Author: Jagjit Singh, CoinTelegraph; Compiler: Deng Tong, Golden Finance
1. How is Bitcoin priced?
Market forces of supply and demand influence the price of Bitcoin. When there are more sellers, prices usually go down and vice versa.
Compared to fiat currencies such as the US dollar, British pound, euro and Japanese yen, Bitcoin (BTC) is a cryptocurrency that is not issued by any government or legal agency. To create, store and transfer BTC requires a distributed network of users and cryptographic protocols.
Investors conduct business transactions directly rather than through intermediaries. The peer-to-peer Bitcoin network eliminates trade restrictions and streamlines business transaction processes. The world's first cryptocurrency was proposed by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 and launched in January 2009.
The number of businesses that accept Bitcoin helps increase Bitcoin’s usability and perceived value. However, the price of Bitcoin is highly volatile and is affected bymedia reports, investor sentiment, regulatory news and other factors, resulting in rapid price fluctuations. Even at the height of its popularity, it was challenging to find precise answers to common questions, such as, What determines the price of Bitcoin? Who sets the price of Bitcoin? Does Bitcoin have intrinsic value?
The market dynamics of supply and demand that affect the prices of other goods and services also determine the price of Bitcoin. If there are more buyers than sellers, prices may rise, and vice versa. Additionally, it’s important to note that Bitcoin’s price is not determined by a single entity, nor is it traded at a single location (such as a stock exchange).
Instead, each market or exchange determines its price based on supply and demand and other factors such as technological advancements, security measures, and regulatory developments.
2. What factors will affect the price of Bitcoin?
Factors that influence the price of Bitcoin include the supply and demand for Bitcoin, competition from other cryptocurrencies, news, production costs, and regulation.
Supply and Demand
Everyone with an economics background knows the law of supply and demand, that is, the supply and demand market Forces combine to determine the market price and quantity of a particular commodity. For example, as prices rise and sellers produce more, demand for an economic good falls, and vice versa.
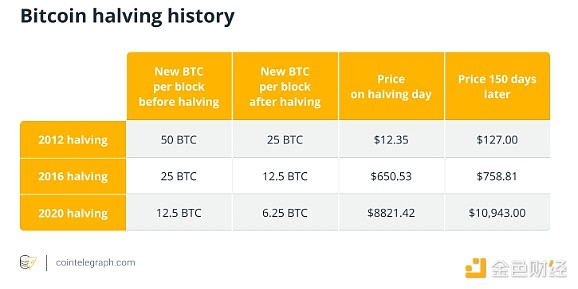
The basic economic principles of supply and demand play a crucial role in the valuation of Bitcoin. Bitcoin’s supply has a hard cap of 21 million coins, which contributes to the digital currency’s scarcity. Once the cap is reached, miners will no longer receive new Bitcoins to verify transactions.
Similarly, an event called the Bitcoin Halving halves the reward for mining a new block every four years (approximately), thus reducing the rate at which new Bitcoins enter the market supply. As supply growth slows, if demand remains stable or increases, it could cause Bitcoin prices to rise.
Competition and News< /h3>
Bitcoin competes with numerous cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum (ETH) and Dogecoin (DOGE), each with unique features that attract investor interest. Additionally, news and media coverage can significantly influence investor sentiment, driving price movements based on perceptions of Bitcoin’s future prospects.
Production costs
The cost of producing Bitcoin not only includes direct expenses such as miners’ infrastructure and electricity, but Also included are indirect costs related to the complexity of the cryptographic challenges they must solve. These costs help establish a baseline or "break-even" point for miners, influencing the minimum price at which they deem it economically feasible to mine Bitcoin.
In Bitcoin mining, this break-even point is often referred to as the "floor price" and represents the lowest price at which Bitcoin can be mined profitably when operating costs are taken into account.
In addition, the Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of its cryptographic puzzles based on overall mining power, thereby affecting the rate at which new Bitcoins are produced. These adjustments could slow down or speed up the creation of Bitcoin, affecting the overall supply and therefore its market price.
Regulation
Cryptocurrency regulations are constantly changing, and some countries have adopted a friendly attitude towards cryptocurrencies, such as El Salvador, which made Bitcoin legal tender in 2021, Other countries have taken a less friendly approach to cryptocurrencies. Regulatory developments could have a significant impact on Bitcoin's market dynamics, creating uncertainty that could affect its price.
When authorities impose restrictions, it could put downward pressure on the price of Bitcoin. Conversely, regulatory actions that enhance market access, such as the approval of spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in the United States and improved security measures, could promote greater market participation and potentially lead to higher Bitcoin prices.
3. Why is the price of Bitcoin so volatile?
The inherent value of Bitcoin and the uncertainty of Bitcoin’s future price make it a highly volatile asset.
During halvings, the number of new Bitcoins entering the supply steadily decreases every four years, reducing the asset's inflation rate over time. Bitcoin is no longer a niche asset but a significant player in the broader financial landscape, as of this writing the tenth largest asset by market capitalization, according to CompaniesMarketcap. Additionally, media coverage can have a disproportionate impact on asset prices, a phenomenon not unique to Bitcoin.
However, the immediacy and ubiquity of information today, driven by digital media and social media platforms, means that news (positive or negative) can quickly affect investor sentiment, thus affecting asset prices across the board. This effect is amplified in highly speculative markets, where investor sentiment plays a crucial role, as is often the case with cryptocurrencies.
The approval of a U.S. spot Bitcoin ETF on January 11 had a significant impact on Bitcoin’s price, attracting institutional capital and increasing demand. As of this writing, the price of Bitcoin has soared 33% since January 11 as traditional financial investors and institutions rush to invest.
Given such high volatility,can the Bitcoin price go to zero? This scenario is extremely unlikely, but is technically possible under extreme conditions, such as a catastrophic technical failure that undermines the security of the blockchain or a complete loss of confidence among all users and investors. However, these scenarios are extremely unlikely due to Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, widespread adoption, and robustness of its underlying technology.
Additionally, second-layer innovations like the Lightning Network aim to solve usability and scalability issues, which can improve Bitcoin’s value proposition. Unlike Ethereum’s ERC-20 token standard, which facilitates the creation of tokens and smart contracts on its network, Bitcoin is not designed to natively support complex smart contracts or token standards.
Nonetheless, innovative solutions are being developed to expand Bitcoin’s capabilities in this area. For example, developments such as the RSK (Rootstock) platform are bridging this gap by introducing smart contract functionality to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
In addition, the BRC-20 token standard represents an innovative approach to introducing tokenization capabilities directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. As an experimental standard, BRC-20 is designed to enable the creation, minting, and transfer of fungible tokens, similar to how the ERC-20 standard operates on Ethereum and other Ethereum Virtual Machine-compatible networks.
4. How high can Bitcoin actually rise?
Bitcoin’s potential future price is subject to widespread predictions and speculation, affected by a variety of factors that influence its price trajectory, including market adoption, regulatory developments, technological advancements within the blockchain ecosystem, and more Determinants include broad economic conditions.
Market adoption is important becauseGreater acceptance of Bitcoin for investment and trading can spur demand. Governments and financial institutions around the world can help or hinder Bitcoin’s growth through regulatory actions, depending on whether they impose restrictions or provide users with security and clarity.
If technological advancements improve Bitcoin’s scalability, security, and use cases, they may have a beneficial impact on Bitcoin’s value. Additionally, Bitcoin's attractiveness as an investment may be affected by macroeconomic variables, including inflation rates, currency depreciation, and investor sentiment toward traditional and digital assets.
Another aspect to consider is Bitcoin’s growing reputation as “digital gold,” ultimately propelling it as a store of value and safe-haven asset. This comparison not only highlights Bitcoin’s potential as a hedge against economic fluctuations, but also illustrates its clear advantages over traditional investments such as gold due to its digital form and limited supply.
Given these variables, predicting the specific value that Bitcoin might reach is challenging. Significant fluctuations have been observed in historical trends, with periods of sharp price increases interspersed with corrections. Leveraging technology using an S-curve framework, one can predict Bitcoin’s future acceptance and growth trajectory. The model suggests that as Bitcoin evolves and overcomes initial adoption challenges, it may gain wider acceptance, mirroring the path taken by other disruptive technologies.
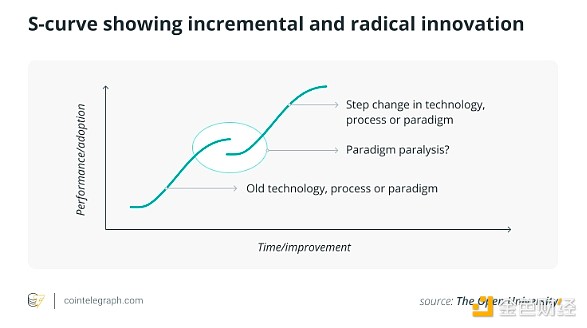
However, as mentioned above As mentioned above, the theoretical upper limit of Bitcoin price is highly speculative and depends on further progress. As with any investment, potential profits are not guaranteed; therefore, caution should be used when speculating on Bitcoin's future price movements.
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance
 JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Xu Lin
Xu Lin JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance JinseFinance
JinseFinance Nulltx
Nulltx Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph