Author: sovryn, Translation: 0xjs@黄金财经
With the launch of Ordinals, Bitcoin native assets have gained momentum in 2023. Casey Rodarmor, founder of the Ordinals protocol, plans to launch the Runes protocol when Bitcoin halves in April 2024.
This guide gives you an understanding of Bitcoin Runes tokens and how they will affect the Bitcoin ecosystem.
1 What is the Runes protocol on Bitcoin?
The Runes protocol is a token standard for issuing homogeneous tokens on Bitcoin, aiming to provide users with a more efficient way to create homogeneous tokens.
Runes will be released in April 2024, coinciding with the upcoming Bitcoin halving.
(1)Who created the Runes protocol?
Bitcoin developer Casey Rodarmor proposed the Runes protocol in September 2023 as an optimized token standard for issuing alternative assets on Bitcoin.
Since then, he has been working on the protocol with the goal of launching it in April 2024. Rodarmor is a well-known developer in the crypto space. He is the creator of the Ordinals protocol, which developers have used to develop various token standards for issuing native assets on Bitcoin.
Although the Runes protocol has not yet been released on the Bitcoin mainnet, some developers are already building projects based on it. These projects include Runealpha, PipeBTC, and RSIC, to name a few.
(2)Why was the Runes protocol created?
Rodarmor described Runes as a simple protocol with minimal on-chain footprint and responsible UTXO management in his blog post.
UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) is a unit of Bitcoin value associated with a specific address on the blockchain, representing funds that have not yet been spent and can be used as input for new transactions.
Runes is different from the BRC-20 token standard, which is complex and not based on UTXO. The latter feature has led to the BRC-20 token standard generating too many junk UTXOs, causing congestion on the Bitcoin network.
Runes aims to replace the inefficient BRC-20 token standard based on Ordinals.
In addition, the Runes protocol also strives to do better than other existing Bitcoin alternative token protocols such as RGB and Taproot Assets. These existing options rely too much on off-chain data.
For example, Taproot Assets stores metadata for its assets off-chain, making asset information separate from the main Bitcoin layer. Options like Omni Layer and Counterparty require native tokens to operate. In short, Rodarmor believes that these problems make these existing protocols cumbersome and not very user-friendly.
2, How does the Runes protocol work?
Runes' UTXO-based model is a natural integration with Bitcoin, which uses UXTOs. This helps minimize junk UTXOs that can cause network congestion.
UTXO is a specified amount of BTC that you have not yet spent, and you can use it to make new payments. It is the output of a previous Bitcoin transaction, and it can be spent until it is used as an input for a new transaction.
A Rune is assigned to a UTXO via a protocol message that specifies the output, ID, and amount using an OP_RETURN.
OP_RETURN is a unique feature of Bitcoin data storage. OP_RETURN outputs do not consume the UTXO set because they have been proven to be unspendable.
The ID is a numeric identifier for the Rune, while the output specifies the output index to receive the Rune token. The amount determines how many Rune tokens will be transferred.
All rune messages, whether creating (etching) new runes or transferring runes, are encoded in an OP_RETURN output in the transaction. Divisibility, rune name, and other metadata are all in the same OP_RETURN in the same transaction.
The token supply of a Rune is contained in a single UTXO. The supply/transfer amount is a 128-bit unsigned integer, so the maximum value is 340282366920938463463374607431768211455. Each rune has a "divisibility", which is the number of decimals it can have. The maximum is 38. The human-readable maximum supply also has this many decimals, so with 18 decimal places (similar to most ERC-20 tokens), the human-readable maximum supply is 3402823669209384634633.74607431768211455.
UTXOs are used to track the balance of Runes tokens. Interestingly, the Runes protocol does not link the balance record of the token to a wallet address, but instead keeps it in the UTXO.
Runes are transferred via a Bitcoin transaction with an OP_RETURN output that specifies the number of runes from the inputs to the UTXOs.
3, What is the difference between BRC-20 and Runes?
Here are the differences between the BRC-20 and Runes token standards.
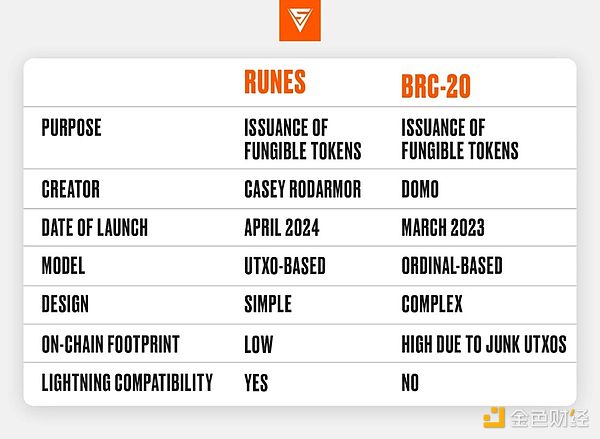
4, What is the RSIC meta-protocol?
Rune Specific Inscription Circuit (RSIC) is a meta-protocol that combines Bitcoin Ordinals with yield mining.
The team behind the RSIC meta-protocol created 21,000 Bitcoin "NFTs" called RSICs using the Ordinals protocol. Each RSIC has ancient runic symbols (an ancient alphabet used by various Germanic languages) and links to earlier inscriptions.
The goal of RSICs is to distribute Rune Coin in the future. RSIC is a project that emerged as a result of the Runes Protocol proposal.
RSICs Airdrop
In January 2024, the RSIC project airdropped 90% of the 21,000 RSICs, screening Ordinals wallet addresses that have been active since the release of the protocol.
Bitcoin Frogs, Nodemonkes, and Bitcoin Puppets Ordinals series holders are the lucky ones to receive free RSICs, which are currently trading at a floor price of around 0.1 BTC ($6,100). The project distributed RSICs to more than 9,000 wallets.
RSICs are able to earn Runes for their holders until the halving event in April.
Then, each RSIC will enter a lottery, where 21 billion Rune tokens will be up for grabs. Holders of these inscriptions can activate their "NFTs" and start earning Runes by transferring them to the same wallet or a different wallet.
5, What will Runes bring to the Bitcoin ecosystem?
Let's take a look at the potential advantages of the Runes protocol.
(1) More Users
The Runes protocol will allow projects to issue different types of fungible tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain, such as security tokens, stablecoins, and governance tokens. This could expand Bitcoin’s utility and attract more users, who will enjoy near-instant, low-cost transactions thanks to the protocol’s potential Lightning Network compatibility. In other words, Runes could help Bitcoin achieve its goal of widespread adoption.
(2) More Revenue
As more people interact with Runes tokens, more transaction fees will be generated. This will increase miners’ revenue, incentivizing them to continue securing the Bitcoin network. With block rewards set to decrease further in April 2024, Bitcoin miners will need more revenue drivers, and Runes could be just the protocol needed to keep miners motivated.
(3) Innovation
As we have already seen from the example of RSIC, the Runes protocol encourages developers to innovate in exciting new ways, giving users the opportunity to experience activities on the Bitcoin blockchain that no one would have thought of before. It will also open the door for developers who want to innovate Bitcoin on the world's most stable and secure public blockchain.
(4) Efficient issuance of fungible tokens
The Runes protocol aims to enable the issuance of assets directly on Bitcoin with as little negative impact as possible. As mentioned earlier, the protocol is improving on the current alternative token protocols that rely on native tokens and off-chain data. In addition, its design is more thoughtful than the BRC-20 token standard, which was launched to show what kind of functions the Ordinals protocol can achieve and is more entertaining. Therefore, the seriousness of the protocol may make Runes more successful than BRC-20 tokens.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Edmund
Edmund JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance