Author: 0xjs@金财经
For the encryption industry, 2023 is not only a year of transition from bull to bull, but also a year of ecological development.
Bitcoin: Ordinals, Inscriptions, BRC20, Atomical, ARC20, Bitstamp, SRC20, Rune, Taproot Assets, RGB and other new concepts are overwhelming;
On Ethereum: Ethereum itself has completed the Shanghai upgrade and completely completed the POS transition, and L2 on Ethereum is also constantly innovating (such as zkEVM L2 mainnet online, super chain, etc. );
On other L1 public chains: there are old public chains that have survived, and there are new POW public chains that have suddenly emerged. The L1 war is still going on, and the data is incomplete. Statistics show that there are currently more than 400 L1 projects in the encryption industry.
New products and new concepts emerge one after another. This is both a great boom for the entire encryption industry and a challenge for encryption users.
This article mainly focuses on Bitcoin, Ethereum and its L2 and other L public chains in 2023. It does not completely summarize their development in 2023 to facilitate users in the new Get a better grasp of the entire crypto ecosystem in one year.
Bitcoin Ecology
From the birth of Bitcoin in 2009 to 2023, in the past 15 years Countless people in the crypto community have attempted to issue assets on Bitcoin. However, most people in the Bitcoin community have chosen to stick to the original intention of Bitcoin as a currency. Therefore, innovation on Bitcoin has always centered around the core functions of Bitcoin (payment, settlement, value storage, etc.), and has been very slow, even at the expense of expelling those who disagree. community members of this culture.
For example, concepts and protocols such as early Colored Coins, MasterCoin, Counterparty, and Omini have not grown on Bitcoin for many years. For example, the reason why Vitalik founded Ethereum One of the main reasons is also because the Bitcoin community does not accept applications other than currency.
But driven by Ordinals and BRC20 tokens, Bitcoin's development in 2023 has completely broken people's inherent impression of it. Multiple protocols on Bitcoin have attracted the attention of many industry players. Innovation and activity on Bitcoin are also at all-time highs. In the words of crypto VC Outlier Ventures, the Slumbering Titan wakes up, and the Bitcoin network will usher in a wave of innovation in 2023.
But we know that the Bitcoin ecosystem is a general term with completely different categories of protocols and tokens. These include Bitcoin Lightning Network, Bitcoin side chain (Liquid Network, RSK), Bitcoin-integrated L1 public chain ICP, Bitcoin L2 (Stacks), Drivechains, Taproot Aseets, Taro protocol, RGB protocol, BitVM, Ordinals protocol and BRC20 token, Atomic protocol and ARC20 token, Rune and PIPE protocol, BitStamp and SRC20, etc.
Described below:
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is the second layer of Bitcoin. It uses RSMC and HTLC mathematical mechanisms in the payment channel to ensure that off-chain transactions in the user's payment channel are safe and trustworthy. In the end It is submitted to the Bitcoin chain for settlement only when it is settled, thereby achieving fast and cost-effective transaction expansion. The Lightning Network is not a blockchain and does not have the ability to handle smart contracts or complex applications. Please refer to Jinse Finance’s previous article “Detailed explanation of the lightning network mechanism”.
In 2023, mainstream CEXs such as Binance, OKX, and Kraken will gradually support the Lightning Network.
In addition, the Lightning Network has become the infrastructure of many other Bitcoin protocols, such as Taproot Assets Protocol, RGB Protocol, and Taro are all built on the Lightning Network .
Liquid Network
Liquid Network is a bit Coin sidechain. It is built on the Bitcoin code base and uses the same UTXO transaction model. In addition to offering L-BTC assets pegged to Bitcoin, Liquid also supports the issuance of a variety of digital assets such as tokenized fiat currencies, other cryptocurrencies, and tokenized securities.
One of Liquid 's key value propositions is enhanced privacy, using confidential transactions to provide faster transactions and greater privacy. This makes it the best blockchain for DeFi use cases. Due to its support for multiple assets, it attracts traders across different digital assets. Hodl Hodl and SideSwap are some of the projects built on top of it.
El Salvador plans to issue $1 billion in bonds on the Liquid Network. In 2023, Bitfinex Securities successfully issued the first tokenized bond on Liquid Network, raising more than $5 million in USDT.
RSK
RSK is a Bitcoin side chain, It introduces smart contract functionality through Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility. This consistency with EVM ensures that it works seamlessly with popular ETH tools and Solidity languages, simplifying the transition of ETH applications to the Bitcoin platform, and allowing Developers leverage existing Solidity resources to accelerate development.
RSK is primarily used for DeFi applications, leveraging its scalability and EVM compatibility. Larger protocols such as Sovryn and RSKswap, which focus on lending and liquidity provision. In addition, there are a number of RSK wallets and stablecoins to facilitate the broader DeFi ecosystem.
Stacks
Formerly known as Blockstack , ranked 4th in 2020 Quarterly renamed Stacks. Stacks is a unique 2-layer blockchain that enhances the functionality of Bitcoin. Stacks does this by connecting directly to the Bitcoin blockchain via a Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism that lets miners pay BTC to mint new Stacks tokens, STX.
Stacks uses its token STX as the native cryptocurrency of the Stacks network, used to fuel smart contracts and reward the open Stacks network miners on and enables holders to earn Bitcoin through Stacking
With its native token (STX), consensus mechanism and Clarity programming language, Stacks enables developers to craft comprehensive smart contracts that can be executed on a regular basis Settle the Bitcoin blockchain while inheriting its security and resiliency.
Stacks has a variety of web3 use cases, such as DeFi projects such as Alex and Arkadiko.
In addition, Stacks plans to conduct a Nakamoto upgrade at the same time as the Bitcoin halving event in April 2024, which will introduce 1:1 Bitcoin support. The asset is BTC, and the execution time is greatly shortened. The block time is shortened from the current about 10 minutes to about 5 seconds, becoming a true Bitcoin layer 2.
ICP
ICP announces ICP in December 2022 The main network integrates Bitcoin, and smart contracts on ICP can hold, send and receive Bitcoin natively without the need for cross-chain bridges or other third parties. ICP uses Chain-key ECDSA encryption, so smart contracts on ICP can control BTC balances without the need for wrapping or bridging. Its direct interface with the Bitcoin main chain enables it to bring smart contract functionality to BTC without the need to wrap the asset (WBTC).
ICP's BTC implementation is relatively new, but it can already be seen that Dapps on ICP are leveraging smart contracts to access native BTC. Currently, there are more than 20 Bitcoin Dapps listed on the ICP official website.
Drivechains:
Drivechains is a proposed With soft forks, sidechains can be created to take advantage of features such as smart contracts and privacy technologies. Drivechains do not rely on a centralized entity to de-peg. Instead, they rely on Bitcoin miners to achieve decentralization at the expense of cost and speed. It allows builders who value decentralization to also use the smart contracts and scale provided by sidechains.
Mainly includes two BIP protocols: BIP300/301. BIP300: Link BTC back to the main chain through computing power hosting innovation; BIP301: Add blind merge mining, allowing miners to provide security for the main chain and side chains at the same time.
Taproot Assets
Taproot Assets protocol is based on Taproot , Taproot was activated on November 11, 2021. It is a soft fork upgrade of Bitcoin, which mainly introduces more complex but more efficient transaction types through Schnorr signatures and MAST The upgrade enhances Bitcoin’s privacy by making transactions indistinguishable, promotes lower fees through efficiency, and paves the way for advanced features like complex smart contracts and optimized multi-signature wallets.
On October 19, 2023, Lightning Network developer Lightning Labs announced the launch of the Taproot Assets protocol. The Taproot Assets protocol is a Taproot-native asset layer built on Bitcoin. The Taproot Assets protocol supports the issuance of assets on Bitcoin and the Lightning Network without causing bloat to the Bitcoin network.
Please refer to this article of Golden Finance "One article to understand Taproot Assets Protocol".
Taro Protocol
Taro is powered by Lightning A new protocol developed by Labs and supported by Taproot. It allows users to create assets on the Bitcoin blockchain and then send them through the Lightning Network, allowing for fast and high-volume transactions with minimal cost. It can be used to issue both fungible assets and non-fungible tokens.
Taro relies on Bitcoin's latest upgrade, Taproot, to build new tree structures that allow developers to add output to existing output It embeds arbitrary asset metadata, uses Schnorr signatures to improve simplicity and scalability, and can be used with multi-hop transactions on the Lightning Network.
BitVM
October 2023, ZeroSync Developer Robin Linus released a new Bitcoin proposal, BitVM, to "verify any computable function on Bitcoin" and introduce arbitrary Turing-complete calculations to Bitcoin.
BitVM implements a NAND gate in Bitcoin script through hash locks and opcodes (OP_BOOLAND, OP_NOT), and moves the calculation logic off-chain. Verifiers can challenge calculations submitted by provers.
BitVM also has some problems: BitVM uses NAND circuits instead of high-level languages, which is very inefficient, slower, more expensive, and more complex; BitVM is very complex , difficult to implement; BitVM is limited to two parties rather than a complete VM allowing any number of users to participate. Please refer to Jinse Finance’s previous report “Interpretation of the new Bitcoin proposal BitVM”.
RGB Protocol
RGB is a Bitcoin and Smart contracts + privacy extension layer for Bitcoin Lightning Network. RGB is the abbreviation of Really Good Bitcoin. The motivation is that due to Bitcoin’s limited ability to support a smart contract execution environment, bringing execution and verification off-chain allows participants to benefit from the security of Bitcoin’s consensus layer while increasing flexibility and scalability.
RGB’s smart contract system is very special. It separates the concepts of smart contract issuer, state owner and state evolution, and combines smart contract code and data Stay off-chain; use Bitcoin as the state commitment layer and Bitcoin Script as the ownership control system; and the evolution of smart contracts is defined by the off-chain schema.
Although the creation and transactions of RGB smart contracts occur off-chain, the creation of smart contracts and smart contract state changes (such as transactions) on RGB move towards the Bitcoin area. Blockchain submissions are recorded on the Bitcoin chain in the form of UTXO. Each transaction has a corresponding UTXO, which has corresponding data on the Bitcoin network. At the same time, the verification of RGB transactions is also off-chain, requiring users to verify the Commitment of the transactions themselves. This is the so-called client verification.
For more RGB protocol content, please refer to the previous article of Golden Finance "Understand the Bitcoin RGB protocol in one article".
RGB Protocol 0.10 version will be released in April 2023. RGB Protocol 0.10 version includes consensus layer, standard library (provided by wallet/transaction used for integration) and command line tools, bringing full support for smart contracts to Bitcoin and the Lightning Network.
Some interesting use cases of the RGB protocol can be found here: https://github.com/22388o/awesome-rgb-protocol
< p style="text-align: left;">
Ordinals, Inscriptions and BRC20 TokensOrdinals: mainly used 2 ideas, 1. Sort each satoshi and assign an ordinal number "Ordinals" between 0 and 2,100,000,000,000,000. 2. segwit and taproot. The SegWit implemented in 2017 and the Taproot upgrade based on SegWit in 2021 script-path spend scripts (script path spending script) allow Bitcoin transactions themselves to include metadata. Combining the two is: inscribing the satoshi that distributes Ordinals. These Inscriptions data (such as pictures, text, audio and video, and even game data) are stored in the Bitcoin taproot script-path spending script in Segregated Witness. Thus it can be tracked, transferred, stored, bought, and sold.
BRC20 standard: an Ordinals standard. Created by Twitter user @domodata on March 8, 2023 to experiment with standards for fungible tokens on Bitcoin with the help of the inscription feature. The BRC20 name is borrowed from the Ethereum ERC-20 token standard. Unlike other Ordinals inscriptions, BRC20 tokens store JSON codes in Bitcoin inscriptions and have only three functions: deployment, minting and transfer. The Bitcoin blockchain itself only records BRC20 inscriptions, and the deployment, minting, and transfer of BRC20 tokens are tracked by an off-chain centralized indexer.
BRC20 token:
ORDI is the first BRC20 standard token. At the same time as the BRC20 standard was released, @domodata launched the first BRC20 experimental token ORDI, with a total issuance of 21 million. Top CEXs such as Binance and OKX have all launched ORDI. ORDI performed thousands of times the myth.
Other well-known BRC20 tokens include: SATS, .COM, RATS, MICE, PEPE, etc.
In addition, a series of ecologies have been formed around the BRC20 token: Unisat (a BRC20 platform integrating wallet, inscription, BRC20 market, domain name, search, etc.), Browser Ordiscan, cross-chain bridge MultiBit Bridge (BRC20-EVM bridge, connects BRC20 tokens to the EVM blockchain to enhance the liquidity of BRC20 tokens), BRC20 version of MakerDAO BitStable (pledge ORDI tokens, BTC etc. to mint stablecoins DAII), BRC20Fi, etc.
Please refer to the previous article of Jinse Finance: Bitcoin Ordinals Theory Manual, Cold thoughts on the hot BRC20.
Atomicals, ARC20, ATOM, AVM
Atomicals utilization And extends Bitcoin's UTXO model. Each Satoshi's UTXO represents a specific Atomical Objects (Digital Objects), allowing creation and management in a decentralized manner on Bitcoin. Complex digital objects (can be NFTs, or FT’s ARC20 tokens).
ARC-20 Tokens ultimately introduce colored coins to Bitcoin, using each Satoshi to represent ownership of deployed ARC-20 tokens unit. This means that each unit of ARC20 tokens is always backed by 1 Satoshi. These UTXO themselves can be combined in Bitcoin transactions, thereby enhancing the programmability of ARC20 tokens. In theory, direct exchange between Bitcoin and ARC20 can be achieved by simply exchanging the input and output of UTXO.
Unlike BRC20 which relies too much on centralized off-chain indexers, according to the definition of the Atomics protocol, ARC20 tokens are completely driven by Bitcoin UTXO and are completely Indexer independent.
In addition, the founder of Atomics expressed great interest in BitVM and saw the potential of its protocol, launching the ambitious AVM.
ARC 20 tokens are mostly named after physical particles. The leading token is Atom, and others include Quark, Proton, Quantum, Electrom, Neutron, and Pepe. , Realm, Dmint, Bitwork, Bitvm, etc.
RUNE and PIPE protocols:
RUNE The protocol is provided by Ordinals Founder Casey Rodarmor proposed to combat BRC20. Casey Rodarmor believes that a large number of Brc20 tokens are meaningless, causing huge congestion on the BTC network and generating a lot of garbage. BRC20 has become a paradise for speculation, and he hopes to change this situation.
Casey's Rune protocol started out as an idea with no specific product. The founder of TRAC launched the PIPE protocol first based on the RUNE idea, inheriting the anti-double-spending feature of Bitcoin utxo, and at the same time solving the on-chain congestion problem caused by repeated ordinal inscriptions. The first token of the PIPE protocol is PIPE, and there are also etch, utxo, rune, lane, etc.
ARC20 and PEPE protocol tokens are minted, purchased or transferred on satsx.io .
BitStamp and SRC20
Ordinal Store data in In SegWit, data in SegWit may be "pruned" by full nodes. To solve this problem, the BTC Stamps protocol emerged. BTC Stamps stores data in the BTC transaction output. The transaction output will not be "trimmed", making it a more secure and non-tamperable permanent protocol.
The SRC20 is equivalent to the BTC Stamps version of the BRC20 token. The disadvantage is that compared to BRC20 tokens, SRC20 is very expensive, 3 times more expensive than BRC20 tokens.
Ethereum and its L2
Bitcoin ecology will develop greatly in 2023, Ethereum It is still developing step by step according to Vitalik’s established roadmap.
First of all, Ethereum successfully completed the Shanghai upgrade in April 2023 and completely completed the transformation to POS.
Secondly, on L2, which is the focus of Ethereum development, Arbitrum will complete the token release in 2023. In addition, there are multiple L2 mainnets online, such as Base and Linea. , Polygon zkEVM, Scroll, Manta Pacific, Mantle, Arbitrum Orbit etc.
Again, among the L2 public chains launched in 2023, there are both the L2 public chain (Base) launched by the exchange and the zkEVM L2 public chain main network ( Scroll) is online, as well as L2 super chain narrative (Base, Arbitrum Orbit, Zora). 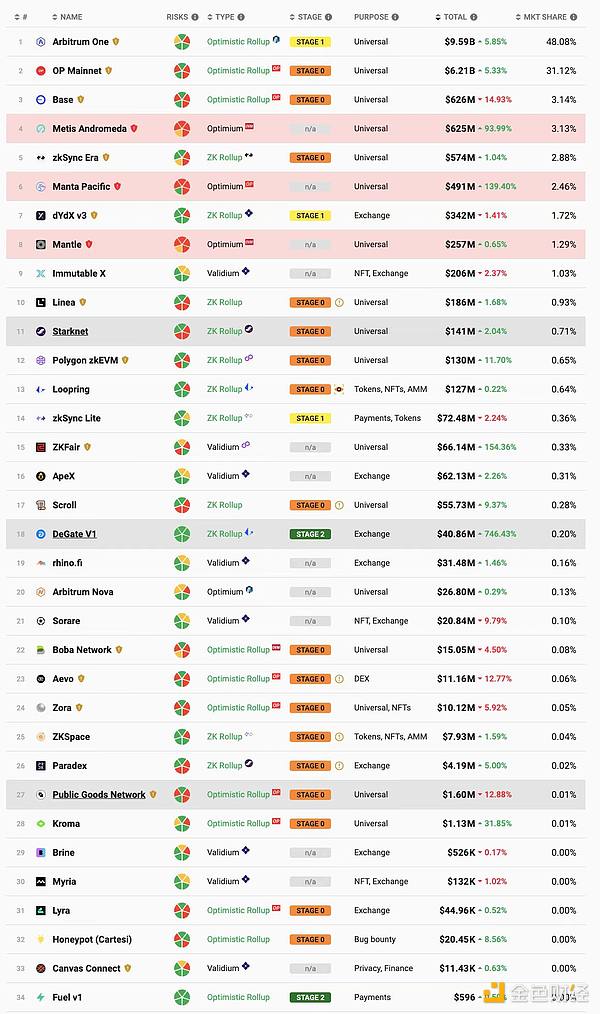
< span style="font-size: 14px;">There are currently 34 L2 public chains online on the mainnet Data source: L2beat
In 2024, the grand narrative of Ethereum and its L2 mainly includes: 1. Ethereum Cancun upgrade; 2. zkRollup L2 public chain (Starknet, Zksync) releases tokens and airdrops; 3. Other zkEVMs except Scroll ;L2 mainnet online; 4. The further prosperity of super chains (OP Stack, Arbitrum Orbit, ZK Stack); 5. L2 sorter decentralization has made great progress; 6. Other mainstream exchanges have successively launched L2 and go online.
Other L1: The public chain war is still going on
Although the current L1 public chain is Bit Bitcoin and Ethereum are the two dominant players, but the L1 public chain war is still going on.
Because with the large-scale application of Web3, the demand for public chains continues to increase.
This is also true.
A number of L1 public chain mainnets will be launched in 2023, the more well-known ones include Sui, Sei, etc.
Even the old L1 public chains will perform very amazingly in 2023.
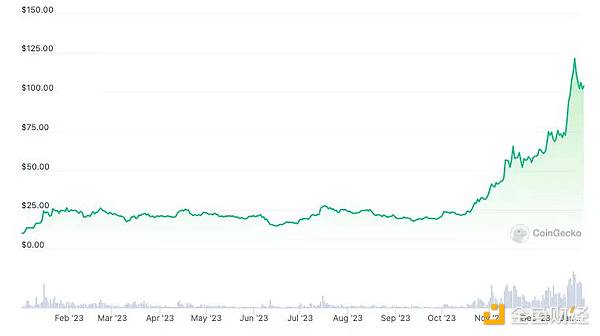
Solana rebounded from the bottom in 2023, and its price rebounded more than 10 times. The MEME currency on it increased astonishingly at the end of 2023, attracting attention. .
 < /p>
< /p>
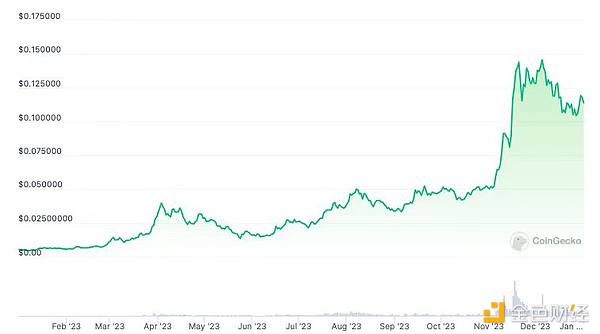
Injective will increase nearly 30 times in 2023.
 < /p>
< /p>
New PoW public chains also have opportunities, and Kaspa will increase by more than 20 times in 2023.
 < /p>
< /p>
According to Coingecko data, there are currently 88 issued L1 public chains and 20 issued L2 public chains.
In addition, according to incomplete statistics, there are currently more than 400 L1 public chain projects in the encryption industry.
Conclusion
Looking back at the history of encryption to date, before 2023, cryptocurrency is obviously Divided into two factions.
One of the factions is Bitcoin, which has a clear goal, which is to use it as a currency and follow the path of "separation of government and currency." The other group is other L1 public chains, which aim at Dapps that are highly trustworthy, cannot be tampered with, and are not controlled by one party, thereby enabling new use cases and businesses that were previously impossible. In 2023, the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem represented by Ordainals and BRC20 tokens seems to indicate that the two factions are moving toward integration.
As some industry insiders once analyzed, the fundamental innovation of cryptocurrency is "block space", which is a novel commodity that can be used for extremely A wide range of use cases (such as currencies and Dapps).
Bitcoin, Ethereum and other L1 public chains and the ecology on them are all like this.
Reference materials:
Detailed explanation of the Lightning Network mechanism
Atomical Documentation
bitcoin-unchained
Understand the Taproot Assets protocol in one article
Understand the Bitcoin RGB protocol in one article
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance


 < /p>
< /p> < /p>
< /p>

