Comparing data redundancy on Arweave and IPFS
This article will explore the redundancy mechanisms of Arweave and IPFS, and which option is safer for your data.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Source: Chain Tea House
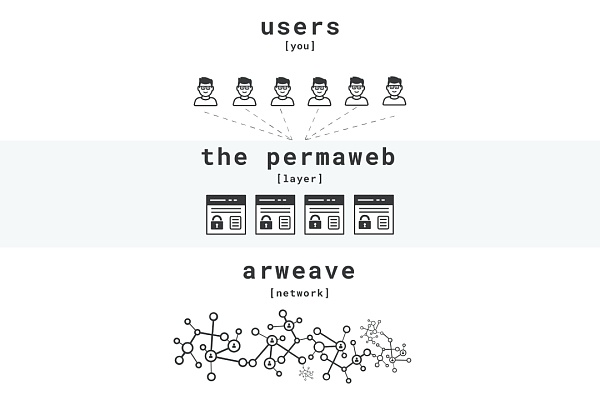
Arweave is a decentralized data storage solution that provides permanent and immutable data storage services through its Blockweave technology and native cryptocurrency AR tokens. Users can pay a one-time fee to store data permanently and earn rewards by contributing unused storage space.

As a tool to help anyone store data permanently, Arweave works by distributing information across a network of computers called nodes or miners. This approach is different from the traditional Internet, because today's Internet is controlled by servers of a few companies, which may be paralyzed or quietly change content at any time.
Arweave provides services for a parallel internet (called Permaweb) through a wide network of nodes. All of these nodes make money by providing storage for existing data for a long time and storing new data upon request by customers. Arweave uses its native cryptocurrency AR to run the service, and when people spend tokens to store data, they pay AR to miners, and store a portion of AR in a donation fund to guarantee unlimited permanent storage.
Arweave runs through an innovative data structure called Blockweave, which links each block to the previous block and a historical block (recall block). Miners must provide Proof of Access (PoA) before adding a new block to ensure the integrity and immutability of all data. Users only need to pay a one-time fee to store data permanently, with part of the fee used for initial storage costs and the other part going into a donation fund for future storage costs. Spora, a succinct proof of random access, further improves the efficiency and security of the network. Bundling improves the efficiency of data upload and network performance by combining multiple transactions into one large transaction. Through these mechanisms, Arweave implements a decentralized, permanent data storage network.
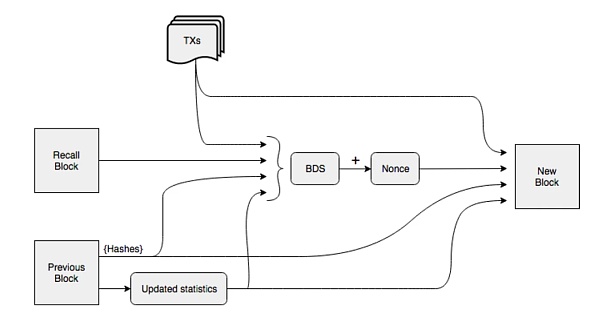
Blockweave is Arweave The core data structure of Blockweaving improves the design of traditional blockchain and realizes efficient, reliable and permanent data storage. The following is a detailed analysis of Blockweaving:
3.1.1 Basic structure
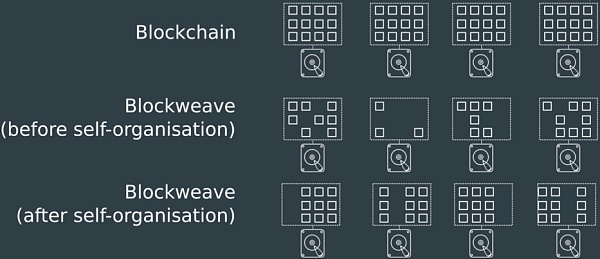
The main difference between Blockweaving and traditional blockchain is its link structure. Each block in traditional blockchain is only linked to the previous block, while each block in Blockweaving is not only linked to the previous block (parent block) but also to a historical block (memory block). This dual link structure increases the redundancy and security of data storage.
Parent block: Like traditional blockchain, each block in Blockweaving is linked to its direct previous block, forming a basic chain structure.
Recall Block: Each block is also linked to a randomly selected historical block. This link is random in order to increase the redundancy and accessibility of the data.
3.1.2 Data Verification Process
In block weaving, miners need to verify a randomly selected historical block before generating a new block. This verification mechanism is called Proof of Access (PoA). PoA ensures that all stored data blocks can be accessed and verified. In order to increase the chances of obtaining mining rewards, miners will store more historical data blocks, thereby increasing the redundancy of the data.
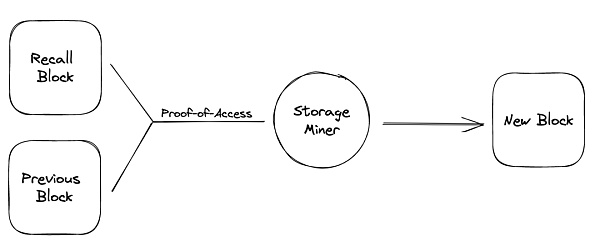
Random Selection: By randomly selecting historical blocks for verification, it is ensured that miners cannot foresee the specific data blocks that need to be verified, and thus must store a large amount of historical data.
Data integrity: This mechanism ensures the integrity and immutability of data and increases data security.
3.1.3 Redundancy of data storage
The dual link structure of block weaving greatly increases the redundancy of data. Since each block is linked to multiple blocks, even if some nodes fail or lose data, other nodes can still recover the data through redundant links. This design improves the durability and fault resistance of data.
Multiple links: Through the dual links of parent blocks and memory blocks, the storage of data in the network is highly redundant.
Data recovery: In the event of node failure or data loss, other nodes can use redundant links to recover data, ensuring high data availability.
3.1.4 Blockweave Construction and Mining
Miners are rewarded by generating new blocks in the Arweave network. In order to generate new blocks, miners must be able to access and verify the specified historical blocks. This mechanism incentivizes miners to store more historical data, improving the overall data storage and security of the network.
Mining process: Miners need to verify randomly selected historical blocks, generate new blocks and receive AR token rewards.
Incentive mechanism: This mechanism encourages miners to store more data, increase data redundancy and network security.
3.1.5 Data immutability and security
Since each block in the blockweave is linked to multiple blocks and verified through the PoA mechanism, it ensures that the data cannot be changed or deleted once stored. This immutability provides high security and prevents data from being maliciously tampered with or deleted.
Immutability: Once data is stored in the block weave, it cannot be changed or deleted, ensuring the integrity of the data.
Security: Multiple links and random verification mechanisms improve the security of data and prevent malicious tampering.
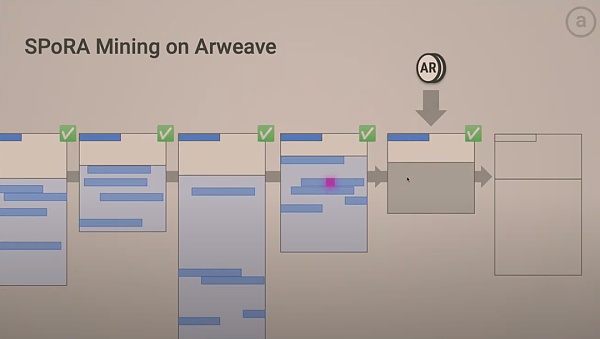
Succinct Proof of Random Access (Spora) is an important consensus mechanism used by Arweave to improve the efficiency and security of its network. Through Spora, Arweave is able to improve the efficiency of data storage and access while ensuring data integrity and security. The following are several key aspects of Spora's detailed analysis:
3.2.1 Basic Principles
Spora (Succinct Proofs of Random Access) is an improved Proof of Access (PoA) mechanism. The core idea is to verify new data blocks by randomly selecting historical data blocks to ensure data integrity and security. This randomness reduces the possibility of cheating by miners while increasing the security of the network and the redundancy of data.
3.2.2 Data Verification Process
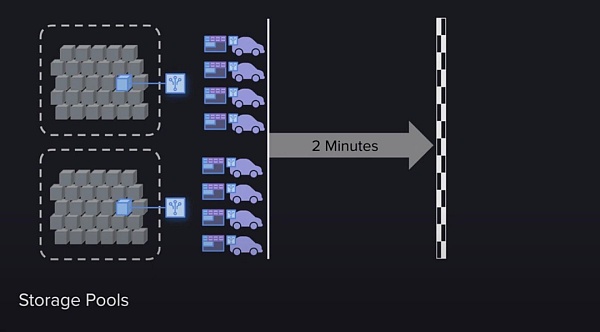
In Spora, miners need to verify a randomly selected historical data block before adding a new block. This random selection process makes it impossible for miners to foresee the specific data blocks that need to be verified, and thus cannot selectively store data. In this way, Spora ensures that miners must store a large number of historical data blocks to increase their mining chances, thereby improving the redundancy of data and the overall security of the network.
3.2.3 Improving Miners' Incentives
Spora enhances the incentive mechanism for miners. Since miners must store more historical data blocks to increase the probability of successful mining, this encourages them to invest more resources in storing and maintaining data. Miners not only receive mining rewards by verifying and storing data, but also increase their competitiveness in the network by increasing the amount of data stored.
3.2.4 Improvement of Energy Efficiency
Compared with the traditional Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism, Spora is more energy-efficient. PoW requires miners to verify transactions through complex calculations, which results in a large amount of energy consumption. Spora greatly reduces the consumption of computing resources by randomly accessing and verifying historical data blocks, thereby improving the energy efficiency of the network. This efficient verification process not only reduces energy costs, but also reduces the impact on the environment.
3.2.5 Security and Anti-Attack
Spora enhances the security and anti-attack of the network through its randomness and data redundancy. Since miners cannot predict the data blocks that need to be verified, it makes it difficult for malicious attackers to carry out targeted attacks. In addition, the large number of historical data blocks stored by miners also increases the amount of data that attackers need to destroy, thereby improving the overall security of the network.
3.3 Bundling
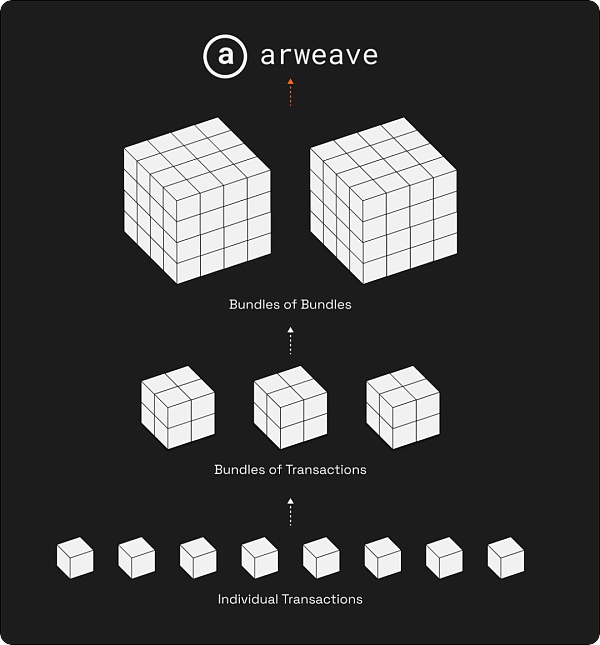
Arweave's bundling technology is one of its key innovations to improve data upload efficiency and network scalability. Through this technology, Arweave can effectively handle large-scale data uploads and improve user experience and network performance. The following is a detailed analysis of the bundling technology:
3.3.1 Basic Principle
The core idea of the bundling technology is to merge multiple small transactions into a large transaction, and then upload this large transaction to Blockweave. This method reduces the frequent upload operations of a single transaction, thereby reducing network congestion and improving the efficiency of data transmission.
3.3.2 Improved Efficiency of Data Upload
Without bundling technology, each uploaded transaction needs to be processed and recorded separately, which not only increases the burden on the blockchain, but also leads to inefficiency in the data upload process. Through bundling technology, multiple small transactions are packaged into a large transaction and uploaded, reducing the number of transactions on the chain, thereby greatly improving the efficiency of data upload.
3.3.3 Network Scalability
Bundling technology significantly improves the scalability of the Arweave network. In large-scale data upload scenarios, such as non-fungible token (NFT) projects, media file storage, etc., bundling technology can effectively handle a large number of concurrent upload requests, avoiding network congestion and performance bottlenecks. For example, Arweave successfully uploaded 47GB of data in a bundling operation, which is difficult to achieve in traditional on-chain data storage solutions.
3.3.4 Transaction Certainty and Developer Experience
Through bundling technology, developers and users can know the results of data upload with greater certainty, because the upload success rate of large transactions is higher than the success rate of multiple small transactions uploaded separately. This certainty improves the developer experience, allowing them to focus more on application development without having to worry about the complexity of underlying data storage.
3.3.5 Cost-effectiveness
Bundling technology not only improves the efficiency of data upload, but also brings significant cost-effectiveness. In the traditional on-chain data storage model, each transaction requires a fee, while bundling technology reduces the number of transactions by merging transactions, thereby reducing the overall transaction cost. This is an important advantage for users who need to store large amounts of data.
3.3.6 Data integrity and security
Bundling technology ensures the integrity and security of data. Although multiple transactions are merged into one large transaction, the data of each small transaction remains intact and cannot be tampered with. In this way, even if there is a problem during the upload process, the security and integrity of the data can be ensured by repackaging and uploading.
Wildfire is an incentive mechanism in the Arweave network that aims to enhance the overall user experience by optimizing data dissemination and improving network performance. The following is a detailed analysis of the Wildfire mechanism:
3.4.1 Basic Principles
The Wildfire mechanism uses a ranking system to incentivize nodes to respond quickly and satisfy data requests. Nodes are ranked according to their speed and efficiency in propagating data in the network, and nodes with higher rankings will receive more requests and rewards. This mechanism ensures the rapid distribution of data in the network and improves the overall performance of the network.
3.4.2 Data Propagation Efficiency
The core of the Wildfire mechanism is to improve the efficiency of data propagation. After receiving new data in the network, a node will propagate it to other nodes as quickly as possible. Nodes with fast propagation speed and quick response will have an advantage in the ranking, thereby obtaining more request processing opportunities and corresponding rewards.
Fast Propagation: After receiving new data, a node quickly propagates it to other nodes to ensure the rapid flow of data in the network.
Efficiency priority: Through the ranking mechanism, nodes are encouraged to optimize data dissemination efficiency and improve the overall performance of the network.
3.4.3 Node ranking system
The Wildfire mechanism incentivizes nodes to improve data dissemination efficiency by ranking their performance. The ranking system scores nodes based on the speed and reliability of their response to data requests. Nodes with high scores enjoy higher priority in the network and receive more request processing opportunities and rewards.
Response speed: The speed at which a node responds to a data request is an important indicator of ranking. The faster the speed, the higher the ranking.
Data reliability: The reliability of the data provided by the node is also a key factor in ranking. The more stable the data provided, the higher the ranking.
3.4.4 Incentive and reward mechanism
The Wildfire mechanism incentivizes nodes to improve data dissemination efficiency by rewarding high-ranking nodes. Nodes get higher rankings and more rewards by quickly and reliably disseminating data. This reward mechanism ensures the active participation of nodes in the network, improving the overall performance of the network and the availability of data.
Ranking Rewards: Nodes with high rankings get more request processing opportunities and corresponding rewards.
Economic Incentives: Nodes get economic rewards by providing fast and reliable data dissemination services, which incentivizes nodes to continuously optimize performance.
3.4.5 Network Health and Robustness
The Wildfire mechanism not only improves the efficiency of data dissemination, but also enhances the health and robustness of the network. By incentivizing nodes to respond and disseminate data quickly, the Wildfire mechanism ensures the stability and efficient operation of the network under high load and high demand conditions.
High Load Adaptation: Under high load conditions, the Wildfire mechanism ensures that data can be disseminated quickly and efficiently in the network.
Improved robustness: By optimizing the performance of nodes, the Wildfire mechanism enhances the overall robustness and reliability of the network.
AR Token is the native cryptocurrency in the Arweave network and plays multiple key roles, from incentivizing miners to paying for data storage to maintaining the economic balance of the entire ecosystem.

The following is a detailed analysis of the AR token:
Payment of data storage fees: When users store data on the Arweave network, they need to use AR tokens to pay a one-time storage fee. These fees guarantee the permanent storage of data.
Incentivizing miners: Miners receive AR tokens as rewards by storing and verifying data. This mechanism encourages miners to actively participate in data storage and maintenance, ensuring the security and reliability of the network.
Arweave's business model is different from traditional subscription services. Users only need to pay a one-time fee to store data permanently. Part of these fees are used to pay for the initial storage costs, and the other part goes into the Endowment Fund for future storage costs.
Initial Storage Cost: The fees paid are immediately used to pay for the initial storage and access of the data.
Endowment Fund: About 86% of the fees go into the Endowment Fund, which is used to incentivize miners in the long term and ensure the durability of the data.

The Endowment Fund is designed similarly to a traditional economic donation structure, aiming to pay for future storage costs through interest and appreciation. The interest generated by the initial fees paid by users is used to pay miners' long-term storage fees, ensuring that data can be permanently preserved.
Fund Operation: The funds and interest accumulated by the Endowment Fund ensure that miners receive continued economic incentives for many years to come.
Expected Cost Reduction: As data storage costs are expected to continue to decline, the interest income of the Endowment Fund is sufficient to cover long-term storage costs.
4.4 Token Supply
Initial Supply: 66 million AR tokens.
Circulating Supply: 55 million AR tokens
Gradual Halving: Similar to the halving mechanism of Bitcoin, it ensures the scarcity and long-term value of the token supply. However, the difference is that AR tokens use a gradual halving mechanism, which means that the issuance of tokens will gradually decrease in each small cycle. 4.5 AR Token Distribution
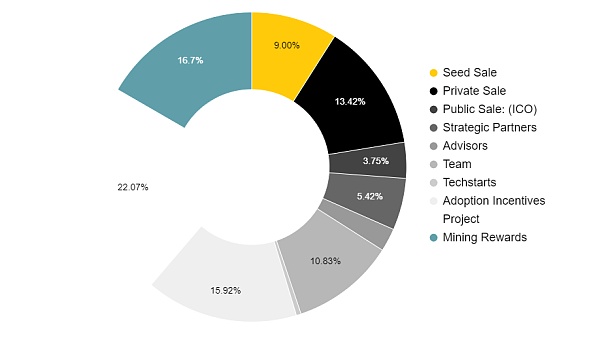
Seed Sale: 9%.
Private Sale: 13.42%.
Public Sale: (ICO): 3.75%.
Strategic Partners: 5.42%.
Advisors: 2.42%.
Team: 10.83%.
Tech Startups: 0.5%.
Adoption Incentives: 15.92%.
Projects: 22.07%.
Mining Rewards: 16.67%.
AR Tokens incentivize network participants in a variety of ways:
Miner Rewards: Miners are rewarded with AR Tokens for storing and verifying data, increasing their motivation to participate.
User Payments: Users pay AR Tokens to store data, ensuring that their data can be preserved forever.
Revenue Sharing: Arweave introduces Profit Sharing Tokens (PST), developers can get small dividends by building and operating applications, promoting the development and innovation of the ecosystem.
The performance of AR tokens in the market is affected by many factors, including the increase in storage demand, the development of the ecosystem, and the market's recognition of decentralized storage solutions. The value of AR tokens increases with the growth of the network and the increase in user demand.
Market Demand: As the Arweave network grows and user demand increases, the market value of AR tokens also increases accordingly.
Ecosystem Development: More developers and projects join the Arweave ecosystem, driving the demand and value growth of AR tokens.
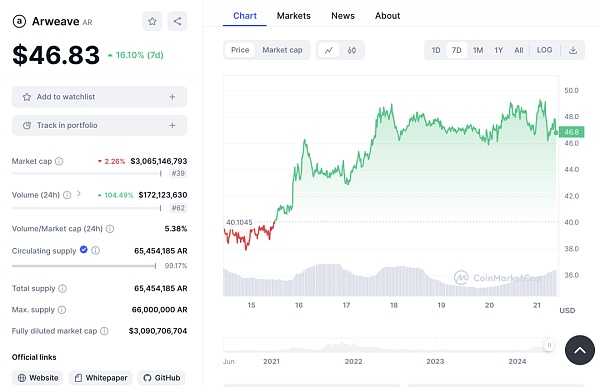
As of now, the market performance of AR tokens is as follows:
Price: $46.83, up 16.10% in the last 7 days.
Market Cap: $3,065,146,793, down 2.26% recently.
24-hour trading volume: $172,123,630, up 104.49% recently.
Trading Volume/Market Cap Ratio: 5.38%.
Circulating Supply: 65,454,185 AR, accounting for 99.17% of the total supply.
Fully Diluted Market Cap: $3,090,706,704.
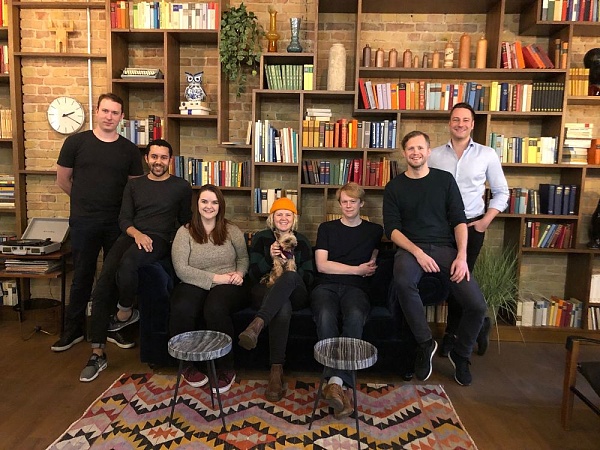

Arweave is a decentralized data storage protocol with a core team of experienced technical experts and industry leaders. Founder and CEO Sam Williams graduated from the University of Nottingham with a solid background in blockchain technology. Chief Operating Officer (COO) Sebastian Campos Groth graduated from Georgetown University and worked at Techstars, responsible for the daily operation of the project. Legal Director Giti Said graduated from the University of Vienna and is responsible for handling legal affairs. The team also includes a number of technical and business experts, such as Richard Pardoe, co-founder of Liquity, and Andy Bell, engineering director of Movement Labs, who jointly promote the development and innovation of Arweave.
1. KYVE
Introduction: KYVE is a blockchain storage middleware built on Arweave, providing a standardized verification and archiving framework.
Cooperation Highlights:
KYVE mainnet was launched, with more than 2000 TB of data uploaded.
KYVE has established strategic partnerships with 19 projects and plans to hold community growth events in 2024.
2. Irys (formerly Bundlr)
Introduction: Irys is an expansion solution for Arweave that increases Arweave's permanent data throughput through bundling transactions.
Cooperation Highlights:
In September 2023, Irys completed the processing of 1 billion transactions.
In October 2023, Irys cooperated with Solana Mobile to store DApp Store applications.
3. ArDrive
Introduction: ArDrive is a decentralized cloud storage application, similar to Dropbox or Google Drive for Web3.
Highlights of Cooperation:
In February 2023, ArDrive was fully decentralized and stored on Arweave.
In May 2023, ArDrive 2.0 was launched, adding dark mode, wallet generation, and large file upload features.

Since its establishment, Arweave has successfully raised US$37.3 million through multiple rounds of financing. Its main investors include Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), Union Square Ventures, Multicoin Capital, Coinbase Ventures and other well-known institutions. The following are some major financing events:
1. Seed round financing
Time: 2017
Amount: US$5 million
Main investors: Andreessen Horowitz (a16z)
2. Private placement round financing
Time: 2019
Amount: US$8.3 million
3. Public Offering Round (ICO)
Time: 2018
Amount: 15.7 million US dollars
Description: Public offering through the Initial Coin Offering (ICO) attracted a large number of early investors.
4. Subsequent financing
Time: 2020
Amount: US$8.3 million
Main investors: Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), Union Square Ventures, Coinbase Ventures
5. Latest financing
Time: 2023
Amount: US$8.3 million
Main investors: a16z, Coinbase Ventures, Multicoin 6. Project Evaluation
Arweave belongs to the decentralized data storage track. Through its innovative Blockweave technology, it realizes the function of permanent data storage. The core goal of the project is to provide an efficient, secure and scalable data storage solution that enables data to be permanently stored and cannot be tampered with.
Here are some decentralized data storage projects similar to Arweave:
1. Filecoin
Introduction: Filecoin is a decentralized storage network that uses IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) technology to drive storage nodes through economic incentives.
Core Technology: Proof of Replication and Proof of Spacetime.
Features: Users pay for storage on demand, supporting large-scale data storage and retrieval.
2. Siacoin
Introduction: Siacoin is a decentralized storage platform that uses blockchain technology to achieve secure and low-cost data storage.
Core technology: Smart contracts and storage proof.
Features: Users pay Siacoin tokens to rent storage space, providing low-cost distributed storage solutions.
3. Storj
Introduction: Storj is a decentralized cloud storage platform based on blockchain, where users can store data through a distributed network.
Core technology: Sharding technology and distributed hash table (DHT).
Features: Data is encrypted and stored in nodes around the world after being sharded, ensuring data security and privacy.
Permanent Storage: Users only need to pay a one-time fee to store their data permanently on the Permaweb, without the need for monthly subscription fees.
Decentralization: Storing data in a decentralized manner reduces the risk of relying on centralized servers.
Strong Support: Arweave has received support from well-known investors including a16z, Coinbase Ventures, and Union Square Ventures.
Widely used: It is used as the default metadata storage platform by OpenSea and Solana's NFT project Metaplex, ensuring the long-term validity of NFT data.
1. High initial cost
One-time payment: Although Arweave's one-time payment model can ensure permanent storage, the initial cost may be higher than the on-demand payment model. This may cause financial pressure for some users, especially small businesses or individual users.
Fee transparency: The one-time payment fee structure may not be as transparent as the on-demand payment model, and users need to have a comprehensive understanding of its fee structure before deciding to use Arweave.
2. Insufficient network effect
User and developer appeal: Although Arweave's technical advantages are obvious, its user and developer ecosystem is still developing and may not be as attractive as some mature decentralized storage projects.
Market awareness: Arweave's market awareness may not be high enough compared to competitors such as Filecoin, and more marketing and community building are needed to increase its popularity and user base.
3. Technical and development challenges
Development complexity: Arweave's block weaving and other technologies may be complex for developers, and developers need to invest more learning costs to understand and apply these technologies.
Technical bottlenecks: Although Arweave provides efficient storage solutions, it may still encounter technical bottlenecks when facing large-scale data storage and processing, which requires continuous technical improvement and optimization.
As an innovator in the field of decentralized data storage, Arweave has achieved permanent storage and efficient management of data through its unique Blockweave technology and powerful economic incentive mechanism. Its one-time payment and permanent storage business model not only solves the problems of data loss and high costs in traditional storage systems, but also provides users with reliable and long-term data storage solutions. Although Arweave still faces some challenges in technology and market promotion, its expanding ecosystem and diverse partnerships have laid a solid foundation for it. With the growing demand for blockchain technology and decentralized storage, Arweave is expected to become a leader in this field in the future, providing more secure, transparent and efficient data storage services to users around the world. Through continuous technological innovation and market expansion, Arweave is steadily moving towards its goal of becoming a leading global decentralized storage solution provider.
This article will explore the redundancy mechanisms of Arweave and IPFS, and which option is safer for your data.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance100 billion WhatsApp messages are sent every day. Most blockchains are not designed for storage. If you want to store 100 billion WhatsApp messages on Ethereum or any blockchain, it will be extremely expensive.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceThis article explores how Arweave and IPFS store, maintain, and access files, and how this affects the reliability and durability of digital assets.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceA new world of horizontal scaling awaits us in AO, but none of this would be possible without the pair of DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network) projects that underpin AO.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceSince its launch in 2018, Arweave Ecosystem has been considered one of the most valuable networks in the decentralized storage circuit.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceWhy is Arweave not a replacement for Filecoin, but a more significant innovation worthy of attention?
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceDuring this Chinese Spring Festival, a big event happened in the Arweave ecosystem.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinanceThis event is poised to host more than a hundred Arweave ecosystem developers and investors, offering attendees exclusive perks such as product testing opportunities, AR airdrop rewards, and practical merchandise.
 Samantha
SamanthaCryptocurrency investments have experienced turbulence in recent times. However, it is possible to see strong returns, particularly as many retail ...
 Bitcoinist
Bitcoinist