Exploring Berachain: Analysis of Native Protocol and Technical Key Points
Berachain is an EVM-equivalent L1 blockchain built on the Cosmos SDK.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
Main changes in Berachain's consensus mechanism, token economics model and its unique ecosystem.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a network consensus mechanism. The more native tokens staked in the network, the higher the security. It is also the most widely used mechanism in recent years.
However, the native token of the PoS network can be used to pay gas fees in addition to staking, and serves as the base currency within the ecosystem. Because of this design, an increase in the number of stakes on a PoS network will cause a decrease in the liquidity of the DeFi ecosystem and the activity within the network, forming a self-contradictory situation.
This lack of liquidity will have a negative impact on the entire ecosystem, such as causing excessive slippage on decentralized exchanges (DEX) and inhibiting the development of many protocols that run on token deposits. As a result, many ecosystems have recently been forced to conduct too many airdrops or build their own L2 or application chains in order to ensure a certain amount of liquidity, which has dispersed the liquidity of the entire blockchain ecosystem and reduced the user experience.
On the Ethereum mainnet, due to the attention gained by the restaking protocol, ETH staking continued to grow, reaching a historical high of about 28%, but we can observe that the Ethereum network traffic is obviously declining, with the average daily gas fee of only about 5 Gwei.
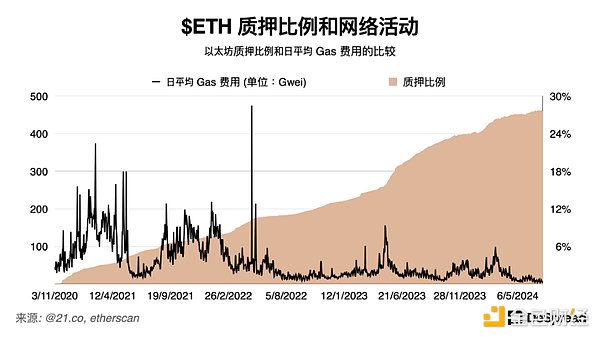
This PoS structure brings a problem. Users cannot stake tokens on both the liquidity protocol and the network itself at the same time, resulting in conflicting incentives for verification nodes and the protocol.
Of course, many foundations are aware of this problem and try to coordinate the interests of both parties by providing financial support, technical guidance and marketing support to protocols that contribute to the ecosystem, but this still makes it difficult to reflect the opinions of ecosystem members such as network users and verification nodes, and may even lead to the problem of power centralization due to over-reliance on foundations.
If one of the core concepts of blockchain is to create an environment where "Can’t be eveil" rather than "Don’t be eveil", then a new system is needed to improve the problem that PoS cannot have both ecosystem liquidity and network security at the same time. Berachain aims to solve the above problems of PoS networks by building a structure that can simultaneously supplement the liquidity of the ecosystem and the security of the network through token economics based on game theory.
In this article, we will learn about Berachain's consensus mechanism and token economics model, the main changes of the testnet v2 released in June 2024, and introduce the unique ecosystem built on it.
Berachain is built with BeaconKit, which uses the Cosmos SDK to build a customizable EVM execution environment. It is an EVM-compatible L1 network.
General blockchain projects usually have the development team publish a white paper outlining their technical vision, recruit potential users through various activities, and build the project's community. Berachain started to form their community with an NFT project called "Bong Bears". Bong Bears was launched in 2021, when the NFT market was hot and received strong support from the then popular DeFi project Olympus DAO community. Since then, Bong Bears holders have successively received airdrops of derivative NFTs such as The Bond Bears, The Boo Bears, and The Baby Bears, and continued to expand the community.
During this period, the word Berachain was just a meme in the Bong Bears community, but the developer Dev Bear actually started to develop Berachain, and it has now entered the testnet stage.
Many recent blockchain projects, although they have invested a lot of time and money to build a loyal community, often lose users after the token airdrop, and Berachain's way of building a community is different from these projects, and naturally attracts the attention of many cryptocurrency users.
Another key factor that makes Berachain the L1 that many users are looking forward to is its design of "Proof of Liquidity (PoL)", a consensus protocol that uses game theory token economics to solve the problem that the PoS network cannot unify the rewards of participants.
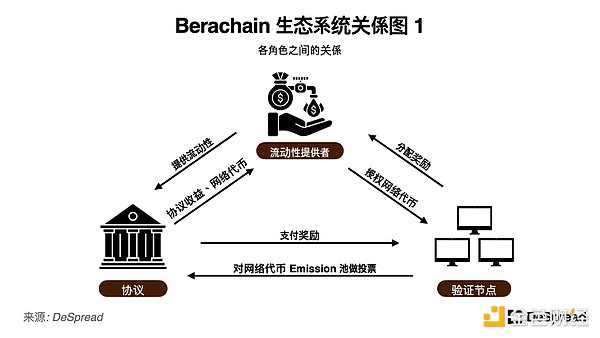
The participants of Berachain's PoL consensus mechanism have the following roles and related relationships.
Validator: Participates in network validation by operating a Berachain node.
Liquidity Provider: Provides liquidity to protocols within the ecosystem.
Protocol: Provides specific services to users on the Berachain network and requires liquidity within the network.
In Berachain's PoL mechanism, liquidity providers who provide liquidity to the liquidity pool of a specific protocol can be rewarded with Berachain network tokens, which are issued as rewards in each block, and liquidity providers can delegate the received tokens to validators to indirectly participate in the network verification process. In the process, liquidity providers can earn interest from the liquidity they provide, and can also earn income through network validators. At first glance, this structure seems to be roughly the same as PoS, except for the order of staking assets in the liquidity protocol of the PoS chain and then depositing the received liquidity tokens in another protocol to profit from it.
However, in PoS, competing liquidity protocols lead to the diversification of tokens and the dispersion of liquidity, while Berachain builds this function into the chain, preventing the problem of liquidity fragmentation at the bottom layer.
In addition, validators on Berachain have the right to vote on the liquidity pool that allocates block rewards, which means that network validators have the right to directly increase the rewards of specific liquidity pools. Compared with PoS, this function allows liquidity providers and protocols to participate more closely in the consensus mechanism of PoL. 2.1.1. Ecological Flywheel We can predict that the protocols launched on Berachain will use investment funds, self-issued tokens and protocol fees to provide these incentives to validators, obtain their votes and ensure the initial growth of the protocol.
This will also incentivize validators to distribute the rewards obtained from the protocol to network token delegators to ensure that they can obtain more voting rights, and distributing the rewards obtained from the protocol to liquidity providers will encourage them to provide liquidity to the protocol again, creating a virtuous cycle, thereby further strengthening network security.
In this way, Berachain's PoL mechanism, with projects and liquidity providers as the main participants, improves the problem of not directly participating in the network consensus mechanism in the traditional PoS structure. These three entities are closely connected, exchanging liquidity and incentives, forming an ecological flywheel, where value flows from liquidity providers to protocols, protocols to validators, and then back to liquidity providers.
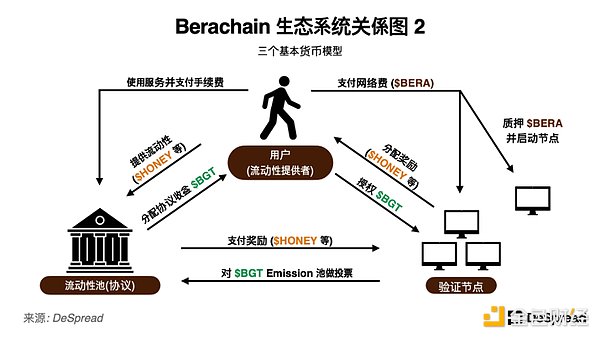
In order to better utilize the flywheel characteristics of PoL, Berachain adopts a three-token model, using the following three types of network tokens.
$BERA: This token is used as the network fee of Berachain, and the gas fee will be destroyed. A validator must stake 69,420 $BERA to activate a node.
$BGT: Inflation reward allocated to the liquidity pool by validators' votes. This token is bound to the account and cannot be transferred or traded. After providing liquidity, liquidity providers can use the received $BGT to take the following actions.
Destroy $BGT at a 1:1 ratio and obtain $BERA
delegated to validators
$HONEY: a stablecoin, pegged to 1 US dollar, as a reserve currency in the Berachain ecosystem. Currently issued in the form of wrapped USDC on the test network, it may be converted to an overcollateralized form in the future. A 0.5% fee is charged upon issuance, which will be distributed to $BGT holders.
Substituting the above three-token model into the participant relationship diagram of Berachain, we can summarize the following points.
Since $BGT, which determines the distribution of inflation rewards, is not tradable and can only be obtained by providing liquidity, the structure of Berachain prevents certain whales from obtaining a large amount of $BGT in a short period of time to influence governance. This structure encourages protocols that wish to obtain $BGT to attract liquidity in the Berachain ecosystem to have to convince validators with a large amount of voting power through the process of allocating incentives.
This social consensus behavior among Berachain ecosystem participants leads to increased security and liquidity of the Berachain network, helping to attract more users to the Berachain ecosystem.
As more and more users join the ecosystem, network usage increases, and $BERA burned for gas fees will also increase. Not only that, as the demand for collateral and transaction assets in the ecosystem protocol increases, the demand for $HONEY will also increase, all of which will bring profits to $BGT holders.
With its loyal community and unique PoL mechanism, Berachain has won wide attention and achieved remarkable results. It launched its first test network "Artio Testnet" in January 2024, and then the number of active wallets reached 1 million within 8 days.
However, since Berachain uses CometBFT based on the Cosmos consensus mechanism to run EVM, compatibility and scalability issues with EVM were discovered during the test network. In June 2024, Berachain launched its second test network "bArtio Testnet", which solved these problems faced by the first test network and improved other defects related to the PoL mechanism.
During the development of the chain, the Berachain team built an EVM-compatible framework called "Polaris" to connect the Cosmos-based CometBFT consensus mechanism and the EVM execution environment.
Polaris achieves compatibility between CometBFT and EVM through precompile technology that can translate and store two different program execution environments. Berachain's Artio testnet is built using this framework.
However, as the test progressed, the following limitations of Polaris were discovered.
The consensus engine of the Cosmos SDK waits for the EVM to complete transaction processing before creating a block, so too many transactions at the same time will cause a bottleneck.
Polaris will not work properly when pre-compiling unstructured calculations, resulting in EVM compatibility issues.
To overcome these problems of Polaris, the bArtio testnet launched BeaconKit, an EVM-compatible framework from the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain. 3.1.1. BeaconKit Unlike Polaris, BeaconKit clearly separates the execution layer (EVM) and the consensus layer (CometBFT), and the two layers are connected and compatible through EngineAPI. This architecture allows BeaconKit to work with standard Ethereum execution clients (Geth, Erigon, Nethermind, etc.).
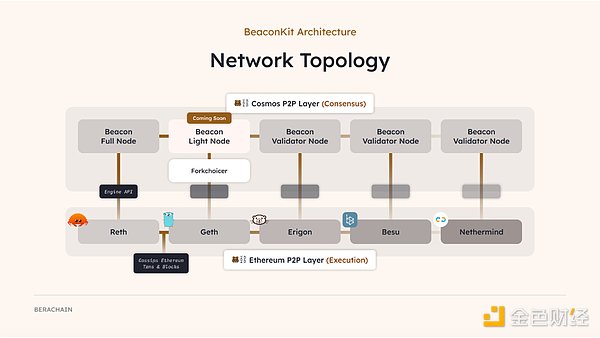
BeaconKit Architecture, Source: Berachain Blog
Because the bArtio testnet uses the same execution client as Ethereum, it is able to provide an EVM execution environment that is 100% identical to Ethereum. When the Ethereum execution environment is updated, Berachain only needs to install and run the client provided by Ethereum to replicate the updated effect of the EVM execution environment from the Ethereum mainnet, without any special operations on the Berachain network.
In addition, unlike Polaris, BeaconKit's execution layer and consensus layer run independently, so bottlenecks in one layer will not affect the other layer. At the same time, when a validator creates a block, the validator will propagate the status of all transactions in the block to other validators. This "Immediate Execution" mechanism greatly improves the transaction processing speed and solves the scalability problem of Polaris.
In addition to changing the EVM-compatible framework to BeaconKit, in order to strengthen the PoL mechanism of the bArtio testnet, the Berachain team also made the following changes.
Changes in validator participation conditions: In v1, only a small amount of $BGT was required to activate a validator node, while the bArtio testnet changed its conditions to 69,420 $BERA to increase the amount of stake and security in the network.
Changes in penalty conditions: In v1, the validator's misbehavior would jointly affect the validator node and the liquidity providers who delegated $BGT to the validator, reducing the $BGT of these participants. In v2, the penalty conditions are changed to only reduce the $BERA staked by the validator, separating the roles of $BGT and $BERA in the PoL ecosystem and strengthening the responsibility of the validator.
Changes in block creation permission criteria: In v1, a validator’s permission to create new blocks changed with the amount of $BGT they were authorized to grant, while in v2, the amount of authorization no longer affects the permission to create new blocks, and every validator has an equal opportunity. However, block rewards still change based on the amount of $BGT authorized.
Increase in validator cap: In order to improve the decentralization and security of the network, the Berachain team has removed the 100 validator cap. As of July 16, there are 150 validators participating in validating the Berachain network. The following table summarizes the changes from the Artio testnet to the bArtio testnet (the following conditions may change before the mainnet is launched). After testing the PoL mechanism on the Artio testnet, the bArtio testnet is currently fine-tuning the details and parameters of PoL in preparation for the actual mainnet launch.
Since its launch, the daily transaction volume of the bArtio testnet has gradually increased, with about 3.2 million transactions and 860,000 active wallets. More than 150 projects are also preparing to build new protocols on Berachain to take advantage of the advantages brought by EVM compatibility, scalability and PoL mechanism.
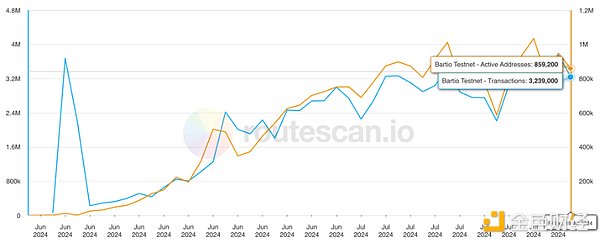
Berachain daily active wallets and transaction volume, source: Beratrails
In a typical L1 network, the foundation usually issues tokens and allocates part of them to the ecosystem for development funding, hackathon programs, etc. to help build the ecosystem.
The Berachain team also has an incubation program called "Build-a-Bera", but "Build-a-Bera" only uses the funds of the Berachain team to provide seed investment and mentor support for incubation projects, and does not distribute Berachain tokens through grants or hackathons.
Berachain co-founder Smokey The Bera also criticized the subsidy system of other networks. The reason why the Berachain team can take this position is that the essence of Berachain's PoL consensus mechanism is to distribute $BGT to users who contribute liquidity to the liquidity pool, thereby achieving the effect of supporting ecosystem projects.
Compared with the ecosystem incubation programs of other networks, Berachain does not directly provide assets to the protocol development team, but the "consensus" of the network participants can guide the liquidity of the protocol, which can be said to be a healthier form of ecosystem growth.
Due to the PoL structure of the incentive mechanism for network participants, communication and consensus between validators, protocols, and liquidity providers in the Berachain ecosystem are even more important for the growth of the ecosystem. Although Berachain is still in the beta stage, this has led to many collaborations, and some protocols have even tried to play multiple roles at the same time and tried to run validation nodes themselves.
Next, let's explore some of the protocols in the Berachain ecosystem. 4.1. Native dApps Berachain's native dApps are built by the team as the infrastructure responsible for the basic functions of the ecosystem. Currently, there are three types of native dApps running on the testnet, namely BEX, Bend, and Berps. BEX: A decentralized exchange that allows users to trade or create their own trading pools without intermediaries.
Bend: A decentralized lending protocol that allows users to borrow $HONEY with a variety of assets as collateral or earn interest by providing $HONEY liquidity.
Berps: A decentralized perpetual contract exchange that allows users to create leveraged positions using $HONEY as collateral or provide liquidity for position holders' trading profits by depositing $HONEY and earn trading fees.
Before other protocols are launched, these native dApps will provide basic DeFi functions to users in the nascent Berachain ecosystem, and will also serve as a channel for distributing $BGT to liquidity providers participating in the nascent ecosystem. In the current bArtio testnet, users can also observe that the liquidity pools currently eligible for $BGT are also composed of native dApps.
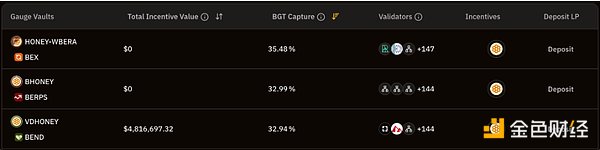
Berachain Treasury Scale, Source: BGT Station
Native dApp further strengthens Berachain's three-token economic model by leveraging $HONEY as the main collateral asset, expanding its usability and distributing the revenue generated by the protocol to $BGT holders.
In addition, the economic model has also become a catalyst for the diversification of the ecosystem, encouraging development teams that release protocols on Berachain to use the PoL mechanism in a variety of ways and be creative, rather than just providing an infrastructure.
DeFi protocols on other networks basically pay additional rewards to liquidity providers to attract liquidity, and then use that liquidity to attract user traffic to generate protocol revenue.
However, the DeFi protocol on Berachain does not incentivize liquidity providers, but rather incentivizes validators to build the following flywheel.
The protocol distributes rewards to validators who vote for them, thereby encouraging more users to delegate $BGT to the validator.
In order to obtain more rewards, users continue to delegate $BGT to those validators who have received rewards. As the amount of $BGT delegated increases, the validator's voting power for rewards increases, which helps the liquidity pool generate more $BGT rewards.
In order to obtain the $BGT rewards generated by the liquidity pool, users bring in more liquidity from the outside, and the protocol's traffic and revenue also increase.
Repeat the process of 1-3. In the process of building this flywheel, we can also see that some protocols provide users with more convenience and added value by negotiating with users on the basis of the benefits and future added value of the protocol, while some protocols strengthen the rights of the protocol by aggregating decentralized liquidity to increase their benefits.
4.2.1. Kodiak
Kodiak is a DEX that provides centralized liquidity (Concentrated Liquidity AMM, CLAMM) for trading pools such as Uniswap v3, allowing users to concentrate their liquidity in a specific area, thereby providing more efficient $BGT mining than BEX.
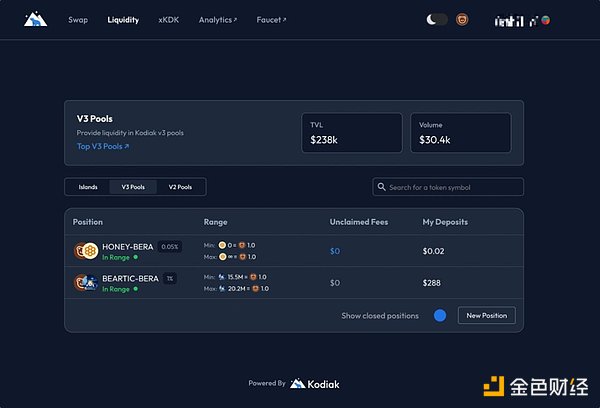
Kodiak V3, Source: Kodiak
Kodiak has two tokens, $KDK and $xKDK, which users can exchange within the protocol, as described below.
$KDK: Reward tokens paid to liquidity providers and traders.
$xKDK: Kodiak's governance token and non-tradable token. Holders are allocated a share of the revenue generated by Kodiak, including fees from user transactions and rewards from other protocol submissions.
The centralized liquidity supply allows users to mine $BGT with higher capital efficiency, but if the price fluctuation exceeds the liquidity supply range, the liquidity deposited by the liquidity provider will not be able to be used for trading, and $BGT and transaction fees cannot be obtained. Therefore, if you want to continue to obtain rewards, you must constantly manage the liquidity range.
In response to this, Kodiak has added the Kodiak Islands vault function, which can automatically adjust the liquidity coverage range according to market conditions, solving the problem that liquidity providers must constantly manage the liquidity coverage range, and also solving the problem of idle liquidity caused by the deviation of the concentrated liquidity coverage range, to ensure that Berachain maintains sufficient trading liquidity. In the process of automatically adjusting the liquidity coverage, Kodiak also establishes a complementary relationship with native dApps by enabling BEX.
Currently, Kodiak is running a validation node on the bArtio testnet, so it is also possible to synchronize with the validation mechanism in the future. How the protocol will develop in the future remains to be seen. 4.2.2. Infrared Infrared is a liquidity staking protocol in the Berachain ecosystem. It runs a Vault to provide liquidity to the liquidity pool on behalf of users, and entrusts the $BGT generated by the liquidity deposited by users in the Vault to the validation nodes run by itself. Users of Infrared can obtain $BGT's liquidity token $iBGT and governance token $IRED.
$iBGT: The token that liquidates $BGT. Users can use $iBGT in other DeFi protocols to earn additional income.
$IRED: Infrared's governance token, which has the power to determine the $BGT voting rights of Infrared validators and can be allocated to the revenue generated by Infrared.
Infrared ensures that it provides users with two functions of $BGT, including redemption of $BERA and voting rights, to attract a large number of $BGT. The more $BGT Infrared collects in the Berachain ecosystem, the more important the role of $IRED with $BGT voting rights will be, so it can be expected that many protocols will design a model that uses $IRED as an alternative role to $BGT.
Kodiak is an agreement of this type and is currently working with Infrared. It plans to open a Kodiak Vault on Infrared to provide Kodiak liquidity providers with the opportunity to mine $IRED.
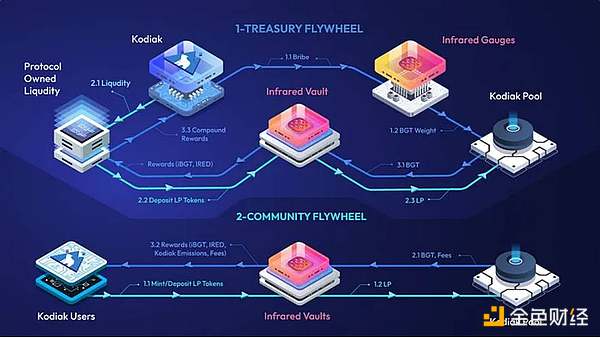
Infrared X Kodiak flywheel, Source: Kodiak Blog
Other DeFi protocols such as Gummi and BeraBorrow will also allow $iBGT as collateral, and we can observe that some projects have begun to create a new ecosystem centered on Infrared.
In addition to $BGT's liquidity pledge, Infrared has recently introduced $BERA's liquidity pledge, and is committed to becoming a protocol that provides a comprehensive solution for liquidity pledge in the Berachain ecosystem.
The DeFi protocol on Berachain is trying to solve the liquidity war within PoL through digital quantified incentives, and provide convenience to users and improve capital efficiency. We can also find that some participants in the PoL ecosystem will first establish a community through NFT and Meme, and use community activities to establish fame and presence before developing the established fame into a window for generating income. Although this method is more qualitative and may be less efficient than the DeFi protocol in terms of incentives, the emergence and combination of derivative protocols in the DeFi ecosystem may hinder new users from entering Berachain, so the demand for solving the liquidity war in this more qualitative way is estimated to continue to increase in the future.
In addition, considering that Berachain originated from an NFT project and has the most admired community, this approach may be a more "Berachain" strategy. 4.3.1. The Honey Jar Honey Jar is a community that developed in 2022 around an NFT called Honeycomb. Its core idea is to build a community-driven flywheel to connect entities and create "Sticky Liquidity" that is not easily dispersed.
Similar to how Berachain has grown, the Honey Jar community has also continued to expand by issuing and airdropping a series of derivative NFTs to its holders. Through the growth of the community, Honey Jar began to collaborate with various projects developed on Berachain to provide NFT holders with various benefits from these projects.
In recent years, Honey Jar has also produced various educational materials about Berachain and provided services such as the testnet Faucet to new users of the Berachain ecosystem. In addition, they have also incubated the community-based rating service project S&P (Standard & Paws) and Bera Infinity, which provides pricing and rewards for contributions in the Berachain ecosystem. Through these plans, Honey Jar proves that it is not just a community, but also a startup studio in the Berachain ecosystem.
Honey Jar also operates a verification node in the Berachain ecosystem. Due to Honey Jar's strong influence in the Berachain community through the various activities and services mentioned above, as of July 2023, Honey Jar has become the verification node with the most $BGT authorized.
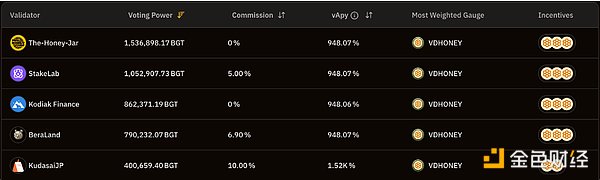
Ranking of authorized $BGT by validator nodes, source: BGT Station
Recently, Honey Jar is preparing for the liquidity war after the launch of the Berachain mainnet, conducting reward negotiations and liquidity cooperation with the protocols to be launched on Berachain. They also established a DAO and expect to distribute the rewards obtained to Honeycomb NFT holders.
Since its initial NFT project, Berachain has built a loyal community and closely linked the interests of the three participants, validators, liquidity providers, and protocols, by introducing the PoL consensus mechanism.
In addition, we can also see that many DeFi protocols are building new models through the Berachain consensus mechanism, and there are also community-based projects that use their own way to try to gain a foothold in the ecosystem.
While the PoL consensus mechanism around Berachain aims to build an ecosystem flywheel, this flywheel may also be a vicious cycle, and there are still the following challenges to ensure the sustainability of Berachain.
$BGT inflation: With $BGT constantly inflating, the liquidity flowing into the external ecosystem to create demand for $BGT is limited. In the long run, the consumption of $BERA must increase, but due to the PoL structure's focus on liquidity, it may be difficult to increase actual network usage.
Possibility of Centralization: As the ecosystem matures, it is possible that powerful cartels will form around certain validators, protocols, and liquidity whales. If the ecosystem only develops around these cartels, it may cause problems for new protocols to enter the Berachain ecosystem, thereby discouraging the enthusiasm of new users.
In order to solve these problems, protocols that can attract new users and drive active transactions must emerge, and ecosystem participants must also reach a consensus to ensure that protocols that have a positive impact on the ecosystem can obtain sufficient liquidity support.
Berachain attempts to integrate liquidity and security into the incentive mechanism, and the success of this attempt will have a significant impact on the entire blockchain industry. Since it is still in the testnet stage, how to deal with these challenges in the future will be an interesting topic.
Berachain is an EVM-equivalent L1 blockchain built on the Cosmos SDK.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance成功项目“的定义很复杂,有别于”Defi/项目的终局是什么“,他并不是单一度量的。
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceBy aligning network token incentives with the economic interests of DeFi users, Berachain is committed to achieving a self-reinforcing growth cycle that promotes market-leading liquidity and yield opportunities, making it the dominant force among L1 blockchains!
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceIn today's blockchain world, Berachain may be the most "anti-traditional" project.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceThis article introduces Berachain, transcending the hype and transforming the technical complexity of its Protocol Owned Liquidity (POL) mechanism into a more understandable ecosystem.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceBerachain is a bear-themed DeFi project run by pseudonymous co-founders: Homme Beta, Dev Bear, Papa Bear and Smokey the Bera. Recently, the project secured $69 million in funding led by Polychain Capital, with Hack VC, shims Capital,Robot Ventures, Goldentree Asset Management and others participating. Through the use of high-performance consensus mechanism, Berachain hopes to bring greater scalability, better security and a phenomenal user experience for its customers.
 XingChi
XingChiBitget Wallet seamlessly integrates Berachain Artio Testnet, offering users easy access to on-chain asset management and DApps. With a commitment to ecosystem support, Bitget Wallet enhances Web3 experience for its 15 million global users.
 Edmund
EdmundBerachain aims to provide high security, decentralization and scalability while leveraging the power of meme culture and community to create a vibrant ecosystem.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceBerachain is an EVM-compatible Layer 1 blockchain built on the Cosmos SDK and secured with a Proof of Liquidity consensus mechanism.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinanceExplore the transformative potential of Berachain Blockchain, a decentralized, open-source platform designed to address key challenges in the blockchain space. This article delves into the intricacies of Berachain, its innovative features, and the advantages that set it apart from other blockchain platforms.
 Bernice
Bernice