Author: Blockchain Research Team of Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Financial Technology Research Institute
With the emergence and popularization of the Internet, digital identities have gradually been integrated into our daily lives, and traditional identities (such as physical documents such as ID cards or household registers) have gradually been replaced by digital identities. substitute. At present, the digital identities we use are mainly centralized digital identities. A single service platform provides identity information management and identity authentication services. Users need to repeatedly submit original certification materials to register different accounts on different service platforms for identity authentication. At the same time, the service platform can unilaterally deactivate or cancel user accounts in accordance with the agreement, and even recycle the accounts and reassign them to other users. If these accounts (such as mobile phone numbers and email addresses, etc.) are associated with other user accounts, log in through SMS verification codes. Or resetting your password will run the risk of using other people's accounts and peeking into other people's information. In addition, various service platforms store a large amount of user identity data. Due to uneven management levels, data leakage cases occur from time to time. In order to solve the above problems, combined with the decentralized distributed ledger technology represented by blockchain, the industry has proposed a decentralized digital identity solution. This article will briefly introduce the principles of decentralized digital identity technology and look forward to its application prospects in the financial industry.
1. What is decentralized digital identity
Digital identity is the mapping of the identity of entities (including people, devices, applications, etc.) in cyberspace and is the digital expression of entity identity. Digital identity mainly consists of digital identity identifiers and identity attributes. The digital identity identifier can be compared to the ID number of the entity identity, and the identity attributes can be compared to all digital information related to the entity identity, such as gender, age, home address, personal hobbies, etc. . Traditional digital identities are centralized digital identities, provided and managed by a single application service platform, and the use of identities is limited to a single platform.
Decentralized Identity (DID) Also known as distributed digital identity or blockchain-based digital identity , is a new type of digital identity that uses distributed ledger technology to have the characteristics of decentralized technology. DID allows users to own and control their digital identity instead of relying on a centralized service provider.
Compared with traditional centralized digital identities, DID has advantages in control, privacy protection, interoperability, security and management costs. In terms of control, users can decide how their identity data is stored and used without relying on third parties. In terms of privacy protection, only the user's identity information can be accessed and used with the user's authorization, which reduces the risk of user information being abused and leaked. In terms of interoperability, following a unified and open standard protocol can share and use user-authorized identity data across platforms, cross-institutions and cross-scenarios, without requiring users to repeat it between different platforms and applications. Register for different accounts. In terms of security, users’ identity data is published and verified through distributed ledgers (such as blockchain), reducing the risk of tampering and abuse. In terms of management costs, users’ identity data can be managed independently by users, and enterprises do not need to invest a lot of resources in storing and keeping user identity data.
2. Decentralized digital identity technology
In recent years, the industry has developed a series of technical standards and protocols around DID. Among them, the DID specifications and protocols of W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) are widely recognized and applied. DID products in the industry basically follow this specification and protocol. In the W3C specification, the components of DID mainly include distributed identification, verifiable credentials and distributed ledgers (as shown in Figure 1).
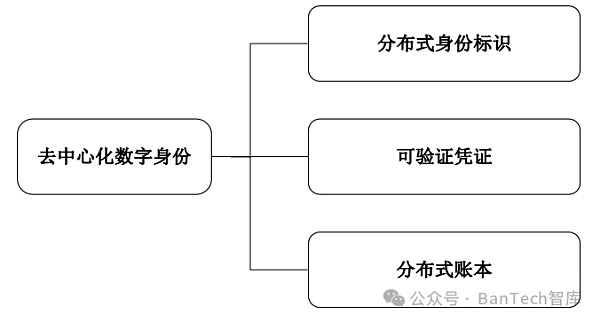
Figure 1 Composition of decentralized digital identity
Distributed Identity Identification (DID Identification) is a string in a specific format (the format is: did:example:123456789abcdefghi), which can be used to represent any entity and is unique in the entire network. DID identification uses a public and private key mechanism to achieve identity authentication through private key signature and public key verification. Each DID identification will be bound to a DID document to record the relevant information of the DID identification, including the most critical public key information. The public key will be released to the distributed ledger along with the DID document and made public to the entire network, while the private key will be kept by the entity itself, thus realizing a decentralized digital identity verification method.
Verifiable Credential, similar to various certification materials in our daily life (such as birth certificate, income certificate etc.), generally issued by a credible authority. In addition to the statement information made by the issuer to the designated user (such as a birth certificate issued by a hospital, including the birth time, place and parents of the holder), the verifiable certificate also contains the issuer's DID identification private key. The generated digital signature information. Since the private key is kept and used by the issuer, others cannot forge it. At the same time, other users can use the public key for quick verification, including verifying whether the certificate is issued by a trusted authority, whether the certificate content has been tampered with, and ensuring the authenticity of the certificate. Credibility and authority.
Distributed ledger is a database based on a peer-to-peer network. Decentralization is one of its core features. All transactions All need to be verified by the consensus mechanism to ensure that the ledger records of all participants are consistent. By using distributed ledgers to register and maintain DID identifiers, store and publish DID documents, even if there is no authoritative centralized CA (certification authority), the DID identifier can be unique across the entire network, and each entity can have one (or more) Unique identity. In addition, all users can obtain the DID identification public key through the distributed ledger to verify the digital signatures and certificates provided by the users.
3. Workflow of decentralized digital identity
The W3C specification also proposes a reference model for verifiable certificate circulation, which consists of identity holders, certificate issuers, certificate verifiers and verifiable data registration centers (as shown in Figure 2).
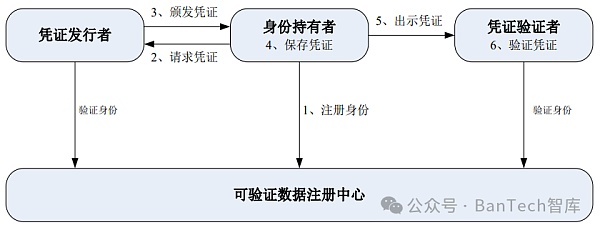
Figure 2 Verifiable Credential Circulation Model
Identity holder is an entity with one or more DID identifiers and Verifiable certificates; the certificate issuer is also an entity, also has one or more DID identifiers, and has certain authority, such as government departments, financial institutions, etc., can issue verifiable certificates based on the statement of an entity, and then provide the certificates to Identity holders keep it themselves; credential verifiers are generally service providers who confirm their identity by receiving one or more verifiable credentials provided by the identity holder and provide services to qualified users; verifiable data registration The center is used to register and maintain DID identification, and uses distributed ledgers (such as blockchain, etc.) to store and publish DID documents.
The workflow of the verifiable credential circulation model mainly includes six links: registering identity, requesting the credential, issuing the credential, saving the credential, presenting the credential and verifying the credential.
Registered identity
Identity holder, certificate issuance Authors and credential verifiers need to first register a DID identifier on the verifiable data registration center to obtain a unique digital identity identifier for the entire network. The operation of registering an identity can be completed by the user independently. A pair of public and private keys is generated through a cryptographic algorithm. The private key is kept by the user himself. The public key is registered to the verifiable data registration center as part of the DID document and is open to all users on the entire network.
Request Credentials
As mentioned earlier, "Digital identity is mainly It is composed of digital identity and identity attributes." Through identity registration, users have obtained a unique digital identity for the entire network, and identity attributes also need to be implemented through verifiable credentials. All entities can issue verifiable credentials, but service providers only accept verifiable credentials from services they trust and recognize. Therefore, users need to choose a service organization that everyone trusts and recognizes as the certificate issuer to issue themselves digital certificates that can be used to prove their identity and rights.
Issuance of certificates
The certificate issuer first provides the user with The identity information of the user will be verified, and upon passing the verification, the user will be issued the digital certificate they need. Since the certificate contains a digital signature generated by the certificate issuer's DID identification private key, the statement content in the certificate can be endorsed, and users can prove their identity and rights by presenting the certificate.
Save the certificate
The certificate issuer issues the certificate to the user Finally, as the identity holder, the user has independent control over the digital certificate with his or her own identity attribute information, and can choose a safe and convenient way to save it, such as saving it locally or in other storage devices, in case it is needed later. and use.
Present credentials
The service provider is providing the user with Before service, you need to serve as a credential verifier to confirm the user's identity and rights, and the user is required to provide corresponding credentials that can prove his or her identity and rights. As an identity holder, the user selects credentials that meet the requirements from the list of saved credentials and provides them to the service provider.
Verify credentials
The service provider acts as a credential verifier After receiving one or more certificates provided by the user, the DID identification of the certificate issuer can be obtained from the certificate, and then the public key of the certificate issuer's DID identification can be obtained from the verifiable data registration center, and then the digital signature in the certificate can be verified. , you can confirm the authenticity of the certificate and whether the content has been tampered with. After passing the verification, the service provider will provide relevant services to qualified users.
In general, the main difference between decentralized digital identity and traditional centralized digital identity is that the service provider authenticates the user's identity There is no need to rely on third-party certification service agencies. Users keep their own identity authentication data (private keys and certificates) and provide them to the service provider when needed. The verification information is stored and published through the distributed ledger. The service provider can obtain the public key of the DID identification from the verifiable data registration center and verify the digital signature and digital certificate provided by the user to confirm the user's identity.
4. Application of decentralized digital identity
Decentralized digital identity can solve problems such as user identity authentication, data sharing and collaboration between different platforms and institutions. The following takes supply chain finance, digital assets and data circulation applications as examples to illustrate the role of decentralized digital identity in them.
Supply chain finance
Problems in supply chain finance Mainly including information asymmetry, as well as insufficient risk prevention and control and supervision levels. Various types of information are scattered in the hands of different participants, and the authenticity of paper documents in offline processes is difficult to verify. Upstream and downstream multi-level suppliers and dealers cannot use the credit of core enterprises for loan financing, resulting in financing difficulties for small and medium-sized enterprises. Decentralized digital identity can provide a unified identity authentication mechanism for supply chain finance. Through verifiable credentials, participants can verify the authenticity and validity of circulation information and documents through technical means, improving risk prevention, control and supervision levels. Make transactions traceable and open and transparent, realize the credit transfer of core enterprises to downstream small and medium-sized enterprises, and solve the financing difficulties and expensive financing problems of small and medium-sized enterprises in the supply chain.
Digital Assets
The main problems with digital assets include The issue of ownership and privatization of digital assets, as well as the authenticity of digital assets at their source. The application of decentralized digital identity technology in the field of digital assets mainly involves digital asset transactions and ownership verification. In terms of digital asset transactions, participants can use decentralized digital identities for identity verification without relying on third-party institutions, which helps improve the privacy and security of transactions; in terms of ownership verification, owners of digital assets can verify their identities through Verifying credentials to prove ownership of the asset and verifying it helps prevent theft and fraud of digital assets.
Data circulation
The problems in data circulation mainly include Data sharing and transfer are complex. On the one hand, it is difficult to define the ownership of data. On the other hand, user information is difficult to fully protect, and privacy leaks are prone to occur. Decentralized digital identity plays an important role in the field of data circulation. In terms of data sharing and circulation, by using the decentralized digital identity system, users or institutions can authorize other individuals or institutions to access their data, and at the same time control the data. Access permissions and sharing scope to avoid data leakage and abuse. In addition, combined with verifiable credentials, data buyers can verify the identity of the data seller and the authenticity of the data, avoid data fraud and counterfeiting, and promote the circulation and utilization of data.
Decentralized digital identity applications have broad prospects and can provide more secure and reliable identity authentication and management methods, reducing operation and maintenance risks and costs. At present, decentralized digital identity is still in the process of continuous development and improvement, and domestic application scenarios are mainly based on pilot verification. With the continuous improvement of users' demands for personal information sovereignty and privacy protection, the continuous improvement of relevant domestic laws and regulations, the continuous development of financial technology and the accelerated digital transformation, as well as the continuous exploration of innovative scenarios in cutting-edge fields such as Web3.0 and the Metaverse, It is believed that decentralized digital identity will be more and more widely used and will become an essential infrastructure for building future identity authentication systems, bringing more convenience and security to our work and life.
 Edmund
Edmund








