Author: MrNouman / Source Translation: Vernacular Blockchain
The debate over how to generate passive income from cryptocurrencies has been ongoing for years. Many investors turn to mining and staking as the two most profitable passsive income strategies; however, there is significant confusion surrounding these terms.
Mining and staking are both viable ways to make money without being active in the market, but there are significant differences between them that can affect your return on investment. In this blog post, we’ll explore the pros and cons of each strategy to help you make an informed decision and find the option that best suits your goals.
1. Yield Farming
1) What is Yield Farming?
The process of providing liquidity to DeFi (decentralized finance) protocols, such as liquidity pools and cryptocurrency lending services, is It's called Yield Farming (mining). It’s been likened to Yield Farming because it’s a new way to “grow” your cryptocurrency.

Liquidity Mining (also known as liquidity mining) is currently the most popular method of profiting from crypto assets. When block producers provide liquidity, they receive a percentage of platform fees from decentralized exchanges (DEX) like Uniswap. These platform fees are paid by token exchangers who use liquidity. It’s a win-win situation: Cryptocurrency holders gain more exposure, while protocols benefit from increased liquidity and trading volume.
Some cryptocurrency enthusiasts view Liquidity Mining and Yield Farming as two different investment strategies - mainly because users will receive a reward from the Liquidity Mining system. Liquidity Provider Token (LP Token) as a return for the trading pair.
However, these terms are often used interchangeably. Cryptocurrency Yield Farming can also be called DEX mining, DeFi mining, DeFi liquidity mining or cryptocurrency liquidity mining.
2) How does Yield Farming work?
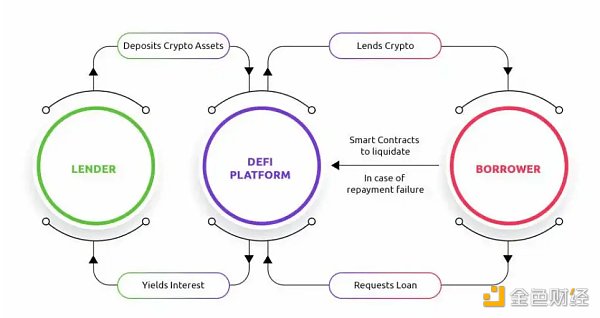
A key concept in Yield Farming is automated market makers (AMMs), which are permissionless automated trading platforms that unlike Traditional trading platforms involving buyers and sellers require users to submit orders. AMMs enable investors to conduct transactions more efficiently and conveniently without the need for intermediaries or third parties. Additionally, thanks to automated market makers, transactions are completed almost instantly, which further increases mining’s appeal to many investors.
Liquidity Providers (LPs) and Liquidity Pools
The automated market maker (AMM) system maintains an order book, which mainly consists of liquidity pools and liquidity providers (LPs).
Essentially, liquidity pools are smart contracts that collect funds and make it easier for cryptocurrency users to borrow, buy, and trade digital currencies. Liquidity providers (LPs) invest funds into liquidity pools and use this funds to promote the DeFi ecosystem. Liquidity pools incentivize them.
3) Advantages of Yield Farming
Mining enables many ordinary investors to earn returns from digital assets without having to have a deep understanding of blockchain technology or develop complex trading strategies. The returns generated through mining allow investors to obtain returns that are unattainable with traditional investment tools. As DeFi continues to grow and evolve, it’s clear that crypto mining will become a more mainstream method of generating passsive income online.
4) Better Yield Farming platform
Different Form companies offer different financial services, most of which are able to generate surprisingly high interest rates. You might get 0.01% to 0.25% APR from the big banks, but these low returns can’t compete with the 20% to 200% profits that some DeFi platforms promise. The higher the interest rate, the higher the risk of the staking pool – this is a key correlation. Be wary of scams and unproven platforms that could cost you money.
The most profitable DeFi platforms (such as Aave, Curve, Uniswap, etc.) are on Ethereum, but Binance Smart Chain (BSC) also has some substance Projects such as PancakeSwap and Venus Protocol can rival the Ethereum network.
Here is a list of some of the better platforms:
-Providing liquidity on Uniswap Sex: The annual rate of return is about 20% to 50%
-Earn interest on Aave: The annual rate of return is about 0.01% to 15%
-Mining on PancakeSwap: annual yield is about 8% to 250%
- Providing liquidity on Curve Finance: Annual yield is approximately 2.5% to 25%
-Yearn Finance: Annual yield is approximately 0.3% to 35%< /p>
The high interest rate (annualized rate of return) of mining pools makes competition extremely fierce. Interest rates frequently fluctuate, forcing liquidity miners to alternate between different platforms. The downside is that every time a miner leaves or enters a liquidity pool, they have to pay gas fees.
2. Staking
1) What is Staking?
Staking is becoming increasingly popular in the cryptocurrency industry as it allows users to support their favorite network or protocol while Earn a passive but high income. It involves holding a certain number of coins or tokens in a secure wallet and participating in the verification process of transactions on certain blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, Polkadot, BNB, Cardano, etc. In return, stakers receive more coins or tokens, which can generate a steady income stream. Since rewards often depend on the volatility of the network, staking can be very profitable if done correctly, making it an attractive option for cryptocurrency enthusiasts looking to diversify their portfolios.
Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS)
In the field of cryptocurrency, there are two core consensus mechanisms that have attracted much attention, namely Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). While PoW is currently the most dominant protocol in the industry, PoS is also growing in popularity.
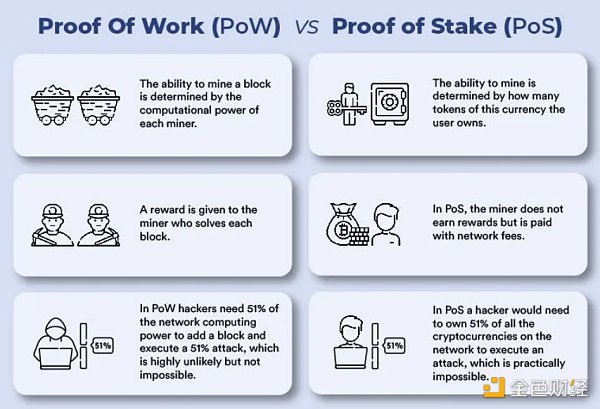
These protocols each have their own advantages and disadvantages. In PoW, miners invest computing power to process (verify) transactions - miners are rewarded for their hard work by being awarded tokens. This makes it a secure system, but PoW is also associated with huge energy consumption.
In PoS, holders stake Tokens from their balance and receive rewards. This offsets mining, thereby reducing energy costs. However, since the protocol utilizes a validator selection algorithm for transaction verification, it can lead to centralization of control if not implemented properly.
Thus, neither protocol is inherently better or worse; understanding the pros and cons of each protocol can help determine which Agreements are best suited to specific situations.
2) How does cryptocurrency staking work?
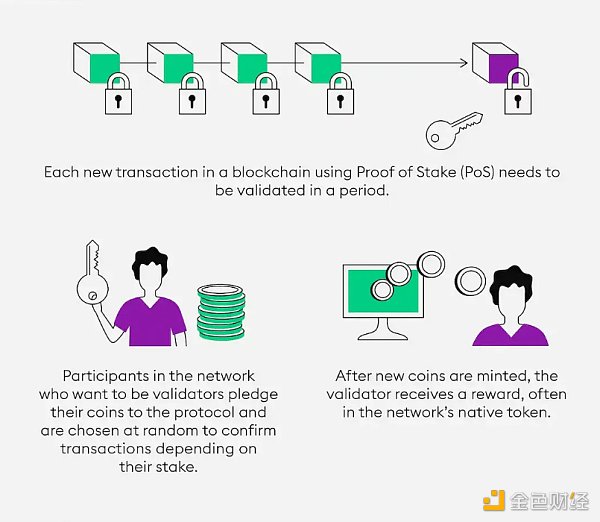
Source: Bitpanda
Staking is the act of committing funds as collateral in the blockchain world Products are a popular way to earn income. It involves locking up a certain amount of cryptocurrency, generating rewards through a verification process, similar to mining but with less work and risk. In return for staking their Tokens, users can receive rewards for contributing to the security and stability of the ecosystem.
3) How to pledge PoS cryptocurrency
To pledge For cryptocurrencies, users must download and sync the wallet, and transfer tokens. Users can set their wallet’s staking settings, check statistics for staked tokens, and keep an eye on the blockchain for rewards. Make sure all network security settings are up to date and have the highest level of protection enabled to ensure that staked funds are not put at risk. Additionally, data should be backed up as frequently as possible, as unexpected events can cause outages that could put funds at risk. Staking cryptocurrency is a great way to reward yourself by actively protecting your wallet and supporting the consensus of the network.
The following are the most commonly staked cryptocurrencies:
-Ethereum (ETH)< /p>
-Cardano (ADA)
-Tezos (XTZ)
-Polygon(MATIC)
-Theta(THETA)
These five cryptocurrencies offer high potential rewards for users willing to lock their funds within the network for a period of time. While rewards vary in each case, staking these five coins is considered more reliable than other coins.
4) The impact of DeFi on staking
Due to DeFi Platforms are decentralized and therefore less susceptible to security breaches than traditional banking applications, which they are generally more secure than. DeFi settings also provide users with incentives such as access to high annualized yields, additional governance privileges, or voting rights that other financial systems cannot offer.
Investors participating in DeFi should take some additional precautions when staking, including:
-Consider the security of the DeFi platform;
-Determine the liquidity of the pledged Token;
- Investigate whether rewards are inflationary;
- Diversify with different staking platforms and initiatives.
3. What is the difference between mining and staking?
Choosing between mining and staking as a form of investment can be a little tricky. While both offer the potential for additional income, it's important to understand which one is right for your situation and goals.
While the terms "mining" and "staking" are sometimes used synonymously, there are some clear differences between them.
Profitability: The profits generated by mining and staking vary greatly, and are usually measured by the "annualized yield" (APY). express.
For example, miners who join a new project or method early can make considerable profits. According to CoinGecko, possible returns range from 1% to 1,000% APY. Unlike mining, staking returns typically fluctuate between 5% and 14%.
Risk Level: Mining offers higher returns, but it also comes with greater risks. One of the reasons is that since crypto mining is often used in newer DeFi projects, there is a higher risk of “pull and pull”. Staking is more common on established PoS networks where risk is lower.
However, whether mining or staking, volatility brings a certain degree of risk. If the token value drops unexpectedly, both miners and stakers may lose funds. There is also the possibility of liquidation, which may happen if your investment is not covered by your collateral.
Complexity: Staking is often viewed as one of the simpler passive income techniques as it only requires investors to select a pledge pool and lock their cryptocurrencies. It also does not require a large initial investment. Mining, on the other hand, can be time-consuming because investors must decide which tokens to lend and on which platform, with the possibility of changing platforms or tokens repeatedly. Ultimately, how you choose to actively manage your investments may determine whether you choose staking or mining.
You only need one crypto asset to start staking. On the contrary, mining allows you to make money from trading pairs.
Liquidity: When comparing mining vs. staking, the winning strategy is obvious for investors looking for liquidity of. Both strategies require cryptocurrency investors to own a certain amount of crypto assets in order to be profitable. However, unlike staking, investors do not need to lock up their funds when mining – with this technology, they have full control over the cryptocurrency and can withdraw it at any time.
Inflation: PoS Tokens tend to be affected by inflation, and any benefits given to stakers are generated by newly created Tokens supplied. Staking a minimum of your Tokens entitles you to benefits that are proportional to the amount staked and keep pace with inflation. If you miss staking, the value of your current assets will decrease due to inflation.
Duration: Both require users to stake their funds on different blockchain networks for a period of time. Some also have required minimum dollar amounts.
Transaction fees: Miners can switch pools frequently every week. They are constantly adapting their strategies to increase revenue and fully maximize returns. This is why gas fees are undoubtedly a major issue for miners who freely switch liquidity pools, but this fee can be overlooked when comparing mining vs. staking. Even if miners find greater rewards on another network, they must account for any switching costs.
Security: Staking is generally more secure because stakers participate in the strict consensus process used by the underlying blockchain.
On the other hand, mining (especially based on newer DeFi protocols) may be more vulnerable to hackers. Especially if there are vulnerabilities in the smart contract code.
Temporary losses: Due to cryptocurrency price fluctuations, miners may experience temporary losses in bilateral liquidity pools. Rising values of digital assets do investors no good. For example, if an investor deposits funds into a mining pool and the price of a cryptocurrency surges, that investor would be better off keeping those cryptocurrencies rather than adding them to the pool. Investors may also suffer temporary losses if the value of their Tokens declines.
Staking will not result in temporary losses.
The similarity between mining and staking is that they are two of the most popular ways for cryptocurrency enthusiasts to earn passive income.

4. Which summary is better?
Staking is an excellent choice for investors who don’t care about short-term price fluctuations, but care about long-term investment returns. Avoid locking funds for staking if you may need to quickly retrieve the funds before the staking period expires.
For investors who prefer short-term methods, mining is a good choice. It does not require fixed capital. You can switch between platforms to find higher annualized returns. Mining can generate more revenue when taking a short-term approach. Compared to staking, this is a high-risk endeavor. Tokens with lower transaction volumes generally benefit the most from mining, as this is the only practical way to trade them.
In general, both mining and staking have specific advantages. Staking generally has lower risks and does not require locking funds, making it suitable for situations where quick operations are required. In the long term, mining provides greater flexibility and can switch between different platforms and tokens to obtain higher yields. Mining helps diversify your investment portfolio and earnings can be reinvested to earn more interest. Although mining may bring higher income, consider the cost of switching platforms and tokens. In general, staking is safer and more stable and suitable for long-term investment.

Staking and mining are two concepts that are still somewhat new, and they are sometimes even used as synonyms. Both involve holding cryptocurrency assets to generate interest. For both cases, finally answers to some frequently asked questions:
1) Is mining better than staking? In most cases, mining offers higher rewards than staking. However, these returns are dynamic. On the other hand, due to the fixed annualized rate of return provided by the staking strategy, users can ensure their returns at the end of the staking period. Ultimately, it all comes down to your own risk appetite and investing style.
2) Is mining more risky than staking? Mining (especially leveraged mining) can be risky as it is subject to price fluctuations associated with certain tokens; however, many miners have experienced positive returns through this strategy.
3) Is staking a type of mining? A bit like. Liquidity mining is a derivative form of mining, and mining is a derivative form of staking.
4) Is mining profitable? Yes, returns typically fluctuate between 5% and 30%, depending on the specific DeFi protocol and asset class involved. While every investment strategy carries risks, staking offers an interesting option for traders looking for higher yields without taking on too much risk.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance










