Zero-knowledge proof will be one of the most basic technologies of Web3, and most projects will be related to zero-knowledge proof. In other words, zero-knowledge proof will have a far-reaching impact and penetrate into every corner of Web3.
Keep this in mind! (Speaking of this, let's look back in two years)
First, let's talk about what Web3 is. Simply put, Web3 is the decentralized Internet (Decentralized Web). If you don't talk about decentralization, you can't talk about Web3.
The premise of the impossible triangle
When it comes to decentralization, you can't do without blockchain. When it comes to blockchain, you can't escape the blockchain impossible triangle. In other words, decentralization, scalability, and security cannot be achieved at the same time.
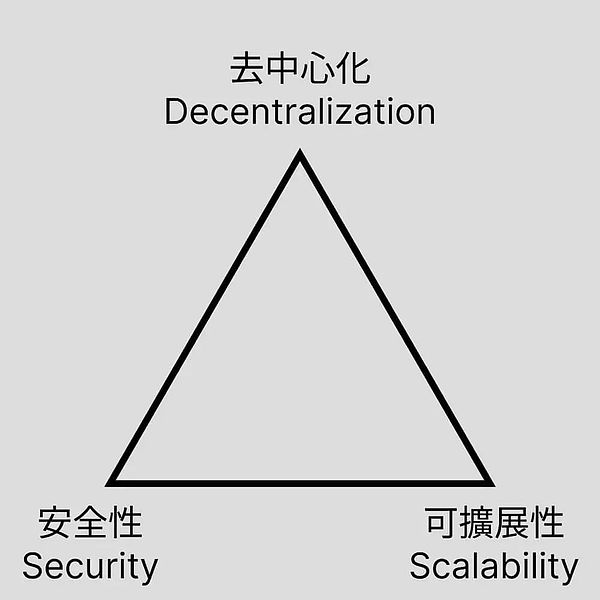
But this is based on a certain technical condition. Under certain technical conditions, if you want to improve one or two aspects, you must sacrifice other aspects. For example, many current projects claim to be able to achieve TPS of thousands or even hundreds of thousands. There is nothing else, just sacrificing security and decentralization. Therefore, such projects do not have a strong security foundation, and if they do something more outrageous, they are actually Internet projects that are covered in the sheep's clothing of Web3. It is a dog's meat under the guise of sheep.
What if technology advances?
However, it is not impossible to have all three, and this requires technological progress to achieve. When technology achieves a breakthrough, it is possible to achieve overall improvement. To give a simple example, if computing power and network speed are improved, TPS can be improved without sacrificing security and decentralization.
Technological progress may lead to unilateral breakthroughs or all-round breakthroughs. For example, the development of storage proof allows PoC consensus to achieve similar security as PoW consensus. Therefore, blockchain may not need to use energy-consuming methods to provide decentralized basic trust. The development and widespread application of Byzantine consensus allows some scenarios with less security requirements to provide a degraded security foundation based on PoS. The development and progress of cryptography has enhanced the security of transactions, and security and ease of use may be taken into account. The development of zero-knowledge proof may provide all-round breakthroughs, that is, it can provide all-round support for decentralization, security and scalability.
What is zero-knowledge proof?
Simply put, zero-knowledge proof is a cryptographic method that allows one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that certain information is true without providing any additional information.
This is too abstract. To put it simply, there are two aspects here:
1. Proof: that is, you can use a proof string (a fixed-length quasi-random number) to prove something. This thing can be a piece of stored data, a completed calculation, etc.
2. Zero knowledge: that is, it proves relevant information to you but does not leak relevant information; it proves to you that a calculation has been done, but does not reveal the specific calculation information and input data.
It is still too abstract. Let's talk about it in more detail: For example, if you store a piece of data in Baidu Netdisk, how do you know that Baidu Netdisk has not lost or tampered with your data? You don't know unless you download it and make a comparison, which is very troublesome, so you simply choose to believe it. If something really goes wrong, you will sue it afterwards.
For another example, you rent a virtual machine in Alibaba Cloud and execute a program. How do you know that the execution result of this program is correct? You just assume it is correct. You think, why would Alibaba Cloud go to such lengths to deceive me? So you believe it. But there is no guarantee or proof here.
However, if technology advances, Baidu Netdisk or Alibaba Cloud computing platform can provide you with a proof that you can easily verify after each storage or calculation, a mathematically rigorous proof, you will not choose to simply believe, you can choose to verify. This is especially important in decentralized networks. Remember: Don’t Trust, Verify!
If these proofs are publicly verifiable, that is, anyone including you can verify, and at the same time do not expose privacy, then it is perfect. This is zero-knowledge proof.
Why zero-knowledge proof is everywhere
First, let’s take a look at why Baidu Netdisk or Alibaba Cloud does not provide this kind of proof? The reason is simple. Zero-knowledge proof is a new technology. Although it is developing rapidly, it is still immature. The current cost of use is still very high. In simple terms, generating proofs is much more expensive than doing it all over again, by orders of magnitude, so it’s not practical.
However, in a decentralized network, the situation is slightly different. First, decentralized networks are expensive in themselves. For example, Ethereum computing, you can see it by looking at the gas fee. It’s so expensive because each node has to repeat the same calculation, so the cost is thousands of times that of centralized computing. If we can do the calculation off-chain and submit the proof directly to the chain, then the calculation only needs to be done once and it can be guaranteed to be safe. This is the theoretical basis of zkRollup. Most zkRollup calculations are centralized, but its calculations are submitted to the decentralized network for verification, which borrows the security of Layer 1, and the network is expanded through grading. In other words, the network has expanded, but the security has not been weakened, and the decentralized foundation is still the same.
Not only can zkRollup use the security foundation of Ethereum Layer 1 through zero-knowledge proofs. We can also directly innovate Layer 1. With zero-knowledge proof, we don’t seem to need to do repeated calculations on Layer 1. We only need decentralized verification. Depreciation has derived zkVM. For example, Aleo is a new emerging blockchain network that uses zero-knowledge proof for off-chain calculations and on-chain verification. Its security is guaranteed by a large number of verification nodes.
So, since zkRollup can expand Layer 1 through zero-knowledge proof, can other applications also do so? Of course. This is why many applications now directly run a Layer 2 and submit proofs directly to the main chain to borrow security and achieve decentralized trust. In this way, a large number of Web2 applications can be grafted onto a secure blockchain network, and can be directly connected to BTC, Ethereum or Filecoin, etc.
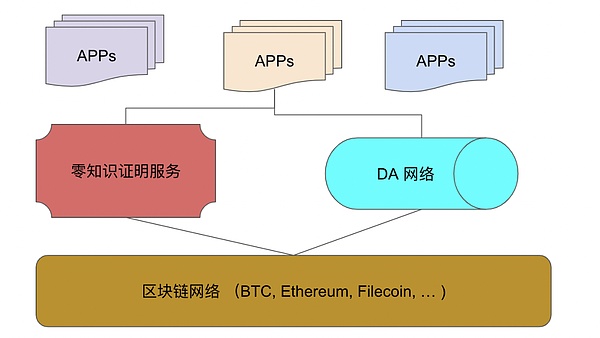
With zero-knowledge proof as the basis, there is a chance to transfer Web2 applications to Web3. A possible Web3 architecture is:
There are some sufficiently decentralized blockchain networks, and the consensus they adopt is mainly PoW or PoC, or there are PoS networks that already have a strong ecosystem. They establish decentralized network trust, which is the security foundation of Web3;
The zero-knowledge proof service layer is used to provide zero-knowledge proof services and link applications and secure blockchain networks;
The decentralized storage network builds the DA layer and uses zero-knowledge proof technology to ensure privacy and data security;
Various applications use centralized computing, build proofs through the zero-knowledge proof service layer, and verify through the blockchain network to ensure correctness and integrity; data storage uses a decentralized storage network, and also uses zero-knowledge proof to ensure correctness and integrity.
How long do we have to wait?
Someone may ask, the current Web3 applications don’t seem to be like this? That’s right, it’s not the case. Web3 is still a seedling, just starting out.
Currently, from the application layer, Web3 either places contracts on Layer 1 and relies on repeated calculations to provide security, or simply puts tokens into contracts to disguise as Web3 (without decentralized security). A welcome trend is that many Web3 projects can be run in Rollup, so that Layer 1 can be used to provide security through OP or ZK methods. However, we can see that Web3 is still very niche at present, and it is still dominated by finance (DeFi). GameFi and SocialFi, which have been talked about for several years, are also constantly trying.
Imagine that if there is no decentralized storage (sufficiently decentralized DA network), data cannot be decentralized, and applications with large amounts of data interaction cannot be Web3. In addition, zero-knowledge proof technology has only proved its feasibility in theory, and its efficiency and cost-effectiveness need to be greatly improved in engineering and methods. These two parts are the key to the future development of Web3. When both aspects have made substantial breakthroughs, the era of decentralization of the entire Internet has arrived, and the era of Web3 has also arrived. By that time, whether it is Baidu Cloud or Alibaba Cloud, it will also need to prove that its services are verifiable through a decentralized trust network, otherwise, there will naturally be new application paradigms to adapt to this demand.
I don’t know how long it will take. But the trend is clear. Don’t have too high expectations for the short term, and don’t underestimate the power of long-term gradual development. Maybe the singularity will be in the next cycle.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Weiliang
Weiliang JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance