Author: Paul Veradittakit, Partner at Pantera Capital; Translation: Jinse Finance xiaozou
Sahara AI's mission is to create a more open, fair, and collaborative AI economy that makes it as easy as possible for people to participate. Using blockchain, Sahara ensures that all contributors (data contributors, labelers, model developers, etc.) are fairly compensated, data and models remain sovereign, AI assets are secure, and permissions can be created, shared, and traded.
1、AIStack Status
The current AI stack can be divided into the following layers:
Data is collected from a variety of sources (e.g., web scraping, public datasets, user-generated data) and must comply with licensing requirements to avoid legal issues. Data is annotated according to the task at hand (e.g., classification, object recognition).
Data is fed into the model, which adjusts its internal parameters (weights) to minimize error. This requires fairly expensive and time-consuming computation.
The user experience of creating an AI agent typically involves using tools like TensorFlow and requires technical expertise.
Model training requires expensive processing.
Each layer is highly competitive and diverse, and for the most part, one way of doing it has proven to be the most efficient. For example, data collection is best done with large public datasets (such as books) and fine-tuning with specialized data (research papers). Model training is best done on specialized hardware, AI agents should be easy to use with plug-and-play resources to build a developer community, and computing resources should be distributed so that providers of computing resources are accurately rewarded. These combined will lead to better AI models and stronger communities.
Web2 companies are working in this direction, but face severe limitations because their designers are centralized. From a business and technical perspective, these companies aim to restrict access and isolate different parts of the stack, resulting in different security standards, database designs, backend integrations, and monetization strategies. In fact, such designs are poorly designed and cannot cope with the shift in the economic model of AI.
For example, OpenAI has built a very powerful base model and started to attract community builders through its permissionless GPT wrapper market, but only allows surface-level prompt customization and does not support reconstruction of the underlying model. The company purchased all its computing resources with investors' money and expects to lose $5 billion by the end of this year.
2.AICollaborative Economy
The Sahara platform provides a one-stop service for all AI development needs throughout the AI lifecycle: from data collection and annotation, to model training and services, AI agent creation and deployment, multi-agent communication, AI asset trading, and crowdsourcing of AI resources. By democratizing the AI development process and lowering the entry barriers of existing systems, Sahara AI provides equal access to individuals, businesses, and communities to jointly build the future of AI.
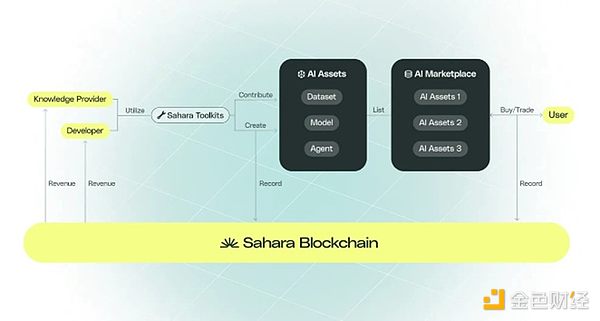
The above figure summarizes the user journey, depicting how AI assets go from creation to use to achieving user stickiness in the Sahara AI ecosystem. Notably, all transactions within the platform are immutable and traceable, ownership is protected, and asset provenance is recorded. This supports a transparent and fair revenue sharing model, ensuring that both developers and data providers are appropriately compensated for generating revenue.
Sahara aims to make it easier for people to participate in the AI economy. Here’s how developers and users can use Sahara:
Developers can use the Sahara SDK and API to interact with any layer of the Sahara blockchain and its AI stack, such as personalized computing power, data storage, and incentive structures, to form their own Sahara AI agents that can be licensed and monetized for use by others.
Through a no-code/low-code environment, developers can create and deploy AI assets through an intuitive interface and pre-built templates.
To participate in AI model training, users simply visit a website where they can complete AI training tasks and be compensated in tradable tokens, ranging from solving basic math problems to short video descriptions.
Users can easily use AI agents through an intuitive UI. Users will have the flexibility to purchase licenses for access and further development, and can even trade AI asset shares.
Users will be able to create their own personalized data “knowledge base” and create specialized AIs using their own data. Just like any other AI, this will allow others to access, while the training data remains completely private and secure.

Companies can also create AI agents (or “business agents”) trained on their own proprietary data, at a much lower cost due to the decentralized AI agent generation and services that the system runs on the Sahara blockchain.
Enterprises can also pay to generate Sahara data, which combines AI automatic annotation and manual annotation to effectively create high-quality, privacy-preserving multi-model datasets.
Except for the enterprise-oriented products that have been used by some well-known customers, all other features have not yet been released, but there are plans for release.
3. Technical Overview
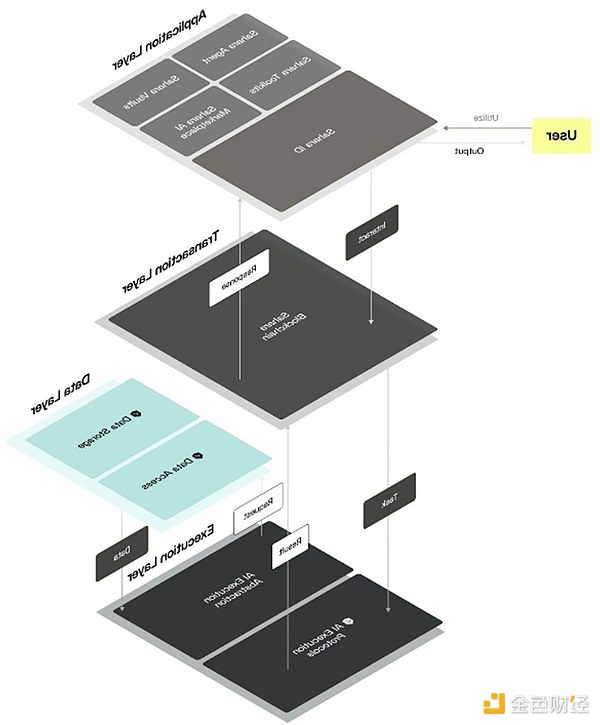
The Sahara team designed the system to be as simple and easy to use as possible, abstracting the complexity required to ensure compatibility, profitability, and security of various parts of the AI stack. Behind the scenes, the Sahara team has developed countless innovations to achieve this goal. To name a few:
The Sahara blockchain minimizes gas fees and is fully EVM-compatible. The Sahara Cross-Chain Communication (SCC) protocol enables secure, permissionless data transfer across blockchains, facilitating trustless interoperability.
Sahara AI-Native Precompiles (SAPs) are precompiled smart contracts used to optimize the performance of AI tasks to reduce computational overhead, including training execution SAPs and inference execution SAPs.
Sahara Blockchain Protocols (SBPs) manage AI assets to ensure accounting responsibility, such as AI Attribution to track contributions and distribute rewards, and AI Asset Registry to manage the registration and provenance of AI assets, AI licenses, and AI ownership.
Data management is performed both on-chain and off-chain, with AI asset metadata, commitments, and proofs on-chain, while important datasets, AI models, and supplementary information are performed off-chain to optimize data retrieval, security, and data availability.
Collaborative Execution Protocols support joint AI model development and deployment across AI training, aggregation, and services. Other models like PEFT allow for technical fine-tuning, Privacy Preserving Compute supports differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, and secret sharing, and Fraud Proofs function as the name suggests.
4. Fully Integrated AI Stack
The team is led by Sean Ren, a tenured professor at the University of Southern California, and Tyler Z, an alumnus of the University of California, Berkeley. The former was listed among the 35 people in technological innovation by MIT Technology Review and was awarded the 2023 Samsung Researcher, and the latter served as the investment director of Binance Labs. Other members of the team have backgrounds or experience from companies such as Stanford University, UC Berkeley, AI2, Toloka, Stability AI, Microsoft, Binance, Google, Chainlink, LinkedIn, Avalanche, etc., contributing valuable expertise.
Sahara is also advised by top AI-native researchers and enterprise customers:
Laksh Vaaman Sehgal (Vice Chairman, Motherson Group)
Rohan Taori (Human Research Scientist)
Teknium (Co-founder, Nous Research)
Vipul Prakash (CEO, Together AI)
Elvis Zhang (Founding Member, Midjourney)
Sahara AI is currently used by over 35 leading technology innovation projects and research institutions, including Microsoft, Amazon, MIT, Motherson Group, and Snap, for various AI services such as Shara Data for data collection/annotation and Sahara Agents for personalized domain agents.
Generative AI is still in its infancy in terms of technology and market size; today’s centralized chat and video tools have limited reach due to the difficulty in integrating the entire AI stack into a single product. Sahara AI is the only company addressing this bottleneck with a modular design that uses blockchain as the backbone for permissionless access, token distribution, and security. The future of AI must be accessible and equitable for everyone to participate, and Sahara AI is the only company moving forward towards that vision.
 YouQuan
YouQuan






