Introduction
A faster and safer blockchain has always been the core narrative that drives the continuous development of crypto industry technology. From the endless L2 expansion technology to high-performance public chains such as Solana, all of them are exploring the performance and security boundaries of blockchains to provide a better experience for blockchain users.
With the explosive emergence of L1/L2 and most of them becoming "zombie chains", the market tells us that superior technology is not the only factor for success. L1/L2 still needs to make great efforts to build its own ecosystem.
EVM compatibility is an important criterion for us to distinguish blockchains. Ultra-high-performance public chains usually give up EVM compatibility to obtain strong enough performance, such as Solana, Aptos and Sui;
Avalanche, Polygon, etc. take into account EVM compatibility and do not pursue extreme performance to ensure that the prosperous Ethereum ecosystem can be seamlessly transferred to themselves.
The trade-off between EVM compatibility and performance reflects whether the blockchain should give up part of the ecosystem that is easy to transform into itself for the sake of extreme performance. The core reason behind this is the limitations of Solidity and EVM themselves.
The Move language has been highly anticipated since its birth. As a new smart contract language developed and designed by Facebook (now META), Move has been born for encrypted assets since its birth.
Compared with programming languages such as Solidity commonly used in the Ethereum ecosystem, Move
is designed with "security" and "high performance" in mind.
Without the need for L2, MOVE uses an optimization technique called "module packaging" to reduce the storage space and computing costs of blockchain transactions. Module packaging reduces storage and indexing costs by packaging multiple smart contracts into one module, and increases execution speed by reducing the steps of bytecode execution.
This also allows the TPS of the Move public chain to often exceed tens of thousands, and can even continue to expand to the 100,000 level.
Aptos and Sui, as the twin stars of Move, once achieved impressive market performance, but there is still a certain gap between them and the traditional EVM ecosystem in terms of ecosystem construction, which also makes the performance of the twin stars weak.
Movement is the game-changer for the current Move ecosystem. Movement is committed to connecting the security and high-performance advantages of the Move language with the liquidity and large user base of the EVM system to achieve a combination of advantages.
Through the Movement SDK, developers do not need to write Move code, they can automatically convert Solidity scripts into opcodes that Move can understand, and obtain interoperability compatible with Ethereum and other EVM networks, perfectly combining the advantages of the Move language with the prosperous Ethereum ecosystem.
Product Solutions and Advantages
2.1 Core Components: M1 and M2
Movement consists of two core components, M1 and M2. Through the combination of M1 and M2, it provides a secure, efficient and decentralized blockchain ecosystem.
M1, as a general Move-EVM blockchain, has gradually evolved into a decentralized sequencer, while M2, as a zero-knowledge Layer 2 based on Move + EVM, has achieved the security and efficiency of smart contracts, enabling users and developers to innovate and operate on a unified platform.
There is a problem of camp division within the Move ecosystem: Aptos and Sui, as the twin stars of Move, although both originated from Facebook's blockchain project, they differ in technical implementation and goals, so Aptos and Sui's Move languages are actually completely different languages, which leads to confusion and division among developers when choosing. Aptos is closer to the Move language in the Facebook DM project, while Sui has been iterating on this basis for six months and is more similar to Solana's semantics and consensus mechanism. Therefore, Aptos Move is more secure, while Sui Move has higher speed and compilation efficiency.
Solution: Movement built an RPC translation mechanism that compiles Sui Move and Aptos Move into the same bytecode to achieve compatibility. In addition, they developed an EVM interpreter called Fractal that allows developers to deploy EVM smart contracts on Movement. As a result, Movement users can operate on the liquidity of EVM while experiencing a unique execution environment and a vibrant ecosystem.
Scalability: M1 will serve as the first general-purpose Move-EVM blockchain, driven by its independent set of validators, and will then gradually evolve into a decentralized sorter that supports M2 and other Rollups built on the Move Stack.
M1 is designed to be decentralized by allowing validators to start quickly, inheriting the security of existing Snowman validators, while requiring minimal hardware. As the network matures during Parthenon testing, more community validators will be allowed to join the network, with the ultimate goal of achieving permissionless decentralization. This will ultimately enable the first permissionless, decentralized shared sorting unit, supporting M2.
In addition, M1 creates the most economically viable shared sorting unit because all transaction fees are distributed back to the token staking validator network, creating a flywheel effect that incentivizes more validators to join the network for higher returns. As sorting fees gradually decrease, M1 will become the center of the next generation of Rollups as it becomes a staking center, ultimately incentivizing Rollups to use decentralized shared sorters.
