Author: Revc, Golden Finance
Foreword
As of 11:30 a.m. Beijing time on the 6th, Trump led Harris by 210 electoral votes to 112 in the US election. Pennsylvania played a crucial role in the US presidential election. It is not only a swing state, but also represents a wider distribution of voters and voter interests.
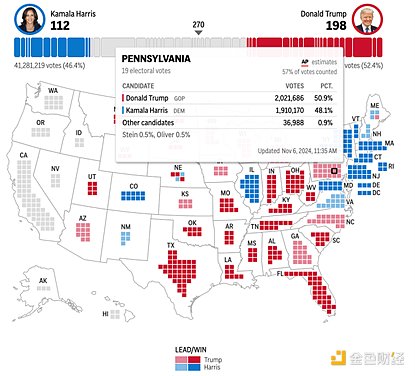
Pennsylvania voters become the decisive force in the general election
1. The weight of electoral votes
Pennsylvania, with 19 electoral votes, is one of the key swing states in the US election, second only to a few large states with more electoral votes. In the election, the victory or defeat of Pennsylvania often determines the entire election result, which is comparable to key states such as Florida and Ohio.
2. Political geography and diverse voter structure
Pennsylvania’s political landscape has a unique distribution:
Urban areas (Philadelphia and Pittsburgh): The largest cities in the state tend to support the Democratic Party, providing a lot of support for Democratic candidates in elections.
Rural areas: Rural areas in Pennsylvania mostly support the Republican Party, similar to rural areas in other swing states, and these areas provide important votes for Republican candidates.
Suburban areas (around Philadelphia): The suburbs around Philadelphia are the real battlefields of the election. These areas are densely populated and have large fluctuations in voter tendencies. In recent years, due to changes in demographic structure and changes in political attitudes, suburban voters have gradually leaned towards the Democratic Party.
3. Historical Status as a Swing State
Pennsylvania has historically swung between the two parties and is a barometer of broader political trends in the United States:
1992-2012: Pennsylvania supported the Democratic Party for six consecutive times, becoming one of the so-called "blue walls" along with Michigan and Wisconsin.
2016 Turn Republican: In a major shift, Pennsylvania narrowly supported Republican candidate Trump in 2016, the first Republican victory in Pennsylvania since 1988, reflecting the changing preferences of working-class voters, especially in rural and industrial areas.
2020 Return to the Democratic Party: Biden's narrow victory in Pennsylvania in 2020 highlights the competitiveness of the state and the importance of working-class, suburban voters. Suburban population growth and changing attitudes of rural voters are affecting the entire electoral landscape.
4. The influence of working-class voters
Pennsylvania has a large working-class population, including blue-collar workers in coal, steel, and manufacturing, especially concentrated in the western part of the state. Due to the importance of economic issues, these working-class voters have seen a shift in political allegiance in recent election cycles. The support of Pennsylvania's working-class voters is uncertain, but critical in determining statewide election results.
5. The importance of "blue wall" states
Pennsylvania is one of the "blue wall" states that traditionally vote Democratic (including Michigan and Wisconsin), and supported the Democratic Party from 1992 to 2016. For Democrats, winning Pennsylvania is often the key to reaching 270 electoral votes. For Republicans, winning Pennsylvania can provide a huge advantage, forcing Democrats to win more challenging states to make up for losses.
Pennsylvania Election Situation and Trends
Pennsylvania has become increasingly competitive in recent years. Here are some key factors:
Suburban voting trends: Suburban areas around Philadelphia, in particular, are increasingly voting Democratic due to demographic changes and voters’ different positions on issues like health care and education.
The shift among working-class voters: Economic issues are at the heart of Pennsylvania, with trade, manufacturing, and energy policies directly affecting Pennsylvania voters, making economic topics particularly influential.
Voting rate and early voting: Pennsylvania expanded mail-in voting in 2020 amid the pandemic, which boosted historic voter turnout and reshaped the campaign strategies of both parties.
Pennsylvania’s Election History – Swing State
Before 1992: Pennsylvania was highly competitive, usually supporting the winner, leaning Republican in some periods, such as Nixon’s victory in 1972 and Reagan’s victory in the 1980s; but leaning Democratic in some closer elections, such as Kennedy’s victory in 1960.
Democratic Dominance from 1992 to 2012: From Clinton’s victory in 1992 to Obama’s victory in 2012, Pennsylvania supported Democratic candidates for six consecutive times, a trend that coincided with the increase in urban and suburban voters.
Turn to Republicans in 2016: Trump’s victory was a historic shift, with Pennsylvania turning Republican by a narrow margin. Trump’s focus on working-class economic concerns resonated with rural and industrial voters.
Return to the Democratic Party in 2020: Biden won Pennsylvania by a narrow margin in 2020, reaffirming the state’s swing position and the importance of suburban and working-class voters. Biden’s victory relied primarily on high voter turnout in urban and suburban areas, further highlighting the key role of these areas.
Summary
Pennsylvania’s diverse demographic structure and historically swing position in elections highlight its key role in the U.S. electoral landscape. Pennsylvania voters tend to prioritize economic policies related to manufacturing and energy. The division between urban and rural and suburban voters in Pennsylvania reflects national trends to a certain extent, and suburban areas are gradually playing a more decisive role in statewide election results.
 Alex
Alex






