Just now, at 2 a.m. on September 19th, Beijing time, the Federal Reserve announced a 50 basis point interest rate cut! After the interest rate cut, the target range of the federal funds rate is 4.75% to 5.00%.
This rate cut exceeded the predictions of most economists!
It also means that the Federal Reserve is more firmly on the side of supporting Democratic candidate Kamala Harris.
This is the first interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve in 4 years. The Federal Reserve FOMC statement stated that confidence in inflation has increased and inflation is continuing to move towards 2%; the risks facing employment and inflation targets are in balance. The Federal Reserve's dot plot shows that the median forecast for the federal funds rate at the end of 2024 is 4.4%, which means that there will be another 25 basis point interest rate cut before the end of the year.
The Federal Reserve raised its forecast for the U.S. unemployment rate in 2024 to 4.4%, and lowered its forecast for U.S. GDP growth in 2024 to 2.0%.
Affected by the news of the interest rate cut, the three major U.S. stock indexes rose further, gold prices hit new highs, and the offshore RMB exchange rate hit a recent high.
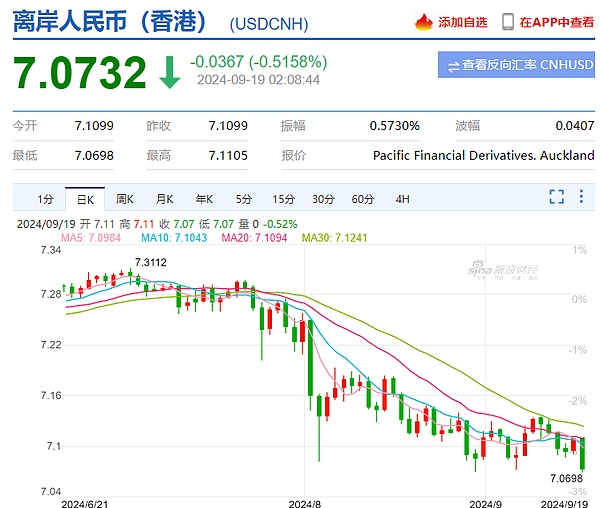
Let's use 10 paragraphs to understand this interest rate cut.
1. This interest rate cut means that the United States has entered a new round of interest rate cuts.
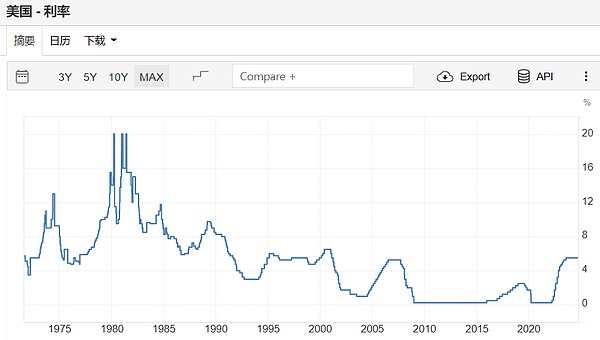
The following figure is a chart of the U.S. dollar interest rate over the past 60 years, and the trend is constantly falling. The rebound in recent years was caused by the massive money supply after the COVID-19 pandemic. The Federal Reserve has raised interest rates 11 times in a row. In the next few years, US interest rates will gradually decline and return to the ultra-low interest rate era before the pandemic.
2. The United States has started a new round of interest rate cuts, breaking the ceiling of China's monetary policy and giving us more room for interest rate cuts.
In the past few years, there has been a rare inversion in the interest rates between China and the United States, with China's 10-year treasury bond yield being about 200 basis points lower than that of the United States. In order to reduce capital outflows from China, China's interest rate cuts are small and limited. After the US dollar started the interest rate cut cycle, China's interest rate cut space will increase in the next few years, and the low interest rate era has arrived.
3. The Fed has started a cycle of interest rate cuts, which is good for China. It has increased the space for China's monetary policy, which is beneficial to the property market, stock market and economy.
But whether the A-share market has bottomed out depends on the property market; whether the property market has bottomed out depends on the economy; whether the economy has bottomed out depends on whether the monetary and fiscal policies are strong enough. China needs to issue more treasury bonds, invest in large and profitable infrastructure, encourage consumption, and also needs to have a larger interest rate cut and reserve requirement ratio cut.
4. In the next two to three years, China's LPR (loan benchmark interest rate) has 80 to 100 basis points of room for interest rate cuts. We must first pay attention to whether China's LPR will be cut at 9:15 am tomorrow (September 20). China has at least one chance to cut interest rates and reserve requirement ratio before the end of the year. After the LPR is cut, the interest rate of provident fund loans may also be cut.
5. Will the interest rate of China's existing mortgage loans be reduced across the board (beyond the loan contract agreement)? The probability is relatively high, and there may be news in the next two months. Recently, the Securities Daily, sponsored by the Economic Daily, has publicly discussed the possibility in the reporter's commentary. Bloomberg has also published short essays many times. Let us wait for the official announcement.
6. Recently, the RMB exchange rate against the US dollar has appreciated significantly. After the US dollar cuts interest rates, how will the exchange rate go? Will the RMB break 7? I think that before and after the US election, the RMB will continue to remain strong with the help of factors such as the US dollar interest rate cut, and it is not ruled out that the RMB exchange rate against the US dollar will break 7. The RMB exchange rate is currently undervalued. In the future, as long as China and the United States fight but do not break, the RMB exchange rate will most likely remain strong and stable.
7. In the next two years, the room for US dollar interest rate cuts is greater than that for RMB interest rate cuts. This is conducive to the RMB exchange rate remaining strong. In addition, the official proposed to prevent "involution" vicious competition, which means that if there is no major change in the international situation, the RMB exchange rate will remain stable, and the practice of stimulating exports through devaluation will not appear in the short term.
8. How will the US election affect the RMB exchange rate and China's economic recovery? If Trump is elected, he will intervene in monetary policy, and the Fed will accelerate the pace of interest rate cuts; Kamala Harris will let the Fed decide for itself. Trump has threatened that he will impose a 60% tariff on Chinese goods after taking office, which will trigger a new round of Sino-US trade war and may cause abnormal fluctuations and depreciation of the RMB; if Kamala Harris takes office, the RMB exchange rate will most likely remain stable and strong.
9. The latest financial data, investment data, consumption data, real estate data, etc. all show that the economy needs to "accelerate" again. After the Fed cuts interest rates until the end of the year, China's macroeconomic policies will be strengthened to sprint to complete the annual target. As for the Chinese property market, there may be big news on September 30 and the days before.
10. After the US dollar cuts interest rates, how will US stocks, US bonds, and the US dollar exchange rate go? Historically, these assets have performed differently after each rate cut, depending on what stage the U.S. economy was in at the time. If it is in a period of vitality after a technological revolution, a rate cut will allow the stock market to continue to rise and the dollar to appreciate; conversely, a rate cut confirms that the economy is not doing well. Within six months or one year after the first rate cut, the stock market will fall back, safe-haven funds will flow into the bond market, and the dollar will depreciate. At present, the market has a large divergence in the trend of the next six months to one year. My view is that the U.S. economy seems to be still in a period of excitement after a new round of technological revolution (such as artificial intelligence), and there is no obvious sign of recession.
Welcome to follow the following public accounts
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance