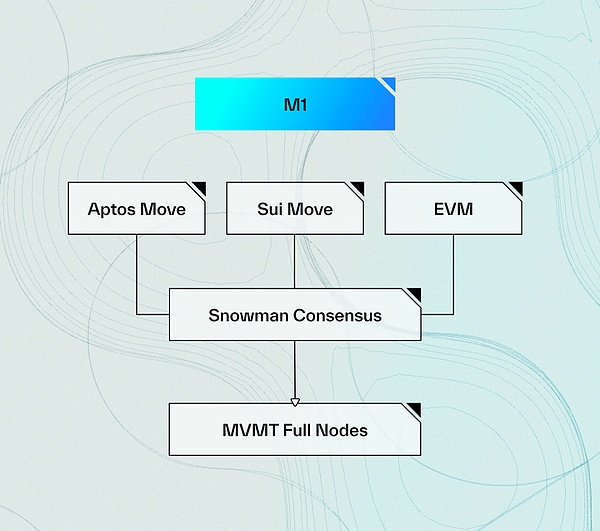
Source: https://x.com/movementlabsxyz/status/1747746334797410811/photo/1
M2: M2 is the first zero-knowledge Layer 2 (MEVM) based on Move + EVM, running on Ethereum, with DA support from Celestia, bringing MoveVM natively to Ethereum. M2 combines Move's strong ownership model with EVM's liquidity to provide a secure and efficient smart contract development platform. It not only supports Aptos Move and Sui Move, but also embeds the EVM interpreter MEVM, enabling Sui, Aptos and EVM users to operate on the same Layer 2. Through high TPS and instant finality, M2 can support large-scale financial transactions and decentralized applications, while providing modular customization options to adapt to different project needs and achieve efficient and flexible blockchain solutions.
To sum up, M1 creates a scalable consensus layer compatible with Move and EVM, and independently creates the native Move consensus and ecology; M2 is responsible for Solidity-Move conversion and transaction execution, directly cutting into the EVM ecology, and becoming a bridge for direct communication between Move and EVM.
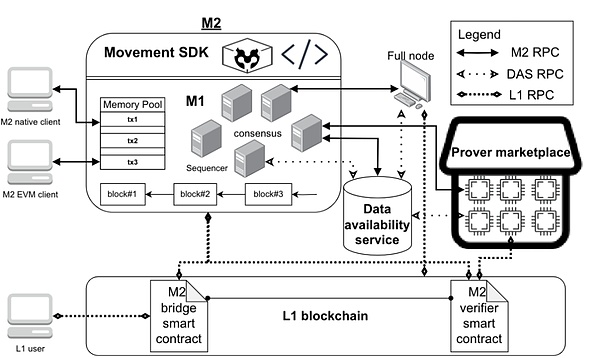
Source: https://www.techflowpost.com/article/detail_18939.html
2.2 Developer's entry point: Movement SDK
Movement SDK is Movement's innovative development tool that allows developers to easily build modularity and interoperability between Move and EVM environments.
Movement SDK combines the security and resource management features of MoveVM with the flexibility and adaptability of Solidity, enabling developers to build and deploy Move-based infrastructure and applications in any distributed environment.
It mainly consists of three core components: MoveVM, Fractal, and custom adapters for sorter networks and DA services.
MoveVM: It is the core execution engine of the Movement SDK, providing a resource-oriented and strictly controlled environment to run smart contracts. Although both are MOVE languages, Sui Move and Aptos Move are two independent blockchain systems, each with its own virtual machine (VM) and toolkit, which are very different. Movement's modular MoveVM is a multi-functional virtual machine designed to be fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and other Move ecosystems. It already supports the deployment of Aptos and EVM code, and will soon support the Sui ecosystem.
Fractal: is a compiler that allows developers to seamlessly deploy existing Solidity smart contracts to MoveVM. This bridge function not only provides Solidity developers with a safer and more efficient execution environment, but also retains the original logic and functionality of the Solidity contract.
Custom Adapter: is the last core component of the Movement SDK, designed to provide seamless integration with the sorter network and data availability (DA) service, ensuring secure connections with various blockchain networks and services.
The Movement SDK not only provides developers with tools for the perfect integration of Move and EVM, but also works with M1 as part of the M2 framework to further enhance the scalability of Movement.
Project Progress
According to the official website of Movement, there are nearly 80 ecological projects deployed on Movement, including star projects such as Babylon and Ethena.
In the tags below the project, we can see that it contains projects of various development languages, which shows the strong compatibility and ecological potential of Movement.
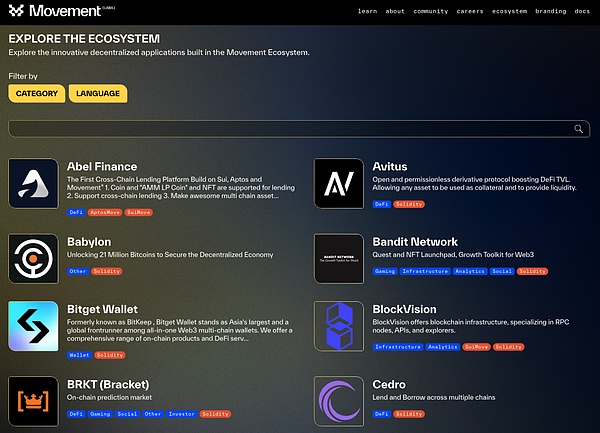
Source: https://movementlabs.xyz/ecosystem/page/1
Note: Movement has launched a test network activity, you can follow the tutorial to participate and get potential airdrop opportunities.

https://twitter.com/BiteyeCN/status/1818523443203358919
Team Background
4.1 Core Members
The two co-founders of Movement Labs are Rushi Manche and Cooper Scanlon, Rushi is 21 years old and Cooper is 24 years old. Both of them studied at Vanderbilt University.

Source: https://www.techflowpost.com/article/detail_18939.html
Rushi Manche started programming at the age of 14 and initially worked at health insurance giant UnitedHealth Group, responsible for the migration of cloud infrastructure.
He began his career in the field of distributed systems and databases, and later came into contact with cryptocurrency during college. This experience laid a solid foundation for him in the field of technology and paved the way for his future entry into the field of cryptocurrency.
Rushi's interest in cryptocurrency began when he learned that Facebook was developing its own blockchain project during college.
He first learned about the news through a New York Times article, which sparked his interest.
At that time, Cosmos had only 5 users and Ethereum had only a few hundred users, while Facebook's user base was in the billions, which brought huge potential for mass adoption of crypto technology.
Rushi studied the Move language in depth and gained a wealth of knowledge from the Move Book, and finally decided to build a career in this field.
Rushi's entrepreneurial journey was not smooth. While at Vanderbilt University, he insisted on developing his own projects despite limited resources.
He also shared his experience of choosing between Avalanche and Cosmos, and finally chose Avalanche as an early backer.
During college, he also founded Ensemble, an AI-driven test tutoring platform that provides free test preparation materials for high school students.
In 2022, Rushi joined Aptos as a software engineer and personally participated in the development of Move language smart contracts, making outstanding contributions to the core DEX in the ecosystem. This experience made him realize the huge potential of the Move language and inspired his passion for entrepreneurship in this field.
Cooper Scanlon is another co-founder of Movement Labs. Before founding Movement Labs, he built and audited the first yield aggregator using the Move language.
In November 2022, Rushi and Cooper, two Vanderbilt University alumni, decided to drop out of school and co-founded Movement Labs.
The creation of Movement Labs marks a new starting point for Rushi and Cooper in the blockchain field. Their team is committed to introducing the Move language to EVM and promoting the advancement of blockchain technology.
Rushi and Cooper's entrepreneurial story demonstrates their deep accumulation and courage in technology and innovation. Despite many challenges, they remain steadfast in advancing their vision and contributing to the development and application of blockchain technology through Movement Labs.
4.2 Financing
Rootdata shows that Movement received investment from Binance Labs in May. In the A round of financing, Movement received investment from top institutions such as Polychain and Hack VC, with a financing amount of 38m. This shows the strong strength and market recognition of Movement.
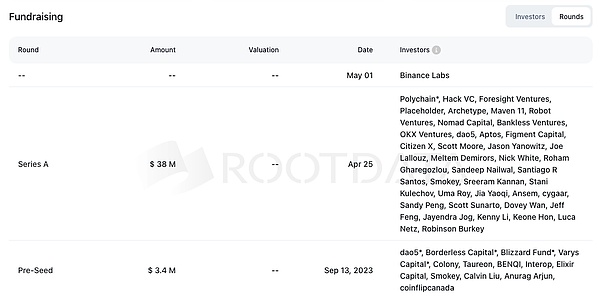
Source: https://www.rootdata.com/Projects/detail/Movement?k=OTMxMg%3D%3D
Summary and Outlook
Movement Labs has taken a different approach in the fiercely competitive Ethereum L2 track and the emerging Move ecosystem, exploring a potential path that takes into account both performance and ecology, and has stood out and won market recognition.
Movment not only achieves the perfect combination of Move and EVM in technology, but also continues to work hard on the construction of the ecosystem, striving to provide developers and users with a safe, efficient and easy-to-use blockchain platform.
With the continuous improvement of Movement's infrastructure and the gradual construction of its ecosystem, we expect Movement to bring more innovations and breakthroughs in the future and promote the development of the entire blockchain industry.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist