At last year's Polkadot Decoded conference in Copenhagen, Polkadot founder Gavin Wood delivered an important keynote speech about the future of Polkadot, which is called Polkadot 2.0.
This new vision aims to bring Polkadot closer to one of Ethereum's original ideas, that of a "world computer" with the goal of providing a wide range of computing capabilities. This computing power does not need to rely on any centralized trust mechanism, while maintaining the robustness and security of the system.
With this new direction, Polkadot 2.0 opens a new path that can fully unleash the power and potential of the relay chain and its parachains! Polkadot 2.0 emphasizes flexibility, especially in distributed computing, where the old one-size-fits-all model is outdated. Instead, Polkadot 2.0 supports a diverse range of computing environments, ranging from ephemeral chains (which may be used for short-term or specific tasks) to high-capacity chains (capable of processing large amounts of transactions and data). It can also take advantage of the inherent advantages of the Polkadot framework, such as security, scalability, and interoperability, to optimize the performance and functionality of these different types of chains.
How Polkadot currently operates and opportunities for improvement
As As Gav explained, the current model originated in 2016, when the first Polkadot white paper was released.
Sharding, the process of splitting a single blockchain into multiple homogenous chains, attracted significant attention at the time. It is considered a key element of Ethereum 2.0 and is widely considered a solution to scalability challenges. However, Ethereum’s later roadmap shifted to a Rollup-based approach.
Polkadot improved the basic sharding concept, introduced flexible heterogeneous sharding, and eventually evolved into a parachain. Polkadot aims to promote an environment where shards can be diversified according to various application needs and simplify communication between them using XCM, Polkadot's cross-chain messaging standard.
On this basis, Polkadot developed into the Polkadot 1.0 we see today. However, even with these advances, Gavin Wood pointed out certain problems with the current architecture:
Inflexible parachain auction model
Strong>, this model may discourage the participation of small innovators in favor of larger teams with better resources.
Allocating all "core" resources for the entire lease period to a single parachain results in inefficiency. If the blocks of the parachain are not filled, validators and teams will waste resources.
As often happens during development, the final product may differ from what was originally intended. As Gav said, "It turns out that when you build it, you realize that you're building something completely different than what you were trying to do in the first place. Often, if you're lucky or have a great team With your support, you can build something better than what you originally built."
Parachains are the focus of Polkadot's vision, but they are too "Chain Centralization”.
In the process of designing and developing Polkadot 2.0, two important concepts in computer science need to be taken into account: Abstraction and generalization .
Polkadot 2.0: Use Elastic Cores to adapt to different computing needs
The main innovation of Polkadot 2.0 is to change the way security resources are allocated in the blockchain ecosystem. Historically, each parachain was viewed as a unit similar to a CPU core, with a certain amount of computing power. This computing power represents the level of security the chain can withstand, just like the performance of a smartphone, which can range from high to low.
However, with the launch of Polkadot 2.0, we will no longer statically assign a core to each chain. Instead, we are adopting a flexible approach to allocating security resources that is tailored to current needs.

How the current core is allocated
Image source: Gav's PPT at Polkadot Decoded 2023
For example, Application chain ( Appchains) may sometimes require less throughput than a full core, so they "skip" a few blocks and give them to other users. In other cases, they may share a core with multiple application chains, or even need to use multiple cores simultaneously when demand is high.
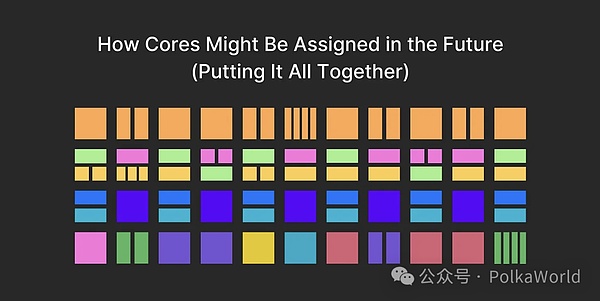
How to allocate cores in Polkadot 2.0 in the future
Image source: Gav's speech at Polkadot Decoded 2023
This kind of adaptability and "flexibility" of resource allocation /elastic core” concept. Here, Tanssi plays a key role. Tanssi simplifies developer workflow by making it easier for developers to design and implement applications that adapt to elastic core.
Rich and secure cross-chain interoperability: Polkadot’s new vision
Polkadot 2.0 goes beyond standalone blockchains and envisions a more connected and fluid blockchain ecosystem. Gavin illustrates this point with a napkin drawing, contrasting the existing relay chain + parachain model with the envisaged "mesh" connection of cores and applications grouped into specific in the field. These fields maintain their uniqueness to ensure specialization, but now they are complexly interconnected.
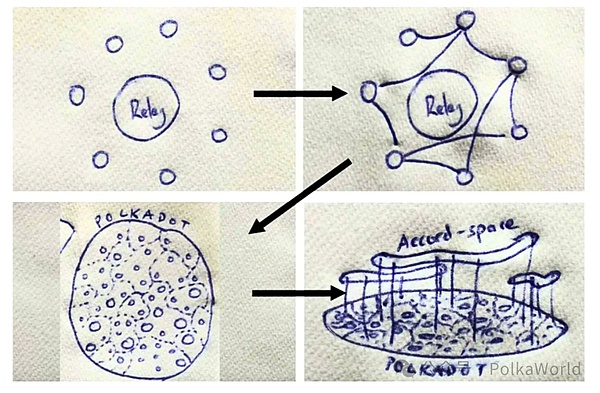
Gavin Wood's draft of Polkadot 2.0 functional description
Image source: Gav Wood's speech at Polkadot Decoded 2023
To enhance this interconnectivity, Polkadot 2.0 is launching an improved consensus mechanism with enhanced security, transactions Routing, parachain performance and overall user experience. Furthermore, to facilitate communication between different areas, "Accords" has been introduced. Accords takes the XCM model a step further and develops a shared set of "laws" that define inter-chain interactions.
Emphasizing the importance of community decentralization, the governance of Polkadot 2.0 is transitioning to a DAO-like structure, emphasizing that the community is indispensable in true decentralization role.
From parachain to application chain to container chain: Tanssi’s role in Polkadot 2.0
Looking at the future of Polkadot, it is clear that flexibility is at the core. Polkadot 2.0 is introducing a new security marketplace, marking a shift from traditional parachain slot auctions. This change is reminiscent of familiar cloud platforms, allowing large companies and small teams to flexibly choose resources based on their needs.
In this evolving landscape, Tanssi’s importance as an application chain infrastructure protocol is unquestionable. Polkadot 2.0, with its democratized Core technology and reduced application chain startup costs, requires a powerful, user-friendly technical support - which is exactly what Tanssi provides.
Imagine a developer who is keen to introduce a novel financial application to the application chain. With Tanssi, they don’t need to pay too much attention to the underlying infrastructure and can focus on designing their unique applications. A core feature of Tanssi is the ContainerChain protocol, which provides application chains with ready-made solutions for block generation, data availability, cross-chain messaging and other integrations. Such a simplified infrastructure accelerated deployment timelines from one month of development time to less than an hour. This efficiency not only facilitates market entry, but also allows developers more time to perfect their apps, enhance user experience, and cultivate an active user community.
In short, Tanssi is destined to become the preferred solution for application chain development, just like game developers prefer Unity or Unreal Engine platforms. It promises to provide a seamless, efficient and user-friendly experience, advancing Polkadot 2.0’s vision of a more connected and adaptable blockchain ecosystem.
When will we see Polkadot 2.0?
According to what Joe from the Web3 Foundation previously shared, Coretime will be launched on Kusama in 2024 Q1 and on Polkadot in 2024 Q2. So far we have seen that Coretime is already on sale at Rococo! Polkadot version 1.2 is also coming, and the biggest new feature is launching Coretime on Kusama!
Recently we have also seen the community begin to discuss the pricing issue of Coretime. View the discussion here "What is the appropriate initial pricing setting for Polkadot 2.0 batch Coretime?" 》
Another exciting development is that the Polkadot Fellowship has votedto pass Referendum 74! This means that when Coretime sales are launched, the destruction of revenue is built in. Polkadot development has never stopped and has been successfully solved. It solves many decentralized problems in building application chains. Decentralized collectors, light clients, OpenGov – all these foundations are necessary to build a resilient (or unstoppable) network.
For Polkadot 2.0, the focus will be on accelerating and supporting the next trillion-dollar Web3 use cases, and Tanssi will be here to help do some of its work .
If you want to know how Tanssi is revolutionizing the application chain space. Follow Tanssi’s latest updates and join their community on Discord, Telegram and Twitter.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance





