This technical research report was researched by ScaleBit Written byLeon
TL;DR
This article conducts an in-depth analysis of the "lost" phenomenon of some runes that have occurred in recent BEVM cross-chain operations, and also proposes ways to avoid such problems from happening again. Safety advice.
Recently, we have noticed that some runes are "lost" in BEVM cross-chain operations, which has aroused concern and concerns in the community. This article will conduct an in-depth analysis of this issue, aiming to provide users with a more comprehensive understanding of the issue. At the same time, it will also use this topic to talk about some precautions in the use of inscriptions and runes that have become popular recently.
Background
Beijing time on December 23, 2023 , some BEVM cross-chain trading users discovered that some COOK and PSBTS held in their accounts were transferred to the cross-chain bridge without their knowledge, and then these users raised questions to the BEVM team. Then BEVM's official Twitter issued a statement, saying that because this part of the runes is not supported by mainstream wallets such as Unisat , when cross-chaining to BEVM , this type of non-mainstream The inscription will be forwarded to the BEVM address as a normal UTXO.
After the ScaleBit security team noticed this incident, they immediately conducted an investigation. After research by the ScaleBit team, it was confirmed that this part of the runes was indeed transferred as a normal UTXO in the same cross-chain transaction and was not "stolen" by BEVM.
Text
Quoting BEVM official website information, BEVM is A BTC Layer2 that uses BTC as Gas and is compatible with EVM. The core goal is to expand the smart contract scenario of Bitcoin and help BTC break through the constraints of the Bitcoin blockchain being non-Turing complete and not supporting smart contracts, so that BTC can be used in Layer 2 of BEVM. Build decentralized applications using BTC as native Gas.
Recently, with the launch of the BEVM Odyssey event, many users have begun to interact with BTC cross-chain to BEVM, hoping to participate in the BEVM ecosystem in the future. Take the initiative. However, during the cross-chain process, some users found that part of the COOK and PSBTS they held were lost. According to the blockchain browser, it was found that this part of the runes had been transferred to the BEVM cross-chain bridge, so the situation mentioned above occurred.
Next, let’s take a look at what happened.
First of all, we found some cross-chain transaction information through the BEVM browser (https://scan.bevm.io/stats). Through analysis , we found that the receiving address of the cross-chain bridge is:
bc1p43kqxnf7yxcz5gacmqu98cr2r5gndtauzrwpypdzmsgp7n3lssgs5wruvy.
Subsequently, we checked on Rune Alpha (a universal browser and service that supports RUNES protocols such as COOK and PSBTS). Its address holds more than 110,000 A large variety of runes including COOK and more than 280,000 PSBTS.
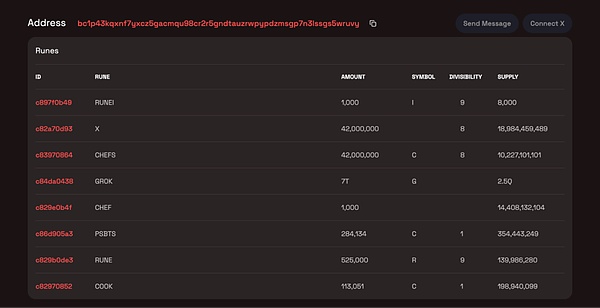
We immediately conducted research and analysis on this part of rune-related transactions.
Let’s take one of the transactions as an example:
https://runealpha. xyz/txs/c1bf015ce01a3610b436fb2e418685855cd7a37143cd52a4d1858a53e610b5f2
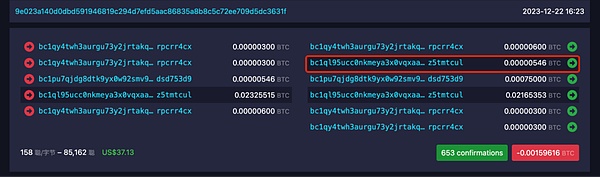
The transaction content is as shown in the picture:
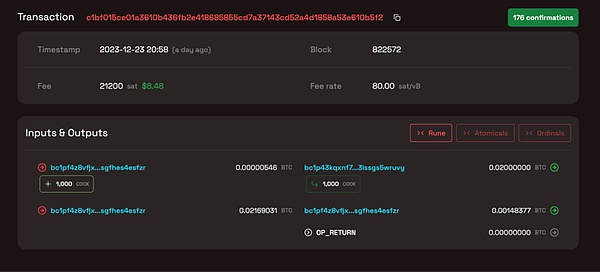
We can see that there are two inputs to this transaction, namely ;0.00000546 BTC (containing 1000 COOK) and 0.02169031 BTC, the output is 0.02 BTC (containing 1000 COOK) and 0.00148377 BTC.
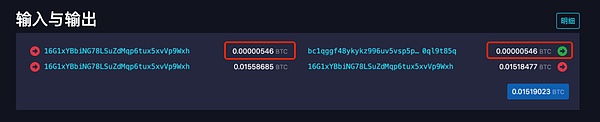
For comparison, we found a transaction that was not a COOK transaction with a cross-chain bridge transaction. The output is as follows:
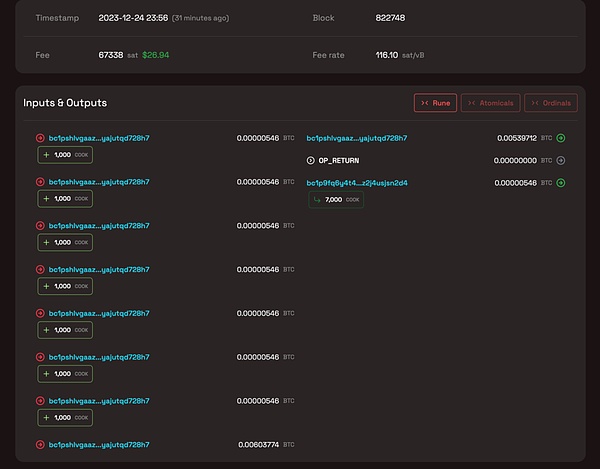
You can see that whether Both input and output contain a UTXO of 0.00000546 BTC.
Why is this? Here we need to know some relevant knowledge.
UTXO
First, let’s understand what UTXO is .
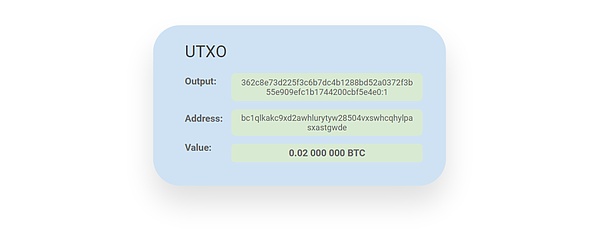
UTXO, full name Unspent Transaction Output, literally translated as Unspent Transaction Output, this is the core knowledge point of Bitcoin. In Bitcoin transactions, each transaction has inputs and outputs. The money someone else pays you is the "transaction input" and the money you receive is the "transaction output."
The core design idea of UTXO is stateless. It records transaction events but not the final status, which means that it only To record change events, users need to calculate the balance by themselves based on historical records. Therefore, the transaction model of Bitcoin is different from the bank account we usually use. It does not have an account. Bitcoin only has UTXO. A UTXO can be thought of as a "coin" of any amount.
UTXO input and change
UTXO, that is Just like coins, they cannot be broken apart and used, so how do you get the input amount together during the transaction, and how do you get change?
For example, Xiao Ming transfers 1 BTC to Xiao Gang. The whole process is like this. Xiao Ming needs to collect enough inputs. For example, in the previous transaction corresponding to Xiao Ming's address, he found a UTXO with a face value of 0.9, which is not enough for 1 BTC. Fortunately, multiple inputs are allowed in the transaction. So Xiao Ming found another UTXO with a face value of 0.2, so that there would be two inputs in this transfer transaction. There will also be two outputs at the same time, one pointing to Xiaogang's address, with a face value of 1 BTC. The other one points to Xiao Ming's address, with a face value of about 0.1 BTC. This output is the change.
In the process of Bitcoin transfer, there is no fixed algorithm for input, and it depends on the implementation of the wallet.
Bitcoin Inscriptions and Runes
Secondly, we You need to know what Inscriptions and Runes are. Bitcoin inscriptions and runes are two important concepts in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The main representative of Bitcoin Inscription is the Ordinals protocol. Ordinals was born in December 2022 with content entirely on-chain and developed by Casey Rodarmor. The protocol utilizes the Sat numbering system. Ordinals track each satoshi in transactions by giving them a serial number. At the same time, users can attach additional data (images, videos, text, etc.) to the Bitcoin blockchain through Ordinals, making each Each Satoshi is unique and thus has the nature of NFT. BRC-20 was created based on this protocol.
Runes Protocol, also known as Runes Protocol. With the popularity of BRC-20, transactions of BRC-20 related tokens account for the majority of the Ordinals protocol. On September 26, 2023, Casey Rodarmor redeveloped a protocol called Runes (which is what everyone now refers to as the Runes protocol) as a replacement for BRC-20. This protocol is a simple FT (Fungible Token, fungible token) protocol based on UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) that enables Bitcoin users to have a good experience. The main representatives of runes are what we mentioned COOK and PSBTS.
The carriers of Bitcoin inscriptions and runes are UTXO, a combination of Bitcoin inscription (Inscription) and Rune (Rune) The key difference is that the inscription is engraved in the SegWit data, while the rune is engraved in OP_RETURN. The data size that OP_RETURN can store is very limited, but it is more than enough for issuing coins. This is not a new technology.
For users to cast inscriptions or runes, they essentially send Bitcoins that match the amount to the protocol, and the protocol returns you a coin with the inscription or runes. UTXO, usually a UTXO of 0.00000546 BTC. Let’s talk about why it is 0.00000546. This is the minimum transaction amount set by Bitcoin.
Transmitting the inscription is also because these wallets recognize the special format of these UTXOs. The wallets use these UTXOs as input through the corresponding protocols, pay additional handling fees, and transfer them to the other party.
Why did the user lose the "rune"?
For users to lose runes, because it is still UTXO in nature, when users use UniSat to perform cross-chain operations on Bitcoin, because UniSat does not The UTXO containing runes in this part is identified and processed as an ordinary UTXO, and the input is sent to the cross-chain bridge.
In fact, not only cross-chain operations, users may also lose runes when performing other Bitcoin transfer operations in wallets that do not support runes. On December 7, a user lost 15,000 COOKs during a BRC-20 swap operation on Unisat.
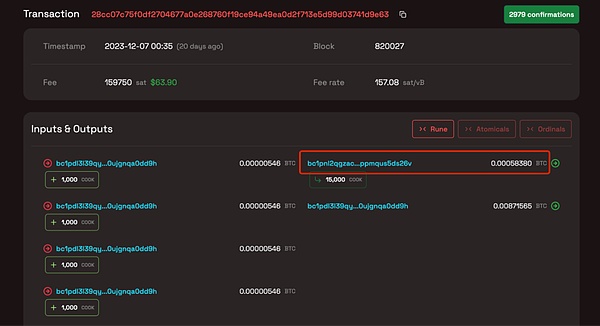
Another interesting thing is that when casting runes on Runes Alpha, it is possible to transfer the user's inscriptions as Gas.
Why has no one reported the missing inscription?
Through BEVM’s official documentation, we found that BEVM cross-chain supports inscription cross-chain. Users only need to use BSwap to transfer their The inscription is cross-chained to BEVM. The wallet used across chains is the UniSat wallet. This is a Chrome plug-in wallet for the BTC ecosystem that helps users store, mint, and transfer BRC-20 tokens. It can identify the user's inscription, thereby avoiding the merging of this part of UTXO. It will only be transferred when the user actively trades the inscription.
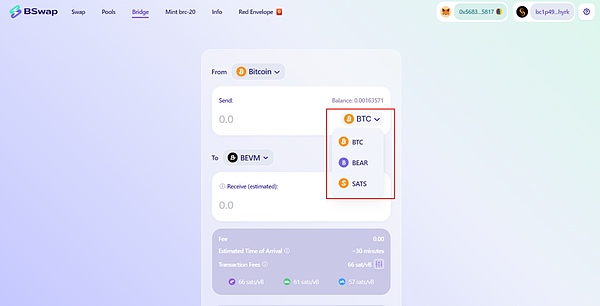
Since Unisat does not currently support the rune protocol, which is why users will "lose" runes across chains without losing inscriptions. A similar situation will occur if you switch to other wallets that do not support runes.
Can the runes still be retrieved?
Now that the runes have been transferred to the cross-chain bridge, can users still get back this part of the runes?
We reviewed the BEVM white paper. BEVM 's asset cross-chain solution is based on Bitcoin's Taproot technology and is integrated ;Schnorr signature + Mast Contract + 1000 BTC Light Node POS network to achieve decentralized cross-chain and management of assets, two-way BTC-BEVM Cross-chain is managed entirely based on the node consensus on the chain, achieving complete coding and trustlessness instead of relying on multi-signature or manual management. This makes the cross-chain security of BTC and Bitcoin assets as secure as BFT POS. It is equally decentralized and secure. Therefore, BEVM officials cannot initiate a separate transfer transaction to withdraw the user's "rune assets".
Since BEVM does not support the rune protocol, the probability of this part of runes being transferred out is completely random. When the escrow contract executes the transaction, these "runes "Asset" may be transferred out as an ordinary UTXO, but the entire process is completely random and not subject to human control. If the withdrawal is to be forced, the consensus of the entire BEVM chain must be completely changed, which will undoubtedly lead to a hard fork of BEVM. .
In general, this incident was caused by multiple reasons:
The wallet used for cross-chain operations does not support runes.
BEVM is a distributed and decentralized managed asset that cannot be withdrawn manually.
Users are not familiar with the rune protocol.
How to avoid this kind of problem from happening again?
For ordinary users, how to avoid this type of problem from happening again? When doing interactive operations, we recommend that users do the following:
Make sure the wallet you use supports Inscription or the Inscription protocol.
Make sure that the protocol you want to interact with (such as a cross-chain bridge) supports the Inscription Rune protocol.
Before using the protocol, first study whether there are any problems during user operation.
Use multiple wallets to manage different assets.
At the same time, developers are reminded that when developing and designing, they need to be fully considered and prepared , Solve possible protocol incompatibility issuesfrom the code level. If not, do research before going online and give clear reminders to avoid unnecessary doubts and troubles.
Summary
The emergence of inscriptions and runes is This important milestone in the continuous exploration and innovation of the Bitcoin ecosystem has greatly promoted everyone's attention and enthusiasm for participation in the Bitcoin ecosystem, and has also played a great positive role in the future development of the Bitcoin ecosystem. However, for now, inscriptions and runes are still in a relatively early stage. We hope that everyone must pay attention to the related risks while participating and avoid being blind.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance









