Over 2,500 Attendees to Participate at Next Block Expo
Additionally, NBX will allocate $2 from each ticket sale to a designated charity collection on Coindot.me.
 Samantha
Samantha
Author: E2M Researcher Steven
Why is it worthy of attention in the near future?
After the adoption of the Bitcoin spot ETF, the next narrative immediately shifted to the narrative logic with Ethereum as the core: May Ethereum Spot ETF + Cancun Upgrade + Restaking and more.
A first look at the development rules of Ethereum
Merge Before Ethereum was more like the development model of a startup company, PoW gave miners block rewards as an early marketing tool, and did not care about the value of the token. The economy is inflating rapidly, and the priority is value accumulation > user experience.
The purpose of Merge is not to improve the performance of Ethereum, but to reduce the consumption of generating a blockchain (PoW converted to POS), using Web2.0 The metaphor is more like the upstream part of an industrial chain reducing costs and increasing efficiency to pave the way for future sustainable development. The token economy has also become deflationary. At the same time, it focuses on user experience and gradually transforms miners' income into pledge income. Gas fee income has also been reduced.
The Cancun upgrade corresponds to the part of The Surge, starting with user experience being the first priority (such as increasing transaction speed and reducing gas fees).
The upgrade cycle interval in the future will be relatively short. In a sense, Ethereum will change the consensus of PoW to PoS after the Shanghai upgrade. It has entered a mature period. Although there will be several major upgrades in the future, it can be seen that the core purpose is to focus on on-chain scalability, simpler verification blocks, cheaper, more powerful and stable performance.
Some thoughts
The development of Ethereum is complex and diverse. In the process of learning the overall development path, there are many unresolved issues to be considered.
Vitalik has a very strong guiding role in the development of Ethereum. In fact, from a company's perspective, a good CEO leading the company to charge forward is a very good way to develop. In the end, all the development of the Ethereum ecosystem driven by Buterin will be Long ETH.
Layer 2 such as Arb, OP, ZKsync, Metis, etc.; Defi such as Aave, Compound, Uniswap, etc., and many sky-high valuation projects are attached to Ethereum. And being able to become a popular narrative for a period of time, Ethereum can more or less reap dividends.
Rather than being similar to Microsoft and Apple, the one that feels closest is NVIDIA. AI development, VRAR, Web3.0, various clouds, computing power centers, any cutting-edge technology cannot bypass computing power, and it cannot do without NVIDIA.
Web 3.0 is in a similar state. It is difficult for any development to develop without Ethereum. The narrative of Ethereum has been quiet for a while, but it has gone round and round because of obstacles. Kun Upgrade has risen together with Ethereum spot ETF, Layer 2, and Eth, including the earlier Defi Summer, NFT Summer, etc., which will drive the price of Ethereum, and projects with a longer half-life need to have sufficient contact with Ethereum.
Many people who want to leave Ethereum basically think with the logic of "Ethereum killer". TON, which was discussed before, is not If you step on Ethereum, you will lose your voice.
The development of Ethereum is very centralized, and the Ethereum chain itself is very decentralized; sometimes it feels like Ethereum is developing in this area The degree of centralization is comparable to that of the Uniswap team, but not as decentralized as some protocols such as Aave and MakerDAO. It also reflects that if a project wants to develop well, it may still have to be centralized in nature.
Perhaps one day Ethereum can develop to an extremely mature stage in the future and then be completely decentralized, but at least as long as Vitalik is still young, I will I feel like that day is still far away. Having said that, Ethereum is just a company that has only been in business for 11 years and is far from mature.
The following content frame is quoted from: https://ethereum.org/zh/history, and other public information.
On November 27, 2013, Vitalik Buterin released the "Ethereum White Paper"
Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin released the first version of Ethereum’s white paper, introducing the Ethereum platform Token system;
Abstract
The white paper defines smart contracts. The concept of Ethereum is mentioned for the first time. The white paper explains that Ethereum can be used as gas on the Ethereum network. When users conduct transfer transactions, deploy smart contracts and other activities, they need to pay a certain gas fee, part of which is gas. It will be paid as a reward to the block validator (also known as the miner). If the initiator of the transaction pays insufficient ether coins, the transaction will not be executed. If the ether coins paid are excessive, the remaining part will be returned to The originator's wallet.
July 22, 2014 00:00:00 +UTC
The pre-sale period for Ethereum is 42 days and can be purchased using Bitcoin.
Abstract
The initial exchange rate was 1 Bitcoin for 2,000 Ethereum coins. This exchange rate remained for 14 days, and then the exchange rate began to decline linearly until it dropped to 1,337 Ethereum coins for 1 Bitcoin. The token sale was held on September 2, 2014. By the end of the day, a total of approximately 18 million US dollars in sales had been obtained, and Yi Gong had sold more than 60 million ether coins. After completing the purchase, the received Ether coins cannot be transferred until the launch of the Ethereum genesis block.
In addition to the more than 60 million pre-sale ETH, there are two other allocations. One amount is allocated to contributors who participated in the early development of Ethereum, and the other is allocated to long-term research projects. The amount of these two ETH amounts is 9.9% of the pre-sale amount of ETH.
That is, when Ethereum was officially released, a total of 72002454.768 ETH had been distributed.

Image source: https://blog.ethereum.org/2014/07/22/launching-the-ether-sale
On March 3, 2015, four important phases were announced on the official blog of Ethereum. According to the Blog, some of Vitalik’s original thinking logic is as follows:
Frontier (border/frontier): Frontier The main use in the launch process is to get mining operations and Ethereum exchanges running so that the community can launch their mining rigs and start building a "live" environment where people can test DApps and obtain Ethereum to upload their Bring your own software to Ethereum. Make Ethereum completely stable among core developers and auditors;
Homestead: Frontier is like a beta version, Homestead is a public beta;
Metropolis: a complete and mature user interactive version, pursuing user experience;
< /li>Serenity: PoW to PoS
July 30, 2015 03:26:13 +UTC
Abstract
The border is The original version of Ethereum, but there is very little that can be done on it. The release follows the successful completion of the Olympic testing phase. It is aimed at technical users, especially developers. Blocks have a fuel limit of 5,000 units. This "thaw" period allows miners to begin operations and early adopters enough time to install clients.
Similar to the cold start of many Web 3.0 projects, "miners" will receive 5 Ether coins for every block they mine on the "Border" mainnet. rewards.
September 7, 2015 09:33:09 +UTC
Block number: 200,000
< /li>Ethereum price: $1.24
Summary< /p>
The Border Thaw fork increases the limit of 5,000 units of gas per block and sets the default gas price to 51 gwei. This will enable the transaction - which requires 21,000 units of gas.
In order to ensure the future hard fork to proof of equity, the concept of difficulty bomb is introduced.
Difficulty bomb, also known as TTD, stands for Total Terminal Difficulty, which is the sum of the difficulty of all previous blocks. When the accumulated mining difficulty value of the entire network reaches TTD, the ETH main network will activate the "difficulty bomb". The "difficulty bomb" is a backdoor function that adjusts the difficulty of Ethereum. Ethereum's PoW block time is not fixed, but the mining difficulty is dynamically adjusted according to the computing power of the entire network. In this way, the block time is fixed within a rough range. The deployment of the difficulty bomb uses a backdoor function to adjust the mining difficulty to a maximum value, so that no miner can produce blocks at this mining difficulty, thereby pushing miners to give up PoW. The PoW-POS conversion does not set a fixed block height, but stipulates TTD as the moment when Merge occurs. Part of the reason is to prevent someone from deliberately sabotaging the Merge process.
This proves in disguise that Ethereum has long been determined to move from PoW to PoS.
The first hard fork of Ethereum , after experiencing multiple security incidents, gradually improved some specifications of smart contracts.
March 14, 2016 06:49:53 +UTC
Block number: 1,150,000
Ethereum price: US$12.50
Summary< /p>
Homeland fork optimizes the creation process of smart contracts.
July 20, 2016 01:20:40 +UTC
Block number: 1,920,000
Ethereum price: US$12.54
Summary< /p>
This fork is an unplanned passive fork, stemming from an attack on Ethereum.
The DAO is a crowdfunding project launched by the blockchain company Slock.it to provide a way for community funding for projects. Community users participate in voting by exchanging their ETH for DAO Token. If the crowdfunding is successful, they can receive a portion of the profit reward. The project completed a 28-day crowdsale in April 2016, raising a total of more than 12 million ETH, accounting for almost 14% of the amount of Ethereum at the time. However, just 2 months later, hackers exploited a vulnerability in The DAO code and stole 3.6 million ETH from the fund pool.
This operation is voted on by the Ethereum community. All Ethereum holders will be able to vote via transactions on the voting platform. The decision to fork received over 85% of the vote. Through the fork rollback, the ETH stolen by the hacker was recovered.
This fork moves funds from the contract in question to a new contract that has only one function: withdrawals. Anyone who has lost funds can withdraw ether from their wallet at a rate of 1 ether per 100 DAO tokens.
Some miners refused to fork because the DAO incident was not a flaw in the protocol. They later formed Ethereum Classic (ETC).
October 18, 2016 01:19:31 +UTC
Block number: 2,463,000
< /li>Ethereum price: US$12.50
Summary
The Orange Whistle fork is a response to the Denial of Service (DoS) attack on the Ethereum network on September 18, 2016 that resulted in transactions Optimize to deal with severe latency issues; primarily resolve urgent network health issues related to undervalued operational code.
November 22, 2016 04:15:44 +UTC
Block number: 2,675,000< /p>
Ethereum price: US$9.84
Abstract
The Pseudo-Dragon fork is a further optimization of Denial of Service (DoS) network attacks, including:
-Adjust opcode prices to protect the network from future attacks.
-Enable "blockchain weight reduction" of the blockchain state.
-Added replay attack protection.
Metropolis’s main job is to repair Ethereum Some problems existing in the network and preparation for the introduction of ZK-SNARKS.
The most influential event that occurred at this stage was the two halvings of the block reward: from 5ETH to 3ETH to 2ETH, which is regarded as PoW. A transitional period for PoS.
At this stage, we begin to consider user experience and how to smoothly move from PoW to PoS in the future.
October 16, 2017 05:22:11 +UTC
Block number: 4,370,000
Ether price: US$334.23
Summary
p>The Byzantine fork paved the way for the introduction of ZK-Snark and began to focus on user privacy and user experience.
- Reduced block mining rewards from 5 Ethereum to 3 Ethereum.
-Delay the difficulty bomb by one year.
-Added the ability to call other contracts without changing state.
-Added certain encryption methods to implement Layer2.
Ethereum is gradually maturing. The consensus has shifted from PoW to PoS. User experience, security, zone decentralization, and scalability are the most important development directions of Ethereum.
February 28, 2019 07:52:04 +UTC
Block number: 7,280,000
p>Ethereum price: US$136.29
Abstract
Reducing the block mining reward from 3 Ethereum coins to 2 Ethereum coins.
December 8, 2019 12:25:09 +UTC
< /li>Block number: 9,069,000
Ethereum Price: US$151.06
Abstract
-Optimized the gas cost of specific operations in the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
-Improve resilience after denial of service attacks.
-Enables Layer 2 solutions based on "zero-knowledge concise non-interactive knowledge argumentation" and "zero-knowledge scalable transparent knowledge argumentation" to have better performance.
-Allows contracts to introduce more creative functions.
January 2, 2020 08:30:49 +UTC
Block number: 9,200,000
Ethereum price: US$127.18
Abstract
Muir Glacier Bifurcation Makes Difficulty Bomb delay. Increasing the block difficulty of the proof-of-work consensus mechanism may increase the wait time for sending transactions and using decentralized applications, thereby reducing the usability of Ethereum.
October 14, 2020 09:22:52 +UTC
Block number: 11,052,984
< /li>Ethereum price: US$379.04
Summary
The pledge deposit contract introduces staking into the Ethereum ecosystem. Although it is a mainnet contract, it directly affects the release timeline of the beacon chain, which is an important part of the Ethereum upgrade.
December 1, 2020 12:00:35 +UTC
Beacon chain block number: 1
Ethereum price: US$586.23
Summary
The beacon chain requires 16,384 accounts storing 32 staked Ether to ensure a safe launch . This happened on November 27, 2020, meaning the Beacon Chain started producing blocks on December 1, 2020.
The beacon chain plays the role of managing, supervising and verifying the blockchain network. The beacon chain uses a random method to select verifiers. Those who succeed in verification will be rewarded, but if there is malicious behavior, they will be punished.
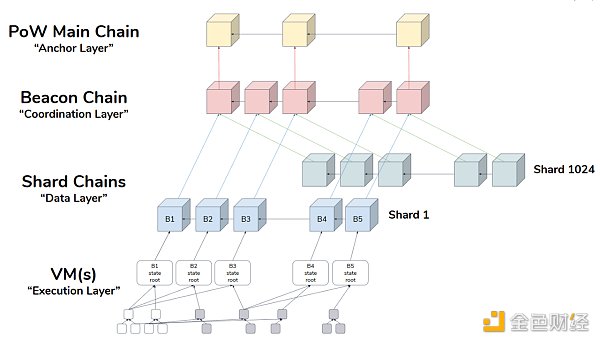
After merging, the time unit of a block will appear in the form of slots and epochs. A slot is created every 12 seconds, and each epoch pack consists of 32 slots. An epoch is a fixed period of time at the end of which verifiers will be reassigned.
To become a validator and gain voting rights, users must invest at least 32 ETH.
Ethereum’s rule is that for each epoch, validators will be randomly assigned to 32 committees, ensuring that each committee is composed of at least 128 validators . The system uses the random algorithm RANDAO to assign 1 validator for each period and also randomly selects a committee for this period. This validator is responsible for proposing blocks, while the committee is responsible for validating and voting on proposals. Once the vote is passed, a block will be generated and the proposer will receive the reward; otherwise, not only will the reward not be obtained, but the deposit will also be forfeited. The same goes for ordinary verifiers: if they follow the rules correctly, they are rewarded, while spoilers are punished. Once the 32 ETH deposit drops below 16 ETH, the validator's eligibility will be terminated.
April 15, 2021 10:07:03 +UTC
Block number: 12,244,000
Ethereum price: US$2,454.00
Abstract
The Berlin upgrade optimizes some Ethereum virtualization fuel costs for machine operations and added support for multiple transaction types.
August 5, 2021 12:33:42 +UTC
Block number: 12,965,000
Ether price: US$2,621.00
Summary
p>The London upgrade introduced EIP-1559, which reformed the transaction fee market. Continue to delay the difficulty bomb until its launch on December 1, 2021.
October 27, 2021 10:56:23 +UTC
Period number: 74,240
Ether price: US$4,024.00
Summary< /p>
The Aquila upgrade is the first planned beacon chain upgrade. It adds support for “synchronization committees”—support for light clients, and adds penalties for validator laziness and slashable behavior as it progresses toward merges.
December 9, 2021 07:55:23 +UTC
Block number: 13,773,000
< /li>Ether price: US$4,111.00
Summary
The difficulty bomb delays a total of 10,700,000 blocks until June 2022.
June 30, 2022 10:54:04 +UTC
Block number: 15,050,000
Ethereum price: US$1,069.00
Summary
Gray Glacier network upgrade delays difficulty bomb for three months. This is the only change introduced in this upgrade, which is essentially similar to the Arrow Glacier and Muir Glacier upgrades. Similar changes were made to the Byzantine, Constantinople, and London network upgrades.
September 6, 2022 11:34:47 +UTC
Period number: 144,896
Ether price: US$1,558.00
Summary
The Bellatrix upgrade is the second planned Beacon chain upgrade, preparing the Beacon chain for the merger. It increases the penalty a validator receives for laziness and for engaging in slashable behavior to its full value. The Bellatrix upgrade also includes updates to the fork selection rules to prepare the Beacon Chain for merging and transitioning from the last Proof-of-Work block to the first Proof-of-Stake block. This includes making consensus clients aware of the total terminal difficulty of 587500000000000000000000.
September 15, 2022 06:42:42 +UTC
Block number: 15,537,394
Ethereum price: US$1,472.00
Summary
The Paris upgrade was triggered when the proof-of-work blockchain exceeded the total terminal difficulty of 587500000000000000000000. This happened on block 15537393 on September 15, 2022, and triggered the Paris upgrade at the next block. The Paris upgrade is a merger transition. The main function of Ethereum ends the proof-of-work mining algorithm and related consensus logic and starts the proof-of-stake. The Paris upgrade itself is an upgrade to the execution client (equivalent to the Bellatrix upgrade on the consensus layer), allowing the execution client to accept instructions from the consensus client connected to it.
April 12, 2023 22:27:35 +UTC
Period number: 194,048
Beacon chain block number: 6,209,536
Ether price: US$1,917.00
Summary< /p>
The Capella upgrade is the third major upgrade of the consensus layer (beacon chain), which enables pledge withdrawals. Capella and Shanghai simultaneously upgraded the execution layer and enabled the pledge withdrawal function.
This consensus layer upgrade allows pledgers who have not provided initial deposit withdrawal vouchers to provide withdrawal vouchers to realize withdrawals.
The upgrade also provides automatic account scanning to continuously process any available reward payments or full withdrawals from validator accounts.
April 12, 2023 22:27:35 +UTC
Block number: 17,034,870
Ether price: US$1,917.00
Summary
p>Shanghai upgrade introduces pledge withdrawals to the execution layer. The Shanghai upgrade coincides with the Capella upgrade, enabling the block to accept withdrawal operations so stakers can withdraw ether from the beacon chain to the execution layer.
PoW is more like an early marketing method for a startup company, with subsidies for stable famous songs (miners’ stable income from mining), PoS is more like equity, and ETH Net issuance.
The Merge significantly changed Ethereum’s monetary policy. By eliminating miner rewards and converting them to staking rewards, it significantly reduces the issuance of new ETH tokens. This constitutes a decrease in daily ETH issuance of approximately 88.7%, equivalent to an annualized issuance rate of 0.52% of the total supply, and then Since the Gas fees under EIP-1559 are destroyed, the net issuance shows a deflationary trend.
There are two key changes:
1.2.1 EIP-1559 introduced by London upgrade : Quotes the fee burning mechanism
Old protocol calculation formula: Gas fee = Gas units (limit ) Gas price per unit
For the simplest on-chain transfer transaction, no matter how busy the chain is, Gas limit is fixed at 21,000. Therefore, as long as the Gas price and Gas limit are clear, we can know how much eth we spent for this interaction. The gas price will change with network congestion, and the gas limit will remain unchanged.
Suppose Alice needs to pay 1 ether to Bob. In the transaction, the fuel limit is 21,000 units and the price of fuel is 200 gwei.
The total cost is: Gas units (limit) * Gas price per unit, that is, 21,000 * 200 = 4,200,000 gwei or 0.0042 Ethereum.
In order to give higher priority, scientists may set a very high Gas fee at once, resulting in a confusing and difficult user experience. Estimate.
New protocol calculation formula: Gas fee = (Base fee + Priority fee) × Gas limit , and the base fee in the next block will increase by up to 12.5%
The base fee will be directly destroyed by the protocol, and the priority fee is the tip set by the user to be paid to the verifier.
For example, suppose Jordan wants to pay Taylor 1 ether. An Ethereum transfer requires 21,000 units of gas and has a base fee of 10 gwei. Jordan paid 2 gwei as a tip.
The fee is 21,000 * (10 + 2) = 252,000 gwei (0.000252 ether).
When Jordan transfers the money, 1.000252 Ether will be debited from Jordan's account. Taylor's account is increased by 1.0000 Ether. The validator receives a tip worth 0.000042 Ethereum. The base fee of 0.00021 Ethereum coins is destroyed.
1.2.2 Paris upgrade
First the Constantinople hard fork, mining The mining reward is reduced from the original 3 ETH per block reward to 2 ETH. Then, The merge converted PoW into PoS, and the mining rewards (160,000eth/day) disappeared directly and turned into staking rewards (1,600eth/day), and the issuance volume dropped sharply by 99%.
On September 15, 2022, after the Paris upgrade, Ethereum officially began deflation.
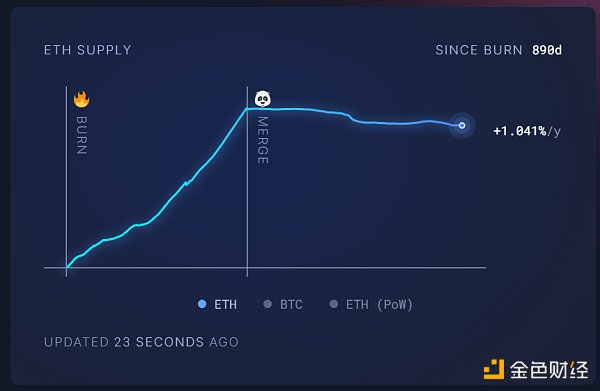
Data source: https://ultrasound.money/
The total supply since the Merge has exceeded 300,000 Ethereum coins. , 981k are destroyed every year, 723k are issued, and deflation occurs at a rate of 0.21% every year.
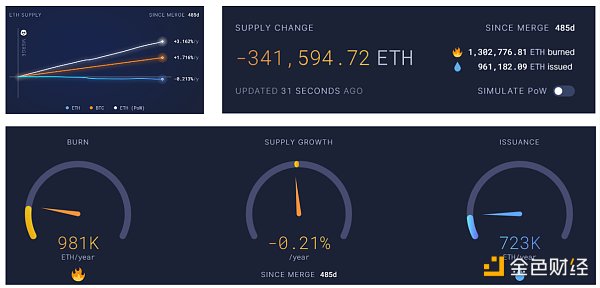
Data source: https://ultrasound.money/
After Merge, Ethereum has solved the problem of high energy consumption. , and then focused on performance issues and cost issues. Layer 2 solves these two problems at the same time, so it has become the most watched track in the Ethereum ecosystem after Merge.
Vitalik Buterin proposed the Ethereum roadmap Vision, the roadmap divides upgrades into several categories based on their impact on the Ethereum architecture. This includes:
Merge: an upgrade involving the move from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake (already Completed)
Surge: Over 100,000 TPS on Rollups
Scourge: Upgrades involving censorship resistance, decentralization, LSD, and MEV risks
Verge: An upgrade involving making it easier to verify blocks
Purge: An upgrade involving reducing the computational cost of operating nodes and simplifying the protocol< /p>
Splurge: Other
These upgrades are done in parallel, which means whichever part is developed faster may be upgraded first.
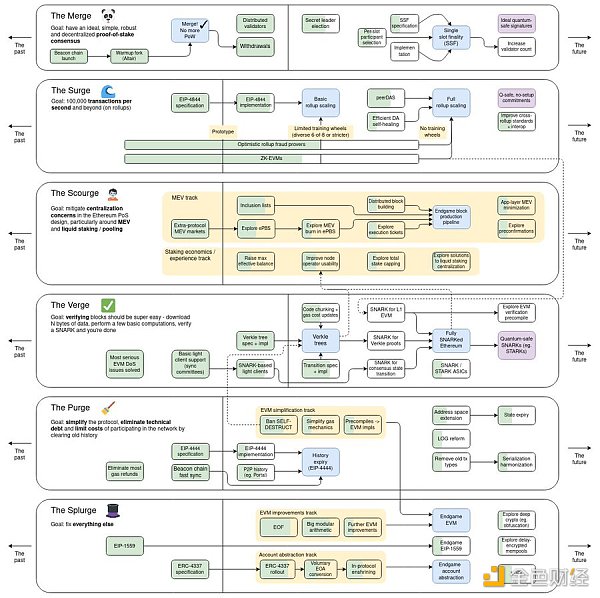
Image source - Vitalik Buterin Twitter: https://twitter.com/VitalikButerin/status/1741190491578810445
After the merger of Ethereum, the most important thing is to improve performance TPS, reduce gas fees, and make Ethereum close to a perfect application.
What kind of TPS and Gas Fee does Vitalik think Ethereum can achieve to be a qualified public chain?
For example: TPS reaches 100,000+. The average TPS of VISA is 2,000, with a peak of 4,000+; the average TPS of Paypal is 200; Alipay can reach 250,000 during busy periods.
This Ethereum upgrade is called Dencun upgrade (Dencun+Cancun), among which Cancun (Cancun, Devcon hosting city ) upgrade focuses on the Ethereum execution layer (Execution Layer), and the Deneb upgrade focuses on the consensus layer (Consensus Layer).
The Cancun upgrade corresponds to the part of The Surge, with the goal of reaching 10+TPS.
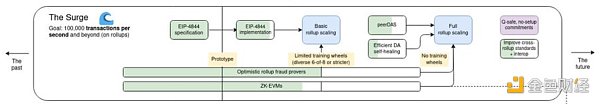
According to Github, the Cancun upgrade will implement the following six EIPs, which we will focus on in the next section.
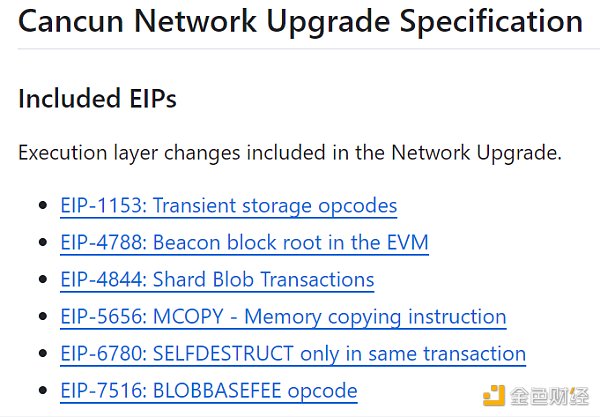
Image source: https://github.com/ethereum/execution-specs/blob/master/network-upgrades/mainnet-upgrades/cancun.md
In addition to Pro-Danksharding (EIP-4844), the Cancun upgrade also includes EIP-6780, EIP-1153, EIP-6475, EIP-4788 and other improvement proposals.
The most important thing in Cancun upgrade The thing is to introduce Proto-Danksharding as a transition for Ethereum's complete sharding expansion, and to introduce similar technologies in advance. The ultimate goal of Ethereum is to divide the main network into 64 slices to achieve 100,000+ TPS.
The background proposed by Proto-Danksharding is that although the Rollup scheme significantly reduces transaction costs compared to the Ethereum main chain, it is not low enough yet. This is because the calldata that provides data availability on the Ethereum main chain still occupies a large cost (16 gas / byte). In the original idea, Ethereum proposed to provide 16MB of dedicated data space for each block in data sharding for Rollup to use, but the actual implementation of data sharding is still far away.
Currently, the data returned by Layer2 to Layer1 is stored in Calldata, and the data is permanently stored in the execution layer. In addition, for security reasons, Calldata requires gas for each step of execution in order to prevent network resource abuse.
After Ethereum completed the merger, it separated the consensus layer (responsible for PoS consensus) and the execution layer (execution of contract code). The job of the execution layer is to execute the data stored in Calldata (which can be considered a type of transaction).
The content contained in Calldata can be divided into two parts:
Execution results
Transaction data - not much use, after verification is valid It’s useless, it just takes long enough to download and verify, and it doesn’t even need to be transmitted to the execution layer - EIP-4844 is to solve the problem of transaction data, which accounts for more than 60% of the entire cost of Calldata.
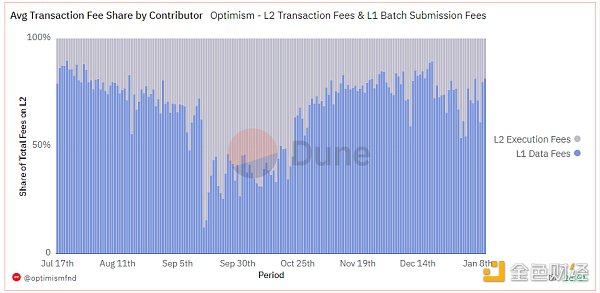 < /p>
< /p>
Data source: https://dune.com/optimismfnd/optimism-l1-batch-submission-fees-security-costs
In fact, as transaction data, there are only verification requirements and no execution requirements. There is no need to transmit it to the execution layer to increase the burden on the execution layer. It can only be stored in the nodes of the consensus layer.
To this end, EIP-4844 introduces a new transaction type—Blob (Binary Large Objects, which is a further subdivision of transaction types), which is more than regular transactions. Carrying a data package (about 125kb), only in the consensus layer, similar to a cache package or an additional plug-in database, a separate data type Blob is designed for the data returned by L2, and it is separated from the Calldata of Layer1. In this way, the Blob data only needs to be able to be accessed and verified by those who need it within a certain period of time. There is no need for the Layer1 execution layer to execute all of it, thus greatly reducing the burden on Layer1.
The size of each blob introduced by Proto-Danksharding is 128 KB, and each Ethereum block plan contains 3-6 blobs (0.375 MB - 0.75MB ), which will be gradually expanded to 64 in the future.
In contrast, the current data size that each Ethereum block can accommodate is less than 200KB. After the introduction of blobs, the data size that Ethereum blocks can accommodate Volume will increase significantly.
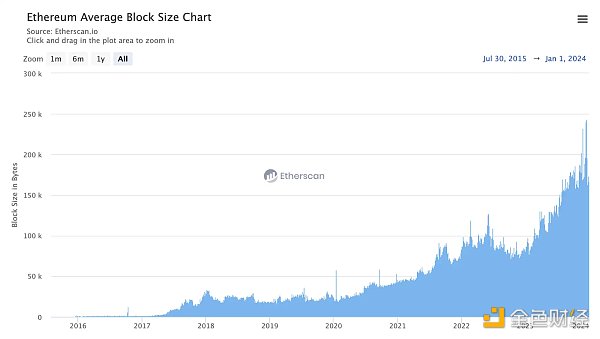
Data source: https://etherscan.io/chart/blocksize
EIP-4844 is the advanced version of Danksharding, designed to Temporary storage and retrieval of off-chain data are achieved through Ethereum nodes, and Layer2 itself compresses off-chain data. Therefore, it is expected to enable L2 to carry more data per blockchain while reducing transaction fees by 10-100 times.
If Dencun successfully achieves the average target of 3 blobs per block after the upgrade, L2 throughput will be increased by nearly 2 times. If the goal of adding 64 blobs to a block is finally achieved, the throughput of L2 will be improved by nearly 40 times.
Proto-Danksharding introduces EIP-1559 to further reduce blob costs
Different types of gas should have different base costs and maximum limits
Blob data costs are cheaper - Blobs do not compete for block space, theoretical gasfee should be lower, naturally cheaper, further reducing costs
What if I want to see transaction data?
EIP-4844 also introduces the KZG (Kate-Zaverucha-Goldberg) commitment scheme as part of the blob verification and proof generation process. KZG commitment is a polynomial commitment scheme that enables submitters to use a short string to commit to polynomials, and supports verifiers to use short strings to confirm stated commitments. Simply put, KZG can simplify the verification of large amounts of data into the verification of small cryptographic commitments.
Comparison before and after the introduction of Proto-Danksharding.
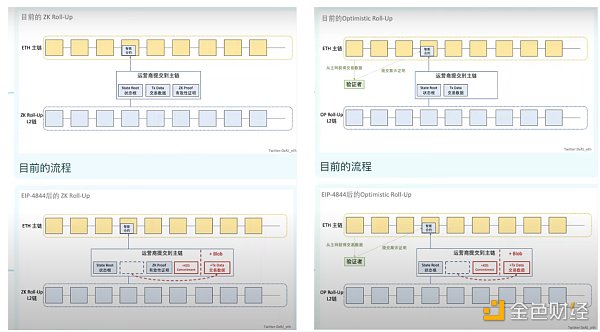
EIP-6780 proposes to modify the SELFDESTRUCT opcode function to prepare for future applications of Merkle trees. Through the subsequent application of Merkle trees, the storage efficiency of Ethereum will be greatly improved.
EIP-1153 allows the protocol to perform temporary storage by adding a transient storage opcode, thereby saving network gas fees.
EIP-6475 is a supporting solution for EIP-4844, which provides better readability and compact serialization by introducing SSZ-encoded transaction types.
EIP-4788 aims to improve the structure of cross-chain bridges and staking pools.
Total TVL
Total TVL has exceeded $20b
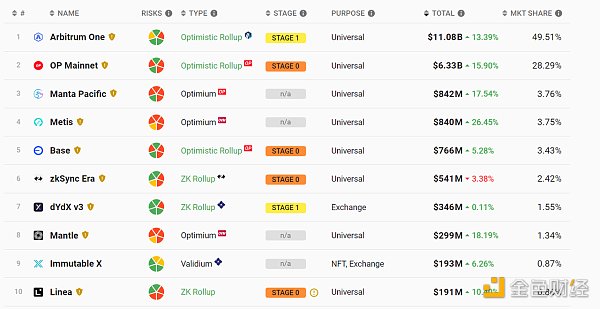
Data source: https://l2beat. com/scaling/tvlLayer2 TVL situation

Although Vitalik believes that ZK is the final solution for Rollup, in fact Arb+OP and other Op systems have already It exceeds 85%. At the same time, many projects are also trying the combination of OP+ZK and constantly iterating.
Data source: https://l2beat.com/scaling/summaryLayer 2 Gas Fee situation
The handling fee of a few dollars for a single transaction may be considered a small amount for OG who are early exposed to web3.0, but Still too expensive for Mass Adpotion.
Data source: https://l2fees.info/Income
< /li>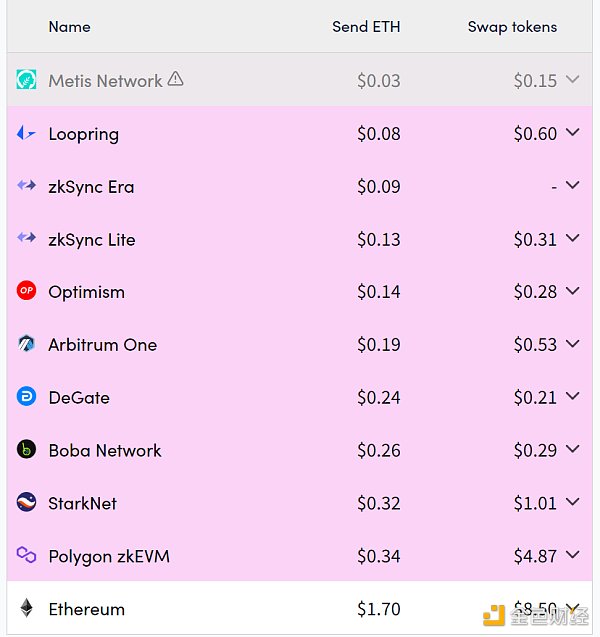
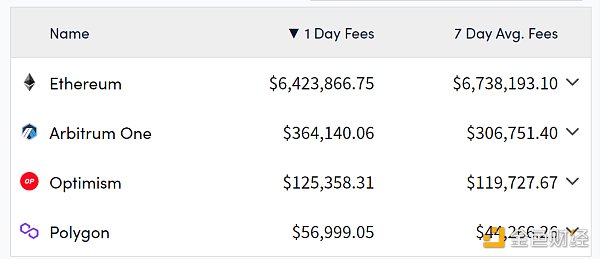
Data source: https://cryptofees.info/, select Layer1 and Layer2 for category, and select the four public chains in the picture for blockchain
Ethereum’s earliest TPS is 108. Theoretically, Layer 2’s TPS can exceed 100,000 transactions/second (TON), but this is not yet available. This level of application is also a point of concern.
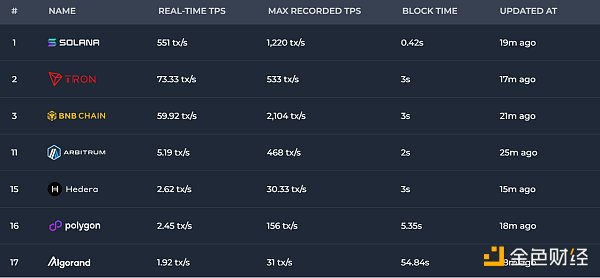
Data source: https://chainspect.app/dashboard/tps
The real-time TPS on Layer 2 is not currently the most to 50.
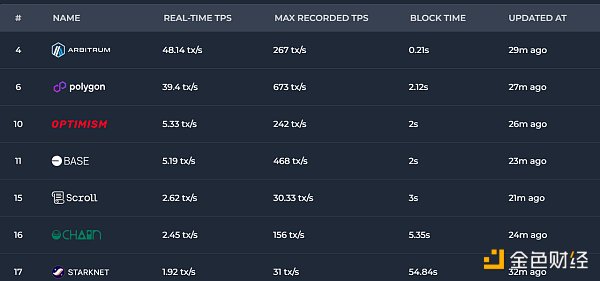
Data source: https://chainspect.app/dashboard/tps?tag=layer_2
Ethereum liquidity is fragmented due to multiple different Layer2? Potential solutions include serializer sharing, decentralized serializers, etc.
CM: It is not easy for money from chain A to go to chain B. The concept of Layer2 is a service layer. Arb mainly focuses on derivatives led by Gmx. The market of Layer2 is relatively small. At the beginning, the task of Layer2 was to subdivide the business of Ethereum into Layer2. The solution now is to solve it through the application layer. To solve the experience problem through cross-chain applications, there will inevitably be a separation of funds from the perspective of the chain, mainly due to security issues.
DZ: It seems that Layer 2 has increased a lot recently? Are expectations for Layer 2 rising? Can the fee be reduced immediately after joining 4844? This will lead to some changes in the pattern, such as Tron's USDT being transferred to Ethereum Layer 2.
In the development process of the Ethereum protocol, Network upgrades and forks have the same meaning, they are changes to the Ethereum protocol that add new rules (in the form of EIPs), which can be planned or unplanned. But the meaning of a hard fork is different. It means that this network update is not fully backwards compatible and may even change the existing functionality of deployed contracts and invalidate some previous transactions.
Main reference source: https://eips. ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-1, namely EIP-1
EIP can be divided into three broad categories:
Standards Track EIP: This type of EIP describes high-impact Any changes to most or all Ethereum implementations, or any changes or additions that affect the interoperability of applications using Ethereum. Simply put, it is any EIP that changes all or most implementation details of Ethereum. It can be subdivided into the following categories:
Core: refers to the possible Forks, modifications that require consensus (such as EIP-5, EIP-101, etc.), as well as changes that are not necessarily consensus but may be related to the "core development" of Ethereum;
Networking: Refers to changes surrounding the Ethereum communications devp2p (EIP-8) and Light Ethereum Subprotocol, as well as proposed improvements to the Whisper and swarm network protocol specifications.
Interface (interface): refers to the modification of the Ethereum client API/RPC definition and standard, calling method name and contract ABI and improvements to language-level standards.
ERC: refers to application-level standards and conventions. It includes Token standards, name registration, URI schemes, account abstraction, etc.
Meta EIP (Meta Proposal EIP): This type of EIP makes changes around the Ethereum process (or events in the process) , including modifications to process, user guides, decision-making processes, development environments and tools, etc. Because this modification requires community users to comply with it, community consensus needs to be reached.
Informational EIP (Information Proposal EIP): This type of EIP is a non-standard improvement that does not propose new features, but only proposes design issues and general guidelines or information for the Ethereum community. opinions and do not necessarily represent the consensus or recommendations of the Ethereum community.
Currently, the EIP repository has separated ERC and EIP. The EIP-7329 proposal proposes to split the ERC specification from the EIP repository into a new repository so that only the core protocol EIP is retained. Therefore, the current EIP repository is aimed at standardizing Ethereum itself and the protocols built on top of it. Track past and ongoing improvements to Ethereum in the form of EIPs. The ERC (Ethereum Request for Comment) repository is for the standardized Ethereum application layer, which tracks past and ongoing improvements to application standards in the form of ERCs. ERC has produced many well-known ERC-20, ERC-721, ERC-1155, etc.

Idea- Pre-draft idea. This is not tracked in the EIP repository.
Draft - The first formal tracking phase in EIP development. When properly formatted, the EIP is merged into the EIP repository by the EIP editor.
Review Review- The EIP author marks the EIP as ready and requests peer review.
Last Call - This is the final review window for the EIP before the transfer. The EIP editor will assign Last Call status and set the review end date ( last-call-deadline), usually 14 days later.
If necessary normative changes result during this period, the EIP will revert to Review.
Final version - This EIP represents the final standard. The final EIP is in a final state and should only be updated to correct errata and add non-normative clarifications.
PRs that move the EIP from the last call to the final call should not contain any changes other than status updates. Any content or editorial proposed changes should be submitted separately from and prior to this status update PR.
Stalled StagnantDraft - Any EIPLast Call that is in either Review or inactive for 6 months or more will be moved to Stagnant. The author or EIP editor can recover from this state by moving the EIP back to Draft or an earlier state. If not resurrected, the proposal may remain this way forever.
EIP authors will be notified of any algorithm changes to their EIP status
Withdrawn - The EIP author has withdrawn the proposed EIP. This status is final and cannot be resurrected using this EIP number. If the idea is continued later, it will be considered a new proposal.
Living - A special status of an EIP that is designed to be continuously updated and does not reach a final status. The most famous of these is EIP-1.
Additionally, NBX will allocate $2 from each ticket sale to a designated charity collection on Coindot.me.
 Samantha
SamanthaCoinbase announced a new partnership with Bitkey, a self-custody wallet from Block, Inc. The partnership will allow users to buy, trade and sell bitcoin via Coinbase Pay in the Bitkey wallet.
 TheBlock
TheBlockEthereum’s core developers have implemented the Shapella upgrade through a hard fork. The highly-anticipated upgrade enables users and validators to withdraw their staked ETH on the network.
 TheBlock
TheBlock Coinlive
Coinlive The ability to withdraw staked Ethereum may soon be here, as Shapella (Shanghai + Capella) unstaking upgrade goes live on the Goerli testnet.
 CryptoSlate
CryptoSlateSTEPN, a crypto web3 app that enables people to earn rewards for exercising, announced a partnership with The Giving Block.
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistLet’s start the second round of “Bitcoin: Knowledge and Perceptions,” a new report by Block based on a massive survey. ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistThe new Block report, “Bitcoin: Knowledge and Perceptions,” is a tour de force. A massive online survey turned into surprising ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistMUSHE (XMU) Whilst the launch of Mushe is set for the 4th of July, the presales have been a huge ...
 Bitcoinist
BitcoinistJack Dorsey said: "Block is a new name, but our purpose of economic empowerment has not changed. No matter how we grow or change, we will continue to build tools to help increase economic opportunity."
 Cointelegraph
Cointelegraph