Author: Starknet; Compiler: Vernacular Blockchain
Blockchain technology continues to develop, with Ethereum achieving a record 2 million daily transactions in January 2024. However, scalability issues between first-layer (L1) chains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum still limit their widespread adoption.
Thus, second-layer (L2) solutions emerged: a series of technologies designed to speed up transactions and reduce costs without compromising the security and decentralization of leading L1 networks. According to L2Beat, L2 expansion solutions have transformed Ethereum, processing 11-12 times more transactions than Ethereum itself.
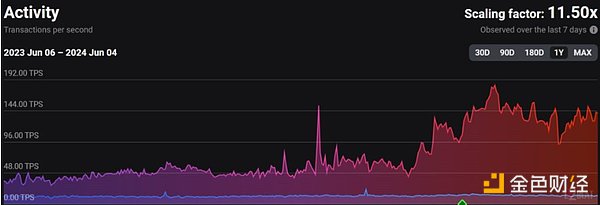
Source: L2beat.com
This article explores the L2 ecosystem, including its key innovations, challenges, and future development directions.
1. The origin of L2
As more and more users conduct transactions on L1, these networks become slower and more expensive. Solving scalability problems on L1 usually means compromising between security or decentralization, two features that all blockchains hope to have. The trade-off of choosing only two of the three desired blockchain characteristics of scalability, decentralization, and security is known as the “blockchain trilemma.”
Solving the blockchain trilemma is particularly important for Ethereum, as it has become the preferred L1 for building decentralized applications (dApps). Of the three desired characteristics, Ethereum chose security and decentralization at the expense of scalability.
In order to expand the number and types of use cases for Ethereum, building more complex dApps must be economically feasible.
L2 solutions have emerged as a way to address these issues by moving most of the heavy computation associated with processing transactions from the base layer to the second layer, increasing transaction throughput, reducing costs, and improving user experience. The goal is to achieve this while leveraging the security and decentralization of the underlying L1 blockchain.
2. Core technologies and frameworks
The total locked value (TVL) of the L2 ecosystem has now exceeded $46 billion, and it includes a variety of technologies and frameworks with unique characteristics. Let's take a closer look at some of the most important technologies:
Rollups - There are two types of Rollups: Optimistic Rollup and Validity/Zero knowledge Rollup. Optimistic rollups assume that transactions are valid by default. They use a mechanism to prevent fraud, enabling network participants to use "fraud proofs" to challenge transactions that are expected to be fraudulent to prove their invalidity. In contrast, validity rollups use "validity proofs" to prove the validity of each transaction submitted to the base layer. These two types of rollups provide higher throughput and lower fees than L1.
State channels - State channels allow participants to conduct off-chain transactions by locking part of the blockchain state to a multi-signature contract. Participants can trade freely off-chain, and the final state is settled on-chain. State channels provide almost real-time transactions and low fees, but have certain limitations in terms of functionality and the number of participants.
Plasma (Shard Chain)-Plasma is a framework for creating layered side chains anchored to the main chain. Plasma chains can process transactions off-chain and only submit periodic updates to the main chain, reducing the burden on the L1 network. Similar to optimistic aggregation chains, Plasma chains use fraud proofs to challenge suspicious transactions.
3. Review the L2 ecosystem
The L2 ecosystem is developing rapidly, and numerous projects and initiatives are working to expand the main L1 blockchain. Although there are some solutions dedicated to bringing scalability to Bitcoin, such as the famous Lightning Network, which uses state channels to provide faster and cheaper transactions on the network, there is no L2 solution for general computing on Bitcoin.
On the other hand, Ethereum has bred a thriving ecosystem of L2 solutions. We will highlight the main players and briefly describe them.
1) Validity Aggregation Chains (also known as Zero-Knowledge Aggregation Chains)
Starknet: The validity aggregation chain with the fastest growing developer community, with local account abstraction and its own programming language (Cairo), optimized for the ability to exploit validity proofs.
zkSync: Another leading validity aggregation chain with local account abstraction, running on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Scroll: EVM-compatible validity aggregation chain, focusing on native-level compatibility with existing Ethereum dApps and tools.
Polygon zkEVM: Developed by L2 scaling veteran Polygon, zkEVM is an EVM-compatible validity aggregation chain.
Linea: Powered by Consensys, the company behind MetaMask, Linea is a validity aggregation chain that can be used directly through MetaMask.
2) Optimistic aggregation chain
Arbitrum: It is the largest optimistic aggregation chain measured by total locked value (TVL) and is compatible with EVM.
Optimism: It is the second largest optimistic aggregation chain measured by TVL and is compatible with EVM.
Base: It is the third largest optimistic aggregation chain measured by TVL and is compatible with EVM.
Many of these projects are still in their early stages, often involving a period of centralized control known as the “training wheels” phase, which allows for controlled system updates and bug fixes. Although initially necessary, these training wheels should eventually be removed to achieve the desired decentralization and trustless operation.
The adoption of L2 solutions has been steadily growing in various fields including decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and on-chain games. The most commonly used types of L2 tend to be optimistic aggregation chains and validity aggregation chains. However, the integration of L2 solutions is not without challenges.
4. Challenges and Solutions
Although L2 solutions have great potential, there are still some challenges that need to be overcome to realize their full potential. From a user's perspective, interacting with L2 networks may be slightly more complicated and require additional steps, such as bridging assets and managing multiple wallets. Improving the user experience through better wallet integration, simplified onboarding, and more intuitive interfaces will be critical to driving mainstream adoption.
That’s why Starknet offers built-in account abstraction features that enable a smoother user experience, such as transaction signing through facial recognition and fingerprint recognition (for example, the Braavos wallet offers both of these features). On Starknet, making Ethereum scale means that a Web2-style user experience is just as important as cheaper and faster transactions.
5. Outlook for L2
As the L2 ecosystem matures, we can expect a wave of innovations, such as the local account abstraction feature on Starknet. Hybrid solutions that combine the advantages of different L2 technologies have begun to emerge, providing dual benefits for optimistic aggregation chains and validity aggregation chains. Advances in validity proofs (such as STARKs) further enhance the scalability and privacy of L2 networks.
Looking forward, the future of L2 solutions is closely tied to the overall development of blockchain technology. As L1 networks continue to evolve and new consensus mechanisms such as proof of stake are promoted, L2 solutions will need to adapt and integrate seamlessly with these changes.
In the coming years, we will see a flourishing of L2 solutions tailored to specific use cases and application areas. Some predict that L2 networks will eventually become the primary layer for user interaction, while L1 will serve as a secure settlement layer. Others envision a multi-layered blockchain architecture, with L2 solutions evolving in parallel with each other, sometimes with a third layer (L3) chain on top of them to create a scalable and interoperable ecosystem.
6. Conclusion
As the L2 ecosystem continues to grow, collaboration and contributions between developers, researchers, and users will be critical to the development of powerful and user-friendly L2 solutions.
By embracing the potential of L2 technology, the blockchain community can overcome the limitations of L1 networks and open up new possibilities for decentralized applications. The road ahead is filled with challenges and opportunities, but with the right approach and a shared vision, we can build a scalable and inclusive blockchain ecosystem that empowers individuals and transforms industries.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance




