The development of AI agents will fundamentally change the way people work, and it will also change the startup landscape. In the past year, the number of startups based on AI agents has skyrocketed from single digits to dozens per month.
In Israel, there has been a surge in the number of startups building AI agents, with a focus on enabling others to integrate and customize these agents to meet the needs of different scenarios.
Many of these companies are leveraging Israel’s strengths in cybersecurity, data science, and enterprise software to build AI agents that can solve vertical industry problems, such as medical diagnostics and predictive security.
At the same time, horizontal applications such as workflow automation and personalized customer engagement have also emerged.
As people begin to look at more of these AI agent-led startups, they will notice that they are following certain common patterns.
For example, a startup that was initially assisted by general artificial intelligence is now transforming into a full “AI organization.”
With every major advance in the field of AI agents, we are getting closer to the trend that we began predicting a few years ago: more and more companies that rely on AI automation to run their business, with humans only responsible for making key strategic decisions.
This momentum has been going on for a few years, but now it feels like a turning point.
OpenAI CEO Altman predicts that this year will be the year that AI agents truly join the workforce. By 2027, at least half of all companies will have launched some form of AI agent.
And this is just the starting point.
In the near future, people may see the entire economy made up of these AI-first organizations. And if you want to build a truly lasting company, you must see this direction of development.
Perhaps companies will employ AI agents, and humans will work with AI agents, or even compete with them.
What will happen next?
Here are five possible evolutionary stages of AI agents:
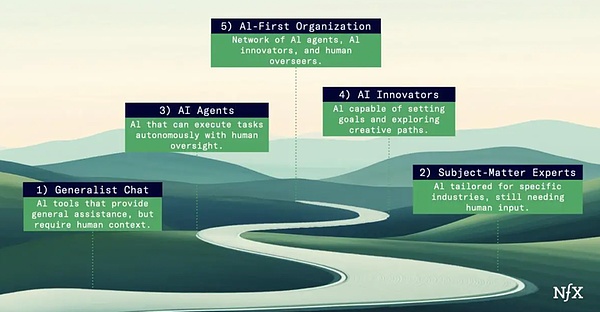
01.Universal Chat
The first wave of AI collaborators are basic models (general LLMs, such as ChatGPT or Claude). They break through the user experience and help people understand the broad capabilities of AI.
However, AI is just a tool, and humans are still ahead in terms of infusing AI with context, rationality, and empathy.
These general-purpose tools are “masters of no master,” as early adopters say. This shifts the AI startup landscape to the first evolutionary stage.
02.Domain Experts
General-purpose AI can read and write, and perform tasks when properly guided. However, general-purpose AI tools still perform poorly in super-specific industry settings.
Soon after the rise of general-purpose AI, we began to see the emergence of true AI domain “experts.”
AI can seemingly solve problems without much prompting from humans, and chat is still the primary interface for these systems, but many companies have built additional industry-specific features on top of chat functionality.
Law is one example, with companies like EvenUp and Darrow demonstrating the power of AI trained on a specific corpus of legal data.
These AIs understand the nuances of legal language and are able to generate professional-grade legal materials.
03.AI Agents (Current Stage)
There are still many great companies operating at the domain expert level of AI.
But in the past year or so, there has been a clear shift from a chat-based value proposition to an action-based value proposition.
General AI tools and domain experts are the true “co-drivers” that can create new connections, generate articles, or provide new materials. But humans still need to take action for these tools to really work.
Starting in April 2023, people will start to see AI perform some more advanced tasks.
The most famous examples of AI agents are in the field of code generation, such as OpenAI’s code interpreter or Cognition’s AI programmer Devin.
But the concept has expanded far beyond code generation and into more complete “job descriptions”.
There are now more and more AI agents that specialize in performing specific tasks. There is huge potential for packaging and combining these tasks to be transformed into real services.
For example, Enso, a company backed by NFX, is creating a marketplace for AI agents for small and medium-sized enterprises.
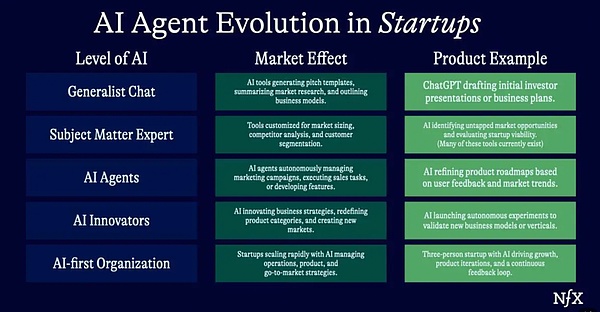
Once people continue to perfect the ability of AI to complete tasks and take action without a lot of human supervision, people can no longer go back.
04.AI agent innovation
Once AI agents are able to perform tasks continuously, people will soon see agents with innovative capabilities. If people allow AI to generate and explore new knowledge directions, its value will be elevated to a whole new level.
People can look at this problem in the same way as thinking about the human brain to solve problems and exercise creativity.
People have task-oriented "if-then" brain presets that help people perform tasks and solve problems.
But we also have an active subconscious mind, the kind of thinking that kicks in when you’re not focused on solving a problem, like when you’re taking a shower or taking a walk.
Have you ever had the experience of struggling with a piece of writing or a problem-solving process, only to find that it came to you easily after a walk?
That’s the result of your subconscious mind being free to explore new creative approaches. Most new, creative ideas come in this state.
AI innovation agents will be able to engage in this subconscious exploration. They won’t be constrained by “if-then” logic statements that foster narrow thinking.
Imagine asking a group of AI agents to develop a software feature on Monday, and by Wednesday you discover that the agents have improved on your initial request and developed a better feature based on trial and error experience and market analysis.

When the goal itself is abstract (increase sales, improve software performance, make users like my app), planning goals and mapping out paths will be key to the next stage of AI agent development.
This is also an important factor in making AI agents truly mature workforce.
Pure automation without critical thinking is a lifeline for the lowest hanging fruit in the economy. But it does not solve the biggest and most valuable problems, creativity is.
The key unlock is trust. People need to have confidence in AI agents to make strategic decisions, not just task-oriented decisions.
Some of this trust must be built through technology. People need two things: explainability and infrastructure. Both of these things could even become industries in their own right.
For example, NFX-backed company Maisa is perfecting “proof of work” for AI agents, a key element in building trust in the entire agent ecosystem.
Another NFX portfolio company, Emcie, is developing the infrastructure needed to create hyper-specific AI agents for individuals and businesses.
This trust will develop culturally. The more people see AI making smart decisions and creating better outcomes, the faster the future will come.
The early adopter group will be key. Small and medium-sized businesses or companies that simply can’t hire human labor to meet their needs will take the first step, while the rest of the ecosystem will watch and follow.
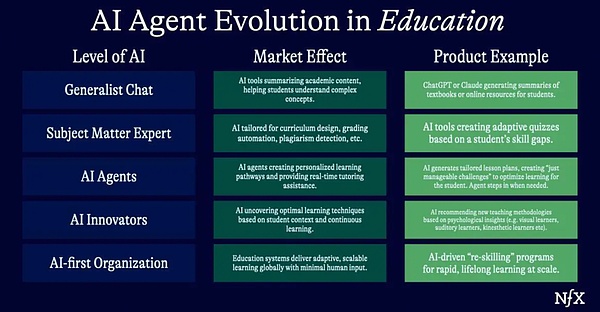
It will touch all industries. For example, in the field of education:
05.AI-First Organization
With agent AI workers, AI innovation, and trust and explainability systems in place, people will finally see the rise of true AI organizations.
These organizations are collections of AI agents and AI innovators capable of a wide range of actions.
This is the AI people often hear about in science fiction.
In the worst case, you can read about this kind of AI in Daniel Suarez’s Daemon, and you can also find it in Naomi Kritzer’s Improving Life Through Algorithms.
These agents can make decisions in complex environments with many potential goals worth achieving.
The difference here is that the AI itself will be able to self-select which goals are best and devise a path to achieve them.
The AI will take most of the actions, and you will work alongside the AI to review and audit the routes it takes.
It is conceivable that self-managed supply chains can oversee the entire process from production to delivery, and give rise to automated financial trading companies composed of many AI agents.
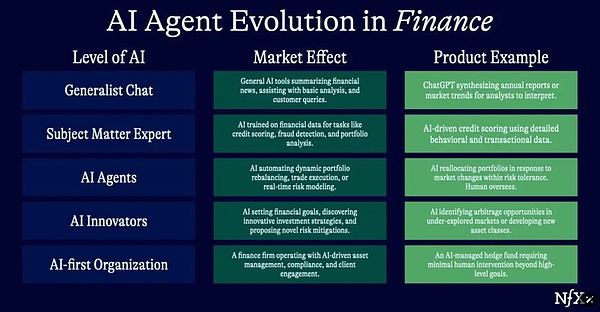
People don’t expect this to happen all at once, it will happen in steps.
As trust and technology develop, AI will begin to take on larger and larger tasks. In reality, we are still in the technology window for AI agent systems.
The people who really understand this are still the builders and hobbyists who are working hard.
But soon, an AI-led organization will emerge and people will have the "ChatGPT" moment. Before ChatGPT, how many people really understood the capabilities of AI?
If you know where people are going, you will be one step ahead.
In Israel, the AI agent market is booming, and startups are taking advantage of local expertise in machine learning, cybersecurity, and automation.
We are seeing more and more companies building basic agent platforms for other companies to customize, such as Enso.
Startups here have begun to address vertical challenges in areas such as fintech, logistics, and healthcare, and are positioning themselves as important contributors to the rapidly developing AI ecosystem.
AI agents are coming, AI innovators are coming, AI organizations are coming.
So now ask yourself, what is holding these things back from coming to my space? How can the barriers be removed? Or, once they are removed, how can I be a primary beneficiary?
Not every company should focus on building AI agent infrastructure.
But you can understand how the overall economics of your space will shift as people unlock these new pools of labor.
Also think about how this will impact your team psychologically - what will it be like to only manage AI employees? Or, conversely, when humans are being managed by AI?
At NFX, it’s our job to look at how transformative technologies work. These shifts are timed, and as technology changes, certain skills will become more important or diminished.
We also need to deal with the psychological changes and the new opportunities that they bring.
AI agents are in their most exciting nascent stage, and this is when great companies are born.
 Weiliang
Weiliang









