Author: Tanay Ved & Matías Andrade Source: Coin Metrics Translation: Shan Oppa, Golden Finance
Key points:
Since March 13 Since the launch of Japanese EIP-4844, several Layer-2 solutions including Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism have adopted blob transactions, and more than 950,000 blobs have been released to Ethereum.
The adoption of Blobs has significantly reduced the operating costs of Layer-2s, and the median blob cost has been reduced to a minimum of $0.0000000005. Make user interaction more affordable.
The blob fee market dynamically adjusts based on demand, as does the average number of blobs per block via subscription blobs ("Blobscriptions") A push up to Target 3 temporarily pushed the fee up to $27 before falling back to close to $0.
Introduction:
EIP-4844 (jokingly called (original-danksharding) went live in March’s Ethereum Dencun upgrade, marking a major milestone for Ethereum’s rollup-centric roadmap. This upgrade aims to improve the scalability of Ethereum Layer-2 solutions and reduce transaction costs by optimizing how they clear transactions to Ethereum Layer-1. This is accomplished by providing dedicated space for “blobs” (fragments of data) that L2 can use to settle transactions more cost-effectively. The ultimate goal is to expand the reach of the Ethereum ecosystem by making transactions more affordable and scalable.
In this week’s Coin Metrics’ “State of the Network” report, we provide a data-driven breakdown of the use of Layer-2 blobs and evaluate Ethereum’s How successful is the EIP-4844 upgrade of the workshop.
What are blobs, sorters, and data availability layers?
As Ethereum has matured, it has transformed into a modular blockchain with various infrastructure working together to achieve its core functionality. Layer-2 forms a piece of infrastructure in the Ethereum stack that enables the network to scale. Over the past few years, a large number of Layer-2 solutions such as rollups (such as Base, Optimism, and Arbitrum) have emerged, with several more under development. These protocols rely on Layer-1 blockchains like Ethereum for data availability (storing/accessing transaction data) and ensuring the settlement of transactions through participants called sequencers, which order and batch commit transactions. To Ethereum L1. However, the costs associated with these operations are still high for Layer-2s.
This is where EIP-4844 comes into play. The upgrade introduces a new transaction type with blobs, temporary packets of data that L2s can use for cost-effective settlement. Blobs are made available to L2s for approximately 18 days - unlike calldata which was previously stored permanently in Ethereum blocks. The ephemeral nature of blobs allows them to be sold cheaply, significantly reducing L2s storage and data costs.
In the previous sections, we will understand the impact of EIP-4844 on Ethereum’s L2 ecosystem and its economics.
Blob transaction adoption
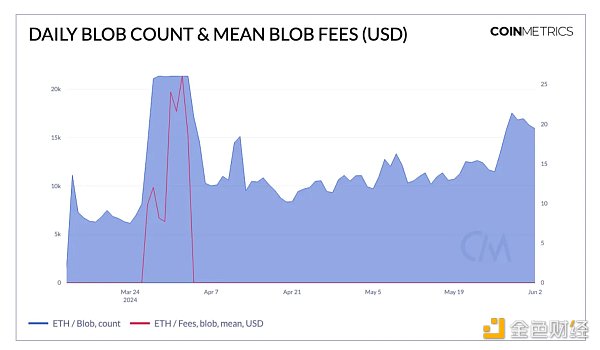
After going online on March 13, several L2s started Adopt blob transactions, starting with zkSync, Starknet and Optimism. Since then, over 950K blobs have been released to Ethereum, with 450K transactions carrying blobs. On average, this equated to 10K blobs per day for most of April, with this number increasing to 17K recently as more Layer-2 came on board and adopted blobs.
p>
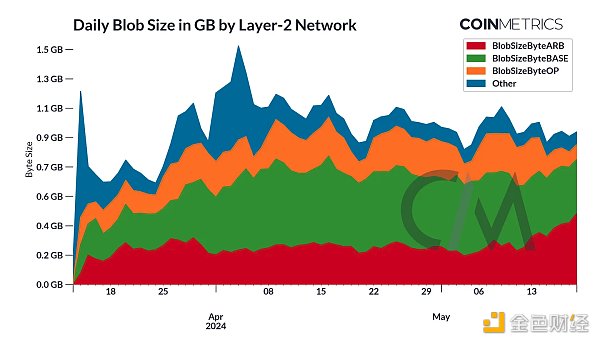
Each blob-carrying transaction can contain up to 6 blobs, each storing 128KB of data. As Layer-2 rollups increasingly use this dedicated space to publish large amounts of data, blob space utilization is expected to increase. A total of 125B bytes of blob space has been used so far, so the blob size is growing compared to the total block size in bytes. This indicates that L2 is moving away from calldata to a more efficient form of data storage. Crucially, blobs are designed to expire after 4096 epochs (approximately 18 days), giving rollups enough time to retrieve necessary data while preventing permanent storage bloat on the Ethereum network.
p>
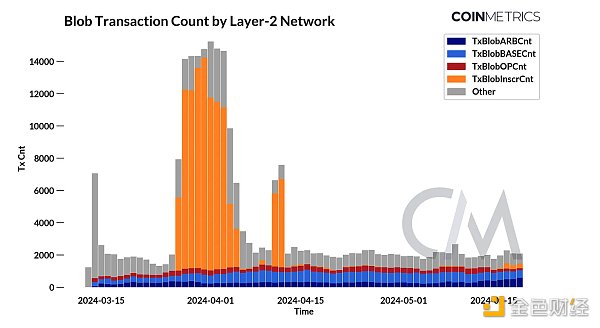
After excluding the impact of inscriptions, Layer-2's adoption of blob storage and blob transactions is relatively stable. While Coinbase’s Base maintains the largest portion of blob sizes and blob transactions, Arbitrum’s impact is significantly stronger. As the number of rollups increases and blobs are used, the number of transactions is expected to continue to increase. Overall, the adoption of blobs is a positive sign that EIP-4844 is achieving its goals of reducing data storage overhead and increasing the scalability of Layer-2 solutions.
p>
Impact of Blob fees and costs
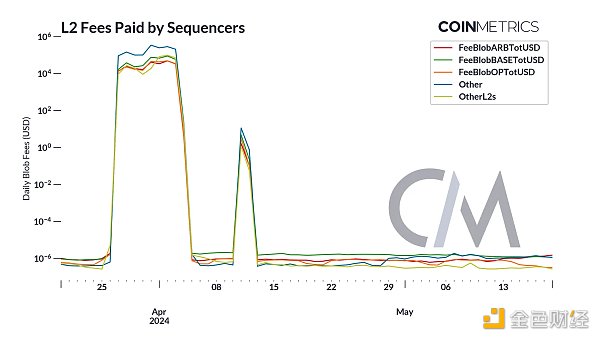
Adopting this efficient storage and transaction type provides L2's Brings significant operating cost reductions. When L2 sorters batch and submit blobs to Ethereum L1, they incur a fee, which is a cost to L2. While weekly fees associated with Arbitrum, Base and Optimism sequencers rose to $700K in April due to the surge in inscription blobs, the cost spent on blob space has dropped to $0.00002.
p>
The increased cost efficiencies of L2s have translated into extremely low fees for end users. Currently, the median blob fee is as low as $0.0000000005, down significantly from a peak of $27, while the total amount paid for blob space is closer to $0.000008. Ultimately, this makes user interactions such as token transfers between wallets, asset exchanges on DEXs, or other smart contract operations more affordable.
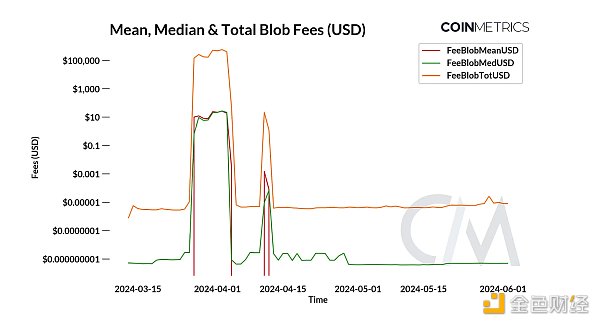
p>
Inscription and Blob Fee Market
EIP-4844 introduces a new transaction type and a A new fee market is used to price blobs. This market is designed to function similarly to EIP-1559's fee market. In this new system, the blob base fee dynamically adjusts based on the supply and demand of blob space within each block.
The blob pricing mechanism operates according to the following principles:
1 .If the number of blobs in a block exceeds the current target of 3, the blob base fee will increase. This is to avoid overusing blob space and keep supply and demand balanced.
2. If the number of blobs in a block exactly reaches the target, the basic blob fee remains unchanged. This indicates that supply and demand for blob space are in balance.
3. If the number of blobs in a block is lower than the target, the base blob fee will be reduced. This encourages greater use of blob space when it is underutilized.
These price dynamics ensure that the blob fee market can adapt to changes in blob space demand, maintaining a stable and efficient fee environment for Layer-2 solutions and users.
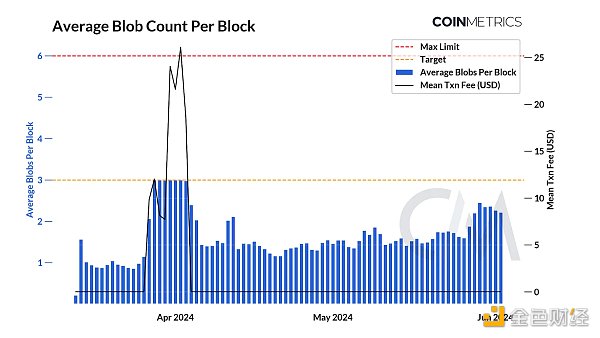
p>
As shown in the chart above, the average daily transaction fee increased significantly to $27 in April as the average number of blobs per block exceeded the target. This increase can be attributed to the proliferation of inscribed blobs ("Blobscriptions"). An inscription is a form of text, image, or other media embedded in a block—or in this case, a blob. From late March to early April, the daily number of inscribed blobs rose to a high of 13K, accounting for over 61% of all blobs. However, since then, Blobscriptions have become less common, bringing blob fees back down to close to $0.
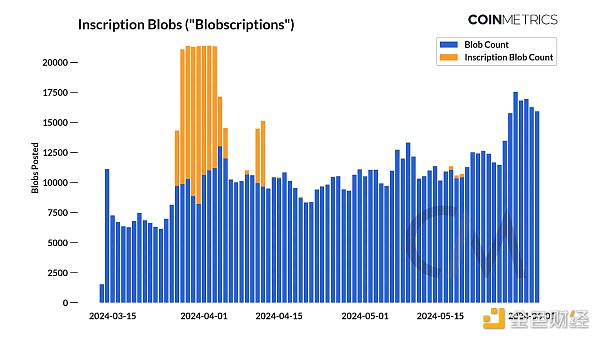
p>
This scenario illustrates how network congestion or high demand for blob space affects blob pricing. While the current blob target per block may increase in the future, monitoring the above conditions is key to understanding changes in blob fee dynamics, especially as the L2 market continues to expand and become more competitive. Blobscriptions may be a temporary situation now, but as more L2s leverage blobs to meet their scaling needs, congestion is likely to reoccur.
Conclusion
EIP-4844 successfully increased L2 adoption through blob transactions, Reduces Layer-2 operating costs and makes transaction fees more affordable for users. However, challenges such as fragmentation across assets, liquidity and user experience in layer-2 solutions, and the need for decentralized sequencers remain. Solving these issues is critical to the continued growth and success of Ethereum’s Layer-2 ecosystem, allowing transactions to become scalable and cost-effective while remaining secure and decentralized.
Network Data Insights
Summary Key Points< /strong>
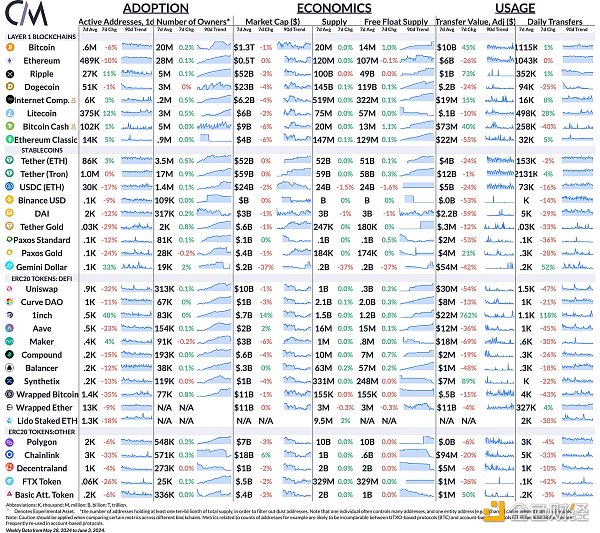
The value of transfers (adjusted) on the Bitcoin network increased by 45%, and the value of transfers on the Ethereum network decreased by 26%. This week, active Bitcoin addresses fell by 6% and Ethereum active addresses fell by 10%.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance









