving path selection strategies can be adopted, such as using obfuscation techniques or random routing.
Transaction obfuscation technology is an effective means to improve the privacy of the Lightning Network. Introducing transaction obfuscation techniques, such as CoinJoin, can make transactions in the Lightning Network more difficult to trace and correlate. By mixing multiple transactions together, transaction correlation is eliminated, thereby enhancing user privacy.
Designing privacy-enhanced payment channels is also one of the important measures. By using zero-knowledge proof technology, transaction amounts and participant identities can be hidden, providing a higher level of privacy protection. Such a payment channel design allows users to enjoy better privacy protection options when conducting Lightning Network transactions.
Improved network analysis protection is essential. Researching and developing more effective ways to protect the Lightning Network from network analysis threats could be achieved by introducing anonymization techniques or cryptographic protection measures. These protective measures can prevent malicious users or attackers from obtaining private information of Lightning Network transactions through network analysis.
We can focus on some alternative L2 scaling solutions that can enable cheap, anonymous and off-chain Bitcoin transactions. This solution would ideally be compatible with the Lightning Network and have a smaller on-chain footprint, while enhancing user privacy protection by introducing obfuscation technologies such as CoinJoin into each transaction. It can complement the Lightning Network and provide users with a higher degree of privacy protection.
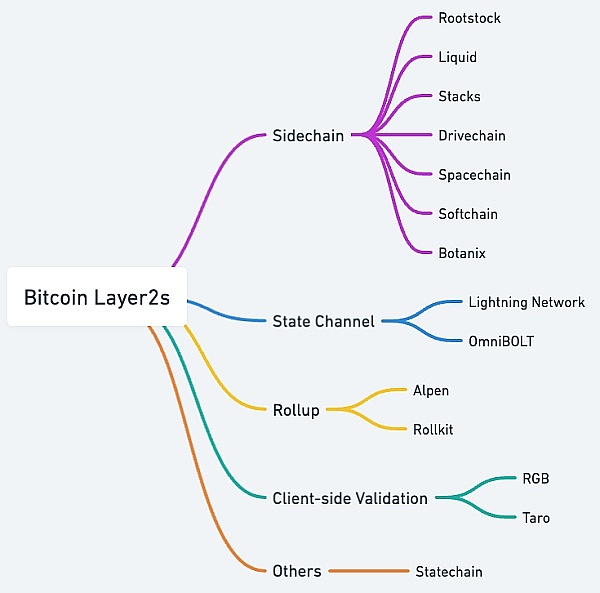
Source: Jeffrey Hu
The privacy potential and challenges of the Lightning Network are a complex issue. We believe that the privacy issues of Lightning Network can be solved by improving routing privacy, adopting transaction obfuscation technology, designing privacy-enhanced payment channels, and improving network analysis protection. With the development and innovation of technology, Lightning Network is expected to further improve the level of privacy protection and provide users with a safer and more private payment experience. These efforts will promote the continuous progress of the privacy protection mechanism of Bitcoin payment and meet users' needs for privacy.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Others
Others Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph