Source: Byte Yuan CKB
In the previous article "Main Dilemmas Currently Faced by Lightning Network (1)", we introduced one of the main factors restricting the development of Lightning Network: liquidity. The liquidity problem can be further divided into two aspects. One is the overall lack of liquidity of the network. It is necessary to lower the threshold for building and maintaining Lightning Network nodes and introduce additional incentive mechanisms to solve it; the other is the problem of liquidity allocation. At present, there are already solutions such as Submarine Swap, channel splicing, multi-path payment, Lightning Pool, Liquidity Advertisement, and loop payment to optimize the liquidity of Lightning Network.
In this article today, we continue to introduce other challenges currently facing Lightning Network and the innovative solutions proposed by the community.
Support for stablecoins
With its excellent high throughput, low latency, low cost and privacy protection, the Lightning Network has become an ideal choice for realizing encrypted payments and an important payment infrastructure for building a P2P economy. In 2021, as El Salvador legalized Bitcoin, the application scope of the Lightning Network has been significantly expanded, the number and amount of payments have risen rapidly, and the payment channels in the network have exceeded 82,000 at one point.
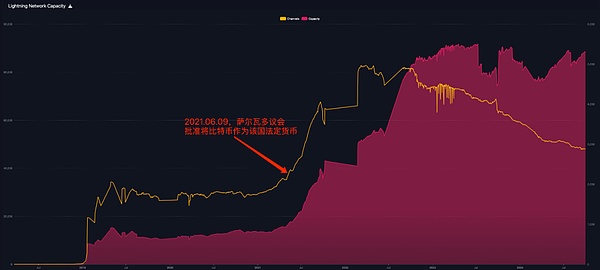
Source: https://mempool.space/graphs/lightning/capacity
However, in the past two years, the development trend of the Lightning Network has changed. From the data chart above, we can observe that the growth rate of funds in the Lightning Network has slowed down, and more importantly, the number of channels has even declined. This phenomenon reflects that the Lightning Network is facing new challenges after its rapid expansion. At present, BTC is mainly circulated in the Bitcoin Lightning Network. However, one of the biggest challenges facing BTC as a medium of exchange is the high volatility of its price. This instability has always been the main obstacle to the widespread application of the Lightning Network. In order for the Lightning Network to truly enter thousands of households and become the preferred method for daily small-amount and high-frequency payments, it is particularly necessary to introduce stablecoin support. After all, in real life, people are accustomed to using currencies with stable value for daily transactions. To this end, on July 23, 2024, Lightning Labs released the first mainnet version of the multi-asset Lightning Network, officially introducing Taproot Assets into the Lightning Network. Taproot Assets is an asset issuance protocol on Bitcoin. The issued assets can be deposited in the payment channel of the Lightning Network and transferred through the existing Lightning Network. The launch of the multi-asset Lightning Network mainnet version marks that stablecoins are officially supported on the Bitcoin Lightning Network, which means that application scenarios such as foreign exchange transactions that achieve global instant settlement through the Lightning Network and the use of Lightning Network to pay for stablecoins to purchase goods will become a reality.
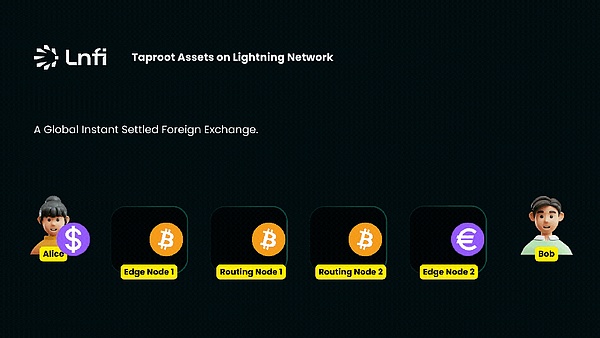
Figure: In the Lightning Network, Alice sends US dollar stablecoins and Bob receives euro stablecoins
In addition, the Lightning Network launched by Nervos CKB, Fiber Network, with the flexibility of the CKB blockchain, natively supports user-defined assets, including Bitcoin native stablecoins minted by decentralized protocols such as Stable++. In the complete beta version released in September, developers can already use Fiber Network to test the Bitcoin native stablecoin RUSD.
We believe that the combination of Lightning Network and stablecoins will release powerful synergies, inject new vitality into Lightning Network, and promote the popularity of crypto payments in daily life.
User Experience
Although Lightning Network has made great progress in technology, there is still room for improvement in user experience. There are still some gaps compared with traditional payment experience, such as:
You need to stay online when receiving/sending payments
Lightning Network payment involves changing the status of funds in the channel, and the channel is shared with others, so you must be online to change the status of funds with the other party. One of the main reasons for Lightning Network payment failure is that the recipient is offline. From the perspective of user experience, this is a significant design flaw. In sharp contrast, neither traditional payment methods (such as bank transfers) nor blockchain payments (such as on-chain USDT transfers) require the recipient to stay online. You only need to know the other party's account or address to complete the transaction.
The main solution at present is to introduce Lightning Service Providers (LSPs). LSPs are able to receive payments on behalf of offline users, thus eliminating the rigid requirement of "staying online". This solution brings the user experience of the Lightning Network closer to existing payment methods, greatly improving its practicality and convenience.
However, this solution also introduces a new challenge: trust assumptions. Users need to give a certain degree of trust to the Lightning Network service provider of their choice. This reliance on third parties is somewhat contrary to the original intention of decentralization and may cause concerns among some users.
Lack of a collection method that can collect any amount multiple times
The invoice in the Lightning Network is the core tool for requesting payment. It is generated by the payment recipient and provides the initiator with all the information needed to complete the transaction. We can simply compare the invoice to the "collection code" in common payment software.
Currently, the default invoice of the Lightning Network is a one-time one, which contains the hash value of a payment and its denomination, and will be invalidated after the payment is successful or timed out. This mechanism leads to a cumbersome operation process: each time a payment is received, a new invoice needs to be generated, copied, pasted, and sent to the payer. This design has a significant impact on the user experience in some scenarios. For example, a merchant who is accustomed to placing a QR code for payment (such as WeChat or Alipay payment code) at the counter will find it very troublesome to use the Lightning Network. Especially when business is busy, the need to frequently generate and transmit invoices may lead to a significant decrease in efficiency and even affect normal operations.
For this reason, the Bitcoin community has also proposed some solutions:
Keysend
The node_id of the Lightning Network node will not change, and it will be exposed to the payer after the invoice is given, so Keysend uses it as a static endpoint. This approach has significant advantages: it relies entirely on the architecture of the Lightning Network itself, without the need to introduce additional protocol support. Its disadvantage is that privacy protection is relatively weak, and sensitive data such as the recipient's node, channel, channel UTXO, etc. will be exposed.
Despite this, the practicality of Keysend has been widely recognized, and most Lightning Network clients have implemented the Keysend function.
LNURL and Lightning Address
LNRUL-pay is a standard that allows users to create a static QR code that can receive multiple payments, greatly improving the user experience. The workflow is as follows:
The user scans the QR code (LNURL-pay) with a Lightning Network wallet
The wallet decodes it, obtains the URL and accesses it using the HTTPS protocol
The server responds and asks for the payment amount (which can also be a fixed amount)
The user fills in the amount and sends the information back to the server
The server returns the traditional Lightning Network invoice
The wallet makes the payment
Lightning Address further optimizes this process. It encodes the user's QR code (LNURL-pay) into a URL similar to an email address. When other users access this URL, the system automatically returns the LNURL-pay request, simplifying the entire payment process.
It is worth noting that most wallets that currently implement the LNURL function use a custodial model. These wallet services assign a Lightning Address to each user, allowing them to easily receive payments. Although this method is convenient, it also introduces a centralized factor, and users need to weigh the convenience and decentralization themselves. BOLT12 is a new Lightning Network technical specification proposal, which aims to implement some of the functions provided by LNURL without using a web server. Although BOLT12 has not yet been merged into BOLT (Lightning Network Technology Foundation), this solution has been supported by most developers. Compared with LNURL, the biggest highlight of BOLT12 is that it can be implemented within the Lightning Network protocol without relying on other network protocols and communication methods.
Conclusion
In addition to the overall lack of liquidity of the Lightning Network and the problems with liquidity allocation introduced in the previous article, as well as the lack of support for stablecoins introduced in this article, there are many areas for improvement in user experience. The development of the Lightning Network also faces many other challenges. For example, LN-Penalty used by the Bitcoin Lightning Network has a storage burden in addition to its own complexity. The implementation of its improvement plan eltoo requires a soft fork of Bitcoin and the introduction of a new signature hash type. For example, for the privacy issue of HTLC, its improvement plan PTLC may be first implemented on the Lightning Network of other blockchains.
Although the road ahead is difficult, with the continuous advancement of technology and the continued efforts of the community, these challenges will eventually be overcome one by one. We have reason to believe that the Lightning Network is getting closer to the goal of large-scale adoption. It will not only change the way encrypted payments are made, but is also expected to become a key force in promoting global financial innovation.
 Alex
Alex
 Alex
Alex Alex
Alex Miyuki
Miyuki Weiliang
Weiliang Joy
Joy Miyuki
Miyuki Miyuki
Miyuki Weiliang
Weiliang Kikyo
Kikyo Alex
Alex