Source: Chain Tea House
1. Project Introduction
Renzo is an innovative restaking DeFi platform. As EigenLayer's Liquid Restaking Token (LRT) ecological project, it has become the entrance to the EigenLayer ecosystem, ensuring active verification services (AVS) and providing higher returns than ETH staking.

Renzo simplifies Ethereum restaking and ensures the security of DeFi investments through Eigenlayer: by enabling ETH deposits to mint EZETH, using active verification services (AVS) to protect applications built on EigenLayer using Ethereum's first-layer security protocol.
The Renzo protocol also provides a smooth way to interact, making interactions between users and Eigenlayer node operators more efficient, which is of great significance in the Ethereum ecosystem. In this way, the inherent complexity of DeFi is simplified, and seamless interaction between users and EigenLayer node operators is achieved, thereby improving the efficiency of the Ethereum ecosystem.
In addition, Renzo not only increases the income opportunities of ETH stakers, but also enhances the security and reliability of services within the Ethereum blockchain, which also marks an important step in the development of DeFi.
In short, at its core, Renzo is about driving the advancement of permissionless innovation on Ethereum and striving to achieve programmable trust acquisition throughout the ecosystem. It has been carefully designed to promote the widespread adoption of EigenLayer by abstracting complex details and presenting a user-friendly interface, thereby increasing participation and engagement.
2. Project Operation
The Renzo protocol operates through a well-structured mechanism, leveraging the EigenLayer framework to simplify the re-staking process on Ethereum.
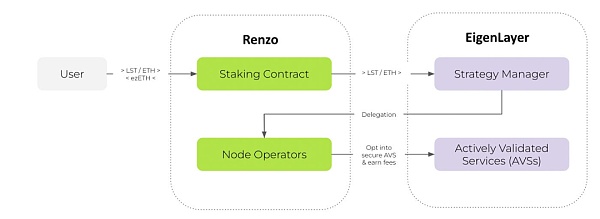
Here is a concise explanation of how it works:
Deposits and minting: Users deposit ETH or Liquid Staking Tokens (LST) to Renzo, and then Renzo mints an equal amount of ezETH (a liquid derivative representing the staked asset).
Securing AVS: Renzo secures Active Validation Services (AVS) on EigenLayer, allowing users to stake ETH and secure these services to earn additional rewards on top of traditional staking rewards.
Strategic Management: As a strategic manager, Renzo optimizes the repricing process by selecting the best combination of AVS to maximize returns while minimizing risk.
Yield Generation: The protocol generates yields through ETH validators, and as AVS goes live, repricing yields are generated through Renzo node operators plugging into these services.
Reward Distribution: The protocol captures the rewards generated by repricing and securing AVS and reflects them in the value of ezETH, providing users with tokens to earn rewards.
Enhanced Participation: Renzo introduces ezPoints and EigenLayer Points to reward users for their participation and contribution to the success of the protocol.
Governance and Decision-making: Governance mechanisms, including snapshot voting and eventual on-chain governance, provide guidance for strategic decisions, such as selecting AVS to support node operators.
Through this multi-faceted approach, the Renzo protocol provides Ethereum users with a dynamic and beneficial reset ecosystem, enhancing yield opportunities and the security of the network. EigenLayer is the core technical component of the Renzo protocol. It provides a new hierarchical structure for the Ethereum network, making asset staking and network verification more efficient and flexible. The design goal of EigenLayer is to enhance the scalability and functionality of the Ethereum ecosystem by allowing existing Ethereum validators to leverage their staked assets to support new and innovative services. Here are a few key aspects of EigenLayer in the Renzo protocol:
1. Layered Validation
EigenLayer works by creating an additional validation layer that is independent of the main Ethereum blockchain. In this layer, validators can participate in more and different types of network activities, such as specific computing tasks or new consensus mechanisms.
2. Resource Reuse
A core feature of this layer is that it allows validators to reuse their staked assets on the Ethereum mainchain. This means that validators can support more services without additional staked funds, thereby improving capital efficiency and lowering the barrier to participation in new services.
3. Enhanced Network Functionality
Through EigenLayer, the Renzo protocol increases the functionality of the Ethereum network, including data verification, transaction execution, and other possible services such as cloud storage or complex data processing tasks. These services, which may have originally required new infrastructure and additional resource investment, can now be achieved through existing validator assets.
4. Rewards and Incentives
Validators participating in EigenLayer can receive additional rewards, which are derived from the services they provide on this layer. This not only increases their overall benefits, but also promotes more validator participation and network growth.
5. Security and Decentralization
EigenLayer is designed with a focus on security and decentralization. Although it adds a new layer on top of the Ethereum main chain, it still maintains the decentralized nature of the network and ensures the security of operations through multiple verification and security protocols.
6. Community-driven governance
EigenLayer and Renzo protocols support decentralized governance, where community members can influence key decisions through voting, such as adding new services, adjusting reward mechanisms, etc. This ensures the transparency and adaptability of the protocol, enabling it to respond to community needs and changes.
By introducing EigenLayer, the Renzo protocol provides a mechanism that enables the Ethereum network to not only support existing staking and verification operations, but also expand to more applications and services, further enhancing Ethereum's position as the world's leading smart contract platform. This technological innovation is of great significance to promoting the long-term development of the Ethereum network and the advancement of decentralized finance (DeFi).
3.2 Ether Stakers

Ethereum Stakers are ETH token holders who choose to stake their assets to earn rewards and maintain network security.
These users use their assets to interact with smart contracts on the Ethereum network to support multiple networks. While they benefit from staking their assets, they also face the risk of slashing when they choose the wrong validators to stake.
Slashing is a penalty for validators who engage in malicious activity or do not meet the standards set by the Ethereum network. Users who choose to stake with malicious validators face the risk of losing their staked funds.
3.3 Active Validation Service (AVS)
Active Validation Services (AVS) in the Renzo protocol is one of its core features, designed to enhance the functionality and security of the Ethereum network. AVS allows stakers to increase their returns by participating in additional validation activities while providing value-added services to the network.
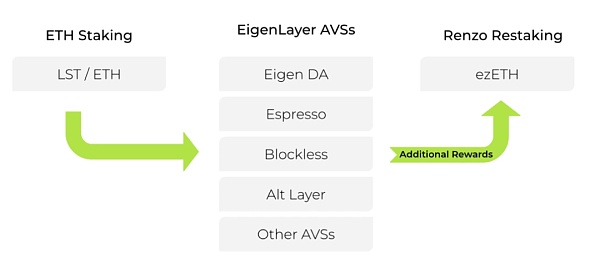
These services are implemented by Renzo through the EigenLayer framework. Here are some key aspects of AVS:
1. Purpose of AVS
The main purpose of AVS is to expand the functionality of the Ethereum network, allowing nodes to participate in other activities that benefit the network in addition to traditional block verification. These activities can include data verification, network security operations, specific computing tasks, etc.
2. How it works
In the Renzo protocol, stakers can choose to participate in different AVS projects. This usually involves locking their staked assets (such as ETH) into specific services that require additional verification activities to maintain their operation and security. In this way, stakers not only support the basic functions of the Ethereum network, but also provide support for other layers and services.
3. Reward Mechanism
Stakers who participate in AVS can receive additional rewards derived from the value-added services they provide to the network. This means that, in addition to basic staking rewards, stakers can significantly increase their overall rate of return by participating in AVS.
4. Risk Management
While participating in AVS can provide higher returns, it may also bring additional risks. These risks may include technical failures, service interruptions, or network attacks. Therefore, the Renzo protocol has designed risk mitigation measures, such as selecting a diverse range of AVS projects and implementing high-standard security protocols.
5. Governance and Selection
AVS projects are typically selected and approved through a decentralized governance process, which means that community members (including stakers) can vote on which services should be included in the protocol. This ensures transparency of the project and community participation.
6. Technical Implementation
Technically, AVS is implemented through smart contracts and the EigenLayer framework, which define the specific parameters of the service, reward distribution, and participation rules. This structure allows for flexible service management and automated reward distribution.
By actively verifying services, the Renzo protocol not only increases the potential returns of stakers, but also brings more functionality and value-added services to the Ethereum ecosystem. These services help improve the efficiency and security of the entire network, while also promoting the development of decentralized finance (DeFi) and other blockchain applications.
3.4 Cross-chain Re-staking
Cross-chain re-staking in the Renzo protocol is one of its innovative features. This feature allows users to reuse staked assets across multiple blockchains, further improving capital efficiency and the convenience of participating in multiple blockchain ecosystems.

The following are the key aspects of the cross-chain re-staking mechanism of the Renzo protocol:
1. Definition of cross-chain re-staking
Cross-chain re-staking allows users to use their staked assets on one blockchain (such as Ethereum), such as ETH, for related activities on another blockchain without withdrawing the original stake. This is achieved by creating a derivative asset (such as EZETH in the Renzo protocol) that represents the original pledged asset, which can be freely circulated and used on other chains.
2. Improved capital efficiency
Through this mechanism, pledgers can participate in the pledge and governance activities of more blockchain projects without increasing additional capital investment. This not only improves the efficiency of the use of original capital, but also enables users to explore new investment opportunities and sources of income.
3. Technical implementation
Renzo uses advanced cross-chain technologies such as bridging and lock/unlock mechanisms to ensure the safe flow of assets between different chains. The user's original assets are locked on one blockchain, while an equivalent proxy asset is generated on another blockchain, which inherits certain properties and rights of the original asset.
4. Risk management
Although cross-chain re-staking provides many benefits, it also brings certain risks, such as cross-chain bridging security issues and liquidity risks. The Renzo Protocol has designed corresponding security measures, such as multi-signature and smart contract audits, to mitigate these risks.
5. Governance and Automation
Cross-chain re-staking typically involves complex governance structures because it must deal with interoperability issues across multiple blockchains. The Renzo Protocol may include automated governance tools that enable users to effectively manage their stakes and voting rights on multiple chains.
6. Ecosystem Collaboration
The successful implementation of cross-chain re-staking relies on collaboration with other blockchain projects and protocols. The Renzo Protocol builds partnerships and compatible standards to ensure the widespread acceptance and use of its cross-chain capabilities.
Through cross-chain re-staking, the Renzo Protocol not only strengthens its position as a versatile DeFi platform, but also pushes the boundaries of blockchain technology, enabling users to seamlessly operate and add value across multiple blockchain ecosystems around the world. This technological advancement opens up new possibilities for the future development of decentralized finance.
4. ezETH Token

ezETH is Renzo’s liquidity re-collateralization token, allowing users to re-collateralize while maintaining liquidity. After users deposit ETH or other approved tokens, they receive ezETH tokens, which have similar value and can be used for trading.
The ezETH token is a token with rewards, so its price increases as its underlying assets and its earned rewards increase. These earned rewards can be reward tokens of ETH, USDC, and AVS. Users can also withdraw their staked tokens and rewards.
Withdrawing assets involves unstaking the deposited assets, which depends on the re-staking strategy and EigenLayer's unstaking protocol. The withdrawal process takes a minimum of seven days, depending on the factors mentioned above.
ezETH tokens cannot be withdrawn directly. Instead, users can sell their ezETH to a balancer, which will convert the ezETH tokens into ETH. This is why the circulating supply of the token is zero, while the total supply is 282,469 ezETH.
5. REZ Token
The REZ token plays a key role in the Renzo ecosystem, allowing holders to participate in the protocol decision-making process, thereby jointly deciding the direction of the protocol and the implementation of key features.

5.1 Features and Functions of REZ
1. Governance
REZ is used to vote on various issues, such as protocol updates, fee structure adjustments, and the addition of new features. This governance model promotes a decentralized decision-making process and ensures that the development of the protocol is in line with the interests of the community.
2. Reward Mechanism
$REZ may also be used as a reward mechanism to incentivize users to participate in the maintenance, operation, and other contributions of the protocol. This includes providing liquidity, participating in the verification process, or completing specific tasks.
3. Trading and Liquidity
As a tradable digital asset, $REZ can be bought and sold on various cryptocurrency exchanges, providing users with a channel to enter and exit the Renzo ecosystem. Its market price may fluctuate based on changes in market supply and demand, protocol development, and the overall crypto market environment.
4. Protocol Security and Participation
Users holding $REZ may participate in the security mechanisms of the protocol, such as providing additional security to the network by staking $REZ, or helping to maintain the normal operation of the protocol by participating in specific network activities.
5. Economic Model
REZ is a key factor when designing the economic model. These parameters need to be carefully designed to ensure the long-term sustainability and economic security of the protocol.
6. Community Building
REZ promotes interaction between users and a collective sense of responsibility for the protocol.
The $REZ token has become a cornerstone of the Renzo ecosystem due to its versatility and its core role in the protocol. It not only provides a mechanism for financial incentives and governance, but also serves as a bridge connecting community members, developers and users to jointly promote the development and innovation of the protocol.
5.2 Supply and Circulation
The total supply of $REZ is 10,000,000,000, and the circulating supply after listing will be 1,050,000,000 (approximately 10.50% of the total token supply).
Binance Launch Pool Allocation: 250,000,000 (2.50% of Total Supply)
Binance Launch Pool Start Date: April 24, 2024
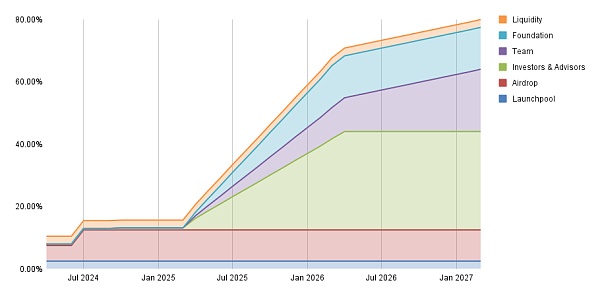
5.3 Token Allocation
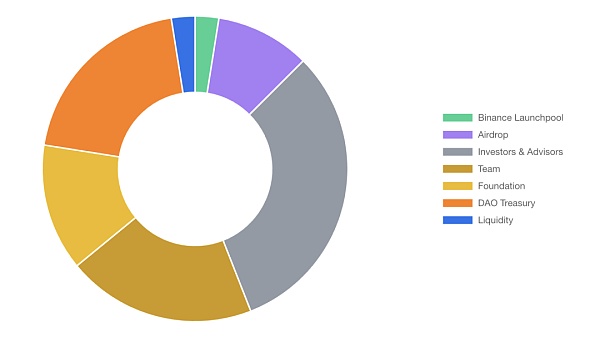
Binance Launch Pool: 2.50% of Total Token Supply
Airdrop : 10.00% of total token supply
Investors & Advisors: 31.56% of total token supply
Team: 20.00% of total token supply
Foundation: 13.44% of total token supply
DAO Treasury: 20.00% of total token supply
Liquidity: 2.50% of total token supply
It is worth mentioning that as a re-staking platform, Renzo has many participating protocols in its ecosystem that allow you to deposit your ezETH into their products and increase the Renzo points you earn, some of which will give you double rewards. These protocols include Pendle, Linea, and Ionic. The entire list can be found at https://app.renzoprotocol.com/defi. Some of the participating protocols do not have tokens, so interacting with them can increase your chances of qualifying for any potential future airdrops in the aforementioned protocols.
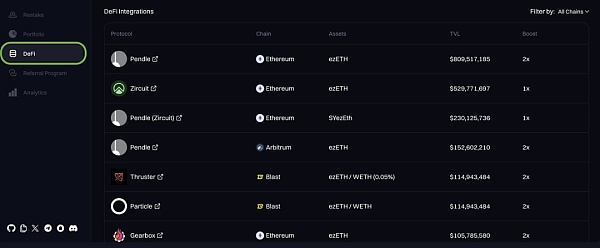
6. Team/Cooperation/Financing Background
Renzo Protocol was founded by Kratik Lodha and Lucas Kozinski in 2023 as a bridge to the EigenLayer protocol for secure ETH re-staking. The Renzo Protocol's mainnet was launched on October 30, 2023, accepting deposits and staking of native ETH tokens.
By January 14, 2024, Renzo Protocol successfully raised $3.2 million in seed funding, bringing its valuation to $25 million. The seed funding round was led by Maven11, with participation from OKX Ventures, Robot Ventures, Protagonist, Bitscale Capital, Re7 Capital, Mantle Network, and Karatage.

On February 21, 2024, Binance Labs also invested in Renzo Protocol for an undisclosed amount.
The protocol aims to grow its mainnet beyond ETH re-staking to accept deposits of wrapped ETH (wBETH) and other ETH liquid staking tokens (LST).

7. Project Evaluation and Analysis
7.1 Track Analysis
Renzo Protocol is mainly active in the field of decentralized finance (DeFi), especially focusing on staking and re-staking services. Renzo is a platform that enhances the efficiency and security of Ethereum staking by providing a re-staking mechanism, cross-chain functionality, and innovative technologies involving EigenLayer.
Here are some projects similar to Renzo that also provide staking or related services in the DeFi track:
1. Lido Finance
Lido is a decentralized staking solution that provides liquidity staking services for Ethereum and several other blockchain assets. Lido allows users to stake their cryptocurrencies while maintaining the liquidity of assets, similar to Renzo's re-staking function, but it is more focused on simplifying the staking process and providing corresponding liquidity tokens (such as stETH).
2. Puffer Finance
Similar to the Renzo protocol, Puffer Finance is also a native re-staking platform that allows users to become Ethereum validators without staking 32 ETH.
While both protocols are important players in the field of liquid re-staking, they focus on different aspects. Puffer Finance focuses on using validator rewards to achieve growth, while Renzo Protocol focuses on diversification of ETH staking. Puffer Finance uses validation tickets to maximize profits, while Renzo Protocol reduces costs through cross-chain capabilities, while working to support mainstream Liquid Staking Tokens (LST) and Layer 2 solutions.
7.2 Project Advantages
One of the major advantages of Renzo Protocol is the combination of ezETH tokens to increase yields. The ezETH token allows users to re-stake assets on multiple projects, thereby obtaining higher returns than traditional staking.
Another advantage is the cross-chain capability, which simplifies the staking process. There is also a user-friendly interface, which provides users with a lower cost and better experience.
The project may also provide multi-token support for wBETH and LST of other projects in the future. By using EigenLayer, Renzo Protocol can provide a secure and trustless staking experience.
7.3 Project Disadvantages
One disadvantage of Renzo Protocol is the lack of transferability of ezETH tokens, resulting in zero ezETH tokens in circulation. This reduces the ability of users to pool ezETH assets from compromised wallets to safer wallets.
Another disadvantage is the long asset unlocking period. During this period, due to the lack of liquidity, the unlocked assets will limit users' access to funds during the unlocking period, which may cause users to lose valuable profit opportunities.
In addition, a major challenge facing the protocol is smart contract vulnerabilities. The Renzo protocol is a new project that relies on a series of smart contracts (including EigenLayer) to operate. Any vulnerability in any smart contract may cause the project to suspend operations.
Another challenge is the volatility of the cryptocurrency market, the instability of ETH asset prices, and the uncertainty in the cryptocurrency space. These will affect users' willingness to interact with Renzo or participate in staking.
8. Project Summary
In summary, the Renzo protocol marks a major leap forward in the DeFi space, simplifying Ethereum re-hypothecation through innovative methods, simplifying user participation and maximizing returns. By directly connecting users to the EigenLayer ecosystem, Renzo not only improves efficiency but also guarantees the security of the blockchain. Its recent financing success reflects the strong trust of the market and highlights the role Renzo plays in making DeFi more accessible and valuable.
Combining its advantages and disadvantages, the Renzo protocol also has certain growth potential in the DeFi field, especially in providing innovative staking solutions and promoting the efficiency of the Ethereum network. However, its success will also depend on technological innovation, market acceptance and the development of the regulatory environment.
 Sanya
Sanya
















